Method for improving yield of lincomycin through streptomyces lincolnensis regulation gene combination modification
A technology of Streptomyces lincosides and lincomycin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of limited research on biosynthesis regulation, unfavorable high-yielding strains of Streptomyces lincosides and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Construction of SLCG_4846 gene deletion mutant:
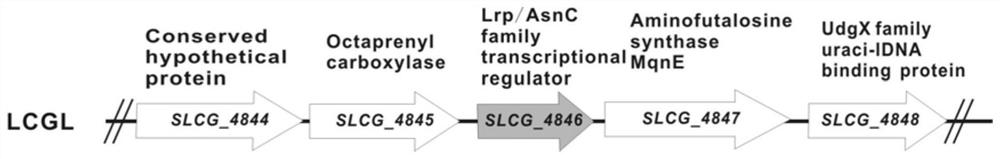
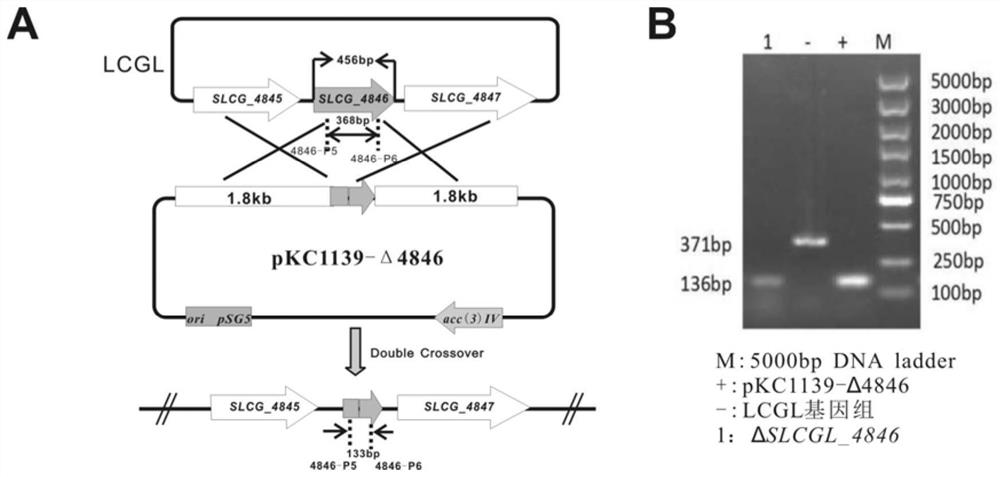
[0059] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, in order to knock out the SLCG_4846 gene in Streptomyces lincoeum, respectively use 4846-P1 / 4846-P2 and 4846-P3 / 4846-P4 as primers and the LCGL genome of Streptomyces lincoeum as a template to amplify the upstream and downstream regions of the SLCG_4846 gene by PCR. A homologous fragment of about 1.8kb. At the same time, the above two 4846-U and 4846-D upstream and downstream fragments were connected to the pKC1139 vector to complete the construction of plasmid pKC1139Δ4846, such as figure 2 Shown in A. Using the protoplast transformation technique, the pKC1139Δ4846 plasmid was transformed into the protoplast of Streptomyces lincoeum, and the positive mutant strains were screened according to the apramycin resistance to obtain the genetically engineered strain of SLCG_4846 gene knockout. 4846-P5 and 4846-P6 were used as identification primers, the plasmid pKC1139Δ4846 was used a...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Construction of SLCG_4846 gene reversion strain:
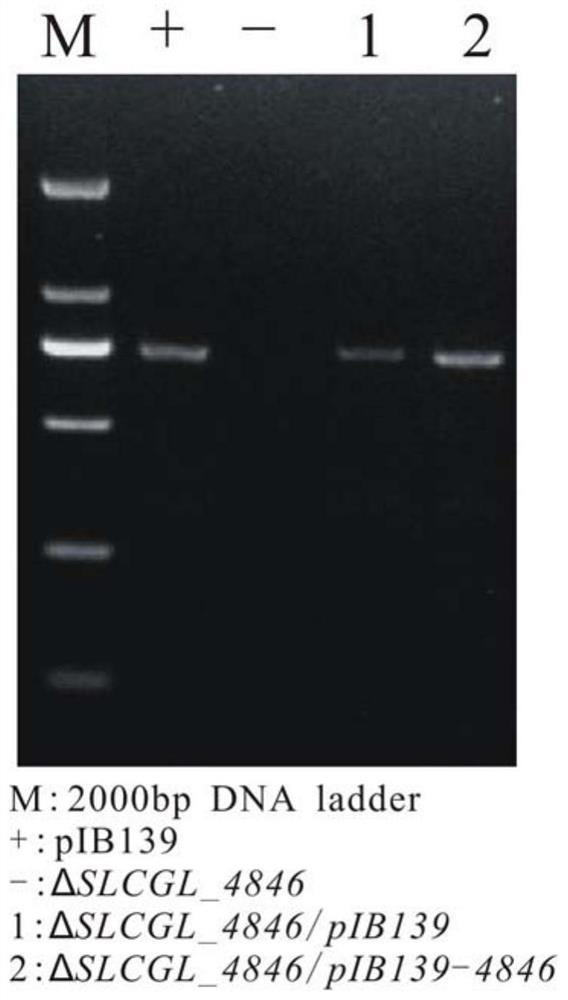
[0062] The SLCG_4846 gene was amplified using the designed primers 4846-P7 and 4846-P8, and recovered by electrophoresis. The recovered SLCG_4846 gene fragment and pIB139 were double-enzymatically digested and recovered using NdeI and XbaI endonucleases, and were recovered by T4DNA ligase. The SLCG_4846 gene fragment was connected to pIB139, and the plasmid pIB139-4846 was successfully obtained. Then pIB139-4846 and pIB139 were introduced into ΔSLCGL_4846 protoplasts by PEG-mediated protoplast transformation method. Through the preliminary screening of apramycin, the apramycin resistance gene (apr, 776bp) was used as the object for PCR identification, and the obtained reverted strain was named ΔSLCGL_4846 / pIB139-4846 and the empty load strain ΔSLCGL_4846 / pIB139 (see image 3 ).
Embodiment 3
[0064] Streptomyces lincoeum mycelium biomass detection:
[0065] The ΔSLCGL_4846 mutant strain and LCGL were inoculated in the liquid TSBY with the same inoculum amount, cultured on a shaker at 30°C for 48 hours, then transferred to 50mLYMG medium and cultured on a shaker at 30°C at 240rpm for 7 days, and samples were taken at different time periods during the period , after washing with absolute ethanol, dry and weigh the dry weight of the bacteria, repeat the sampling twice each time, and obtain the average value, draw the biomass curve of the bacteria according to the experimental data after the measurement, such as Figure 4 As shown in middle B, the deletion of the SLCG_4846 gene will not have a significant impact on the biomass of the bacteria.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com