Maize leaf zebra stripe leaf color gene zb9, InDel molecular marker linked with maize leaf zebra stripe leaf color gene zb9 and application
A molecular marker, leaf zebra technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, to achieve the effects of reliable detection results, improved identification efficiency, and high application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Map-based cloning of the zebra-striped mutant gene zb9 in maize leaves
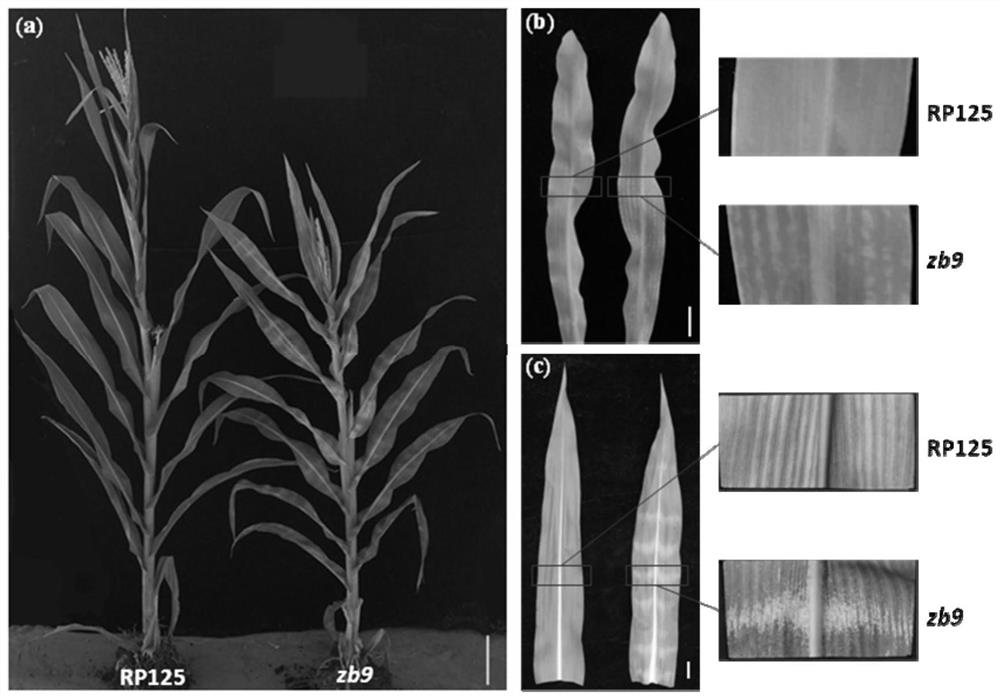
[0035] 1. The zebra-striped mutant of corn leaves used in this experiment was obtained from the Maize Research Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University. figure 1 ), compared with the wild type, the mutant zb9 plants were slightly shorter, and the leaves showed a zebra-striped phenotype. figure 1 Among them, (a) is the whole plant of corn at the silking stage, and the scale is 20cm; (b) is the corn leaf at the four-leaf one-center stage, and the scale is 3cm; (c) is the corn leaf at the silking stage, and the scale is 3cm.
[0036]Zebra stripes appeared on the mutant plants from the beginning. As the plants grow, the zebra stripes become more and more obvious. The old leaves appear before the new leaves. After the silking stage, the zebra stripes are stable until the plants mature and senescence , and named the mutant zb9.
[0037] The above-mentioned corn leaf zebra stripe mutation ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Molecular marker primer design of zebra stripe regulatory gene zb9 in maize leaves
[0043] A comparative analysis of the sequencing of 13 candidate genes in the positioning interval between the wild type and the mutant plant zb9 revealed that a single base mutation occurred on the second exon of the ZB9 gene (SEQ ID NO. Mutation from G to A)( image 3 , Figure 4 ), that is, the zb9 mutant gene is an allelic mutant gene of the ZB9 gene. Primers were designed at both ends of this mutation site to obtain polymorphic InDel markers between wild type and mutant zb9. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0044] Upstream (F): AGTCGCTGTTGGGAGGTTAC (SEQ ID No. 3)
[0045] Downstream (R): CTTCTCCAGGGCTGCTATGT (SEQ ID No. 4)
[0046] PCR amplification was performed with the designed primers. The PCR reaction system was: 7.5 μL of Taq Mix, 0.75 μL of upstream and downstream primers, 1 μL of DNA template, and distilled water to 15 μL.
[0047] The PCR amplificatio...
Embodiment 3
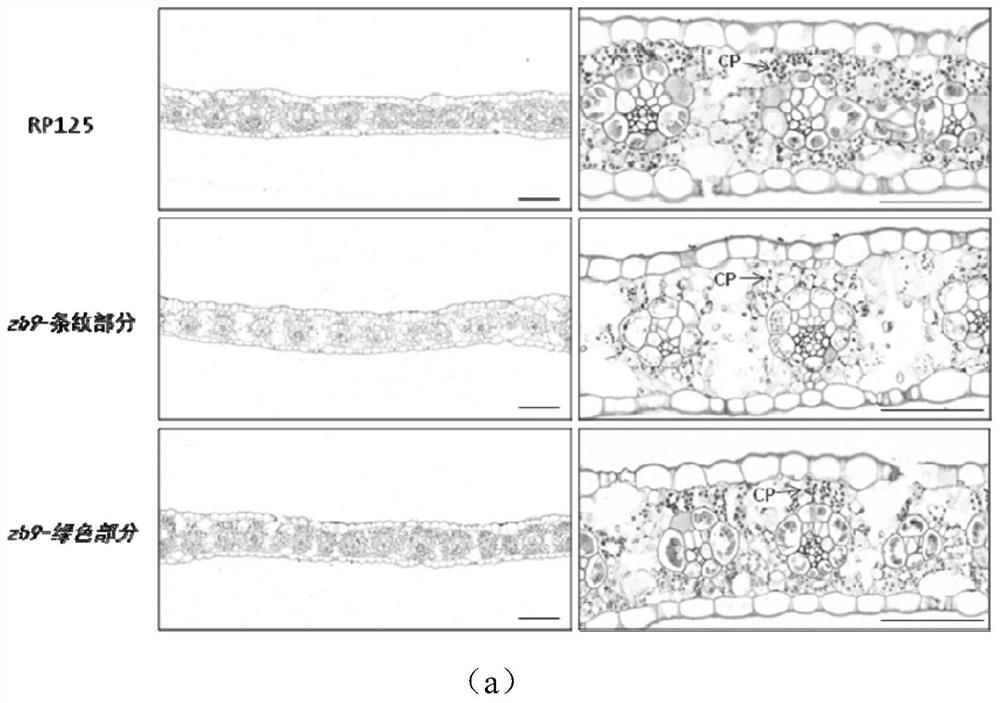
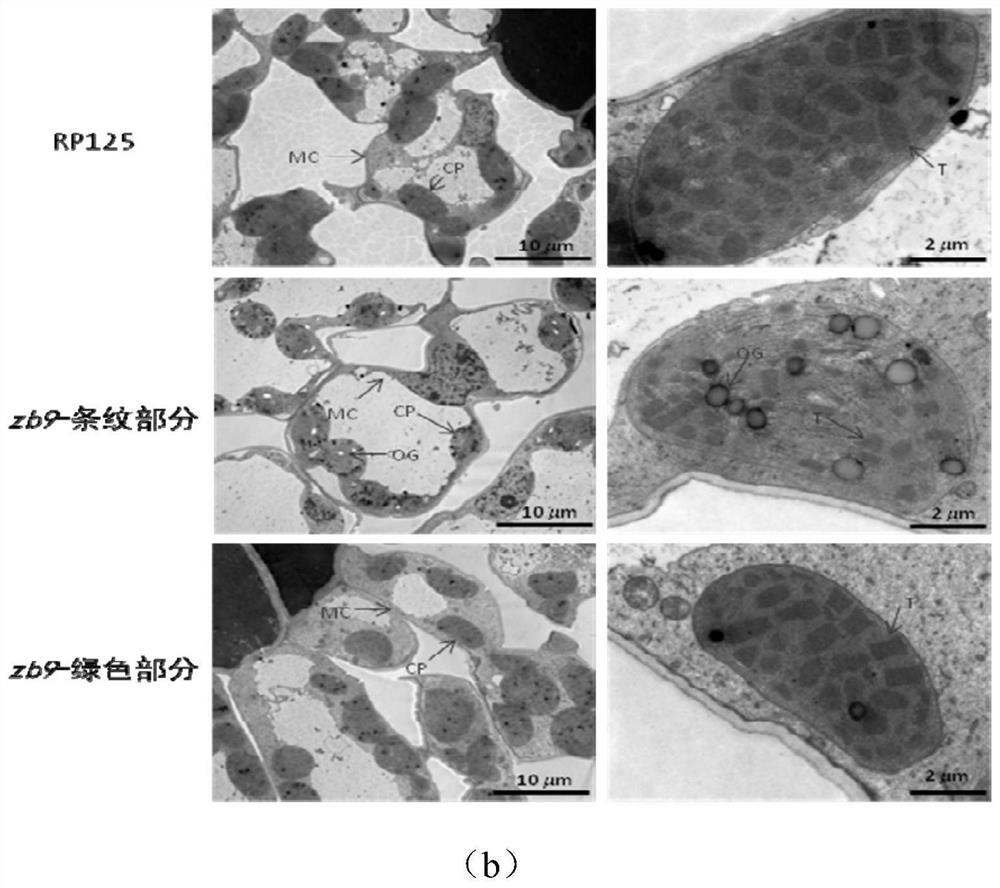
[0048] Example 3 Zebra stripe-related pigment changes in maize leaves and observation of chloroplast ultrastructure
[0049] 1. Changes in related pigments of corn leaves at seedling stage
[0050] The leaves of the zebra-striped mutant zb9 and the wild-type RP125 at the maize silking stage were taken, and the changes in chlorophyll a, b (Chl a, Chl b), total chlorophyll (Total Chl) and carotenoids (Car) were measured, and the results showed that Chlorophyll a and b, total chlorophyll and carotenoids (Car) in the mutants were significantly changed (Table 1). Among them, there is also a big difference in the pigments of the striped part and the green part of the zebra-striped mutant of maize leaves, and the substantial reduction in chlorophyll content has seriously affected the photosynthesis of plants. In this study, the pigment content was determined by conventional spectrophotometer method.
[0051] Table 1 Pigment determination in mutant zb9 and wild-type RP125
[0052] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com