Dispersion confocal autorotation endoscopic detection method and device
A detection method and detection device technology, applied in the direction of measurement devices, optical devices, color/spectral characteristic measurement, etc., can solve the problems of limited measurement accuracy, low accuracy, and difficulty in miniaturization, and achieve high measurement accuracy and high rotation accuracy , the effect of small rotating mass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
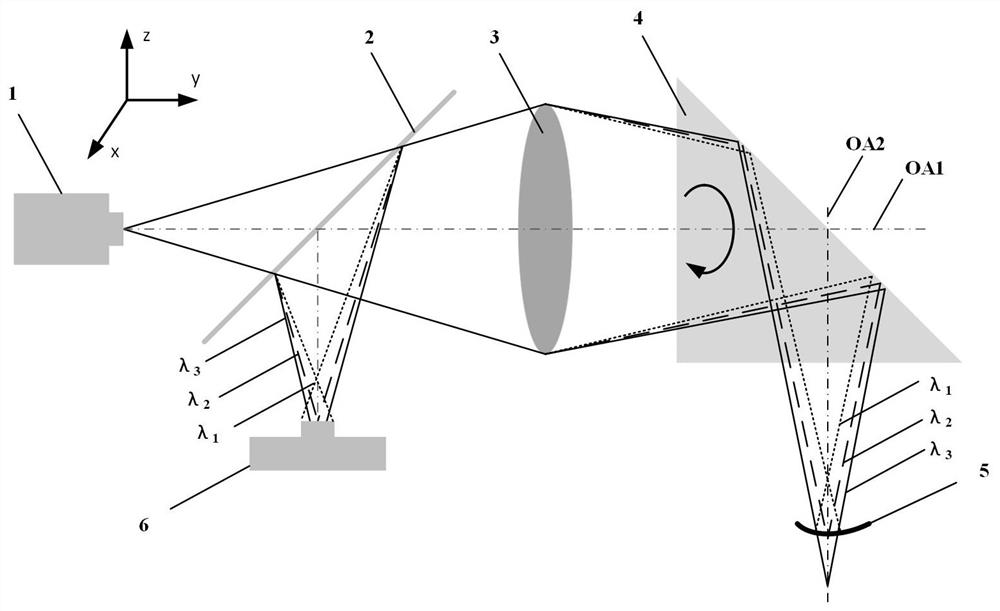
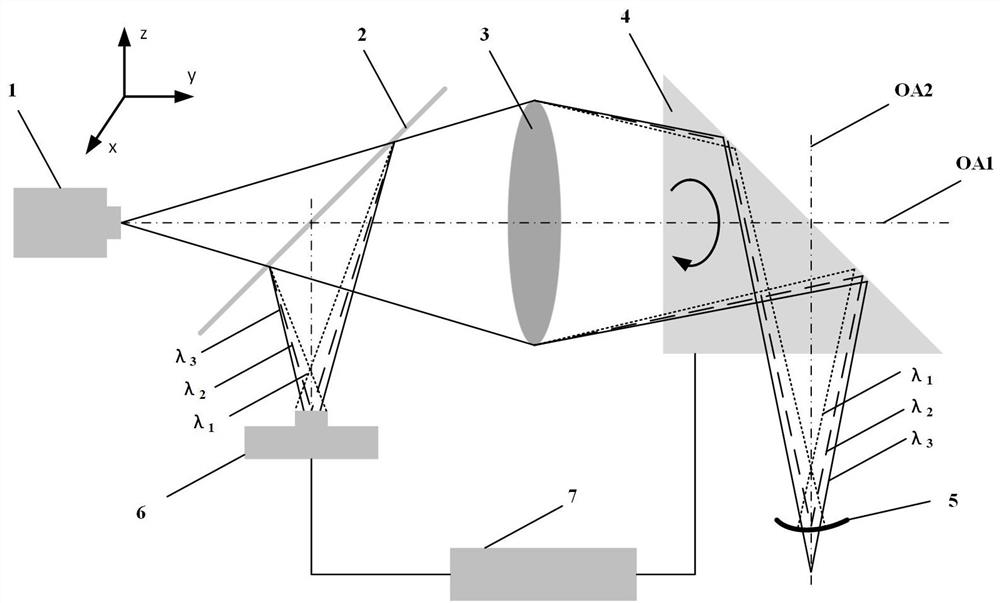
[0031] Such as Figure 4As shown, the fiber-optic dispersion confocal self-rotating endoscopic detection device used in this embodiment includes a multimode fiber-coupled broadband light source 101, a multimode fiber coupler 201, a fiber flange 8, a multimode fiber 9, and a dispersion objective lens 3 (including achromatic lens 301, concave lens 302, convex lens 303, convex lens 304, and convex lens 305), beam deflection mechanism 4 (including cylinder 401, bearing 402, prism 403), fiber optic spectrometer 601, and microprocessor 7. Among them, the multimode fiber-coupled broadband light source 101 is a broadband point light source by collimating and focusing the broadband light source to the multimode fiber, and using the multimode fiber port as the exit port; the multimode fiber coupler 201 is a passive optical fiber The device makes the light entering the coupler propagate along a fixed path to achieve light splitting; the dispersion objective lens 3 consists of an achromat...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Different from Embodiment 1, the displacement information analysis of the measurement beam direction in this embodiment comes from the focus position of the calibrated dispersion objective lens 3 in the measurement beam direction and the discrete spectral signal (including wavelength and intensity information) collected by the fiber optic spectrometer 601 The mapping relationship between the peak wavelengths. In the device of the present invention, components such as the dispersion objective lens 3, the multimode fiber-coupled broadband light source 101, the fiber optic spectrometer 601, the fiber flange 8 and the multimode fiber 9 have non-uniform spectral response characteristics, which often cause the actual displacement-wavelength relationship to deviate from the design The displacement-wavelength relationship (such as Figure 6 shown). In order to construct the actual mapping relationship between the focus of the dispersive objective lens 3 in the direction of the...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the broadband point light source in this embodiment is a common broadband point light source 102 collimated by the collimating mirror 103, then enters the focusing mirror 104 to focus, and is spatially filtered by the spatial filter 104 to obtain a broadband point source that meets the requirements of confocal detection. point light sources such as Figure 10 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com