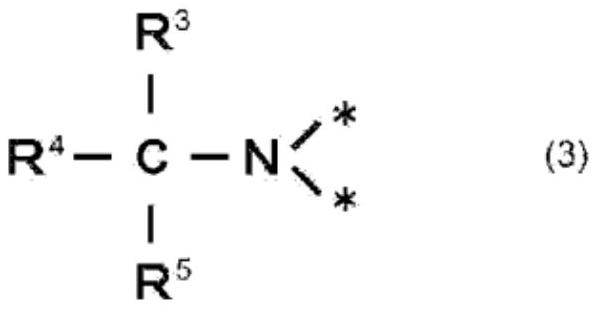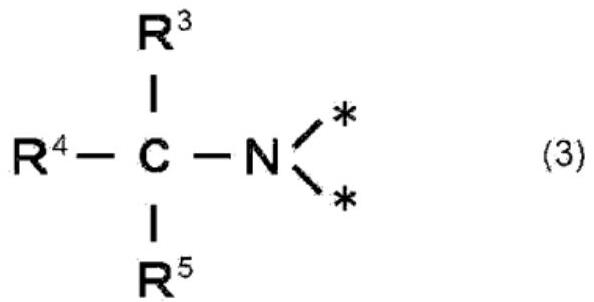Bonding composition, bonding structure of electric conductor, and method for manufacturing same
A technology of bonding structure and composition, applied in conductive connection, conductive materials dispersed in non-conductive inorganic materials, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of inability to apply driving, low heat resistance of solder, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] (1) Preparation of the composition for joining
[0083] As copper powder, D SEM50 Spherical copper powder of 0.16 μm. As a reducing agent, bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane was used. The reducing agent is solid at 25°C, has a melting point of 104°C and a boiling point of over 300°C. As the liquid medium, ethylene glycol was used. The boiling point of this liquid medium was 197°C. These are mixed to obtain a pasty joining composition. The ratio of the reducing agent in the joining composition was 2.5 parts with respect to 100 parts of copper powder, and the ratio of the liquid medium was 22.5 parts with respect to 100 parts of copper powder. In addition, the shear rate of 10s -1 The viscosity of the joining composition at 25° C. was 25 Pa·s.
[0084] (2) Manufacture of joint structure
[0085] The bonding composition was applied by screen printing to the center of a 10 mm square copper plate (thickness 0.5 mm) to form a coating film. The coating...
Embodiment 2
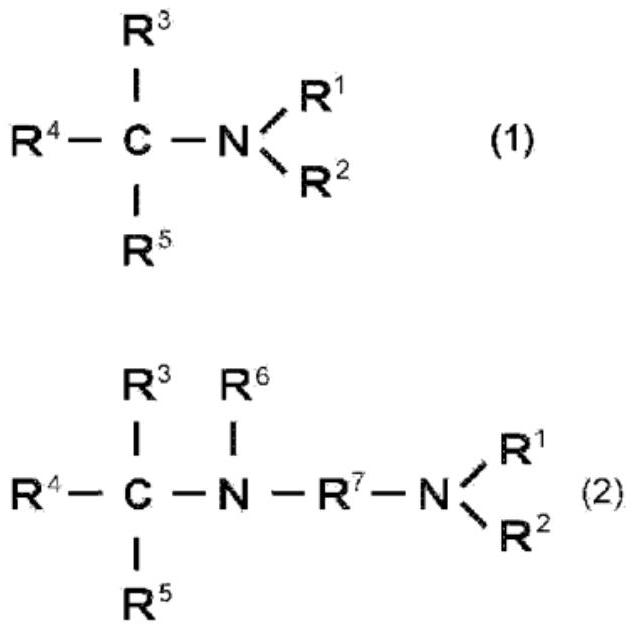
[0088] The ratio of the reducing agent in the joining composition to 100 parts of copper powder was set to 5.0 parts, and the ratio of the liquid medium to 100 parts of copper powder was set to 20.0 parts, in the same manner as in Example 1. It was operated to obtain a paste-like composition for joining. In addition, the shear rate of 10s -1 The viscosity of the joining composition at 25° C. was 42 Pa·s. Furthermore, a dried coating film was obtained under the same conditions as in Example 1. In addition, the content of the liquid medium in the dried coating film was confirmed to be 4% by mass or less. In addition, the bonded structure was produced under the same conditions as in Example 1. It was confirmed by mass analysis by TOF-SIMS that the structure represented by the above-mentioned structure (3) was formed at the copper junction.
Embodiment 3
[0098] Change the copper powder in the joining composition to D SEM50 0.14μm spherical copper powder with D 50 A mixture of flaky copper powders with a thickness of 4.9 μm and an aspect ratio of 13. The content ratio of the spherical copper powder and the flaky copper powder in the copper powder mixture was set to 70% by mass of the spherical copper powder: 30% by mass of the flaky copper powder. In addition, the ratio of the reducing agent was set to 2.5 parts with respect to 100 parts of copper powder. Furthermore, the liquid medium was changed to a mixture of polyethylene glycol 300 and hexylene glycol. The content ratio of each liquid medium with respect to 100 parts of copper powders was set as shown in Table 2. In addition, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and obtained the paste-form joining composition. Shear speed 10s -1 The viscosity of the joining composition at 25° C. was 34 Pa·s. Furthermore, a dried coating film was obtained under the same conditions a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com