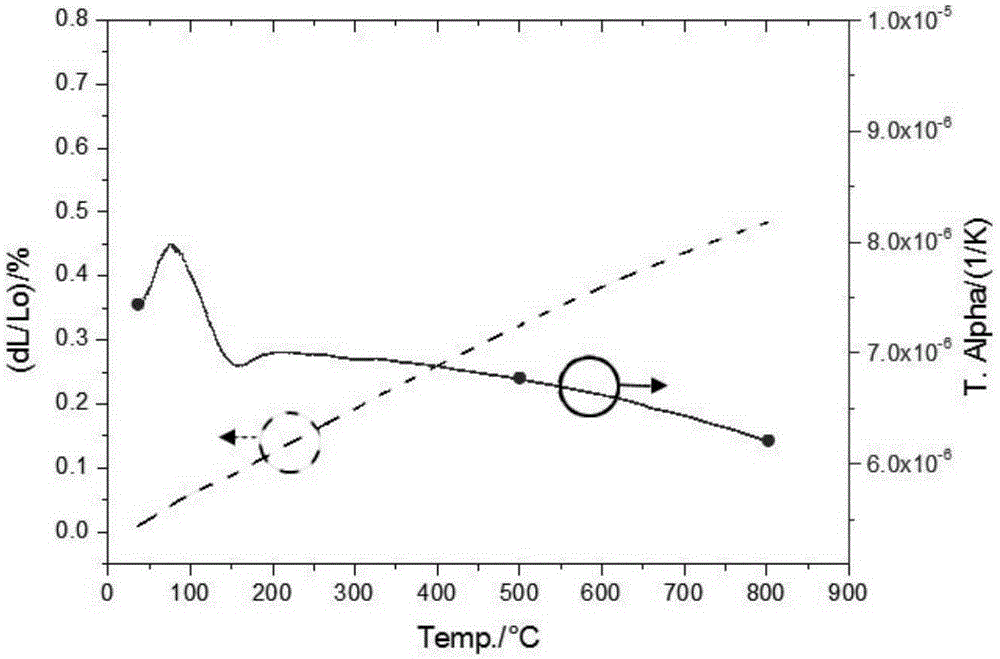
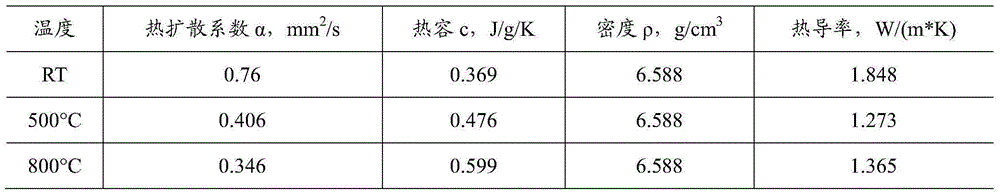
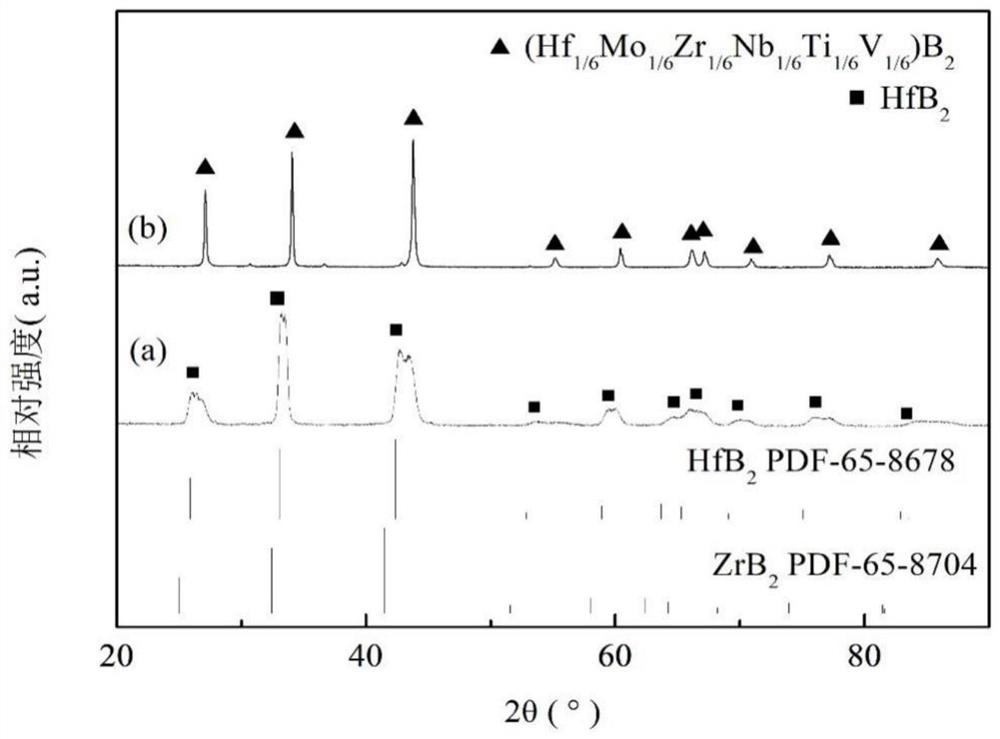
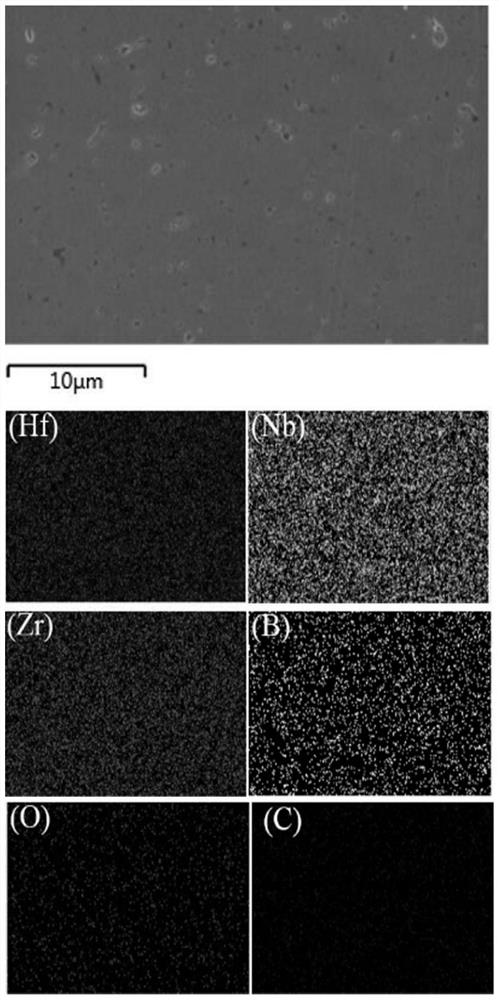
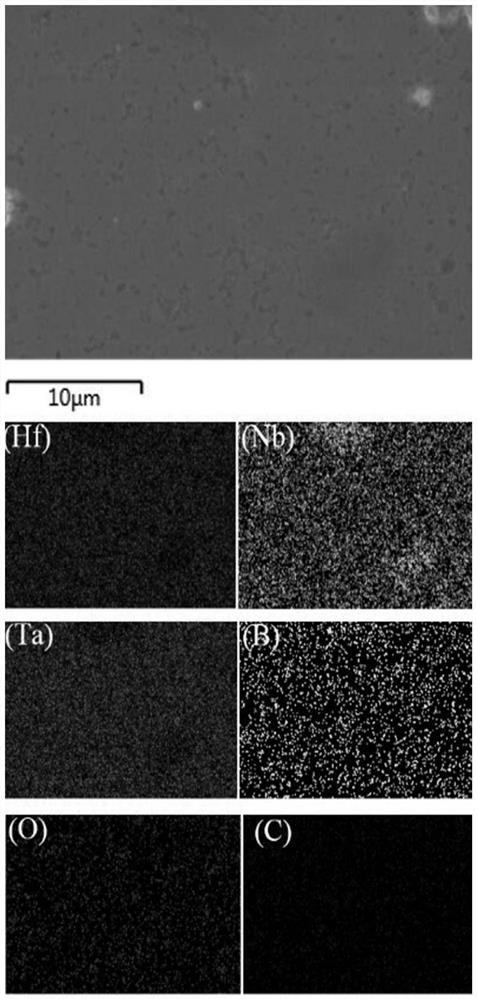
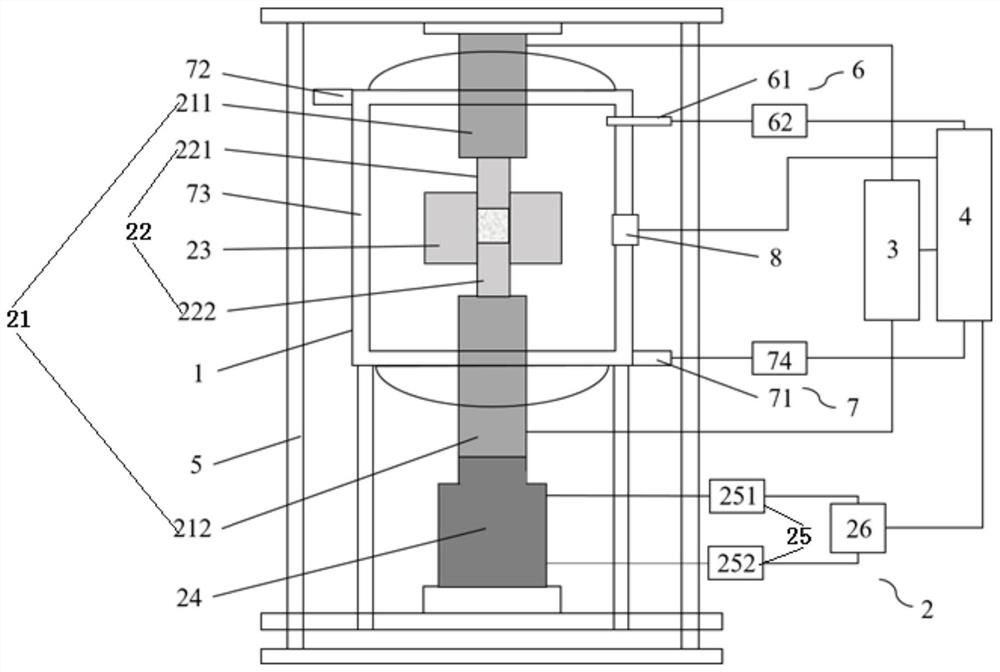
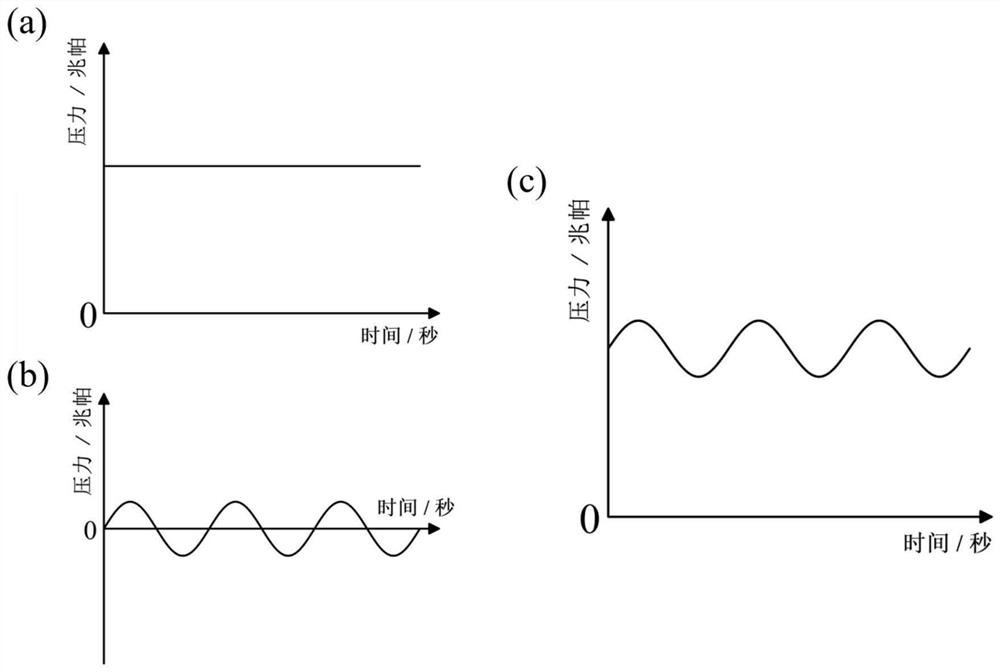
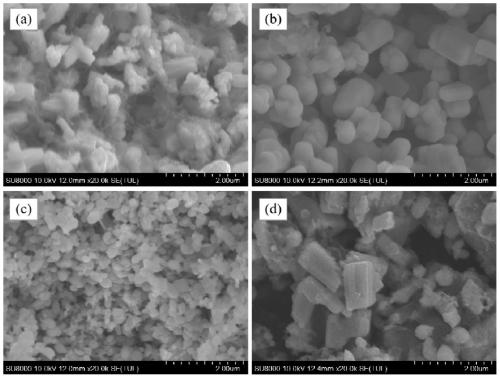
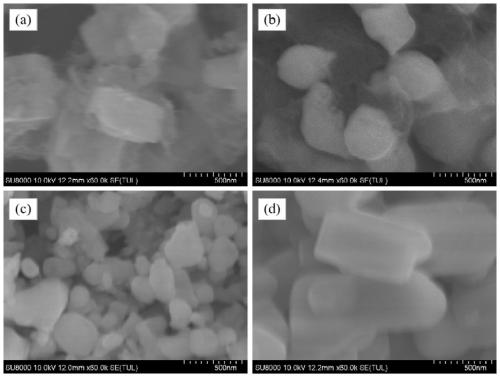
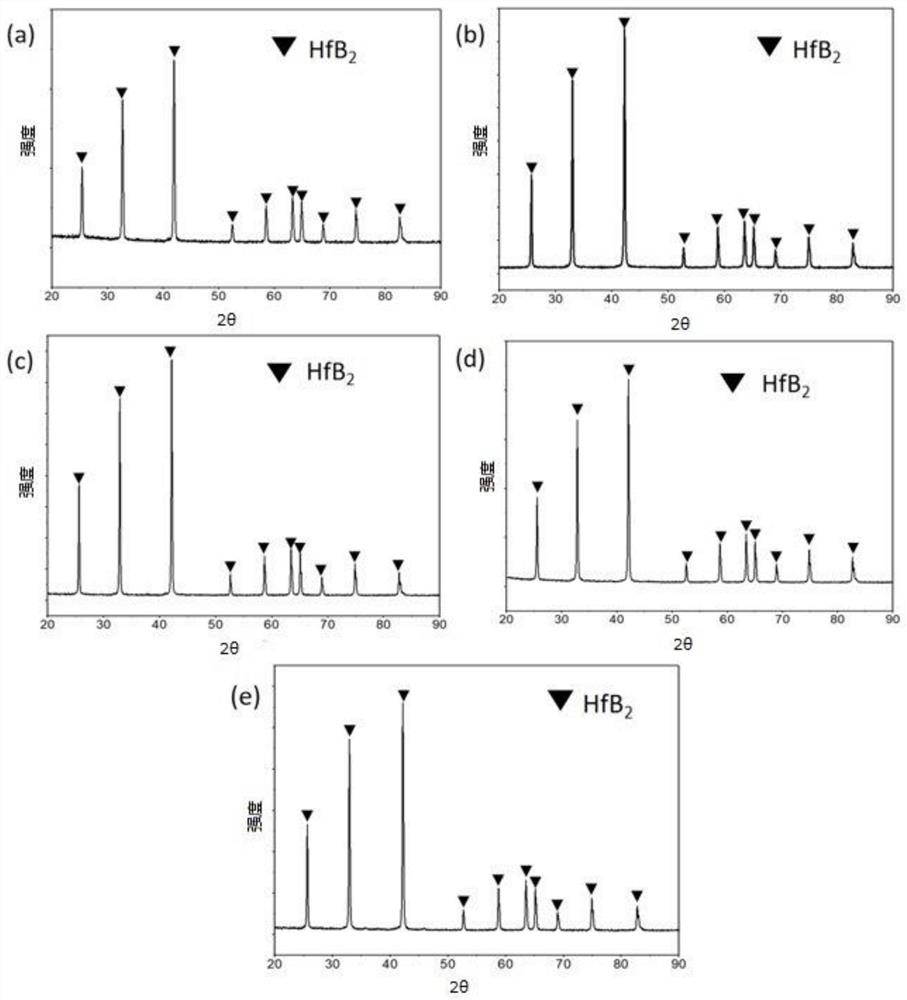
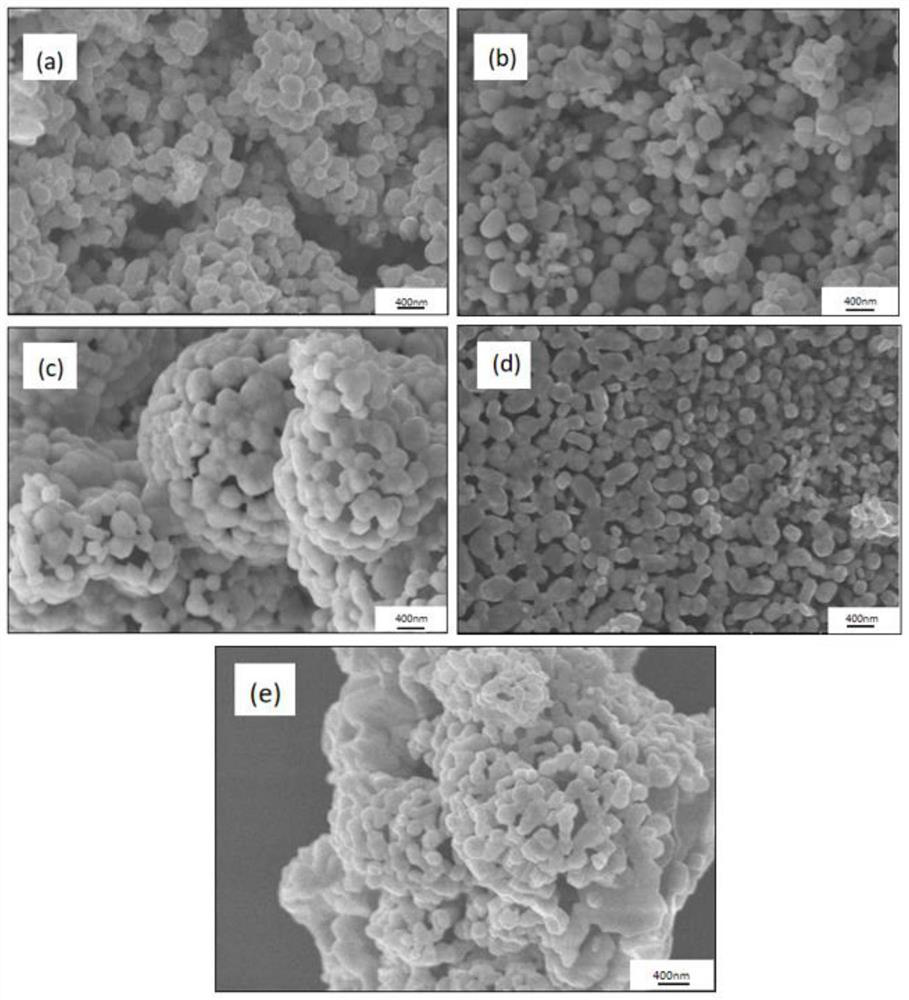
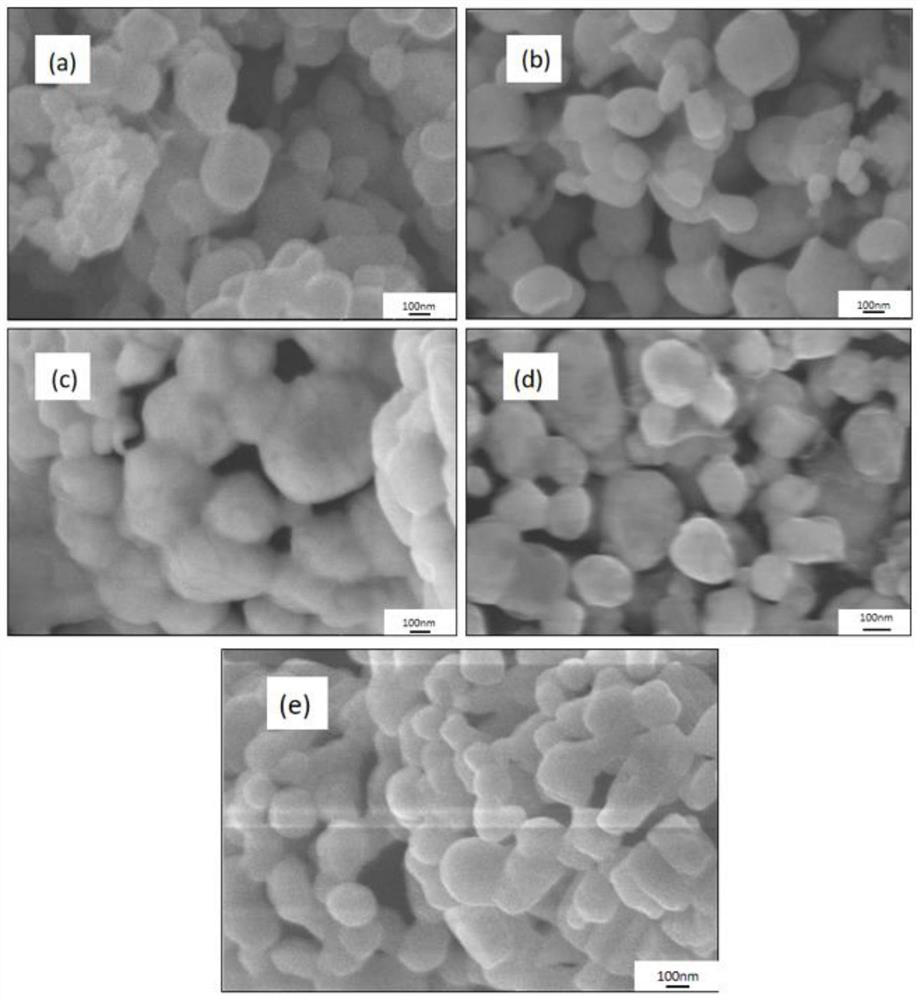
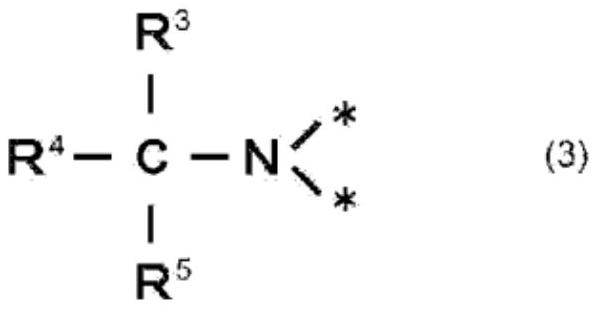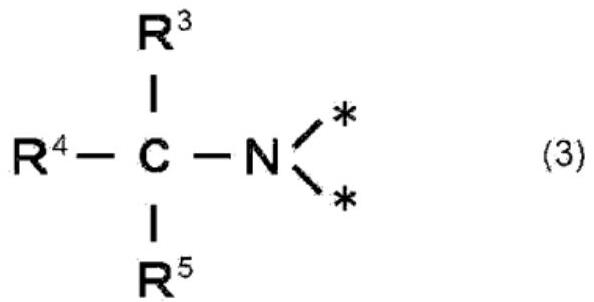Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Improve sintering driving force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Crystalline silicon solar cell front silver paste and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108766618AGood ink permeabilityEasy to fillNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPhotovoltaic energy generationSilver pasteSilver electrode
The invention discloses a crystalline silicon solar cell front silver paste and a preparation method thereof. The front silver paste comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 85-90%of silver powder, 5-10% of an organic carrier, 5-10% of an organic carrier, 1.5-5% of composite glass powder, and 0.05-1% of a silver paste additive. The silver powder in different particle size distribution is cooperatively used, the slurry is good in ink permeability, and the silver powder particles in the grid line are more uniformly and tightly filled, so that the sintering density of the gridline is facilitated, the resistance of the grid lines is reduced, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency is improved. The preparation process of the glass powder is simple, the control is facilitated; the glass powder with different components is compounded and used, so that a series of particles are uniform, the softening temperature is low, and the composite glass powder has good wettability to the silver powder and the silicon substrate, a front silver paste prepared from the composite glass powder is sintered on the front surface of the cell, the silver electrode and the silicon havegood ohmic contact and welding performance, and the adhesion strength of the electrode is high.
Owner:湖南省国银新材料有限公司
Low temperature sintered boride base ceramic materials and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a low temperature sintering boride-based ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The invention solves the problem of over high sintering temperature and pressure and low sintered density of the boride-based ceramic material in the prior art. The boride-based ceramic material is prepared by boride powders, carborundum powders and additives which are the mixture powders of alumina and yttria. The method is as follows: first, the boride powders, the carborundum powders and additives are mixed; second, the mixture is put in absolute ethyl alcohol for ultrasonic cleaning and dispersion, ball mill mixing and drying; and third, the mixture is cooled after hot-press sintering. The prepared low-temperature boride-based ceramic material after sintering at the condition of 1800 DEG C to 1850 DEG C and 30 Mpa are uniform and compact in structure, small in grain size and strong in mechanical property simultaneously, the relative density is above 96 percent and the intensity and toughness are respectively reach 786MPa and 7.12 MPam<1 / 2>. The method is simple and practical in technology, low in cost and easy for popularization.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing perovskite type composite oxide high-entropy ceramic through hot pressed sintering
The invention belongs to the field of high-entropy ceramic materials and particularly discloses a method for preparing perovskite type composite oxide high-entropy ceramic through hot pressed sintering. The A position of the perovskite type composite oxide high-entropy ceramic is occupied by Sr, and the B position of the perovskite type composite oxide high-entropy ceramic is composed of Zr, Sn, Ti, Hf elements and any one selected from the group consisting of Nb, Ta, Mn and Tb elements in a nearly equal molar ratio. The Sr(Zr<0.2>Sn<0.2>Ti<0.2>Hf<0.2>M<0.2>)O<3> (wherein M is Nb, Ta, Mn or Tb) composite oxide high-entropy ceramic material is prepared by adopting a hot pressed sintering technology, and the prepared ceramic material is submicron-sized in crystal grain, compact in structure,simple in preparation process and short in period.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Nuclear reactor core neutron absorbing material terbium titanate pellet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105185424AHigh densityIncrease contact areaNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nuclear reactor core neutron absorbing material terbium titanate pellet. The preparation method of the terbium titanate pellet consists of ball milling, cold isostatic pressing and sintering, also the preparation technology is simplified, the economic cost is low, the needed equipment is simple, and the obtained terbium titanate pellet has uniform structure and superior performance.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Water-based nano-silver electrically-conductive printing ink capable of sintering at room temperature as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN108102464ASmall particle sizeImprove sintering driving forceInksMetallic pattern materialsWater basedIce water
The invention discloses water-based nano-silver electrically-conductive printing ink capable of sintering at a room temperature as well as preparation and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing a reducing agent, a short-chain molecular dispersant and deionized water to obtain a reducing liquid; mixing silver salt and deionized water to form a reaction liquid; adding the reducing liquid into the reaction liquid dropwise and performing reaction after dropwise adding; centrifuging and cleaning to prepare nano-silver particles dispersed by the short-chainmolecular dispersant; mixing a functional aid and deionized water to prepare a composite aqueous solution of the functional aid; and mixing the nano-silver particles dispersed by the obtained short-chain molecular dispersant and the composite aqueous solution and performing ultrasonic dispersion in ice water bath. The electrically-conductive printing ink contains the electrically-conductive filler nano-silver particles, the deionized water and the composite aqueous solution of the functional aid, the viscosity is 8 to 15 cP, the surface tension is 25 to 35 mN / m, and the electrically-conductive printing ink can be sintered at a room temperature; and the electrically-conductive printing ink has low organic matter content and is environment-friendly.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
High-entropy ceramic as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN112830791AIncrease configuration entropyPhasing tendency inhibitionCompression moldingMetal
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic materials, and discloses high-entropy ceramic as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular formula of the high-entropy ceramic is (Me1aMe2bMe3cMe4dMe5eMe6fMe7gMe8h)B2, 0.1< / =a< / =0.9, 0.1< / =b< / =0.9, 0.1< / =c< / =0.9, 0.1< / =d< / =0.9, 0.1< / =e< / =0.9, 0.1< / =f< / = 0.9, 0< / =g< / =0.9, 0< / =h< / =0.9, and a+b+c+d+e+f+g+h=1; Me1-Me8 are any 6-8 of Hf, Mo, Zr, Nb, Ti, V, W, Cr and Ta; the high-entropy ceramic is prepared by the following steps of adding any 6-8 of metal oxides HfO2, MoO3, ZrO2, Nb2O5, TiO2, V2O5, WO3, Cr2O3 and Ta2O5, B4C and carbon powder into a solvent, carrying out ball milling and mixing to obtain mixed powder, carrying out compression molding to obtain a blank, heating the blank to 1400-1600 DEG C, heating the obtained high-entropy powder to 1000-1400 DEG C by adopting spark plasma sintering, filling a protective atmosphere, then heating to 1900-2100 DEG C, pressurizing to 10-100 MPa, and calcining to obtain the high-entropy ceramic. The relative density of the high-entropy ceramic is greater than 98%, the hardness is 35-40 GPa, and the thermal conductivity is 0.1-1 W / (mK).
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing tungsten slab by low-temperature sintering
ActiveCN105478745AWell mixedHigh sintering activation energyTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusHigh densityHydrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses a method for preparing a tungsten slab by low-temperature sintering. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixed tungsten powder is prepared; (2) the mixed tungsten powder is pressed to a slab by a cold isostatic pressing mode; and (3) under hydrogen atmosphere, the slab is heated and sintered, and is naturally cooled to obtain the tungsten slab. The method uniformly mixes the tungsten powder with three particle size ranges in proportion; on the one hand, excellent filling capacity is realized, higher pressing blank density is obtained, and higher sintering density is obtained; and on the other hand, quick actuation of densification process at a lower temperature is guaranteed, and the highest sintering temperature and insulation time are reduced; and in addition, through controlling the slab sintering temperature and time, the phenomenon of difficult elimination of a core hole of the sintered slab caused by the surface dentification speed of the sintered slab far faster than the core dentification speed due to excessive fast heating speed or shorter insulation time in medium-low-temperature phase can be prevented, and each part of the slab has better structure uniformity and higher density.
Owner:XIAN REFRA TUNGSTEN & MOLYBDENUM
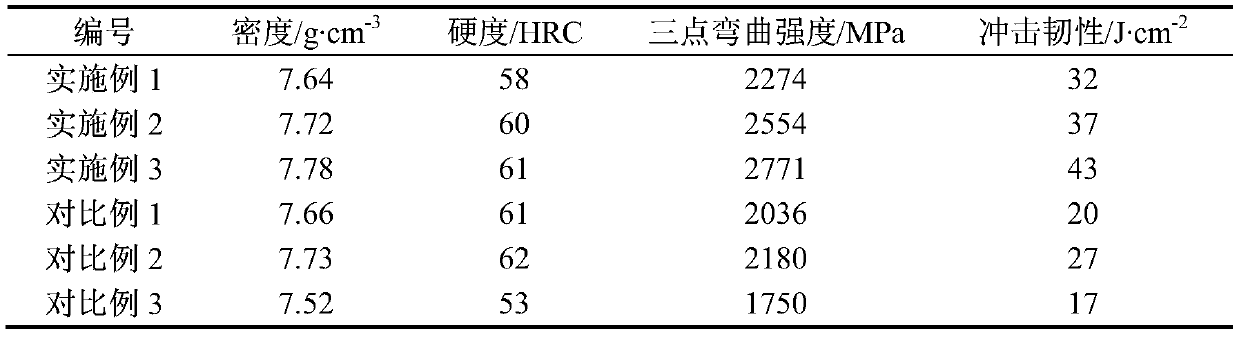
High-performance powder metallurgy pressing sintering type semi-high-speed steel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses high-performance powder metallurgy pressing sintering type semi-high-speed steel and a preparation method thereof. Preparation of the high-performance powder metallurgy semi-high-speed steel is achieved by adopting carbonyl iron powder and carbide powder as raw materials through the processes of ball-milling mixing, cold pressing forming, thermal degreasing, vacuum sintering and the like. The prepared semi-high-speed steel is uniform in chemical component, fine in grain and capable of achieving overall dispersion distribution of carbides, the problems such as componentsegregation and thick carbides existing in a traditional casting method are avoided, and the strength and the toughness of the material are significantly improved. The high-performance powder metallurgy pressing sintering type semi-high-speed steel has the advantages that the technological process is simple, the production cost is low, and the components are easy to control. Compared with semi-high-speed steel prepared through a casting method, the semi-high-speed steel has the advantage that the bending strength and the impact toughness are obviously improved at the same compactness.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of high density BaTi2O5 bulk
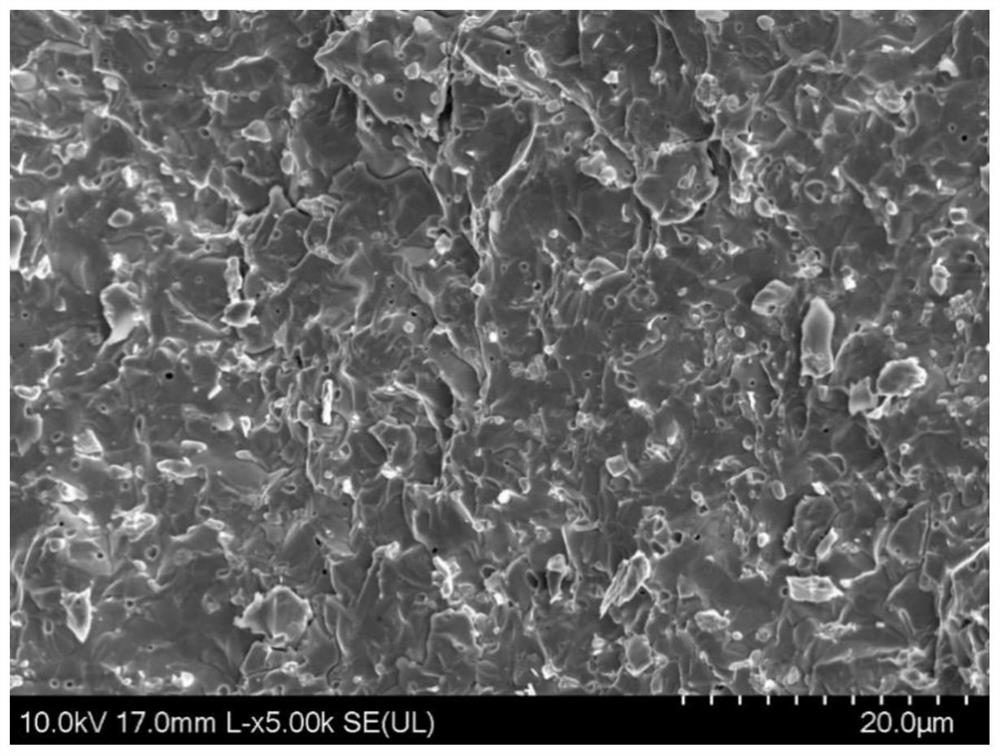
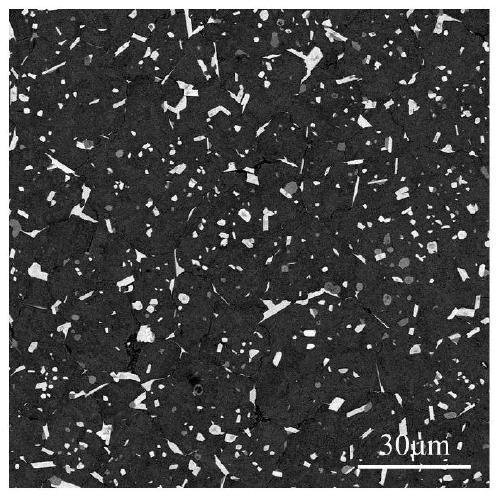
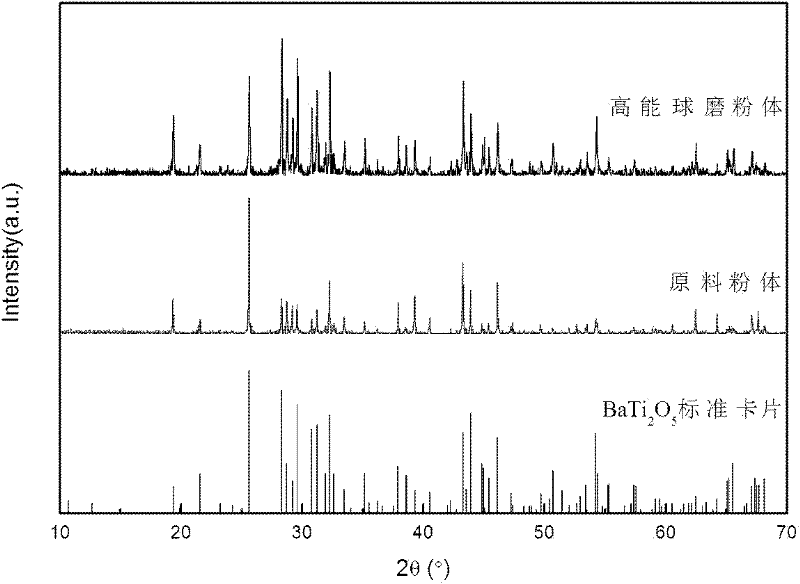
InactiveCN102241508AHigh specific surface areaImprove sintering driving forceAir atmosphereSingle phase
The invention relates to a preparation method of high density BaTi2O5 ceramic bulk. The preparation method of high density BaTi2O5 ceramic bulk provided by the invention is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: 1) placing BaTi2O5 raw material powders into a planetary high energy ball mill for grinding to obtain BaTi2O5 micropowders; 2) placing BaTi2O5 micropowders into agraphite mold, integrally moving into a discharge plasma sintering furnace, heating to the temperature of 980 DEG C-1100 DEG C in vacuum at a speed rate of 80-150 DEG C / min, insulating for 5-15 minutes, and applying the axial pressure of 30-60 MPa, then cooling to the room temperature with a furnace, obtaining a BaTi2O5 sintered body; 3) placing the BaTi2O5 sintered body into a box type electric furnace, heating to the temperature of 800 DEG C-1000 DEG C in air atmosphere at a speed rate of 2-10 DEG C / min, insulating for 12-24 hours, obtaining the BaTi2O5 ceramic bulk. The BaTi2O5 ceramic bulk prepared in the invention has the advantages of single phase, large size and high density (more than 95%) without doping any sintering addtitives, so that the invention has wide application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of boron carbide granulation powder for pressureless sintering
The invention relates to a preparation method of boron carbide granulation powder for pressureless sintering. The invention aims to solve the problems that the density of existing pressureless sintering boron carbide is difficult to be higher than 90% and the mechanical property of the existing pressureless sintering boron carbide is poor. According to the invention, two dispersants respectively directed at nanometer boron carbide and micron boron carbide are used to prepare uniformly and stably dispersed nanometer boron carbide slurry and micron boron carbide slurry respectively. In a spray granulation process, the nanometer boron carbide slurry and the micron boron carbide slurry are instantly mixed in an atomizing disc rotating at a high speed, and then moisture in a high-temperature spray granulation tower is rapidly evaporated, so dry granulation powder is obtained, and the phenomenon of agglomeration is prevented. The method is applied to the field of preparation of boron carbide ceramic.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
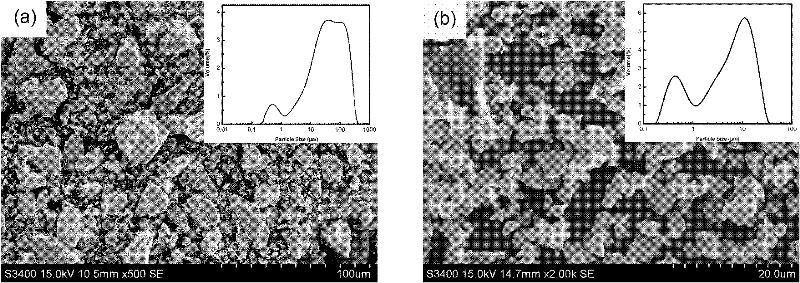
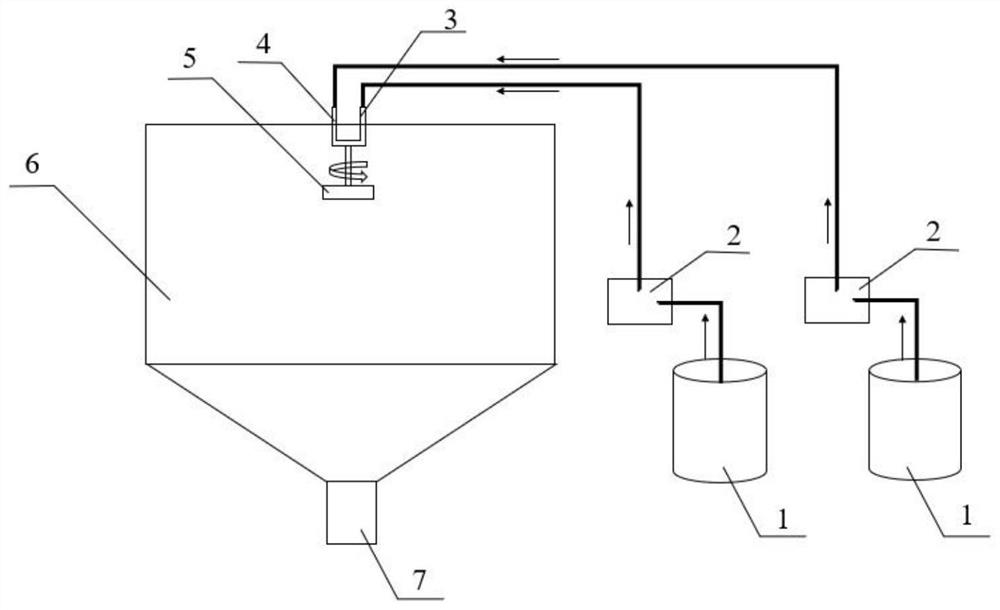
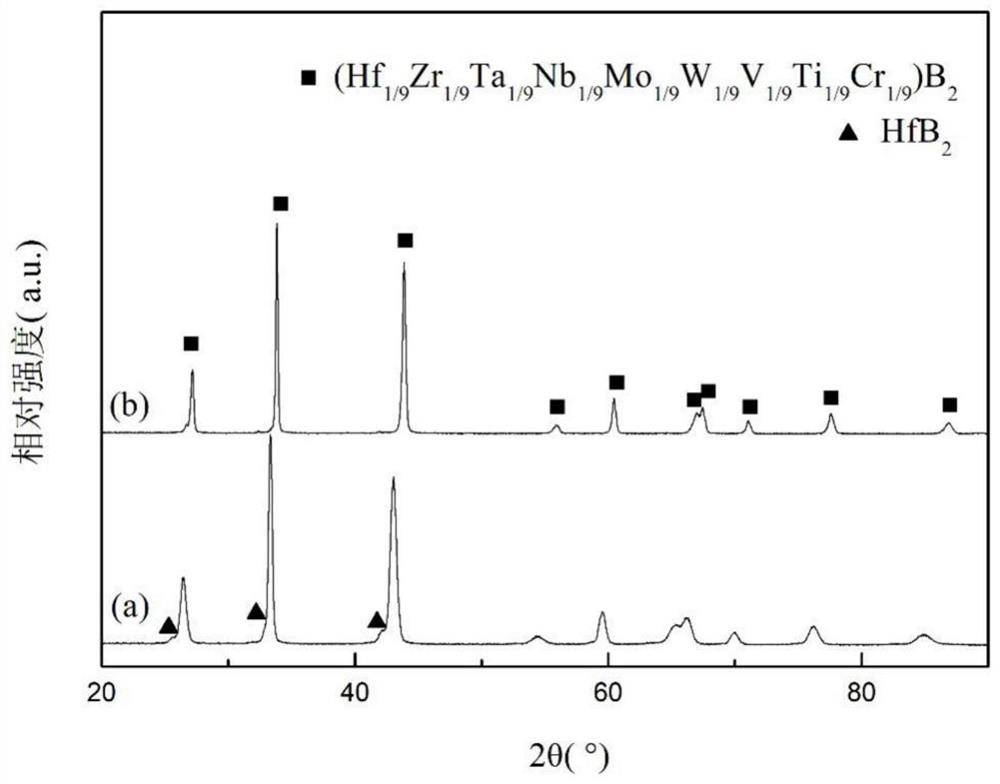
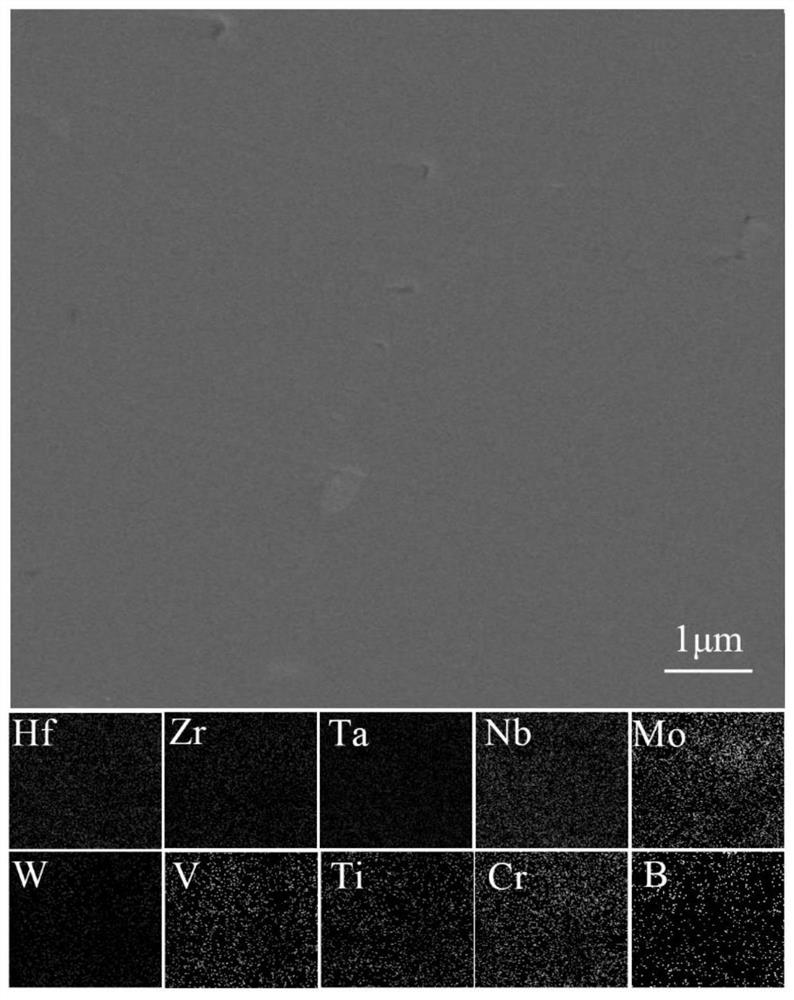
Super-multielement high-entropy ceramic as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic materials, and discloses super-multielement high-entropy ceramic as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular formula of the high-entropy ceramic is (HfxZryTazNbaMobWcVdTieCrf)B2, wherein 0<x<1, 0<y<1, 0<z<1, 0<a<1, 0<b<1, 0<c<1, 0<d<1, 0<e<1, 0<f<1, and x+y+z+a+b+c+d+e+f=1; The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding HfO2, ZrO2, Ta2O5, Nb2O5, MoO3, WO3, V2O5, TiO2, Cr2O3 and amorphous boron powder into an organic solvent, mixing, drying, preparing the obtained mixed powder into a green body, and keeping the temperature at 1,400-1,600 DEG C under a vacuum condition to obtain ceramic powder; introducing a protective atmosphere into ceramic powder at 1,000-1,400 DEG C by spark plasma sintering, pressurizing to 10-100 MPa, performing calcining at 1,800-2,200 DEG C, and obtaining the product. The relative density of the super-multielement high-entropy ceramic is greater than 95%, the hardness is 32-45 GPa, and the room-temperature strength is 1,000-1,500 MPa.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Hafnium-niobium-based ternary solid solution boride conductive ceramic and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic materials, and discloses hafnium-niobium-based ternary solid solution boride conductive ceramic and a preparation method and application thereof, the molecular formula of the conductive ceramic is (HfaNbbMic) B2, a is more than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 0.9, bis more than 0 and less than 0.9,c is more than 0 and less than 0.9 and a+b+c=1, and Me is Zr, Ta or Ti. The conductive ceramic is prepared by the following steps of adding HfO2, Nb, Me oxide, B4C and carbon powder into a solvent, carrying out ball milling and mixing to obtain mixed powder, carrying out die pressing to obtain a green body, putting the green body into a graphite crucible, heating to 1400-1600 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation, and carrying out vacuum heat treatment to obtain (HfaNbbMec)B2 hafnium-niobium-based ternary solid solution boride powder, heating the boride powder to 1000-1400 DEG C by adopting spark plasma sintering, introducing a protective atmosphere, heating to 1900-2100 DEG C, and calcining at the pressure of 10-100 MPa.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Rapid sintering equipment for dynamically loading coupling alternating current and sintering method
InactiveCN111912227AHigh densityImprove performanceMaintainance of heating chambersFurnace typesControl systemMechanical engineering
The invention relates to rapid sintering equipment for dynamically loading coupling alternating current. The rapid sintering equipment comprises the following components including a furnace frame, a dynamic loading system,a sintering control system and an alternating current control system; a furnace body is arranged in the furnace frame, and a closed pressure maintaining cabin is formed in the furnace body; the dynamic loading system comprises a dynamic loading generation part and a dynamic loading control part, and the dynamic loading generation part is arranged in the pressure maintaining cabin and used for heating a sintering material; the dynamic loading control part is arranged outside the pressure maintaining cabin, the output end of the dynamic loading control part is connected with the dynamic loading generation part, and the dynamic loading control part is used for outputting coupled total dynamic loading to the dynamic loading generation part; the sintering control system isarranged outside the pressure maintaining cabin, and the output end of the sintering control system is connected with the input end of the dynamic loading control part; and the alternating current control system is arranged outside the pressure maintaining cabin, the input end of the alternating current control system is connected with the output end of the sintering control system, and the output end of the alternating current control system is connected with the dynamic loading generation part. The equipment can remarkably improve the sintering driving force, inhibit grain growth, improve the density of a sintered body and improve the material performance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing high-performance powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloy product through solid phase deoxygenization
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-performance powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloy through solid phase deoxygenization, and belongs to the field of powder metallurgy titanium. According to the method, TiCl2 serves as a titanium powder deoxidant and is uniformly mixed with titanium powder, and after forming and sintering, a high-performance titanium product is obtained. In the sintering process, TiCl2 conducts redox reaction with the titanium powder and an oxidation film on the surface, the Ti base of generated TiClxOy is removed in the gaseous state, no solid phase impurity particle is generated, and the situation that a second phase is introduced and hinder sintering is avoided; in addition, TiClxOy can break the oxidation film on the surface of the powder advantageously, accordingly, the sintering activity of the titanium powder is improved, densification sintering is promoted, accordingly, a low-oxygen high-density titanium product is obtained, and the excellent comprehensive mechanical properties are achieved. The method provides a new idea for deoxygenization of the powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloy, low-cost powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloy industrialization development is promoted advantageously.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
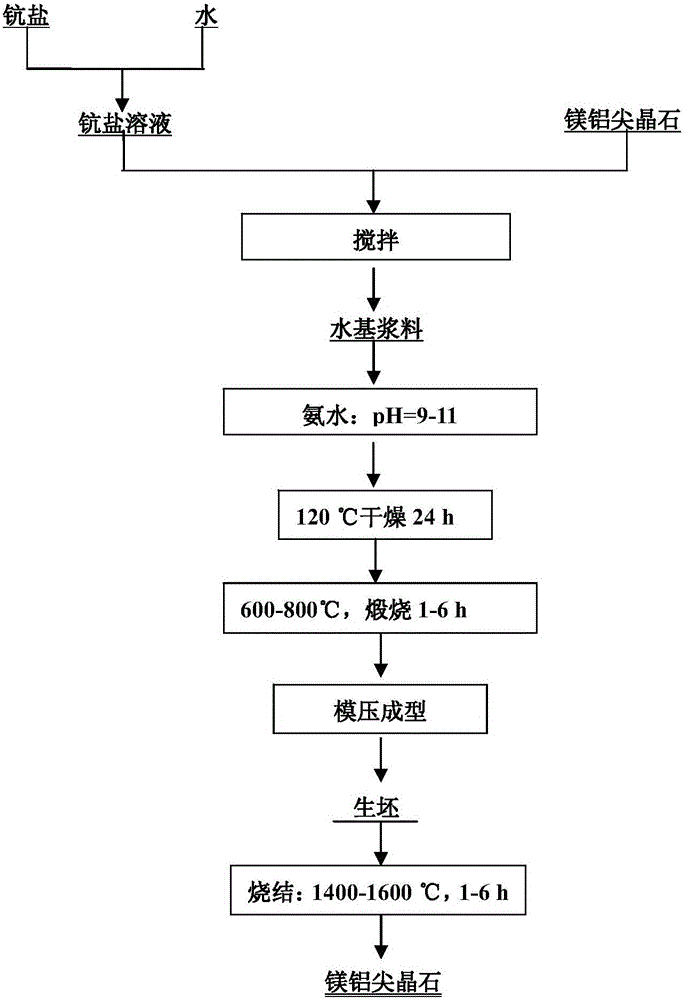
Additive for magnesium aluminate spinel sintering and application method
The invention relates to an additive for magnesium aluminate spinel sintering and an application method.The main constituents of the additive are scandium salt, ammonia water and water.The application method of the additive comprises the following steps of 1, dissolving the scandium salt into the water; 2, adding magnesium aluminate spinel powder to a solution obtained in step 1; 3, adding the ammonia water to adjust pH of water-based slurry obtained in step 2 to be 9-11; 4, then conducting drying for 24 hours or longer in a drying oven at the temperature of 120 DEG C, and then conducting calcination for 1-6 hours at the temperature of 600-800 DEG C; 5, after compression molding conducted on the calcinated powder is completed, controlling the sintering temperature to be 1400-1600 DEG C, and controlling sintering time to be 1-6 hours.By means of the additive for magnesium aluminate spinel sintering, the sintering temperature can be lowered, sintering time can be shortened, sintering compactness can be improved, and a uniform microstructure can be formed easily.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-hardness hafnium-based ternary solid solution boride ceramic as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic materials, and discloses high-hardness hafnium-based ternary solid solution boride ceramic as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular formula of the boride ceramic is (HfaMe1bMe2c)B2, 0.1< / =a< / =0.9, 0<b<0.9, 0<c<0.9, and a+b+c=1; Me1 and Me2 are Zr, Ta or Ti. The ceramic is prepared by the following steps of adding HfO2, Me1 and Me2 oxides, B4C and carbon powder into a solvent, carrying out ball milling to obtain mixed powder, carrying out die pressing to obtain a blank, putting the blank into a graphite crucible, heating to 1400-1600 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation, and carrying out vacuum heat treatment to obtain hafnium-based ternary solid solution boride powder, and heating the ternary solid solution boride powder to 1000-1400 DEG C by adopting spark plasma sintering, introducing a protective atmosphere, heating to 1900-2100 DEG C, and calcining at the pressure of 10-100 MP to obtain the ternary solid solution boride powder.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of boron carbide micro-nano mixed powder for hot pressed sintering
The invention relates to a preparation method of boron carbide micro-nano mixed powder for hot pressed sintering, in particular to a preparation method of boron carbide micro-nano mixed powder for hot pressed sintering, and aims to solve the problem that the high densification degree and the fine grain size of the existing hot-pressed sintered boron carbide are difficult to obtain at the same time. The preparation method comprises the following steps: proportioning nano boron carbide and micron boron carbide according to a certain ratio, mixing, granulating and drying to obtain the boron carbide micro-nano mixed powder which can be directly used for hot-pressed sintering. Compared with traditional direct ball-milling mixing, the method has the advantages that nano boron carbide and micron boron carbide are respectively dispersed into slurry and then mixed, so that the mixing uniformity is greatly enhanced, and sintering is facilitated to obtain a uniform ceramic material. By means of granulation, the powder forms a ball shape, the arch bridge effect of the powder is greatly reduced, the flowability and apparent density of the powder are improved, and hot pressing sintering densification is facilitated. The method is applied to the field of boron carbide ceramic preparation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing high-purity ultrafine zirconium boride powder by grinding aid assisted sanding
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity ultrafine zirconium boride powder by grinding aid assisted sanding, which comprises the following steps: mixing acetic acid, boric acid and sorbitol, and stirring for dissolving at constant temperature to obtain a clarified solution; cooling the clarified solution to room temperature, and dropwise adding zirconium n-propoxide at a constantspeed to prepare zirconium boride precursor sol; sealing the zirconium boride precursor sol, and fully gelatinizing the zirconium boride precursor sol to prepare zirconium boride precursor gel; drying the zirconium boride precursor gel, grinding the dried zirconium boride precursor gel into powder, and calcining the powder in a rubber discharging furnace to obtain inorganic dry powder; preparingturbid liquid from the inorganic dry powder and a grinding aid, and then pouring the turbid liquid into a sand mill for sanding to prepare superfine inorganic dry powder slurry; and drying the superfine inorganic dry powder slurry, and then putting the dried superfine inorganic dry powder slurry into a high-temperature tubular furnace for high-temperature calcination to obtain the high-purity superfine zirconium boride powder. The zirconium boride powder prepared by the invention has high purity, fine particle size and good microstructure, and the mechanical properties and sintering driving force of a sintered body can be enhanced in the subsequent forming process.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparing method for magnesium synthetic material
The invention discloses a preparing method for a magnesium synthetic material. The preparing method comprises the following steps that light roasting magnesium calcium powder is subjected to sufficient fine grinding, light roasting calcium magnesium fine powder is obtained, and in addition, iron oxide red is subjected to sufficient fine grinding; the obtained fine powder and finely ground iron oxide red are subjected to co-grinding, and activated nano calcium carbonate is evenly added in the co-grinding process; water is added in the co-grinding fine powder, the mixture is placed in a rolling machine to be subjected to stirring and wheel rolling, stirring is uniform, and the press heating temperature is larger than or equal to 40 DEG C; wet powder is added in a ball pressing machine to be compacted, and ball blanks are manufactured in the ball pressing process; the obtained ball blanks are naturally dried; and the obtained dry blanks are placed in a kiln to be fired, the firing temperature ranges from 1,600 DEG C to 1,700 DEG C, heat preservation is conducted for 2-6 h, and the magnesium synthetic material is obtained. According to the preparing method, the magnesium synthetic material can be manufactured at the relatively low firing temperature and the short firing time, coal consumption is effectively reduced, the production cost is controlled, sufficient sintering of the magnesium synthetic material is guaranteed as well, and the firing compactness of the magnesium synthetic material is improved.
Owner:北京利尔高温材料股份有限公司
Method for preparing hafnium boride powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing hafnium boride powder. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a hafnium source compound in a first solvent to form a first solution; dissolving a boron source compound and a carbon source compound in a second solvent, and adding polyethylene glycol to form a second solution; adding the first solution into the second solution, and collecting the generated precipitate; and drying the collected precipitate, grinding the dried precipitate into powder, and carrying out high-temperature calcination to prepare the hafnium boride powder. The preparation process is simple, the reaction process is easy to control, the production period is short, the cost is low, the prepared hafnium boride powder has high purity, small particle size, narrow particle size distribution and good microstructure, and the mechanical property and sintering driving force of a sintered body can be enhanced in the subsequent forming process.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for preparing perovskite composite oxide high-entropy ceramics by hot pressing and sintering
The invention belongs to the field of high-entropy ceramic materials, and specifically discloses a method for preparing perovskite-type composite oxide high-entropy ceramics by hot-pressing sintering. The A site of the perovskite-type composite oxide high-entropy ceramics is occupied by Sr, and the B The bit is composed of Zr, Sn, Ti, Hf elements and any element in Nb, Ta, Mn, Tb in nearly equimolar ratio. The present invention adopts hot pressing sintering technology to prepare Sr(Zr 0.2 sn 0.2 Ti 0.2 f 0.2 m 0.2 )O 3 (M=Nb, Ta, Mn, Tb) composite oxide high-entropy ceramic material, the prepared ceramic material grains are submicron order, compact structure, simple preparation process and short cycle.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
A method for preparing high-purity ultrafine zirconium boride powder by grinding aid-assisted sand milling
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity ultrafine zirconium boride powder by grinding aid-assisted sand milling. Acetic acid, boric acid and sorbitol are mixed together, stirred and dissolved at a constant temperature to obtain a clear solution; the clear solution is cooled to room temperature, Drop in zirconium n-propoxide at a constant speed to prepare zirconium boride precursor sol; seal the zirconium boride precursor sol to make it fully gel to obtain zirconium boride precursor gel; gel the zirconium boride precursor The glue is dried and ground into powder, and then calcined in the debinding furnace to obtain inorganic dry powder; the inorganic dry powder and grinding aid are made into a suspension, and then poured into a sand mill for sand grinding to obtain superfine Inorganic dry powder slurry: dry the ultrafine inorganic dry powder slurry, and then put it into a high-temperature tube furnace for high-temperature calcination to obtain high-purity ultrafine zirconium boride powder. The zirconium boride powder prepared by the invention has higher purity, finer particle size and good microscopic appearance, and can enhance the mechanical properties and sintering driving force of the sintered body in the subsequent molding process.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for large-scale preparation of hfo2-tho2 ultra-high temperature oxide composite ceramics
ActiveCN113943156BMaximize high temperature performanceOvercome adverse phenomena such as ion conductionCeramic sinteringCompression molding
The invention discloses a large-scale preparation of HfO 2 ‑ThO 2 The method for ultra-high temperature oxide composite phase ceramics comprises the following steps: HfO 2 Powder, ThO 2 powder and sintering additives are mixed to obtain mixed powder, granulated to obtain powder, and the powder is molded to obtain a composite ceramic green body, and then sintered in an oxidizing atmosphere to obtain HfO 2 ‑ThO 2 Ultra-high temperature composite phase ceramics; the compression molding adopts secondary pressure holding; the invention provides a kind of HfO under normal pressure for the first time 2 ‑ThO 2 A method for sintering and densifying ultra-high temperature oxide multi-phase ceramics. The inventors found that in the presence of sintering aids, the green body obtained by using the second pressure during the pressing process can be sintered in an oxidizing atmosphere to obtain a dense HfO 2 ‑ThO 2 Ultra-high temperature oxide composite ceramics. The preparation method of the present invention can realize low-cost and large-scale production because the sintering is carried out under normal pressure without special equipment.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A high-performance powder metallurgy pressed sintered semi-high-speed steel and its preparation method
The invention discloses a high-performance powder metallurgy pressed and sintered semi-high-speed steel and a preparation method thereof. The invention uses carbonyl iron powder and carbide powder as raw materials, and realizes the preparation of high-performance powder metallurgy semi-high-speed steel through processes such as ball milling, cold pressing, thermal degreasing and vacuum sintering. The prepared semi-high-speed steel has uniform chemical composition, fine grains, and overall dispersed distribution of carbides, which avoids the problems of composition segregation and coarse carbides in the traditional casting method, and significantly improves the strength and toughness of the material. The invention has the advantages of simple technological process, low production cost, easy control of components and the like. Compared with the semi-high-speed steel prepared by melting and casting, the provided semi-high-speed steel has significantly improved bending strength and impact toughness under the same density.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method for preparing tungsten slabs by low-temperature sintering
ActiveCN105478745BWell mixedHigh sintering activation energyTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusHydrogenHigh density
The invention discloses a method for preparing a tungsten slab by low-temperature sintering. The method includes: first, preparing mixed tungsten powder; second, pressing the mixed tungsten powder into a slab by cold isostatic pressing; third, in a hydrogen atmosphere, The slab is heated and sintered, and the tungsten slab is obtained after natural cooling. The present invention mixes the tungsten powders of three particle size ranges uniformly in proportion, on the one hand, it achieves good filling property, obtains a higher compact density and then obtains a higher sintered density; In addition, by controlling the temperature and time of slab sintering, it can be avoided that the surface densification speed of the sintered blank is much faster than that of the core due to the excessively fast heating speed or the short holding time in the medium and low temperature stage. Therefore, it will cause the phenomenon that the pores in the core of the sintered slab are difficult to eliminate, and ensure that each part of the slab has good organizational uniformity and high density.
Owner:XIAN REFRA TUNGSTEN & MOLYBDENUM
A kind of preparation method of nanoparticle toughened high-toughness SIC parts
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano-particle toughened high-toughness SiC part, which relates to a preparation method for a high-toughness SiC part. The invention mainly solves the problem that in the existing process of toughening silicon carbide ceramics with silicon carbide nano particles, the nano particles are easy to agglomerate and combine, and uniform dispersion cannot be achieved. Preparation method: 1. powder pretreatment; 2. micron powder dispersion; 3. primary granulation; 4. nanometer encapsulation; 5. secondary granulation; The invention is used for the preparation of nano particle toughened SiC parts with high toughness.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Cordierite microcrystalline glass for silicon nitride dental ceramic facing porcelain and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113880437AUniform crystallizationLower crystallization temperatureGlass pressing apparatusThermal dilatationKaolin clay
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological materials and preparation thereof, and provides cordierite microcrystalline glass for silicon nitride dental ceramic facing porcelain and a preparation method thereof, the cordierite microcrystalline glass is prepared from the following components by mass: 75-76% of kaolin, 1-2% of SiO2, 9-10% of MgO, and 10-13% of an additive; the additive comprises a sintering aid and a nucleating agent, the sintering aid is CaCO3, the nucleating agent is ZrO2 and TiO2, and the mass ratio of CaCO3 to ZrO2 and TiO2 is (4-5): (3-4): (3-4); the preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a cordierite glass blank; and S2, carrying out crystallization treatment, and cooling to room temperature to obtain the cordierite microcrystalline glass. The thermal expansion coefficient of the cordierite glass ceramic prepared by the method is matched with that of silicon nitride ceramic, and the bending strength, the fracture toughness, the Vickers hardness and the chemical solubility can meet the performance requirements of facing ceramic.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
A method for preparing high-performance powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloy products by solid phase deoxidation
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-performance powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloy by solid-phase deoxidation, which belongs to the field of powder metallurgy titanium. The present invention proposes to TiCl 2 As titanium powder oxygen scavenger, TiCl 2 Mix evenly with titanium powder, form and sinter to obtain high-performance titanium products. During sintering, TiCl 2 Oxidation-reduction reaction with titanium powder and oxide film on the surface to generate TiCl x o y The titanium matrix is removed in a gaseous state without producing solid phase impurity particles, avoiding the introduction of the second phase to hinder sintering, and TiCl x o y It is beneficial to break the oxide film on the powder surface, thereby improving the sintering activity of titanium powder, promoting densification and sintering, so as to obtain low-oxygen and high-density titanium products, and has excellent comprehensive mechanical properties. The invention provides a new idea for deoxidizing powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloys, and is conducive to promoting the industrialization development of low-cost powder metallurgy titanium and titanium alloys.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
A nuclear reactor core neutron absorbing material terbium titanate pellet and its preparation method
ActiveCN105185424BHigh densityIncrease contact areaNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nuclear reactor core neutron absorbing material terbium titanate pellet. The preparation method of the terbium titanate pellet consists of ball milling, cold isostatic pressing and sintering, also the preparation technology is simplified, the economic cost is low, the needed equipment is simple, and the obtained terbium titanate pellet has uniform structure and superior performance.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Bonding composition, bonding structure of electric conductor, and method for manufacturing same
PendingCN112437706AImprove sintering driving forceImprove joint strengthLine/current collector detailsTransportation and packagingLiquid mediumEthyl group
This bonding composition comprises copper powder, a liquid medium, and a reducing agent, wherein the reducing agent has at least one amino group and a plurality of hydroxyl groups, the reducing agenthas a boiling point that is higher than the boiling point of the liquid medium, and the reducing agent has a melting point that is lower than or equal to the sintering temperature of the copper powder. The reducing agent is preferably bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane. The bonding composition preferably has a viscosity at a shear velocity of 10 / s and 25 DEG C of 10 to 200 Pa*s. The bonding composition preferably comprises, relative to 100 parts by mass of the copper powder, 0.1 to 10 parts by mass of the reducing agent and 10 to 40 parts by mass of the liquid medium.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com