Construction method and application of metabolic engineering escherichia coli strain for producing (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid by using acetic acid or salt thereof
A technology of hydroxybutyric acid and metabolic engineering, applied in the field of bioengineering to achieve the effects of improving yield and yield, less energy consumption and fewer steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1. Construction of (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid production pathway
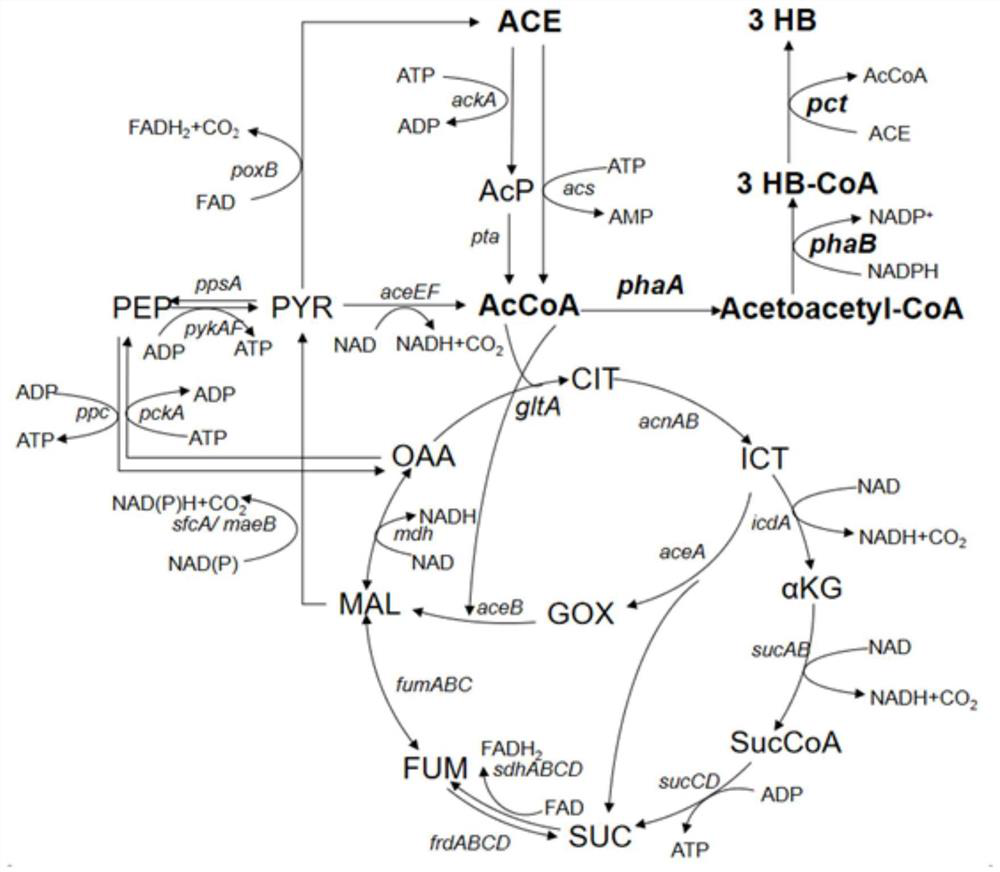
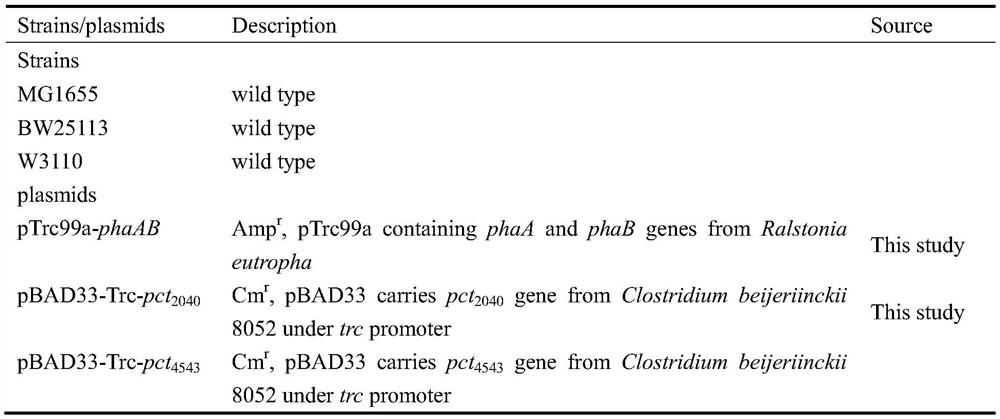
[0022] The enzymes that generate (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate from acetyl-CoA are β-ketothiolase (encoded by phaA from Ralstonia eutropha), acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (encoded by phaB from Ralstonia eutropha) and Propionyl CoA transferase (by pct derived from Clostridium beijeriinckii8052 2040 or pct 4543 coding). Using the pTrc99a plasmid as a vector, the recombinant plasmid pTrc99a-phaA-RBS-phaB (pTrc99a-phaAB for short) was obtained by overexpressing phaA and phaB derived from Ralstonia eutropha at the same time. Using pBAD33 plasmid as vector, overexpress pct derived from Clostridium beijeriinckii 8052 2040 or pct 4543 At the same time, the Trc promoter was added before the gene to obtain the recombinant plasmid pBAD33-Trc-pct 2040 or pBAD33-Trc-pct 4543 . In addition, the pTrc99a vector has a gene lacI encoding the lac repressor protein, which can block the transcription of the target gene cau...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2. optimal host and pct gene screening shake flask fermentation
[0032] Using Escherichia coli MG1655, BW25113, and W3110 as starting bacteria (MG1655, BW25113, and W3110 are provided by The ColiGenetic Stock Center), the plasmids for constructing (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid production pathways were transferred by calcium transfer, and MG1655 (pTrc -99a-phaAB,pBAD33-Trc-pct 2040 ), MG1655 (pTrc-99a-phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 4543 ), BW25113 (pTrc-99a-phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 2040 ), BW25113 (pTrc-99a-phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 4543 ), W3110 (pTrc-99a-phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 2040 ), W3110 (pTrc-99a-phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 4543 ). In Table 3, pTrc-99a-phaAB is abbreviated as phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 2040 abbreviated as pct 2040 , pBAD33-Trc-pct 4543 abbreviated as pct 4543 .
[0033] Shake flask fermentation operation: Pick a single colony on the plate and inoculate it in a test tube containing 3mL LB for overnight culture, then transfer to a conical flask containing 50mL...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3. Fermentation temperature optimizes shake flask fermentation
[0041] Using Escherichia coli BW25113 or W3110 as the starting bacteria, the plasmids for the construction of (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid production pathway were transferred by calcium transfer, and BW25113 (pTrc-99a-phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 4543 ), W3110 (pTrc-99a-phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 2040 ). In Table 4, pTrc-99a-phaAB is abbreviated as phaAB, pBAD33-Trc-pct 2040 abbreviated as pct 2040 , pBAD33-Trc-pct 4543 abbreviated as pct 4543 .
[0042] The composition of M9 medium, the determination method of (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid and acetic acid, and the determination method of cell concentration are the same as those described in Example 2. The shaking flask fermentation operation is the same as that described in Example 2, except that it is transferred to different temperature culture (25° C., 30° C. or 37° C.) after induction.
[0043] The shake flask fermentation results are shown in Table 4....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com