Reagents and analytical methods for permeabilizing and fixing blood cells
A blood cell and reagent technology, applied in the field of cell molecular analysis, can solve problems such as complicated steps, large changes in cell shape, and destruction of epitopes on the cell surface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1, non-fixed cells and fixed cell surface antigen labeling
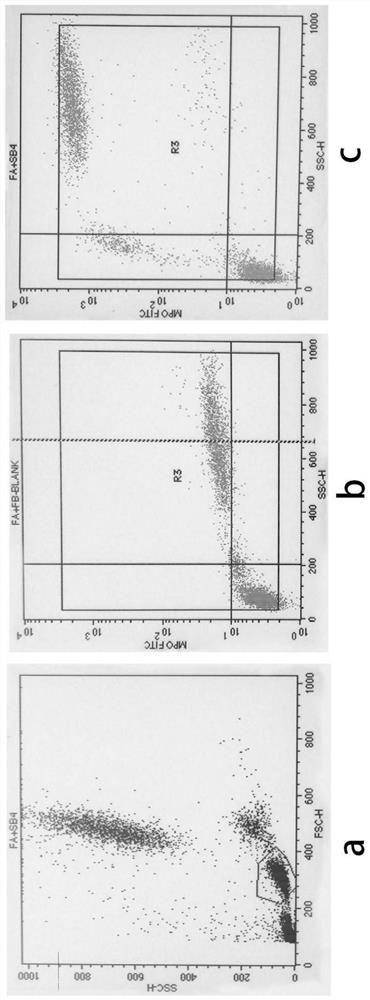
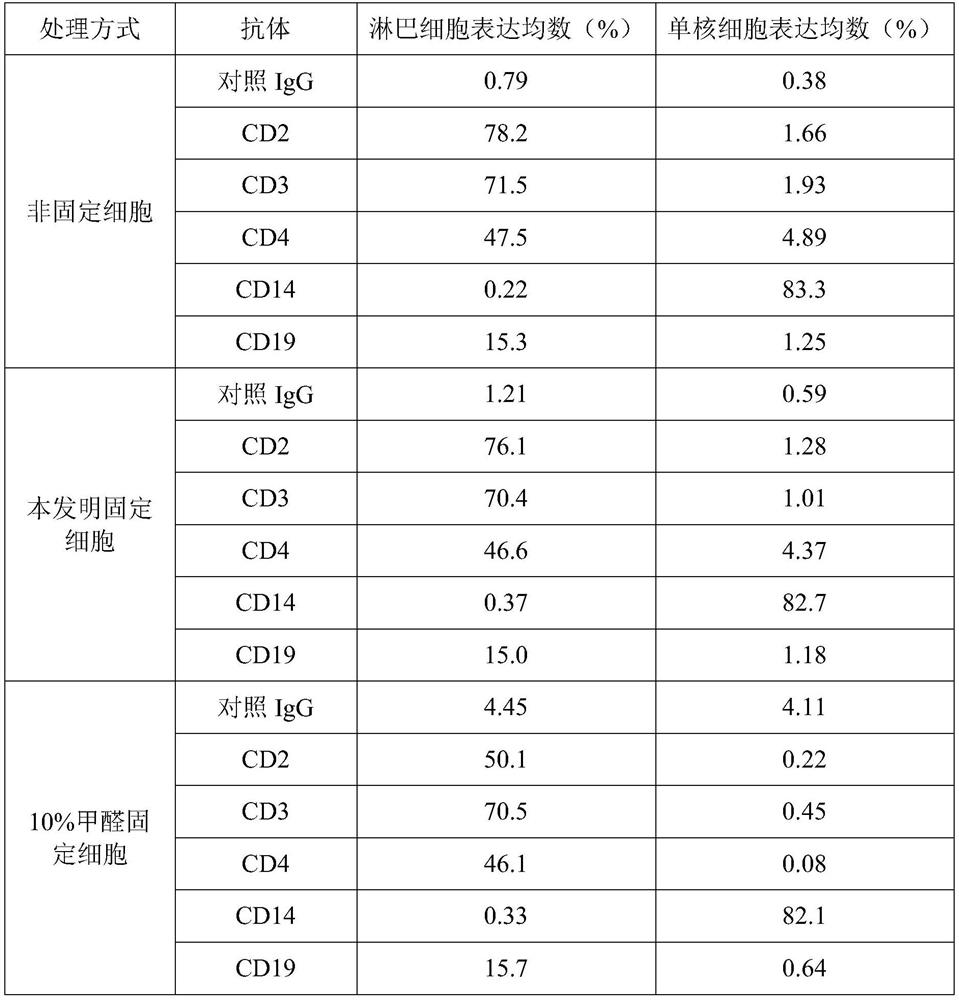
[0052] Table 1 provides 18 cases of whole blood cell membrane surface markers of healthy subjects treated with the reagent of the present invention. The results show that the non-specific binding of antibodies to fixed cells is slightly higher than that of non-fixed cells, but does not produce a large amount of non-specific Fluorescence (negative control) is not enough to interfere with the detection of cell surface marker antigens, and the cells treated with the reagents of the present invention can also maintain sufficient light scattering properties so that lymphocytes, monocytes and granulocytes can be distinguished, and the cell membrane antigens remain Complete and specific. However, when using 10% formaldehyde to fix cells in the prior art, it will increase the non-specific binding of cells (negative control), and change the binding of CD2 epitopes on lymphocytes (decrease in positive expression...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2, Unfixed Cells and Fixed Infiltrated Cell Target Intraantigen Labeling
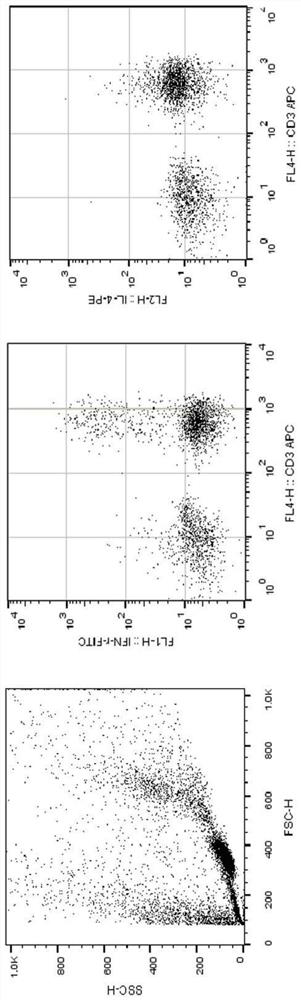
[0056] The experimental method was operated according to the above-mentioned steps, and 18 healthy subjects were labeled with whole blood cells. The results in the table are the average positive expression and signal-to-noise ratio (P / N) of some representative cell target antigens. The P / N is calculated by using the ratio of the special expression of the molecule in the target cell labeled with the monoclonal antibody to the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ratio of the corresponding molecule treated with the isotype control antibody. The internal protein is fixed and retained in place, and the fluorescently labeled macromolecular antibody can penetrate into the cell and bind to the corresponding protein antigen. Dimethyl sulfoxide helps to improve the detection of the intracellular antigen. Intracellular antigen labeling can increase the sensitivity of detection.
[0057] Table 2
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0060]Example 3, evaluating the effects of different concentrations of anionic surfactant BX, amino acid Glycine and different pH conditions on the expression of MPO and Lysozyme in neutrophil cells, the data show that Glycine can reduce the formaldehyde released by diazolidinyl urea The resulting fluorescence quenching of the labeled antibody conjugate improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the detection, and at the same time, the 1.2% BX concentration and the acidic condition of PH5.5 are more sensitive to cell staining.
[0061] table 3
[0062]
[0063]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com