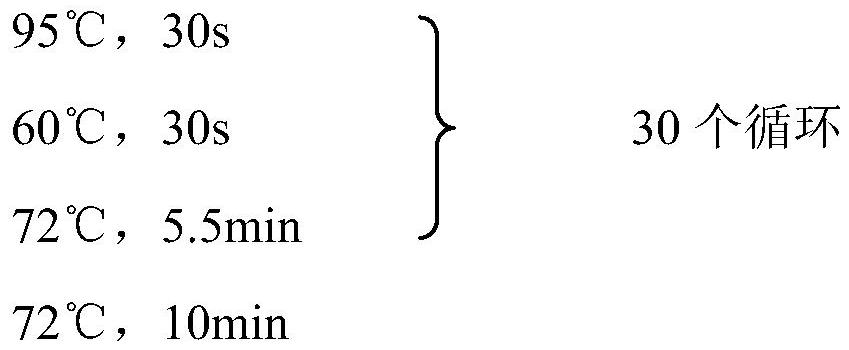
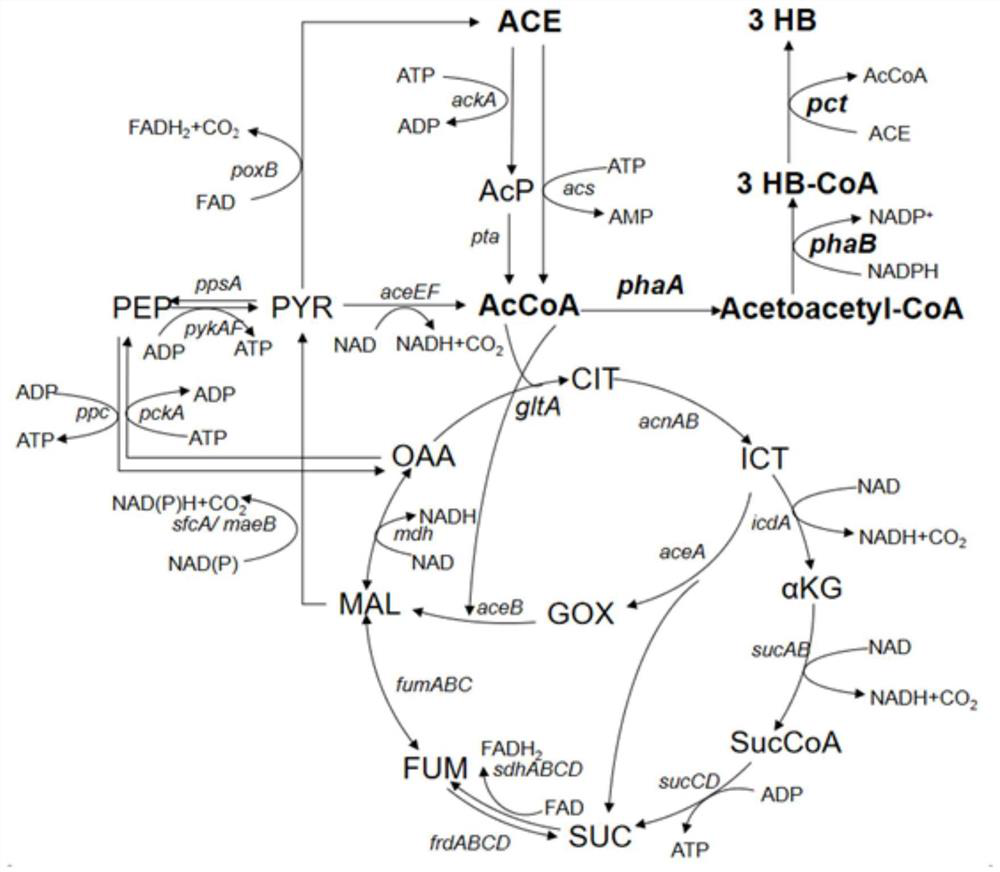
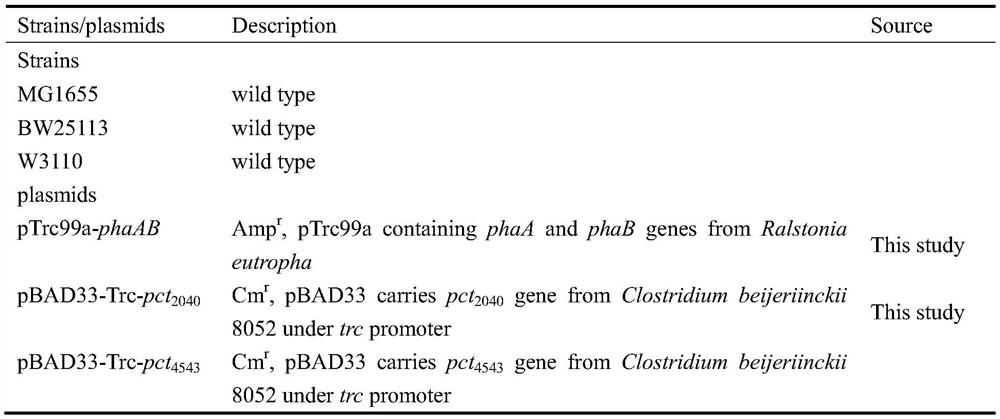
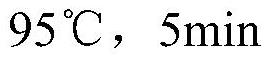Patents
Literature
30 results about "Propionyl-CoA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
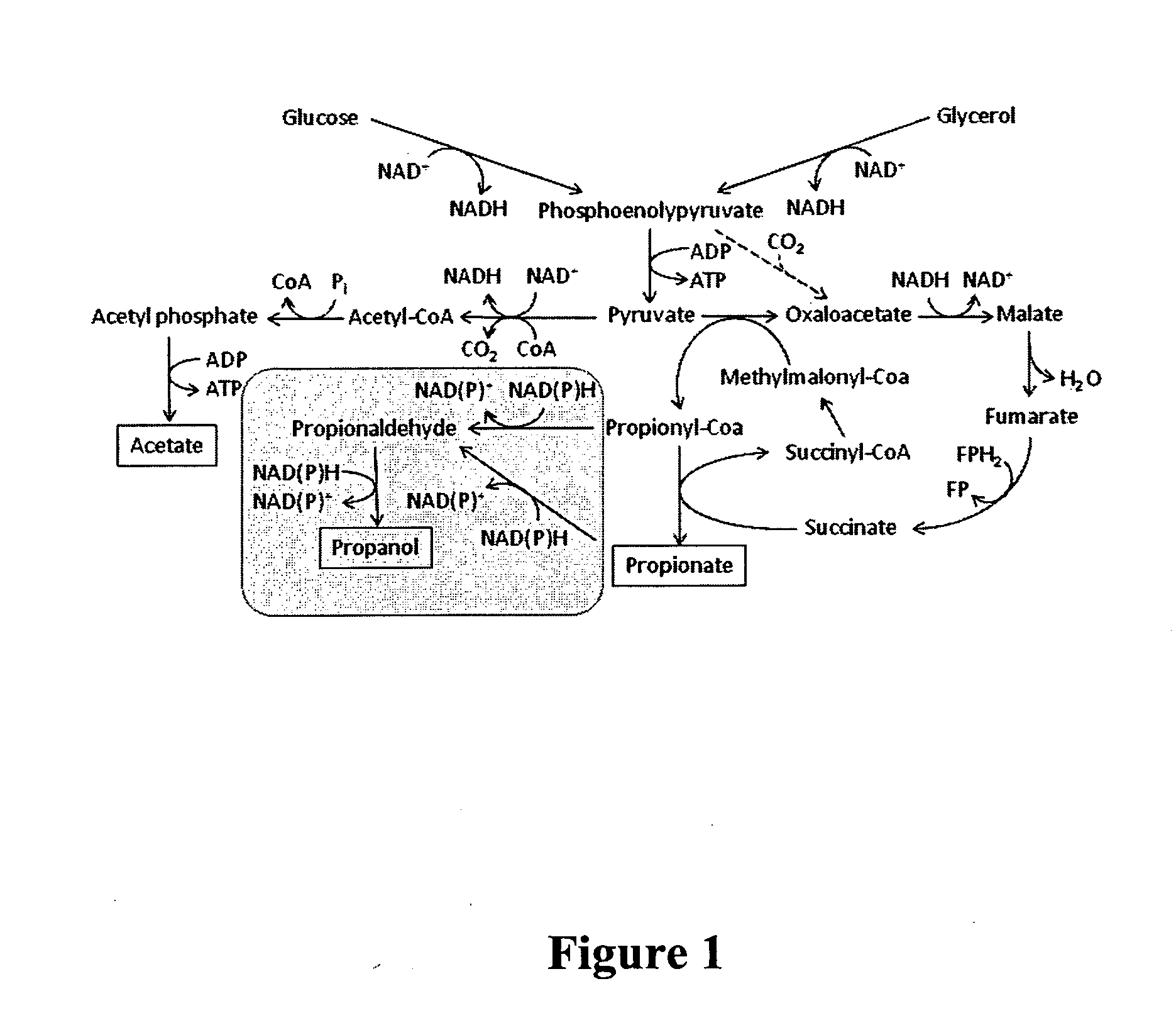
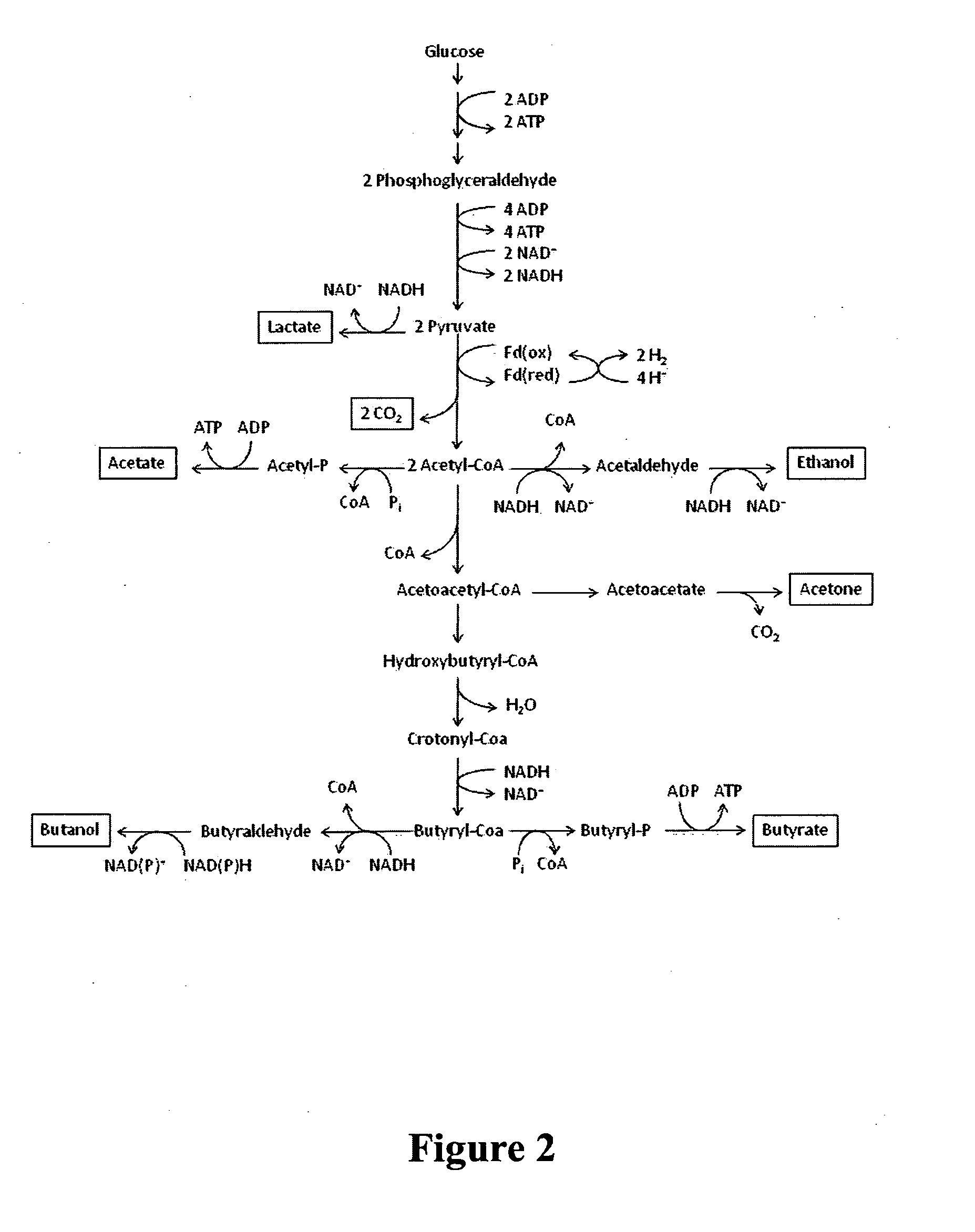
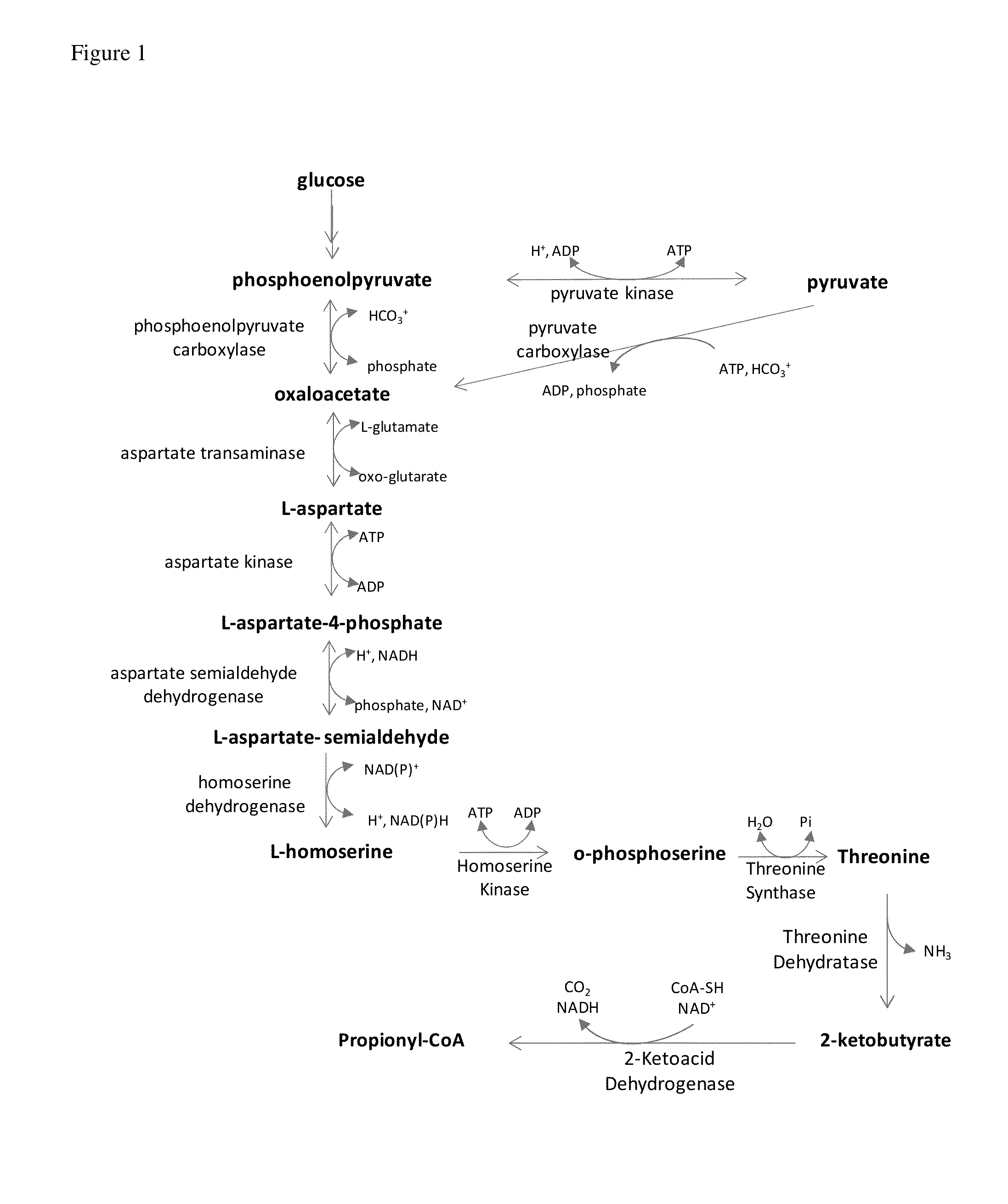
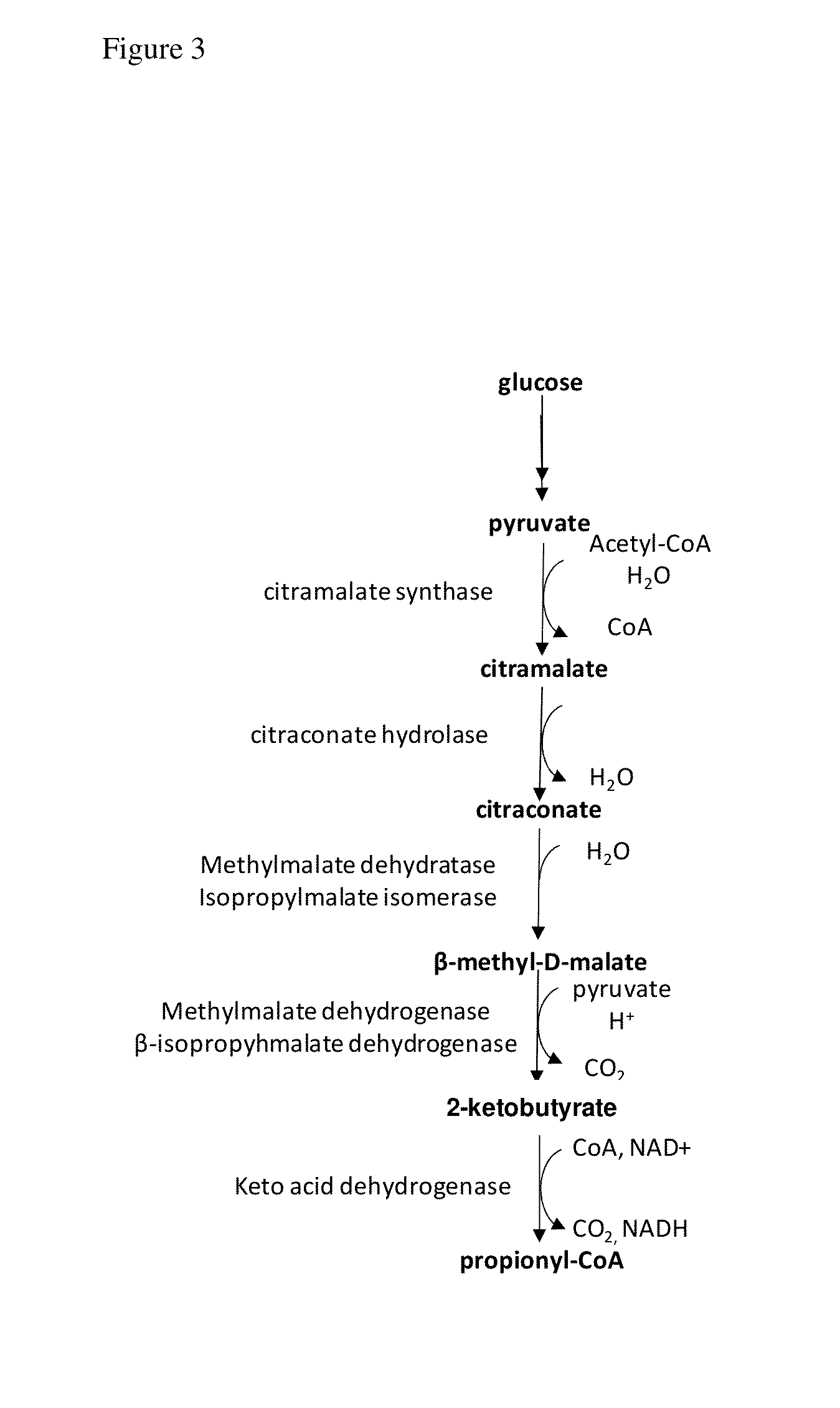
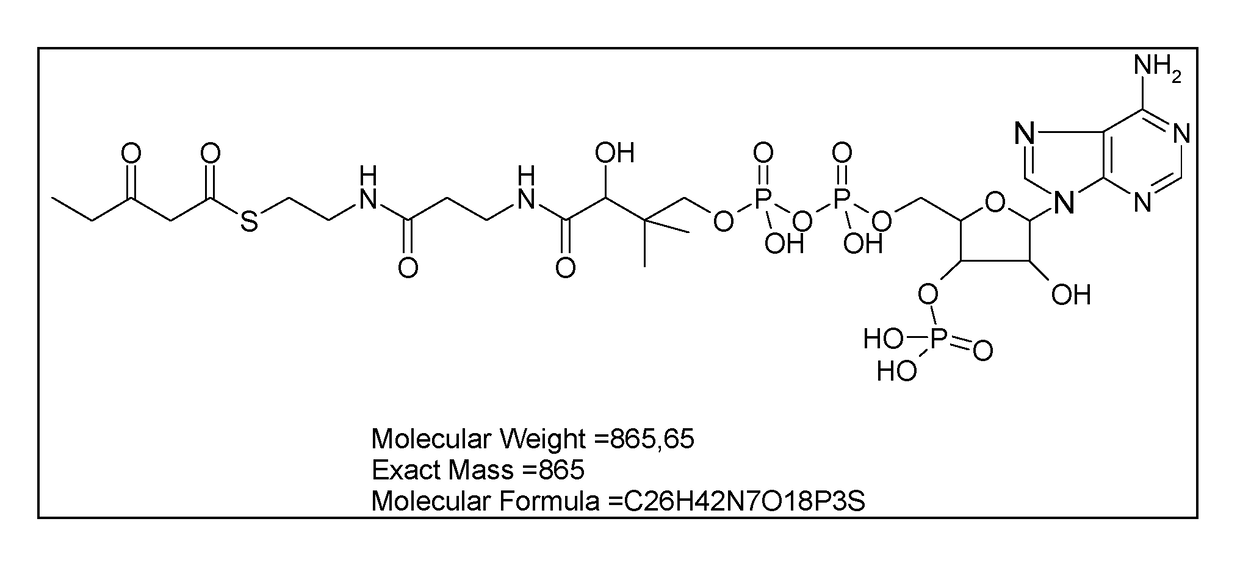
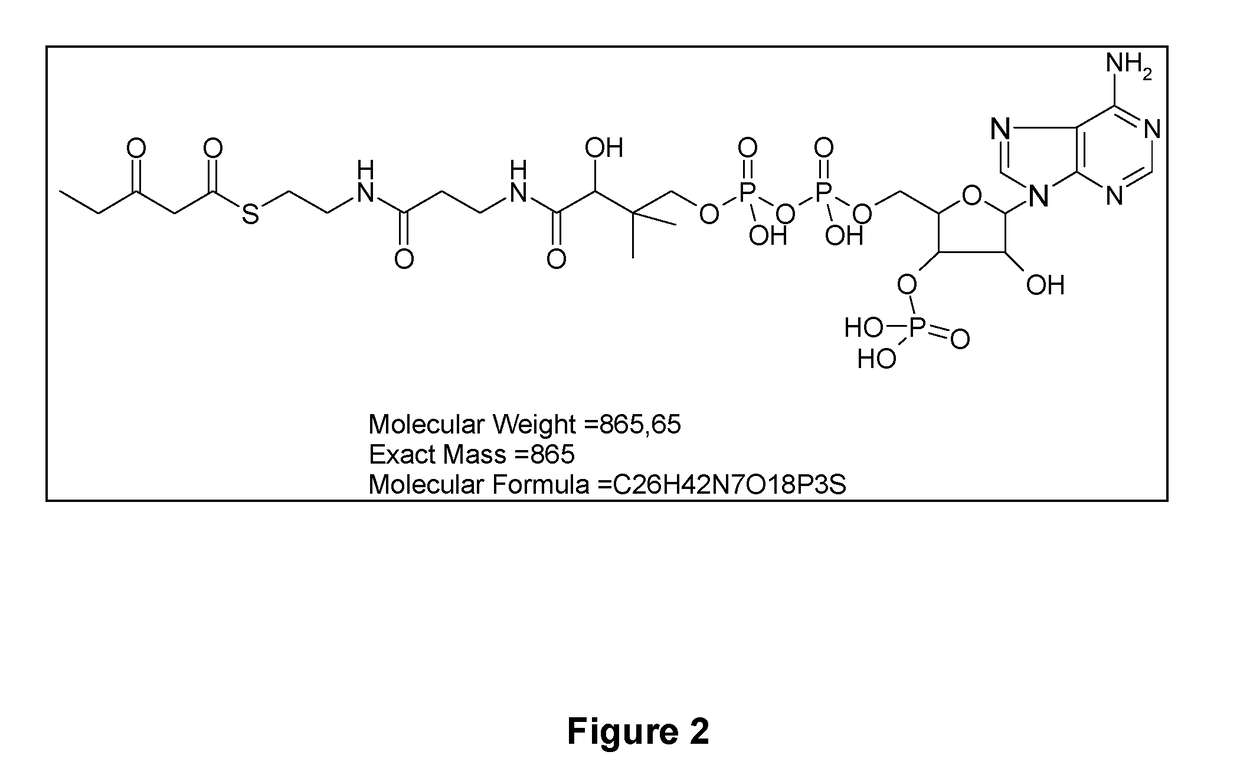
Propionyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of propionic acid. It is composed of a 24 total carbon chain (without the coenzyme, it is a 3 carbon structure) and its production and metabolic fate depend on which organism it is present in. Several different pathways can lead to its production, such as through the catabolism of specific amino acids or the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids. It later can be broken down by propionly-CoA carboxylase or through the methylcitrate cycle. In different organisms, however, propionyl-CoA can be sequestered into controlled regions, to alleviate its potential toxicity through accumulation. Genetic deficiencies regarding the production and breakdown of propionyl-CoA also have great clinical and human significance.
Scattered Branched-Chain Fatty Acids And Biological Production Thereof
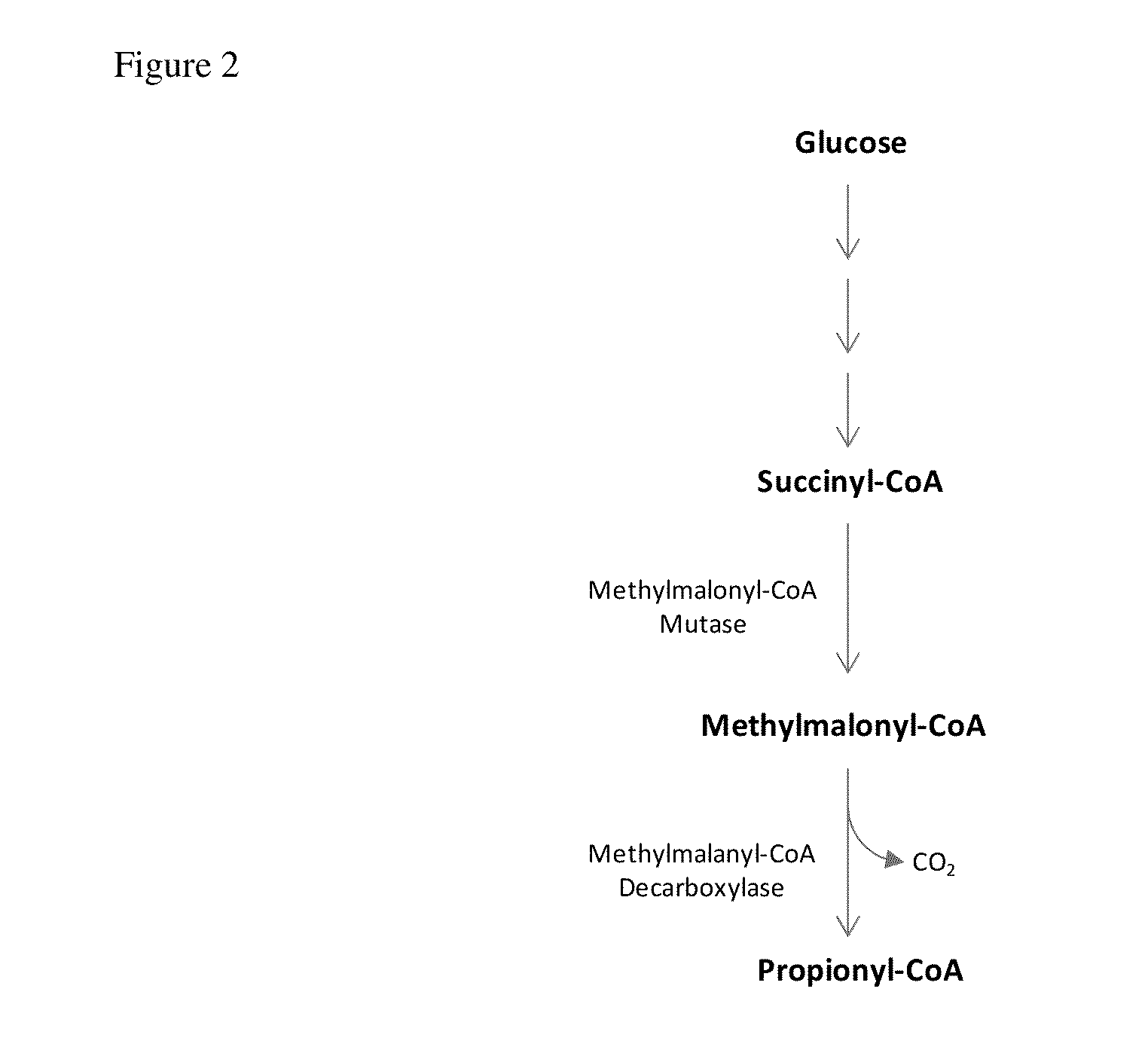
Methods and cells for producing scattered branched-chain fatty acids are provided. For example, the invention provides a method for producing branched-chain fatty acid comprising a methyl on one or more even number carbons. The method comprises culturing a cell comprising an exogenous or overexpressed polynucleotide comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a polypeptide that catalyzes the conversion of propionyl-CoA to methylmalonyl-CoA and / or an exogenous or overexpressed polynucleotide comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a polypeptide that catalyzes the conversion of succinyl-CoA to methylmalonyl-CoA, under conditions allowing expression of the polynucleotide(s) and production of branched-chain fatty acid. The cell produces more branched-chain fatty acid comprising a methyl on one or more even number carbons than an otherwise similar cell that does not comprise the polynucleotide(s). A cell that produces branched-chain fatty acid and the branched-chain fatty acid also are provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Seizure related disorders and therapeutic methods thereof
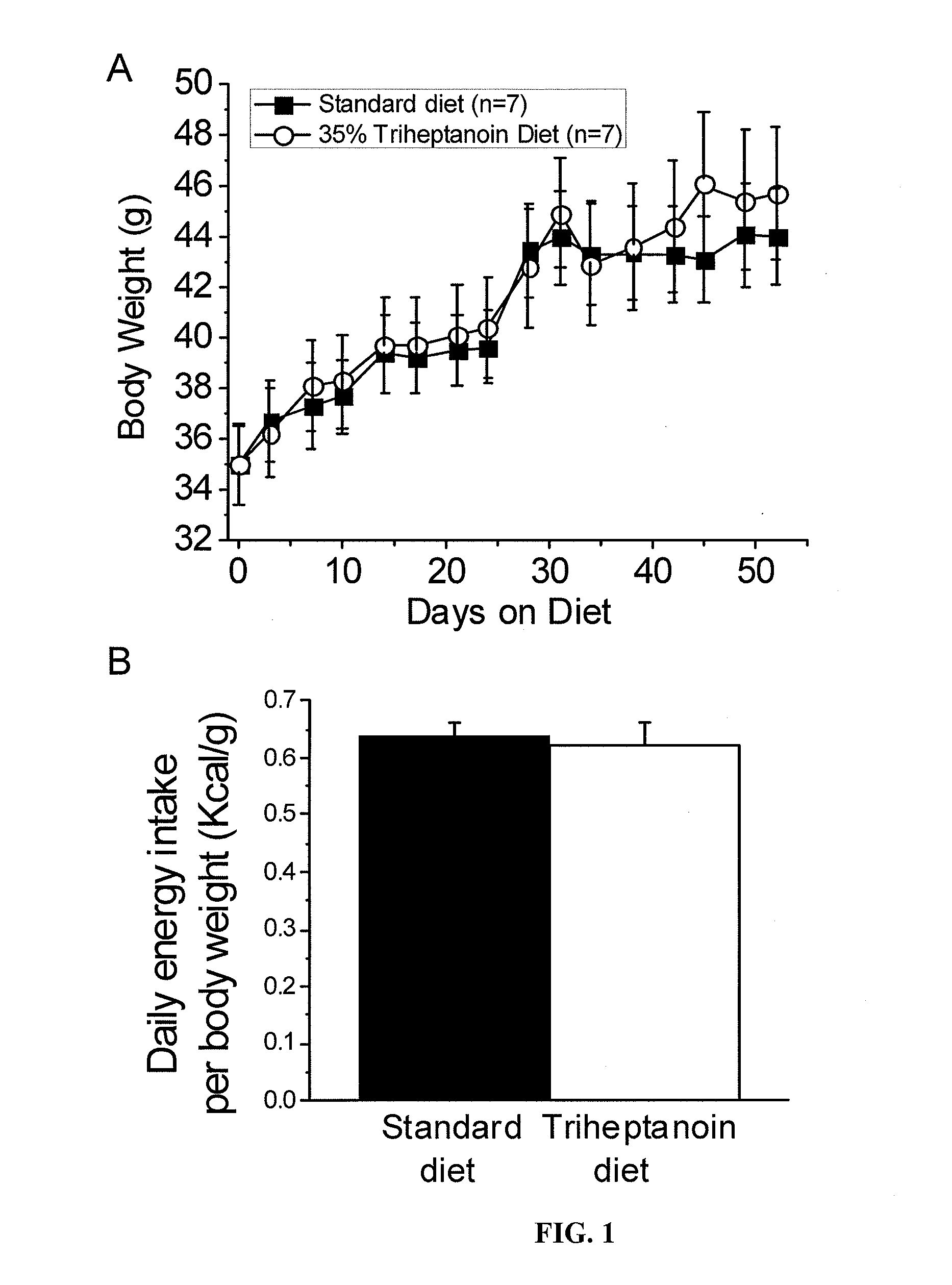
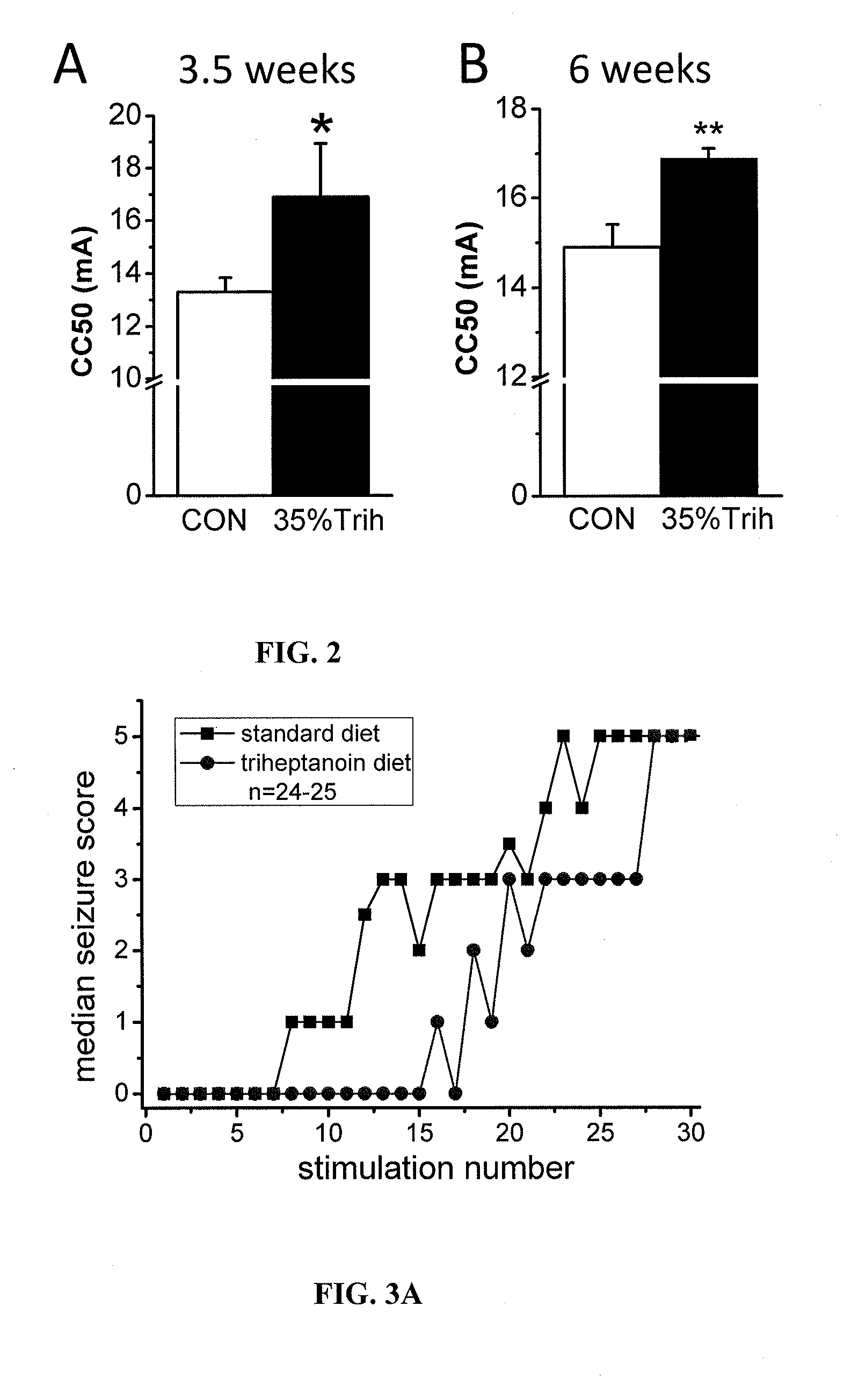
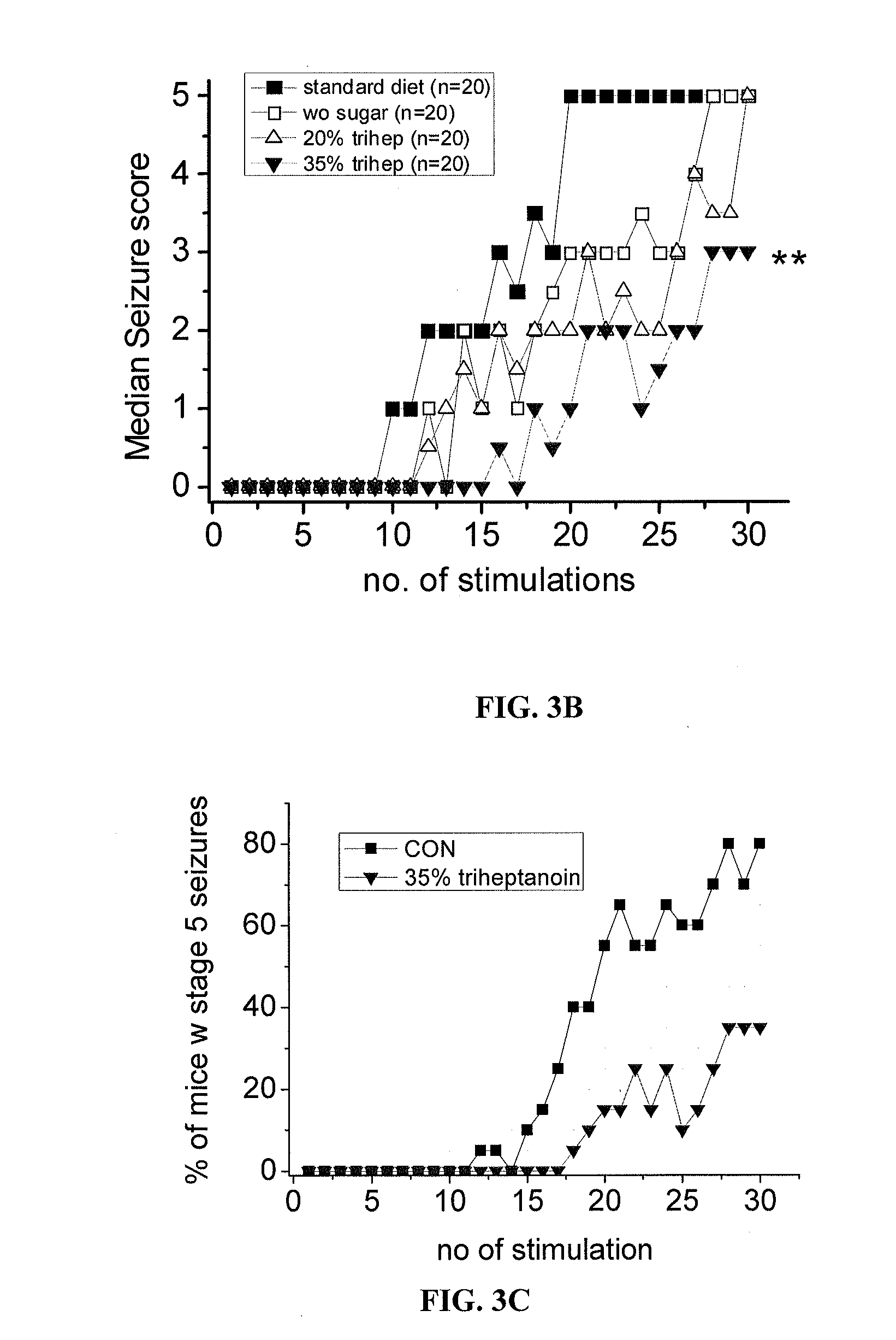
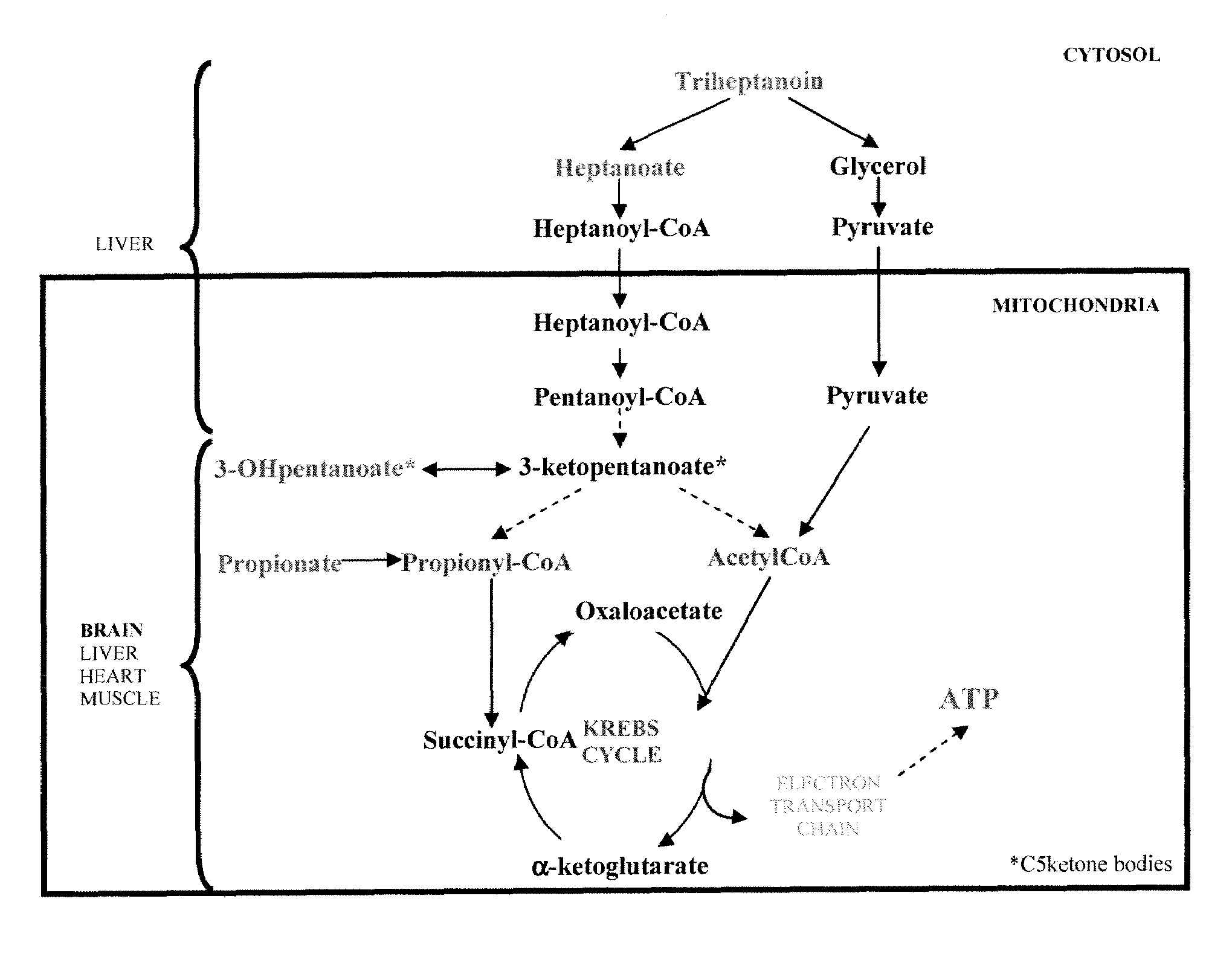
Methods of treating seizure disorders by administration of a therapeutically effective amount of at least one precursor of propionyl-CoA in the absence of a ketogenic diet are provided. The present invention particularly applies to administration of triglyceride oils and preferably, triheptanoin and derivatives thereof.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Engineered microorganisms and integrated process for producing n-propanol, propylene and polypropylene
The invention provides fermentative methods for producing n-propanol. The methods of the invention involve providing a suitable carbon source, a microorganism expressing the dicarboxylic acid pathway, reducing equivalents, and at least one gene coding for an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of propionate / propionyl-CoA into n-propanol. The methods further involve contacting the carbon source and reducing equivalents with the microorganism under conditions favorable for the production of n-propanol. Also provided are methods for producing propylene and polypropylene from the n-propanol and microorganisms suitable for use in the methods of the invention.
Owner:BRASKEM SA +1
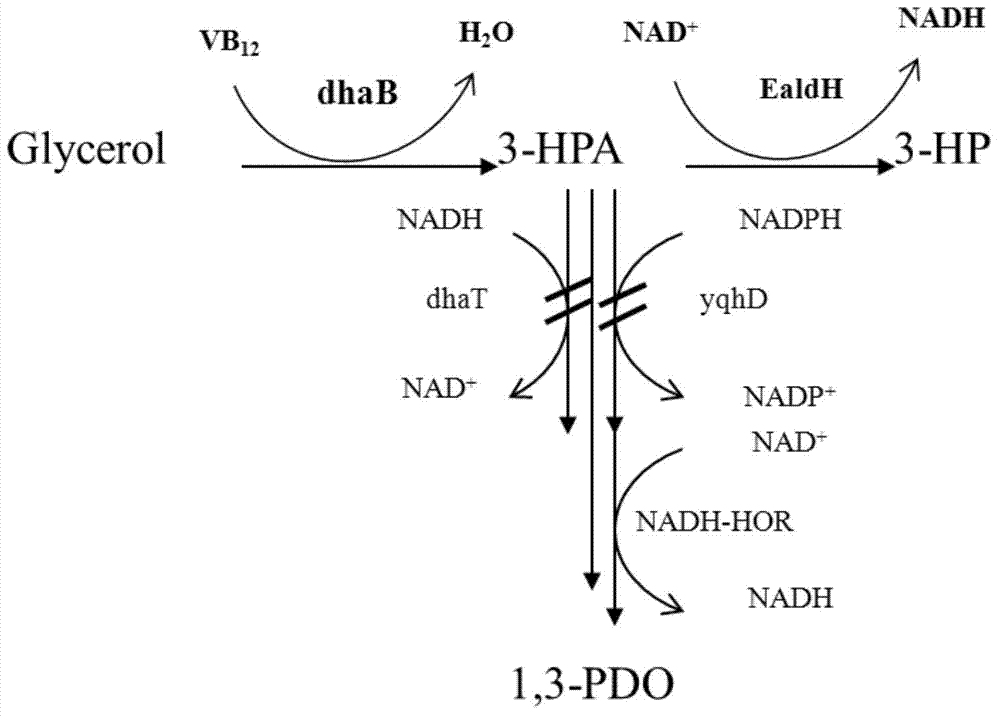
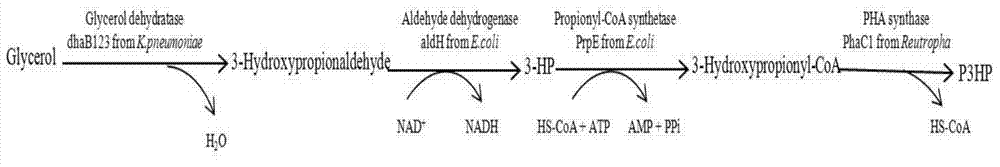
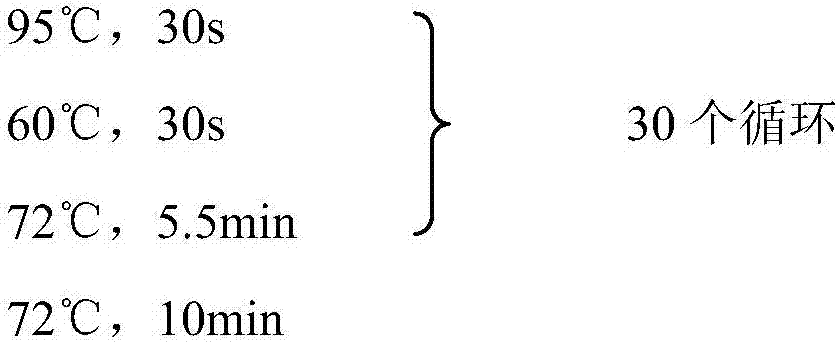
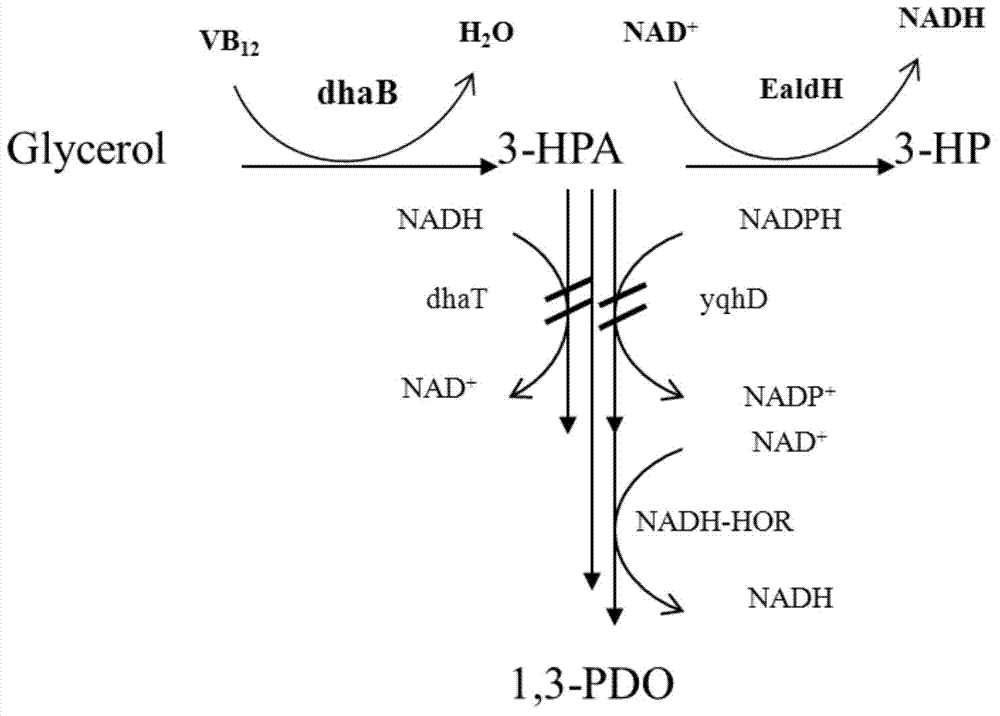
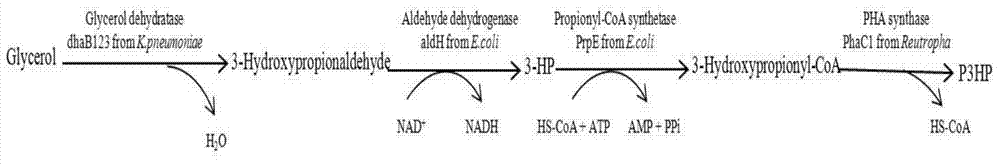
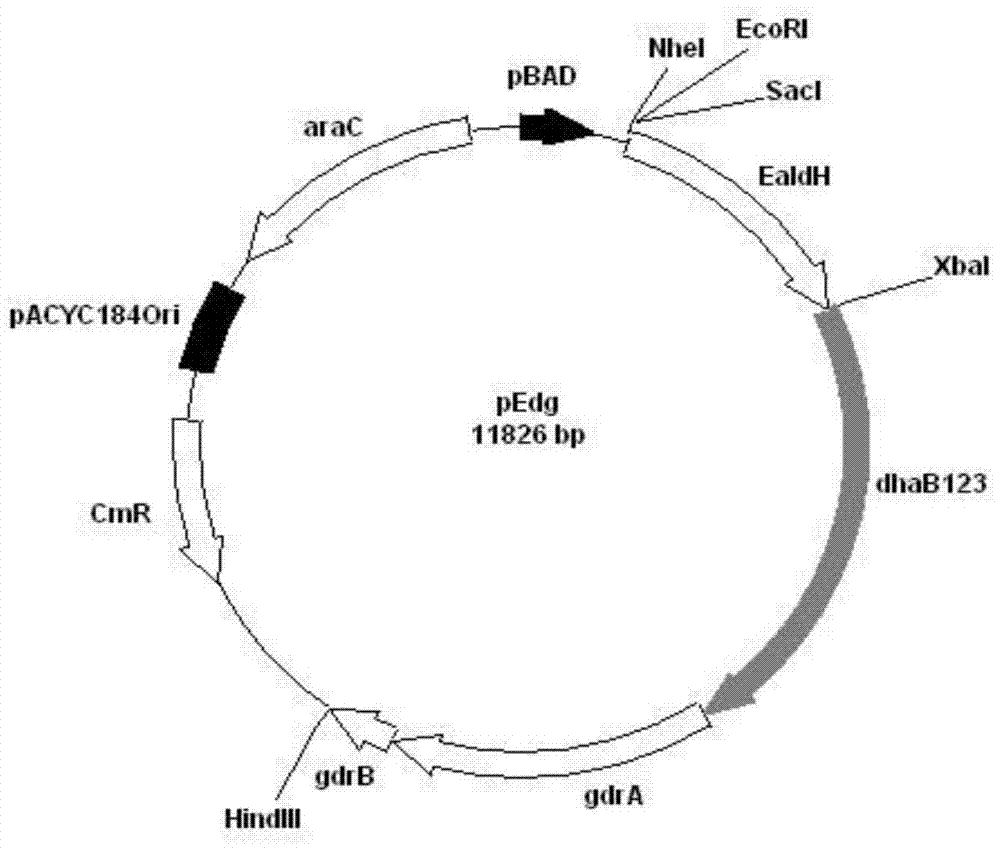
Recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103497922AReduce synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidK pneumoniae
The invention discloses recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombination bacterium is obtained by introducing glycerol dehydratase gene, glycerol dehydratase reactivation enzyme gene, aldehyde dehydrogenase gene, propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase gene into a host recombination klebsiella pneumonia in which 1, 3-propylene glycol oxidoreductase gene and aldehyde reductase / alcohol dehydrogenase gene are knocked out. According to the technical scheme, the production cost of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) is reduced, and 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) can be synthesized at the same time by taking a same thallus as the host.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Anaplerotic Therapy of Huntington Disease and Other Polyglutamine Diseases
The present invention relates to a method for treating and / or preventing Huntington disease and other polyglutamine diseases, comprising the step of administering an effective amount of a precursor of propionyl-CoA to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
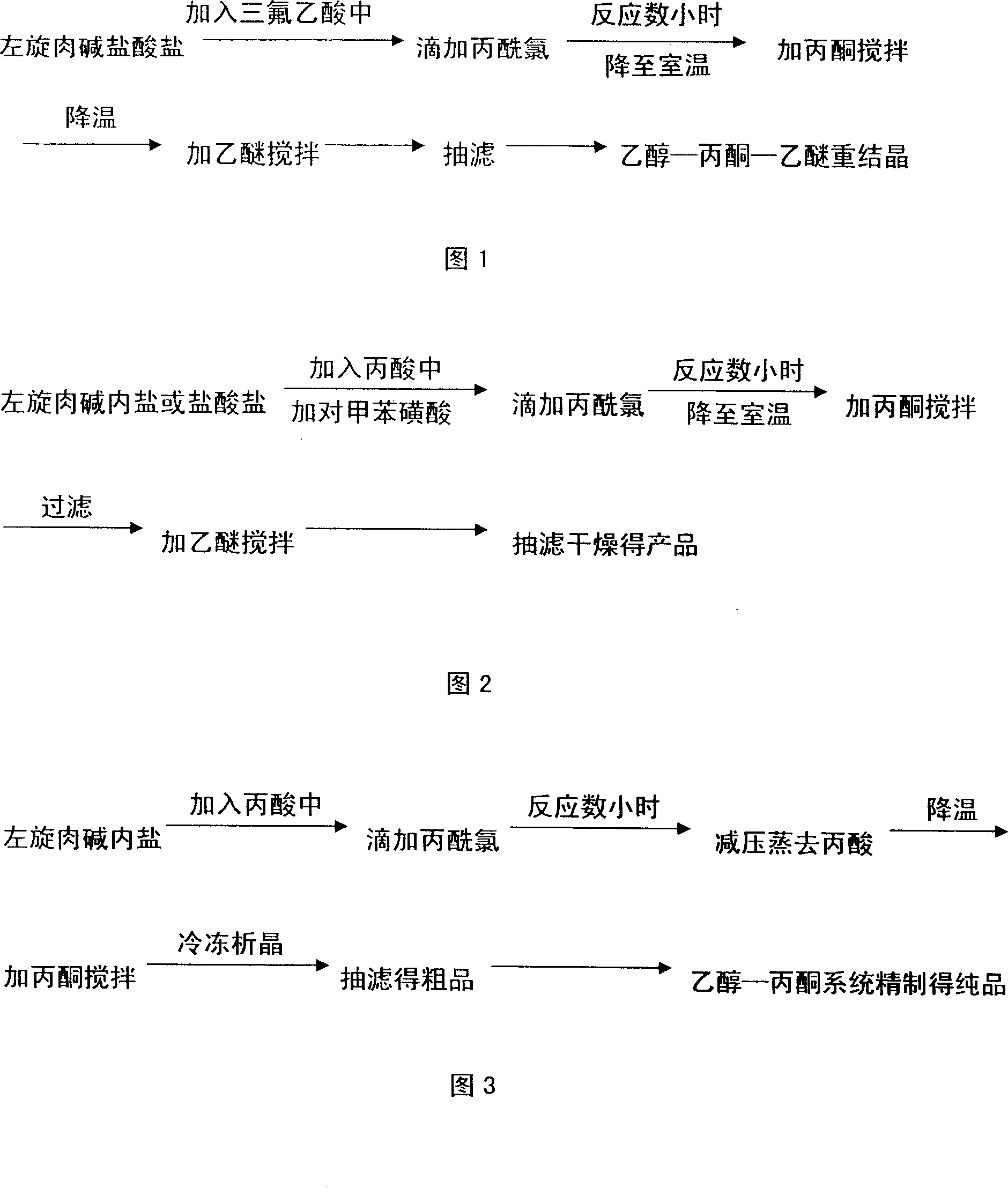
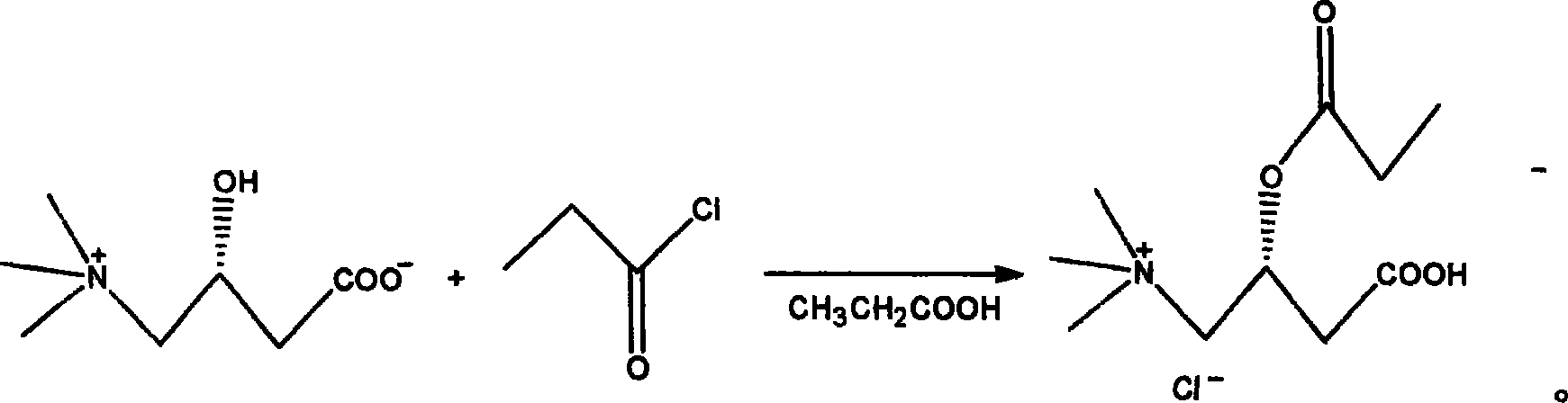
Method for synthesizing propionyl levo-carnitine hydrochlorate
ActiveCN1995010AEasy to purifyShort reaction timeOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationPropionyl chlorideAlcohol
The invention discloses a new synthesizing method of propionyl left-handed carnitine hydrochlorate, which comprises the following steps: 1. adopting inner salt of left-handed carnitine as raw material and propionic acid as solvent; adding propionyl chloride; heating to react; decompressing to evaporate propionic acid; adding acetone; stirring to disperse; cooling to evolve; sucking; drying to obtain rough product; 2. heating to dissolve rough product through alcohol or carbinol; sucking the filtrate; decompressing; distilling to condense; evaporating partial alcohol or carbinol; cooling; adding acetone to stir evenly; cooling to evolve; filtering; drying; obtaining the pure product.
Owner:リャオニンコンセプヌトラシーオーエルティーディー
Genetic engineering bacteria for producing PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) from acetic acid and propionic acid as well as construction method and application of genetically engineering bacteria
ActiveCN108359628AReduce fermentation costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPropanoic acidAcetic acid ear
The invention discloses genetic engineering bacteria for producing PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) from acetic acid and propionic acid as well as a construction method and an application of the genetic engineering bacteria. The method for preparing the engineering bacteria for producing PHA comprises the following steps: improving expression and / or activity of acetokinase, phosphotransacetylase, PHA synthetase, beta-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, succinate hemiacetal dehydrogenase, 4-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, 4-hydroxybutyl CoA:CoA-transferase and propionyl CoA transferase in recipient bacteria, and reducing expression and / or activity of non-CoA-cycle succinate hemiacetal dehydrogenase in the recipient bacteria to obtain the engineering bacteria for producing PHA, wherein the recipient bacteria can grow with acetic acid as a carbon source. The prepared engineering bacteria are used for producing PHA with acetic acid as the carbon source, PHA yield can reach a higher level, and the bacteria have better industrial application prospect. The genetic engineering bacteria have great application value.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Anaplerotic Therapy of Huntington Disease and Other Polyglutamine Diseases
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
New method for producing high-yield ethyl lactate by using saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and application of strain
ActiveCN108642095AIncrease productionLow ability to form ethyl lactateFungiMicroorganism based processesLactate dehydrogenasePhenylethyl Alcohol
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly discloses a new method for producing high-yield ethyl lactate by using a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and application of the strain. High-yield ethyl lactate is produced through the simultaneous heterologous expression of lactate dehydrogenase, propionyl-CoA transferase and alcohol acyltransferase in saccharomycescerevisiae. Pyruvate decarboxylase is completely knocked out from an original strain, and lactate dehydrogenase is overexpressed to obtain the yeast strain with a certain capability of generating L-lactic acid; a strong promoter TEF1 is selected and adopted for overexpressing propionyl-CoA transferase, a strong promoter PGK1 is selected and adopted for overexpressing alcohol acyltransferase, witha homothallic gene HO as an integration site, a copy number of propionyl-CoA transferase is increased, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain capable of significantly increasing the yield of ethyl lactate is obtained, and the yield of ethyl lactate obtained by using the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain reaches 353.1 mg / L; compared with the original strain, the yield of isoamyl alcohol is decreased by49.9%, the yield of phenylethyl alcohol is decreased by 59.2%, and the new method meets the higher requirements of yeast in the related field of liquor and has broad application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
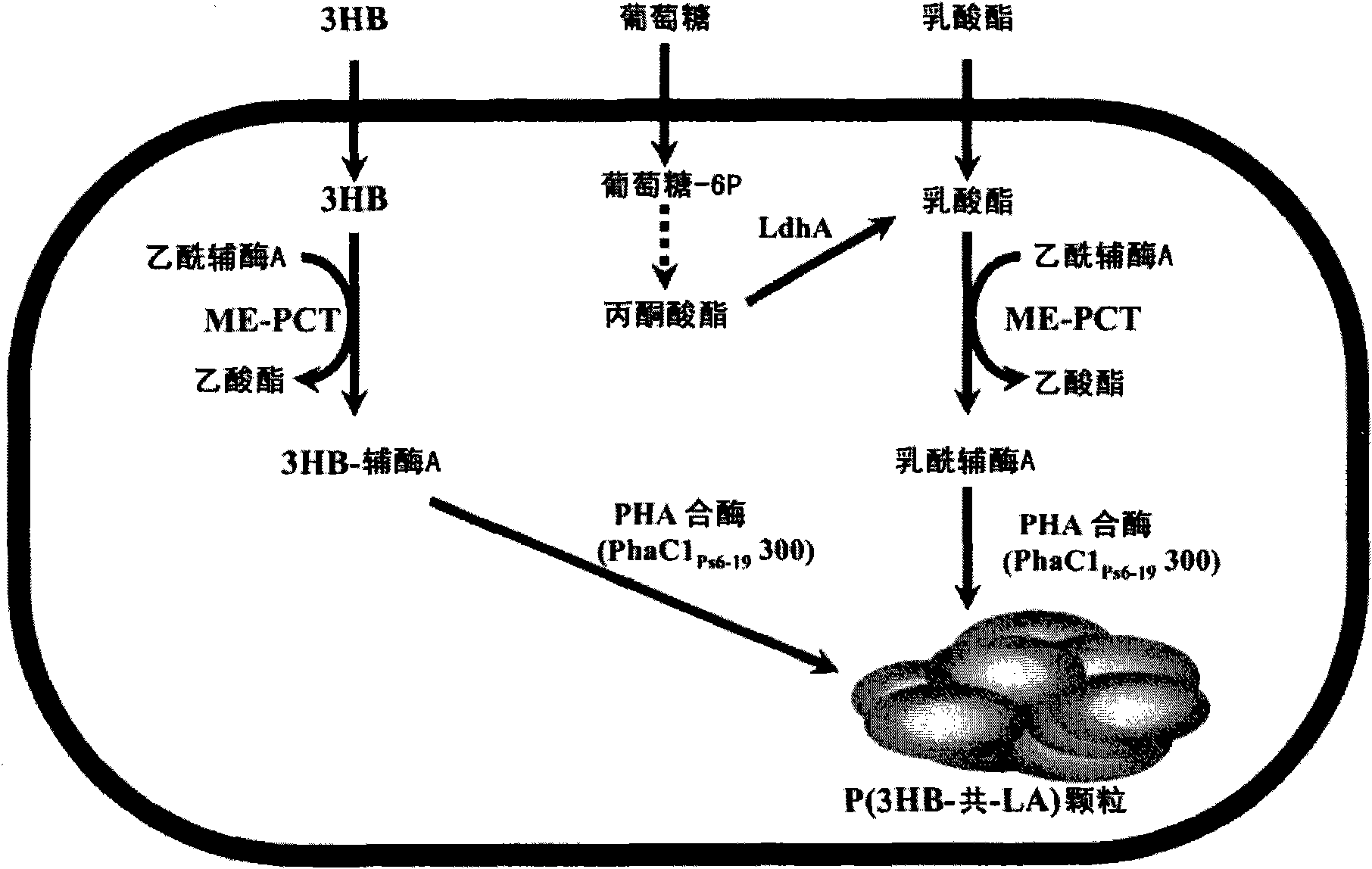
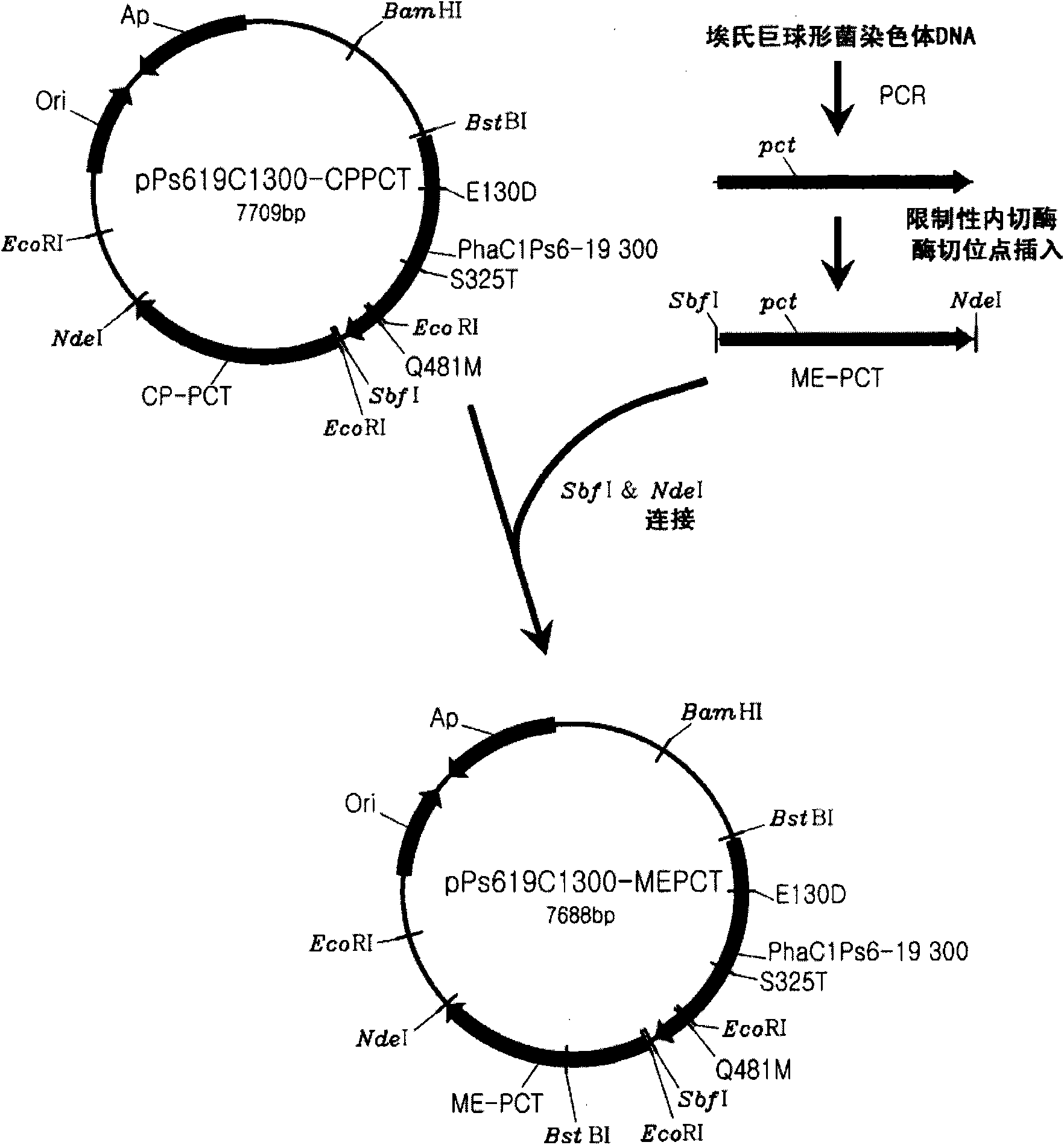
Mutant of propionyl-CoA transferase from Clostridium propionicum and preparing method for PLA or PLA copolymer using the same
ActiveUS8524478B2Increase supplyEfficient supplySugar derivativesProtozoaEscherichia coliMicroorganism
Provided is a mutant of propionyl-CoA transferase from Clostridium propionicum that can convert lactate into lactyl-CoA with high efficiency in a method of preparing a polylactate (PLA) or PLA copolymer using microorganisms. Unlike conventional propionyl-CoA transferase which is weakly expressed in E. coli, when a mutant of propiony-CoA transferase from Clostridium propionicum is introduced into recombinant E. coli, lactyl-CoA can be supplied very smoothly, thereby enabling highly efficient preparation of polylactate (PLA) and PLA copolymer.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Recombinant microorganism producing alkenes from acetyl-COA
Disclosed is a recombinant microorganism, comprising endogenous enzymes that convert CO and / or CO2 to acetyl-CoA. The recombinant microorganism contains a heterologous nucleic acid sequence encoding one or more enzymes that allow the conversion of acetyl-CoA to an alkene with a main chain of 1 to 5 carbon atoms. The heterologous nucleic acid sequence comprises one or more coding sequences encoding one or more enzymes that catalyse the conversion of acetyl-CoA to crotonyl-CoA, and that further catalyse the conversion of crotonyl-CoA to an alkene; or one or more coding sequences encoding one or more enzymes that catalyse the conversion of acetyl-CoA to 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA, and that further catalyse the conversion of 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA to an alkene; or one or more coding sequences encoding one or more enzymes that catalyse the conversion of acetyl-CoA to propionyl-CoA, and that further catalyse the conversion of propionyl-CoA to an alkene. Each coding sequence is operationally linked to a transcriptional promoter.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOENERGIES
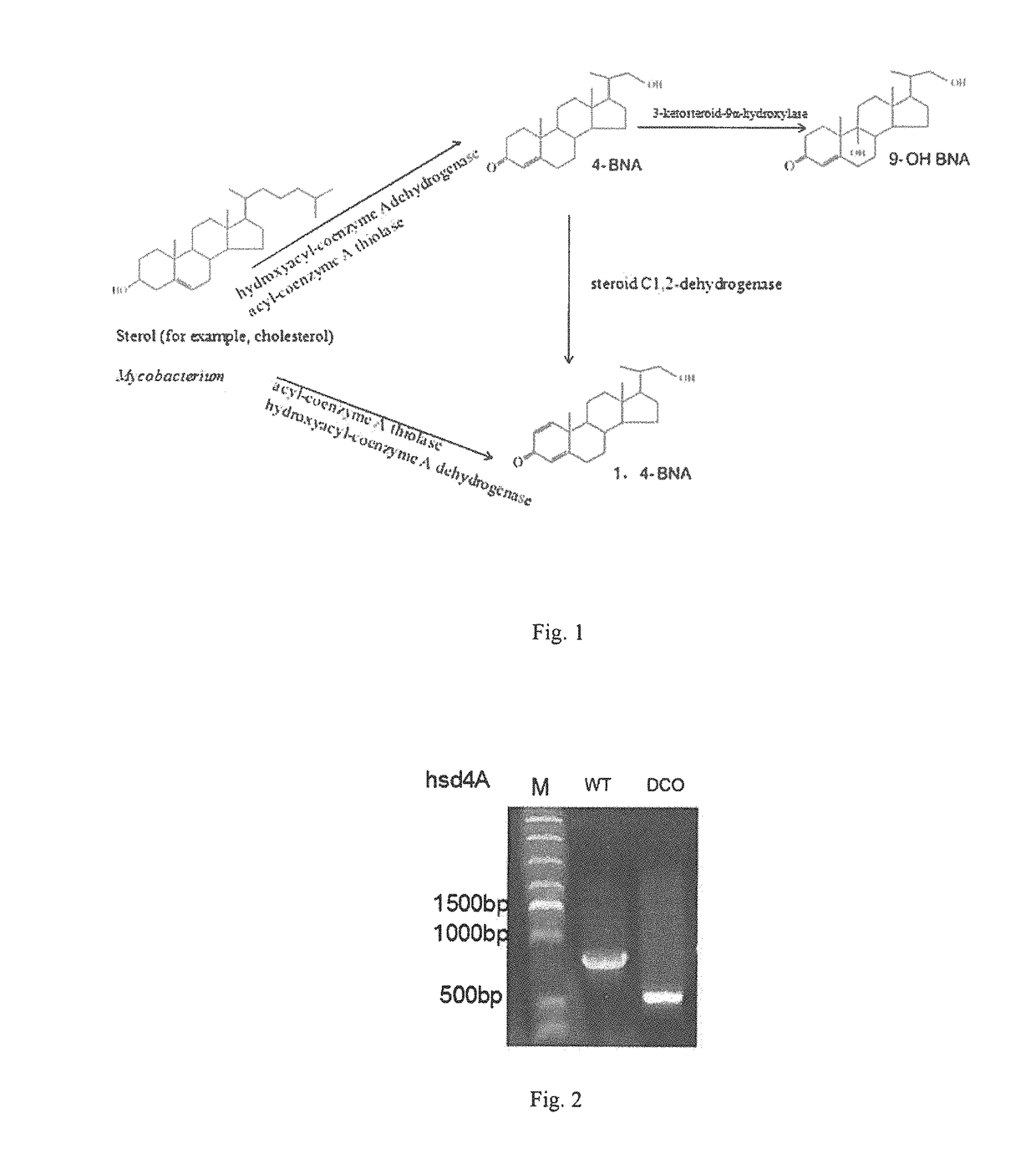
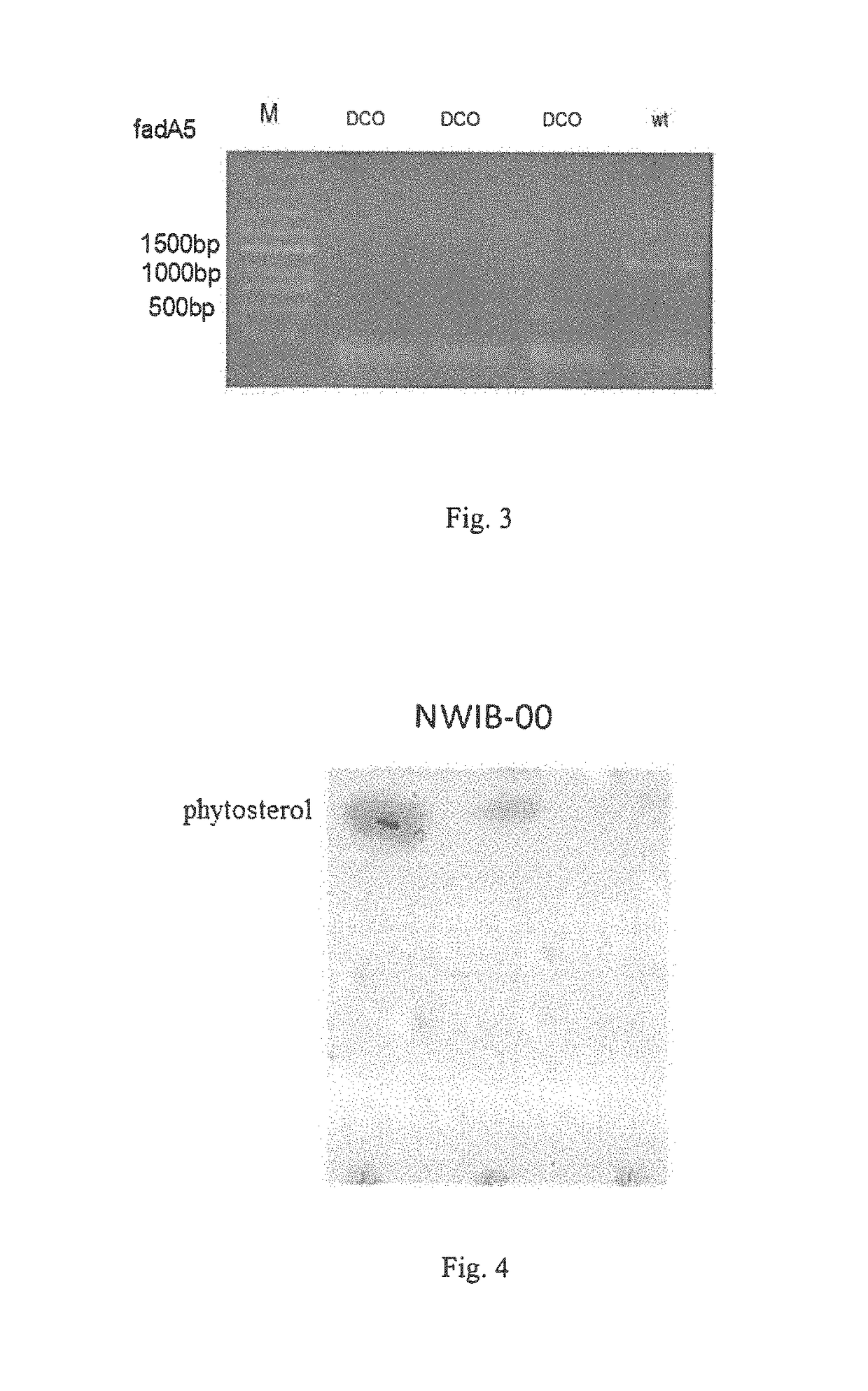
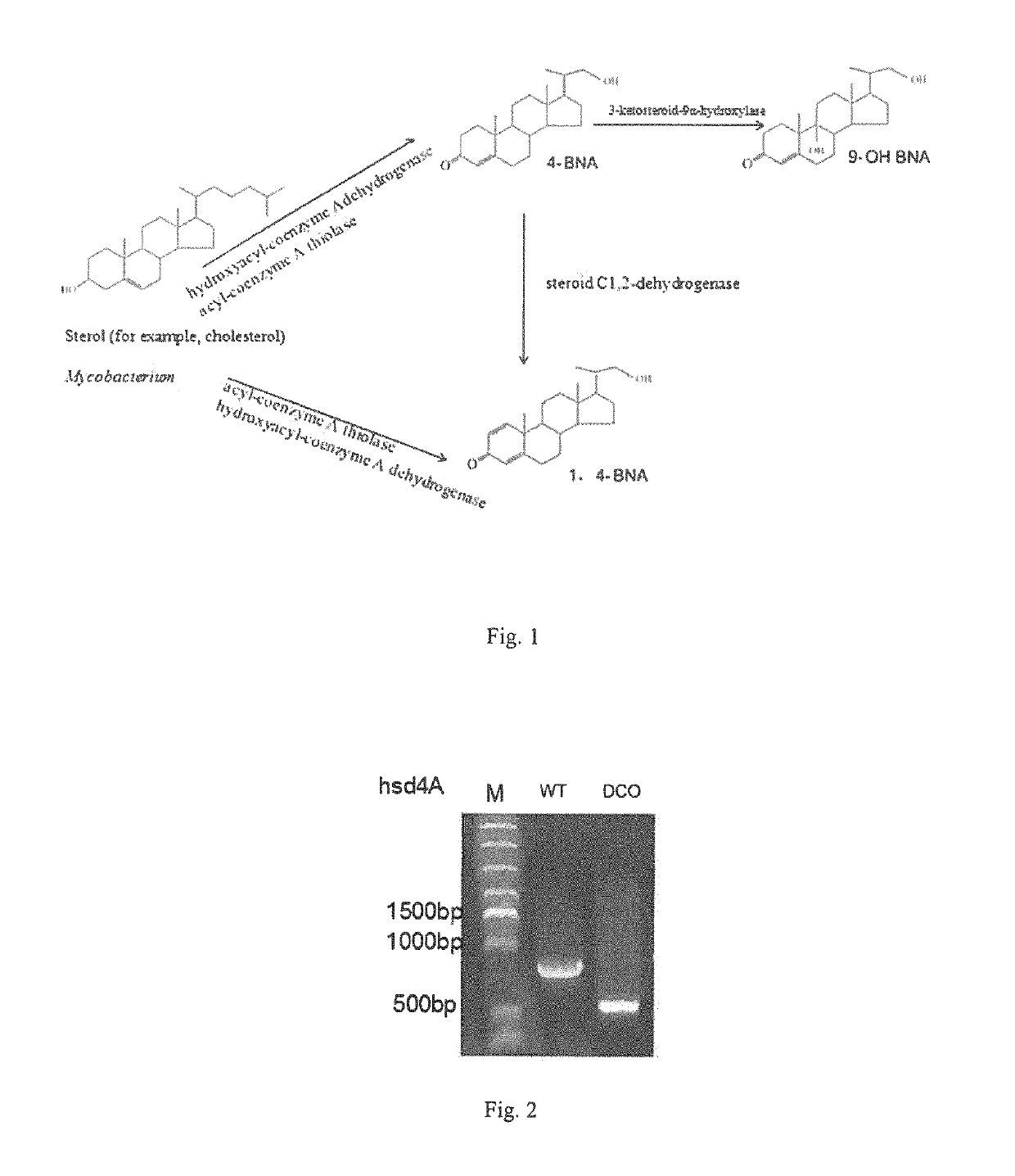
Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme a dehydrogenase gene, an acyl-coenzyme a thiolase gene, genetically engineered strains and a use thereof
ActiveUS20180087082A1Increase productionSimple chemical reactionMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesADAMTS ProteinsAcyl coenzyme A
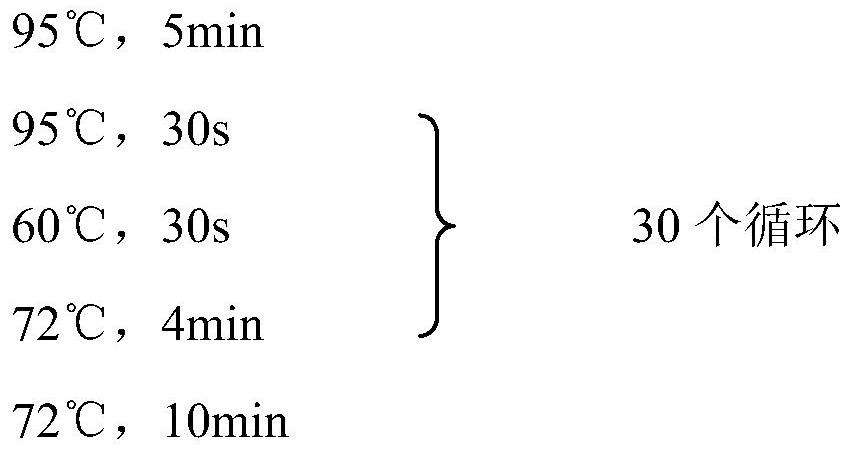
The present invention provides a hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene, an acyl-coenzyme A thiolase gene, genetically engineered strains and a use thereof. The hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene encodes a protein (i) or (ii) as follows: (i) having an amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO 2; (ii) derived by substituting, deleting or inserting one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequence defined by (i) and having the same function as that of the protein of (i). The present invention constructs genetically engineered Mycobacterium strains lacking of a hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene or an acyl-coenzyme A thiolase gene, which are used in the preparation of steroidal compounds, such as 1,4-BNA, 4-BNA, 9-OH-BNA, etc . . . Further, the invention improves the production efficiency and product quality of steroidal drug, improves the utilization of drug precursors, reduces the production costs, and provides the advantages of mild reaction conditions, environmentally friendly, and high economic and social benefits.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant bacteria for synthesizing succinic acid from fixed amount of carbon dioxide, as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacteria
ActiveCN106967662AAvoid excessive dependenceIncrease profitBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPropionyl-CoA carboxylase
The invention provides recombinant bacteria for synthesizing succinic acid from a fixed amount of carbon dioxide, as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. A recombinant bacteria host is escherichia coli, which can express a gene accADBC of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, a gene mcr of malonyl CoA reductase, a gene pcs of propionyl CoA synthase, a gene pcc of propionyl CoA carboxylase, a gene mcE of methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, a gene mcM of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase and a gene sucCD of succinyl-coenzyme A synthase. According to the construction method, recombinant carriers pACYCDuet-accADBC-pcs and pETDuet-mcr-pcc-sucCD-mcEM are transformed into a host cell. The recombinant bacteria constructed through the construction method can adopt glucose serving as a unique carbon source to synthesize the succinic acid, and fermentation is performed for 48 hours, thus obtaining the succinic acid with the concentration of 6.06 g / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Use of propionyl L-carnitine for the preparation of a medicament capable of inducing apoptosis
InactiveUS20020091092A1Inhibit progressStrong antiatherogenicBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsPercent Diameter StenosisApoptosis
The present invention relates to the use of propionyl L-carnitine and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof for the preparation of medicaments useful in the treatment of pathologies whose treatment gains a benefit from inducement of apoptosis, in particular blood vessels, such as restenosis after angioplasty or coronary stenting, or in particular tumors.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103497922BReduce synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniae3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention discloses recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombination bacterium is obtained by introducing glycerol dehydratase gene, glycerol dehydratase reactivation enzyme gene, aldehyde dehydrogenase gene, propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase gene into a host recombination klebsiella pneumonia in which 1, 3-propylene glycol oxidoreductase gene and aldehyde reductase / alcohol dehydrogenase gene are knocked out. According to the technical scheme, the production cost of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) is reduced, and 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) can be synthesized at the same time by taking a same thallus as the host.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
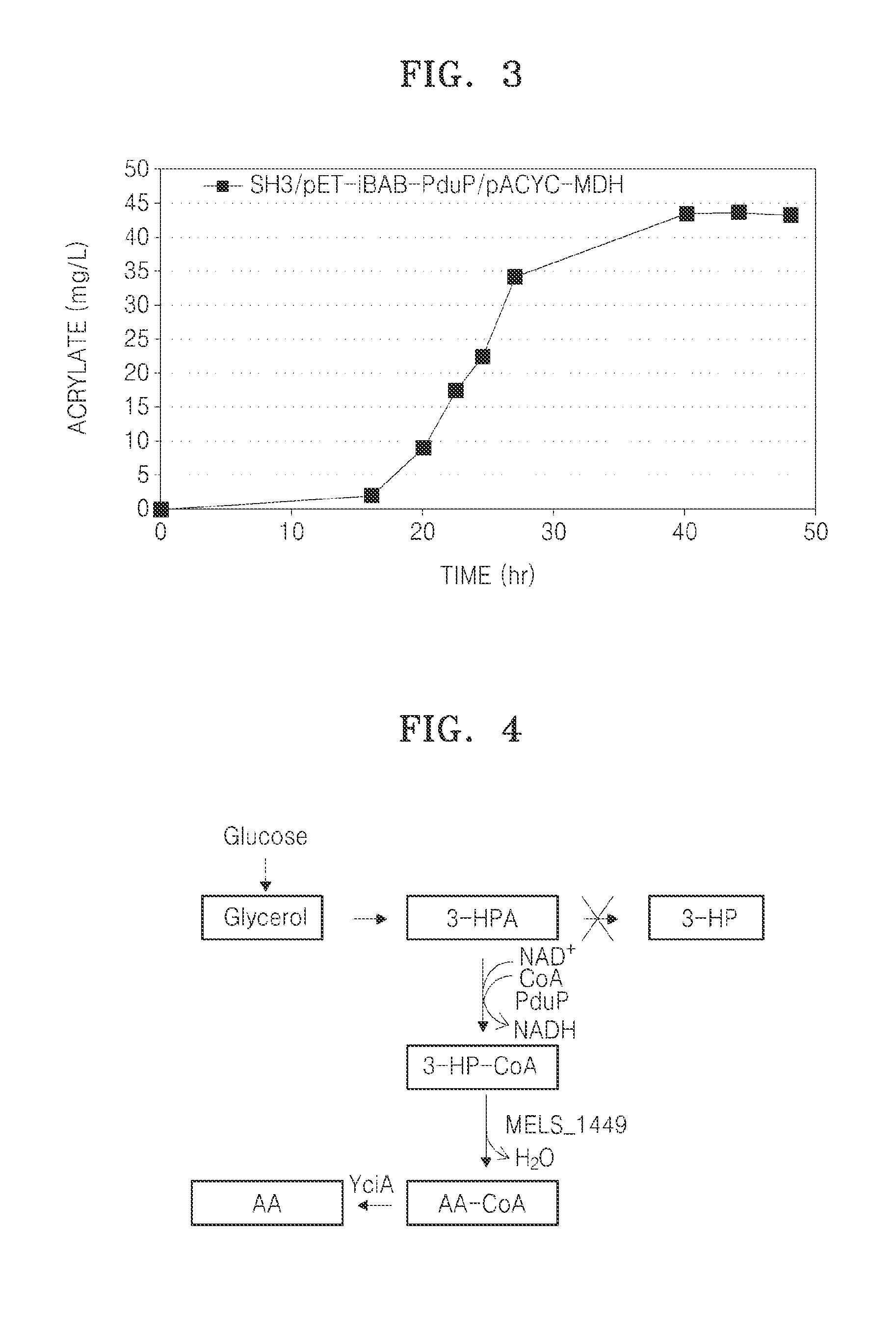
Microorganism having novel acrylic acid synthesis pathway having enhanced activity of coa acylating aldehyde dehydrogenase and method of producing acrylic acid using the same
A microorganism capable of producing acrylic acid, comprising a genetic modification that increases activity of CoA acylating aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) catalyzing conversion of 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde (3-HPA) to 3-hydroxy propionyl-CoA (3-HP-CoA) and a genetic modification that increases activity of 3-HP-CoA dehydratase catalyzing conversion of 3-HP-CoA to acrylyl-CoA in the microorganism in comparison with a cell that is not genetically engineered; as well as a method of producing the microorganism, and a method of producing acrylic acid using the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
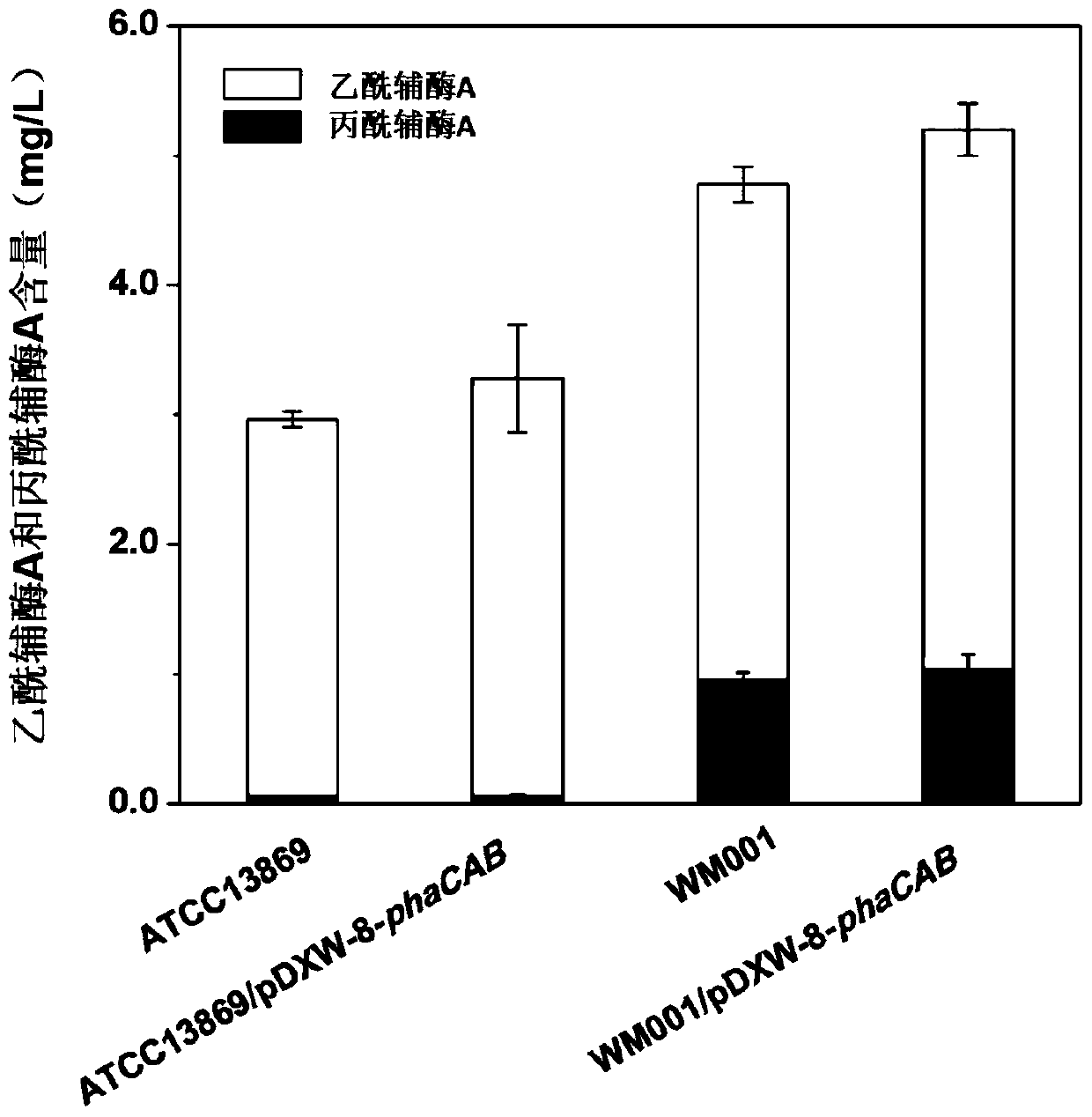
A kind of Corynebacterium glutamicum and its application
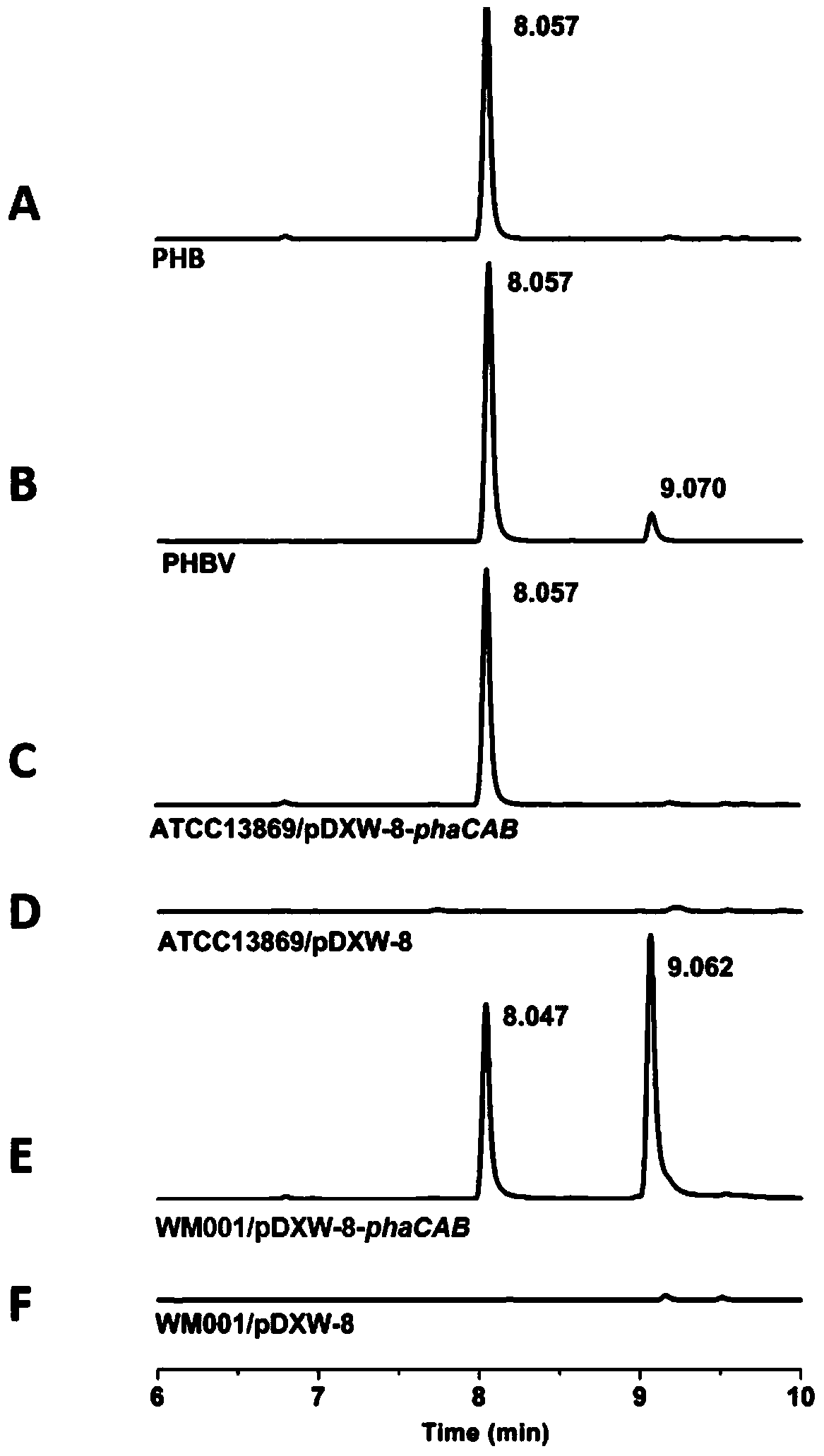
The invention discloses a Corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof, belonging to the field of microorganisms. The Corynebacterium glutamicum was preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on June 1, 2016, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2016303. The Corynebacterium glutamicum can accumulate more propionyl-CoA in cells, which is 15.8 times higher than that of ATCC13869, and can be used for the production of related metabolites using propionyl-CoA as a substrate. After the polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis gene is introduced, the Corynebacterium glutamicum can synthesize PHBV, but the synthetic product is PHB in ATCC13869. The invention solves the current situation of producing PHBV by adding propionate or propionate from an exogenous source, realizes the direct production of PHBV in Corynebacterium glutamicum without adding propionate or propionate from an exogenous source, and reduces production costs.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A new way of high-yielding ethyl lactate produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its application
ActiveCN108642095BLow ability to form ethyl lactateReduce outputFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousLactate dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly discloses a new method for producing high-yield ethyl lactate by using a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and application of the strain. High-yield ethyl lactate is produced through the simultaneous heterologous expression of lactate dehydrogenase, propionyl-CoA transferase and alcohol acyltransferase in saccharomycescerevisiae. Pyruvate decarboxylase is completely knocked out from an original strain, and lactate dehydrogenase is overexpressed to obtain the yeast strain with a certain capability of generating L-lactic acid; a strong promoter TEF1 is selected and adopted for overexpressing propionyl-CoA transferase, a strong promoter PGK1 is selected and adopted for overexpressing alcohol acyltransferase, witha homothallic gene HO as an integration site, a copy number of propionyl-CoA transferase is increased, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain capable of significantly increasing the yield of ethyl lactate is obtained, and the yield of ethyl lactate obtained by using the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain reaches 353.1 mg / L; compared with the original strain, the yield of isoamyl alcohol is decreased by49.9%, the yield of phenylethyl alcohol is decreased by 59.2%, and the new method meets the higher requirements of yeast in the related field of liquor and has broad application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compositions and methods for treatment of movement disorders
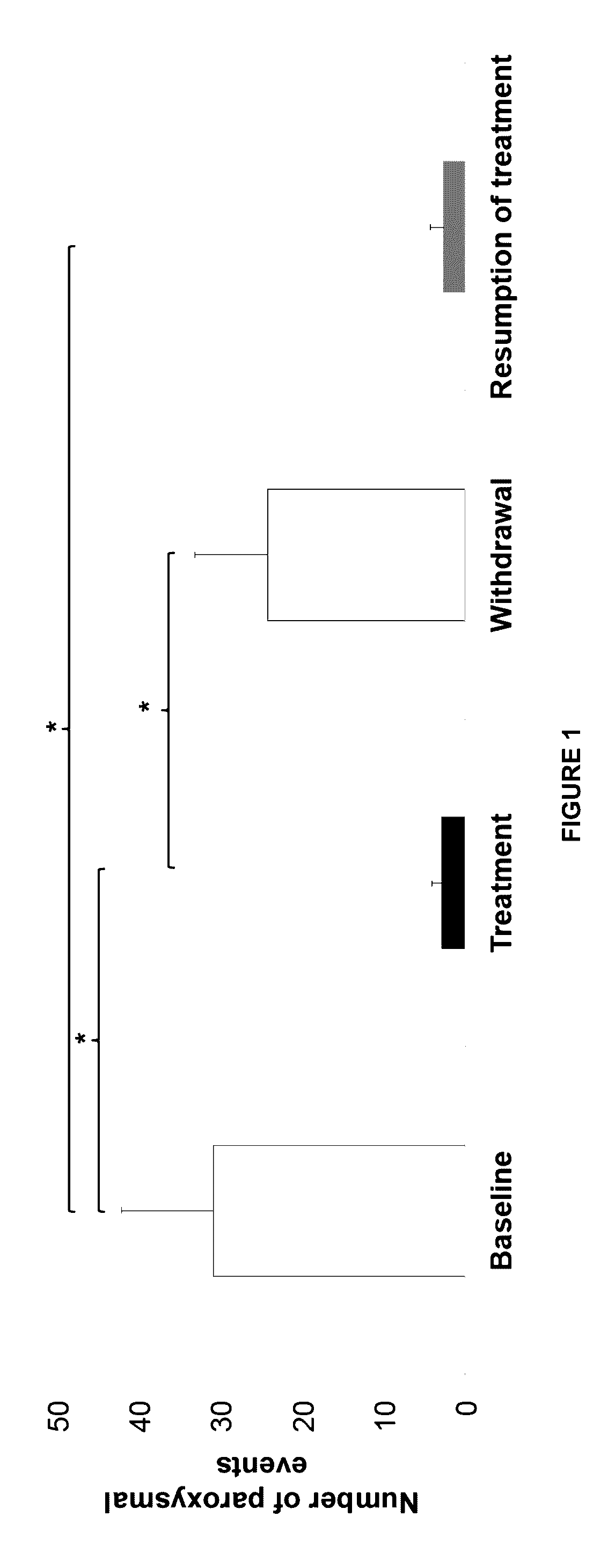
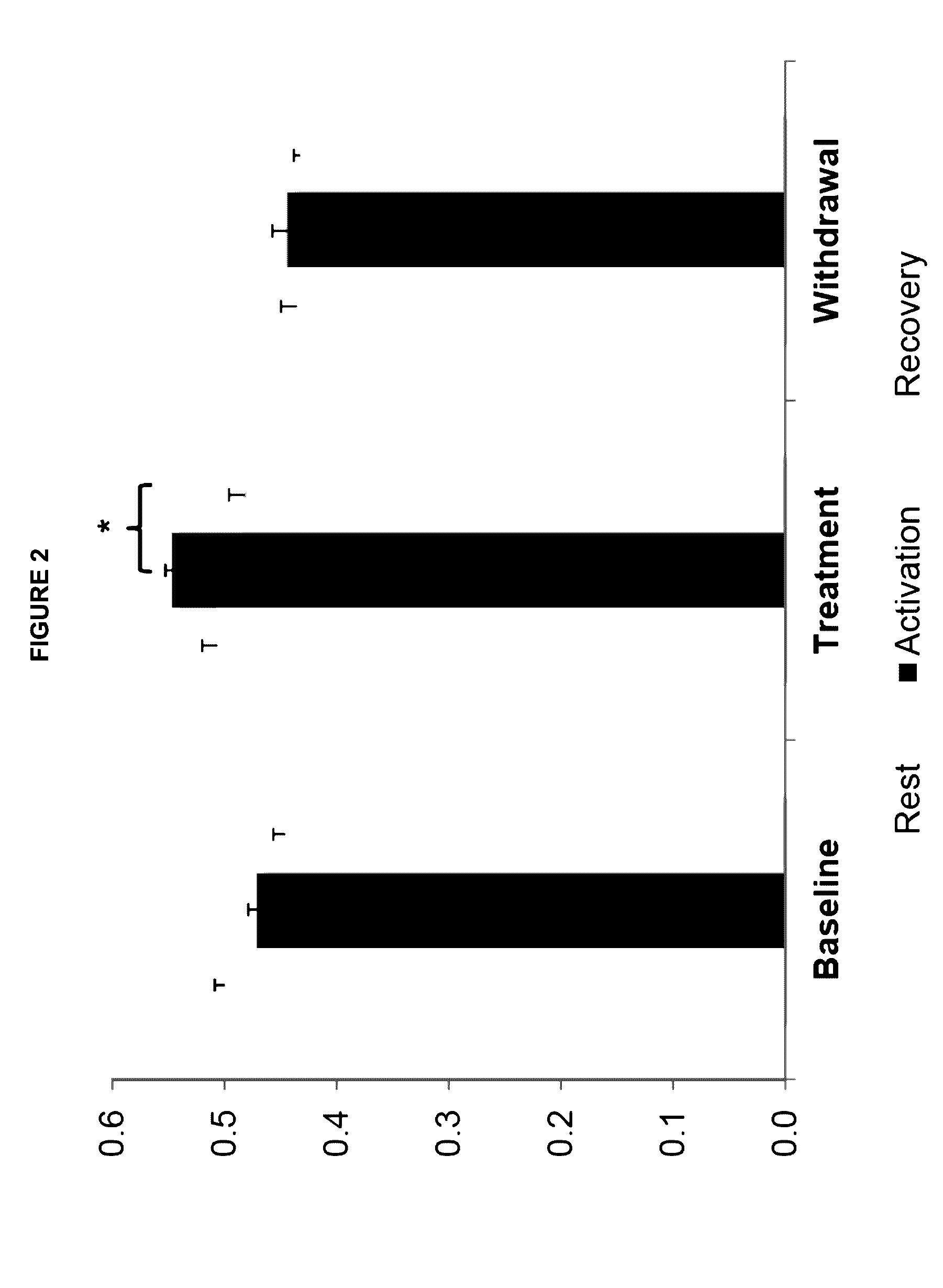
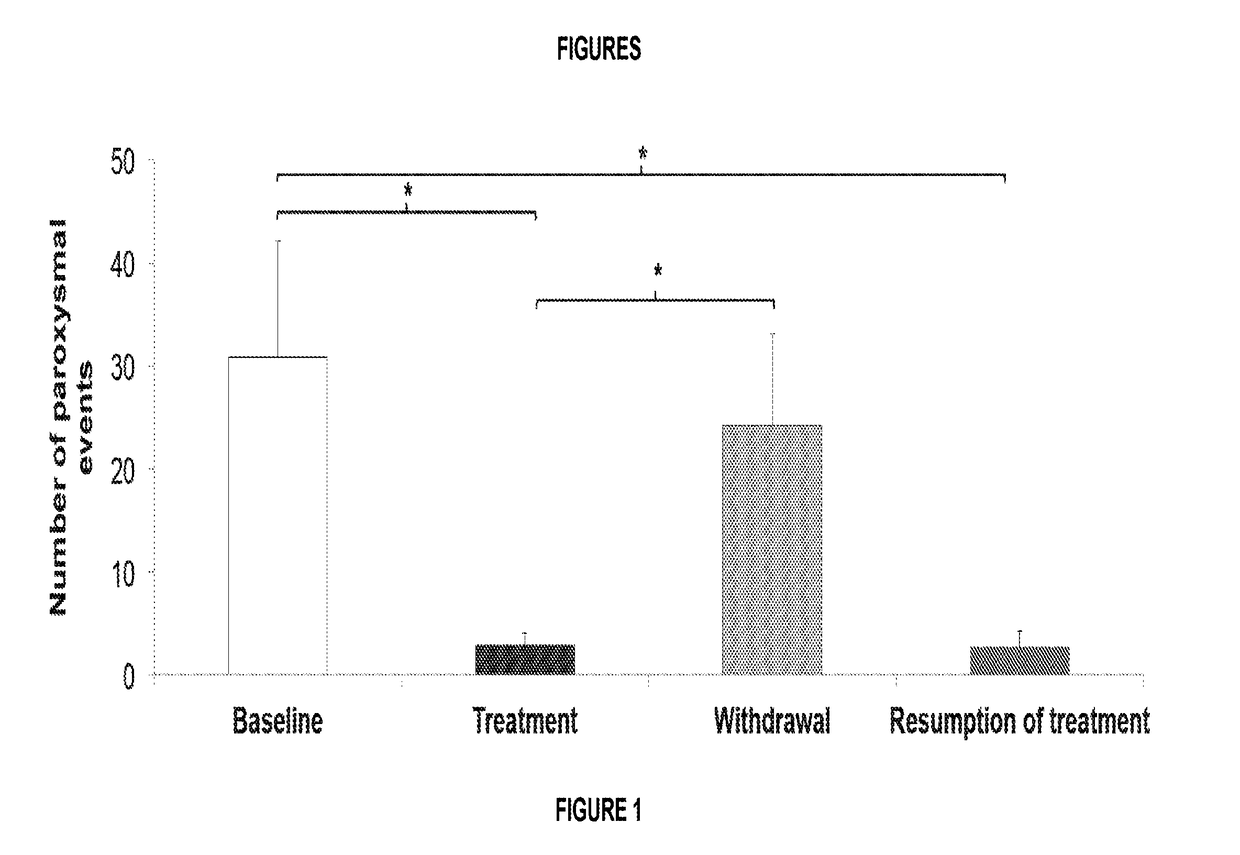
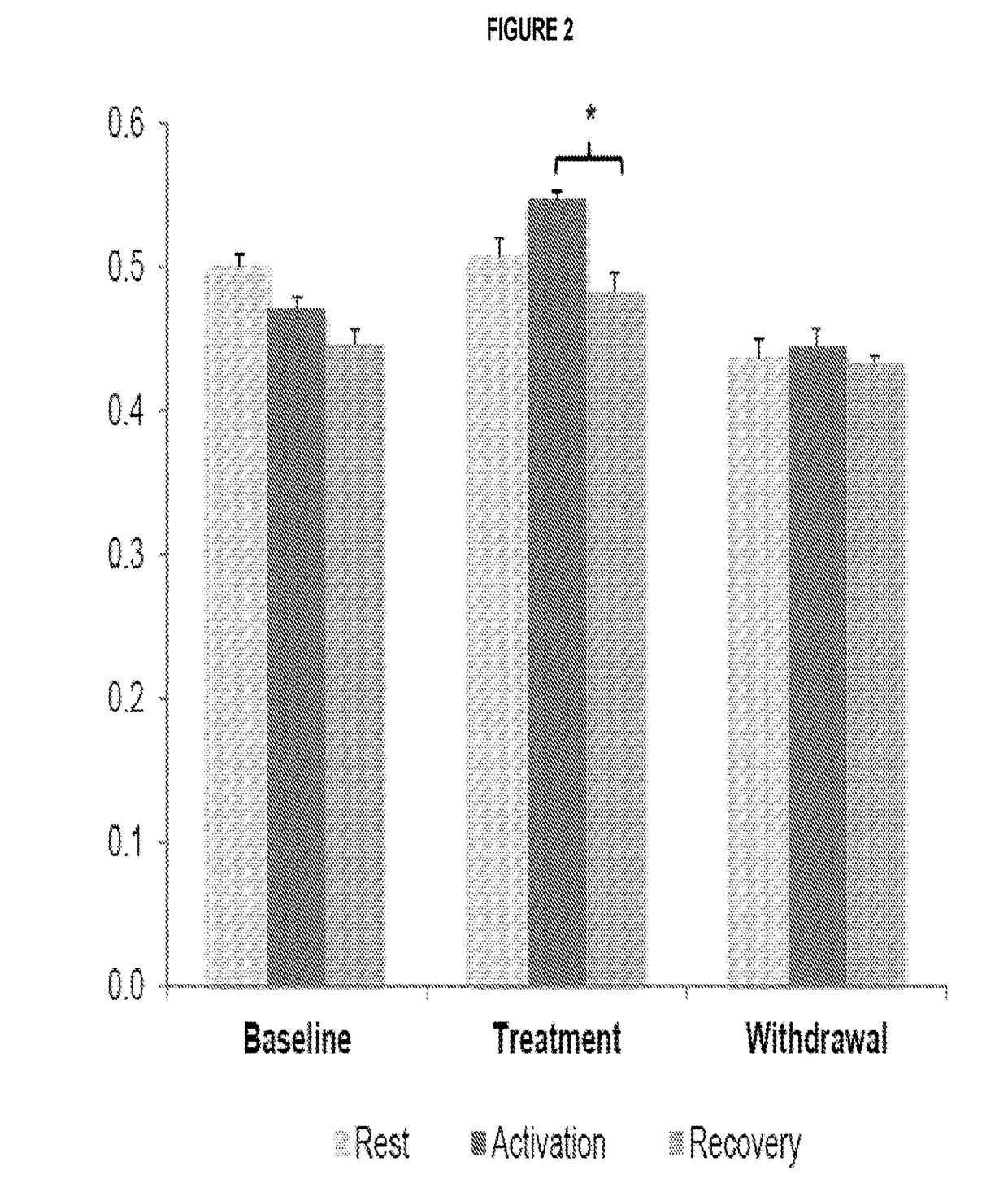
InactiveUS20160296491A1Good treatment effectReduction in paroxysmal manifestationNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicinePropionyl-CoA
The present invention relates to the treatment and prevention of movement disorders with the administration of one or more propionyl-CoA precursors.
Owner:ULTRAGENYX PHARMA
Recombinant microorganism having a producing ability of polylactate or its copolymers and method for preparing polylactate or its copolymers using the same
InactiveCN101679983AEfficient manufacturingMicroorganismsTransferasesMicroorganismMegasphaera elsdenii
Provided are a recombinant microorganism capable of producing polylactate (PLA) or hydroxyalkanoate-lactate copolymers and a method of preparing PLA or hydroxyalkanoate-lactate copolymers using the same. The recombinant microorganism has both a gene encoding a propionyl-CoA transferase from Megasphaera elsdenii and a gene encoding a polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase using lactyl-CoA as a substrate. A propionyl-CoA transferase from Megasphaera elsdenii is introduced into the recombinant microorganism to effectively provide lactyl-CoA, thereby enabling efficient preparation of PLA or PLA copolymers.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Compositions and methods for treatment of movement disorders
InactiveUS20180147175A1Degradation is usually manifestedReduction in dystonic eventsNervous disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsMedicinePropionyl-CoA
The present invention relates to the treatment and prevention of movement disorders with the administration of one or more propionyl-CoA precursors.
Owner:ULTRAGENYX PHARMA INC
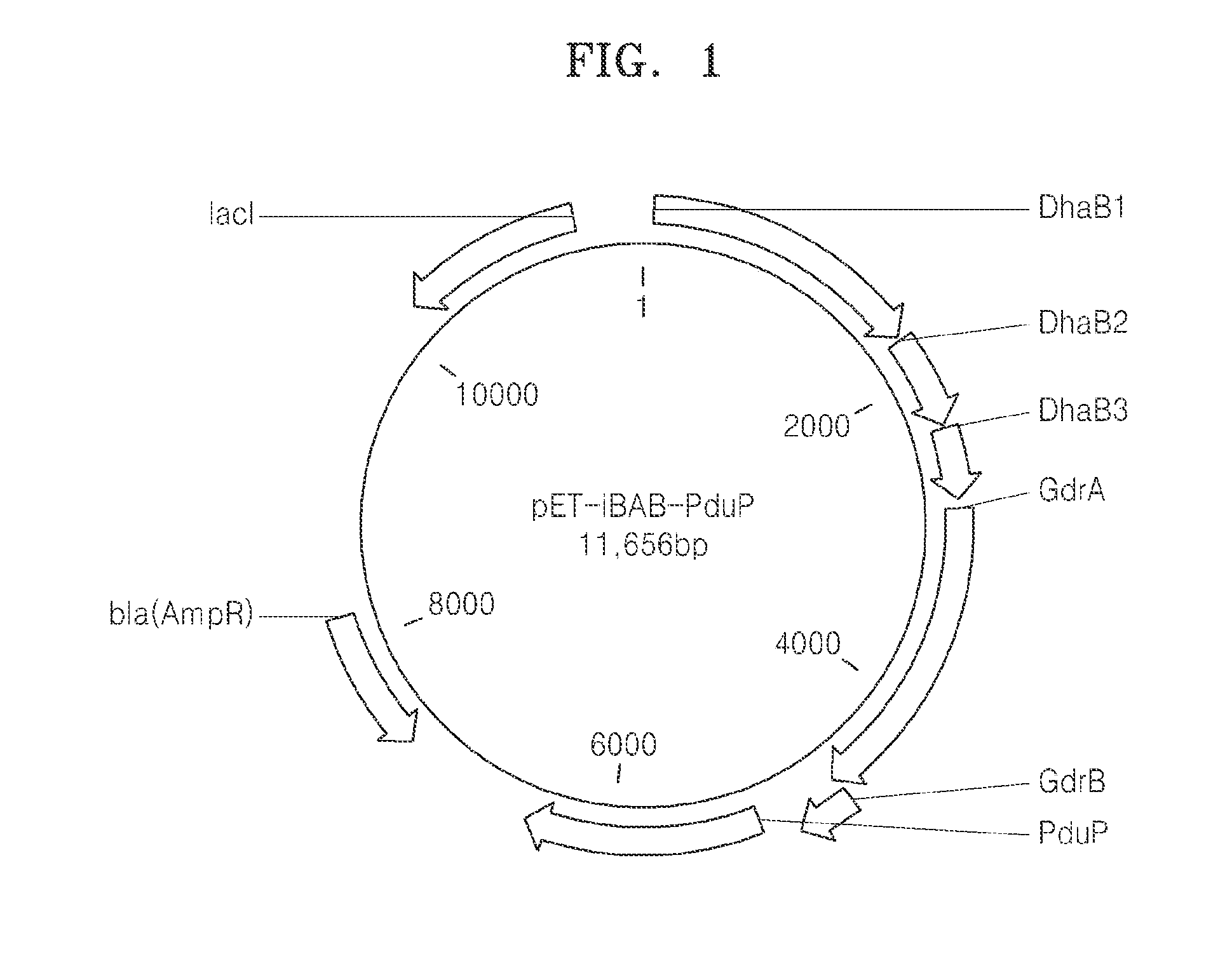
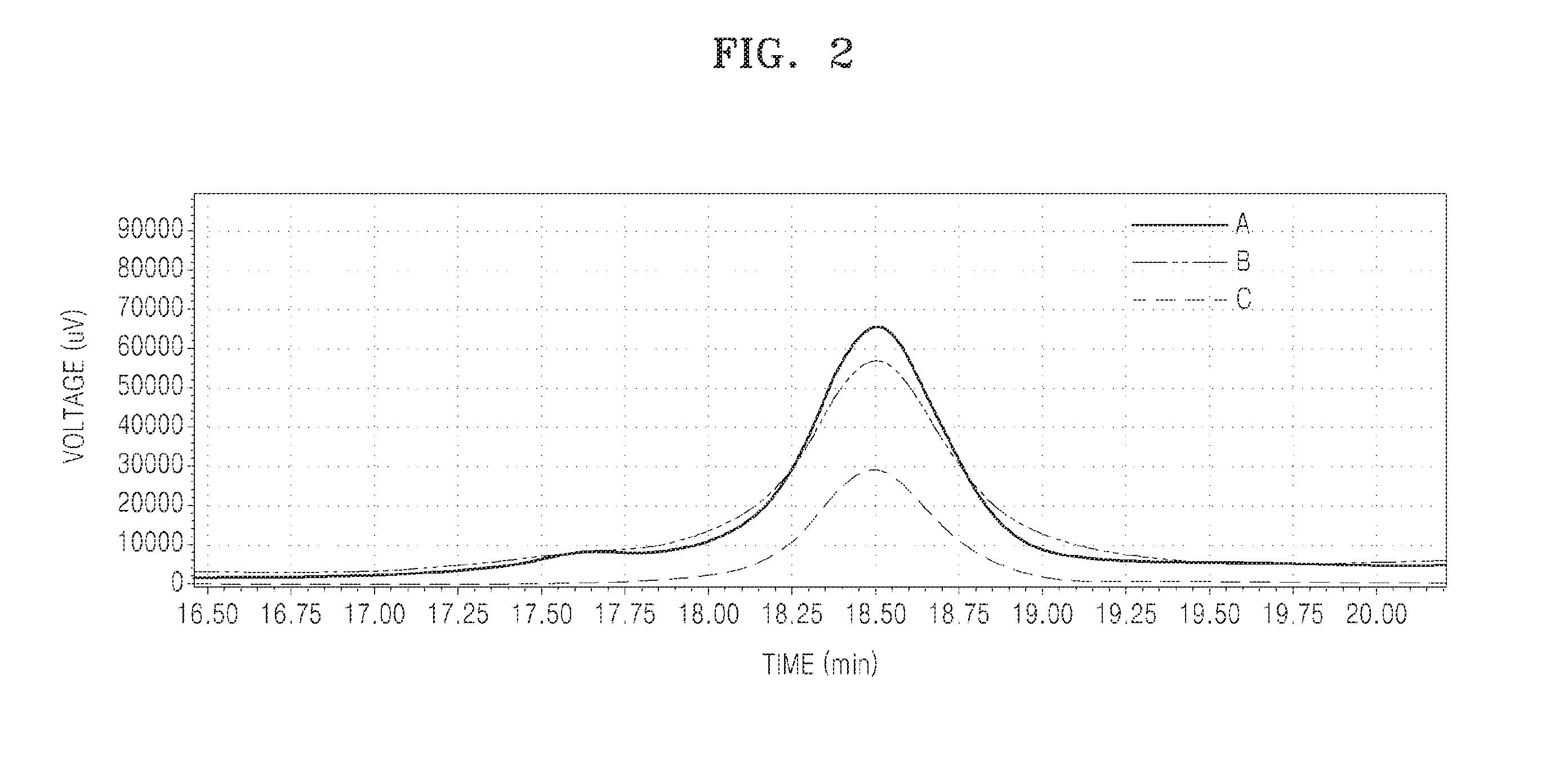
Microorganisms And Methods For Producing Acrylate And Other Products From Propionyl-CoA
InactiveUS20140107377A1Increase gene expressionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesFungi3-Hydroxypropionic acidMicroorganism
This invention relates to microorganisms that convert a carbon source to acrylate or other desirable products using propionyl-CoA as an intermediate. The invention provides genetically engineered microorganisms that carry out the conversion, as well as methods for producing acrylate by culturing the microorganisms. Also provided are microorganisms and methods for converting propionyl-CoA and propionate to 3-hydroxypropionyl-CoA, 3-hydroxypropionate (3-HP) and poly-3-hydroxypropionate.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
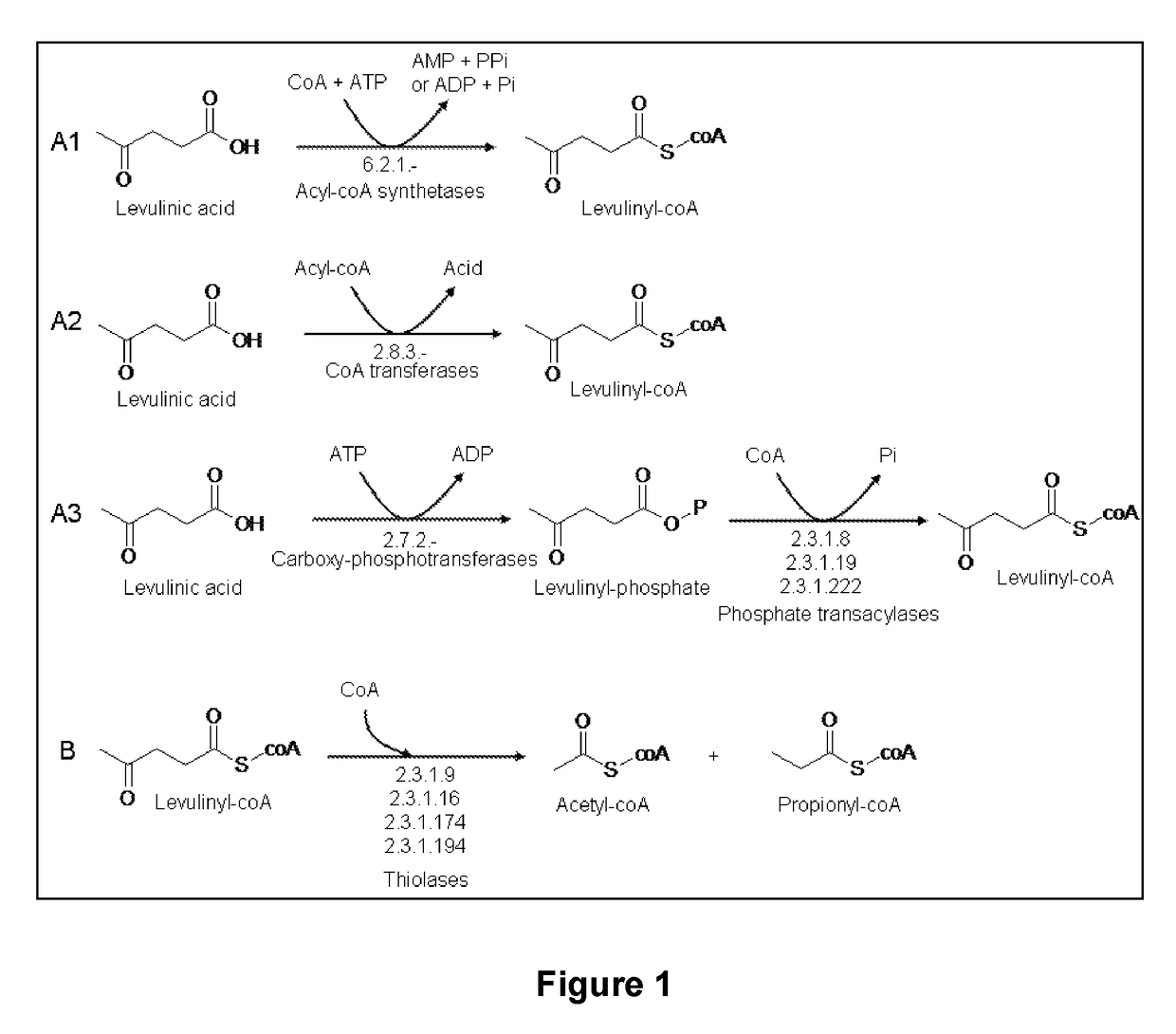
Microorganism modified for the assimilation of levulinic acid
The present invention relates to a genetically modified microorganism for the fermentative conversion of levulinic acid into propionyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA, and to a fermentation process for performing said conversion.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
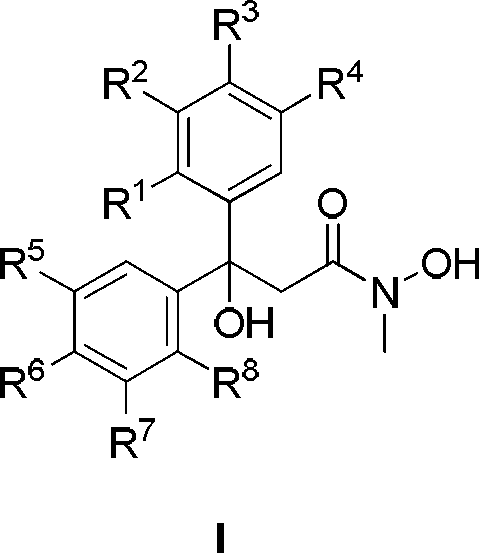
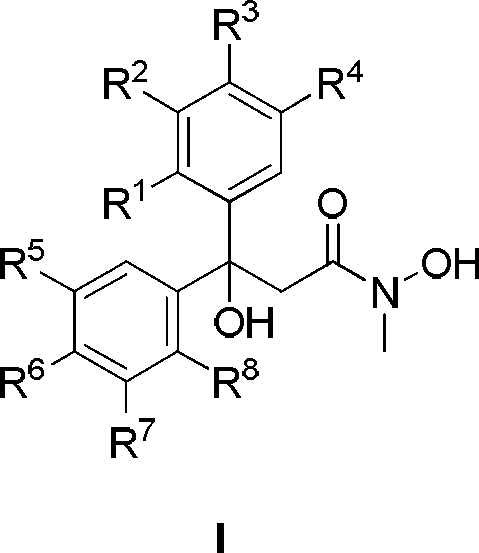
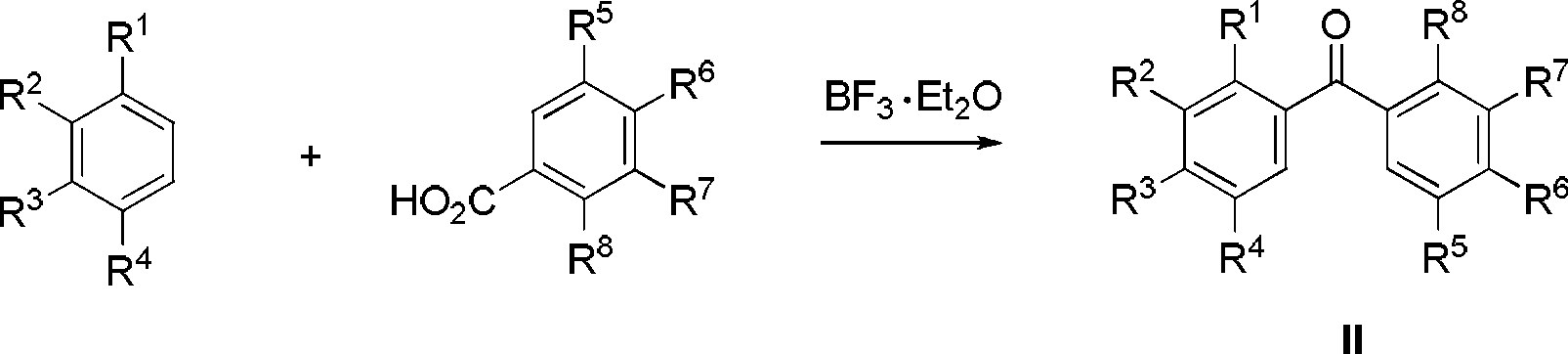
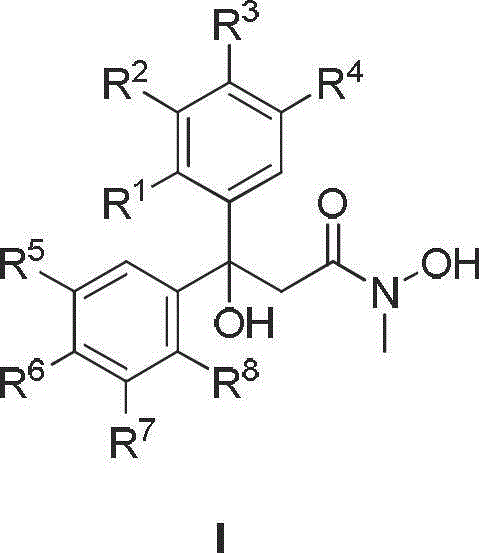
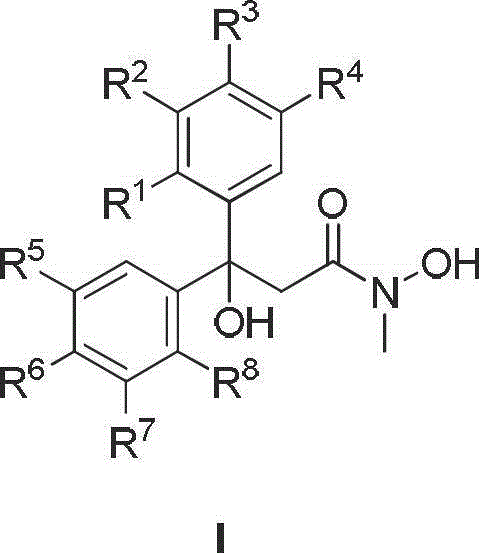
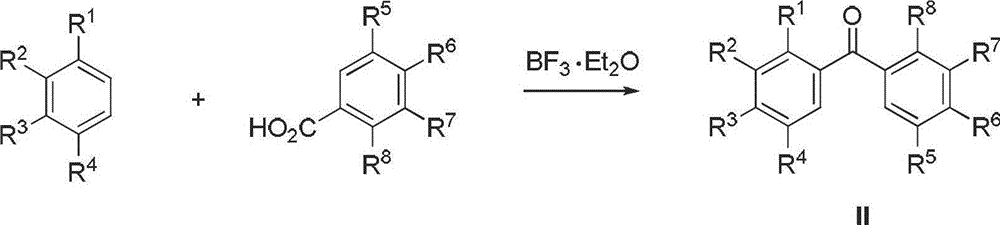
Diaryl propionyl-N-methyl hydroxamic acid type urease inhibitor and synthesis and application thereof
The invention relates to diaryl propionyl-N-methyl hydroxamic acid compounds which have a structural general formula shown in the specification. The diaryl propionyl-N-methyl hydroxamic acid compounds have a good function of inhibiting urease, and can be used for preparing medicaments for resisting gastritis, gastric ulcer, lithangiuria and the like. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the diaryl propionyl-N-methyl hydroxamic acid compounds.
Owner:党晓琴
Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene, an acyl-coenzyme A thiolase gene, genetically engineered strains and a use thereof
The present invention provides a hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene, an acyl-coenzyme A thiolase gene, genetically engineered strains and a use thereof. The hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene encodes a protein (i) or (ii) as follows: (i) having an amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO 2; (ii) derived by substituting, deleting or inserting one or more amino acids in the amino acid sequence defined by (i) and having the same function as that of the protein of (i). The present invention constructs genetically engineered Mycobacterium strains lacking of a hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene or an acyl-coenzyme A thiolase gene, which are used in the preparation of steroidal compounds, such as 1,4-BNA, 4-BNA, 9-OH-BNA, etc. Further, the invention improves the production efficiency and product quality of steroidal drug, improves the utilization of drug precursors, reduces the production costs, and provides the advantages of mild reaction conditions, environmentally friendly, and high economic and social benefits.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of recombinant bacteria for immobilizing carbon dioxide to synthesize succinic acid and its construction method and application
ActiveCN106967662BAvoid excessive dependenceIncrease profitBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliMethyl malonic acid
The invention provides recombinant bacteria for synthesizing succinic acid from a fixed amount of carbon dioxide, as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. A recombinant bacteria host is escherichia coli, which can express a gene accADBC of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, a gene mcr of malonyl CoA reductase, a gene pcs of propionyl CoA synthase, a gene pcc of propionyl CoA carboxylase, a gene mcE of methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, a gene mcM of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase and a gene sucCD of succinyl-coenzyme A synthase. According to the construction method, recombinant carriers pACYCDuet-accADBC-pcs and pETDuet-mcr-pcc-sucCD-mcEM are transformed into a host cell. The recombinant bacteria constructed through the construction method can adopt glucose serving as a unique carbon source to synthesize the succinic acid, and fermentation is performed for 48 hours, thus obtaining the succinic acid with the concentration of 6.06 g / L.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Construction method and application of metabolic engineering escherichia coli strain for producing (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid by using acetic acid or salt thereof
PendingCN112553234AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydroxybutyric acid
The invention provides a construction method and application of a metabolic engineering escherichia coli strain for producing (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid by using acetic acid or salt thereof. The metabolic pathway is as follows: the acetic acid or salt thereof is used for producing the (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid by using beta-ketothiolase and acetoacetyl CoA reductase, and finally the (R) 3hydroxybutyric acid is produced by using the non-specificity of propionyl CoA transferase. According to the method, a modified path is an exogenous metabolic path for producing (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid by acetyl CoA, and the path utilizes the non-specificity of propionyl CoA transferase, so that the steps are fewer than those of the traditional path, and the energy consumption is less. According to the method, the (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid is produced by taking acetic acid as a carbon source in escherichia coli, the yield and yield of the (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid are improved by using different propionyl CoA transferase and host escherichia coli, and the metabolic pathway is proved to have universality in escherichia coli. According to the method, the (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid is produced by taking the acetic acid-containing synthesis gas fermentation liquor as a culture medium through fermentation.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
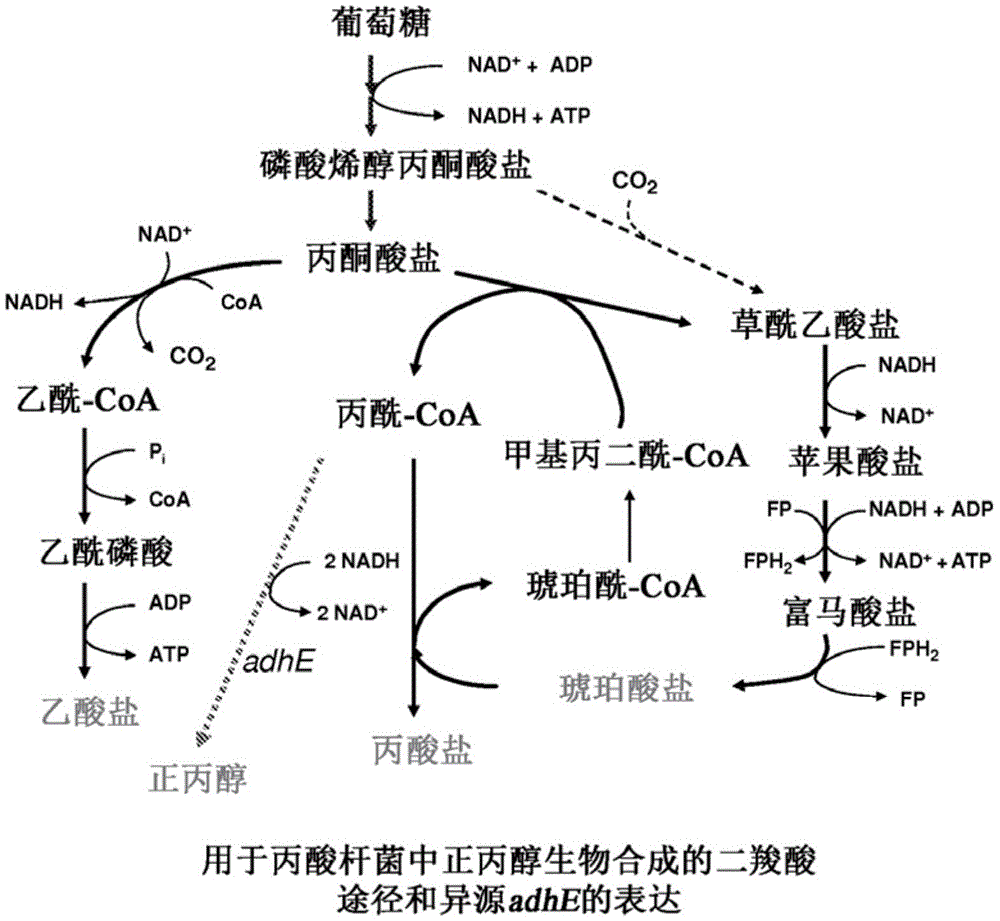
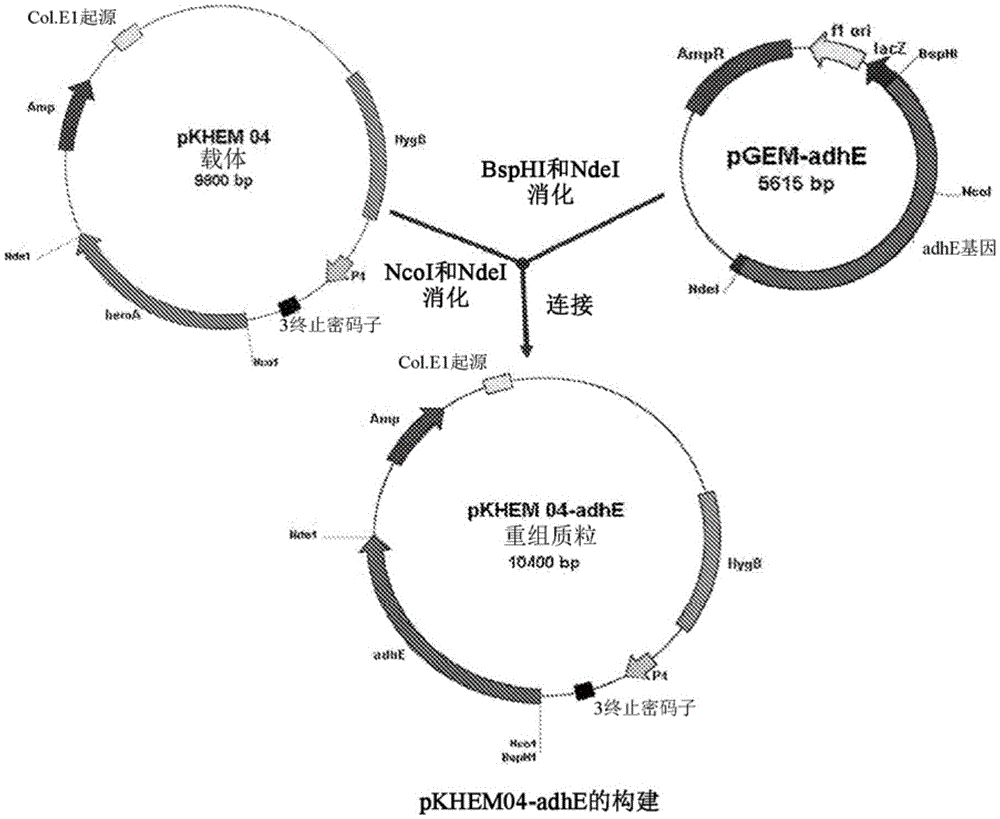
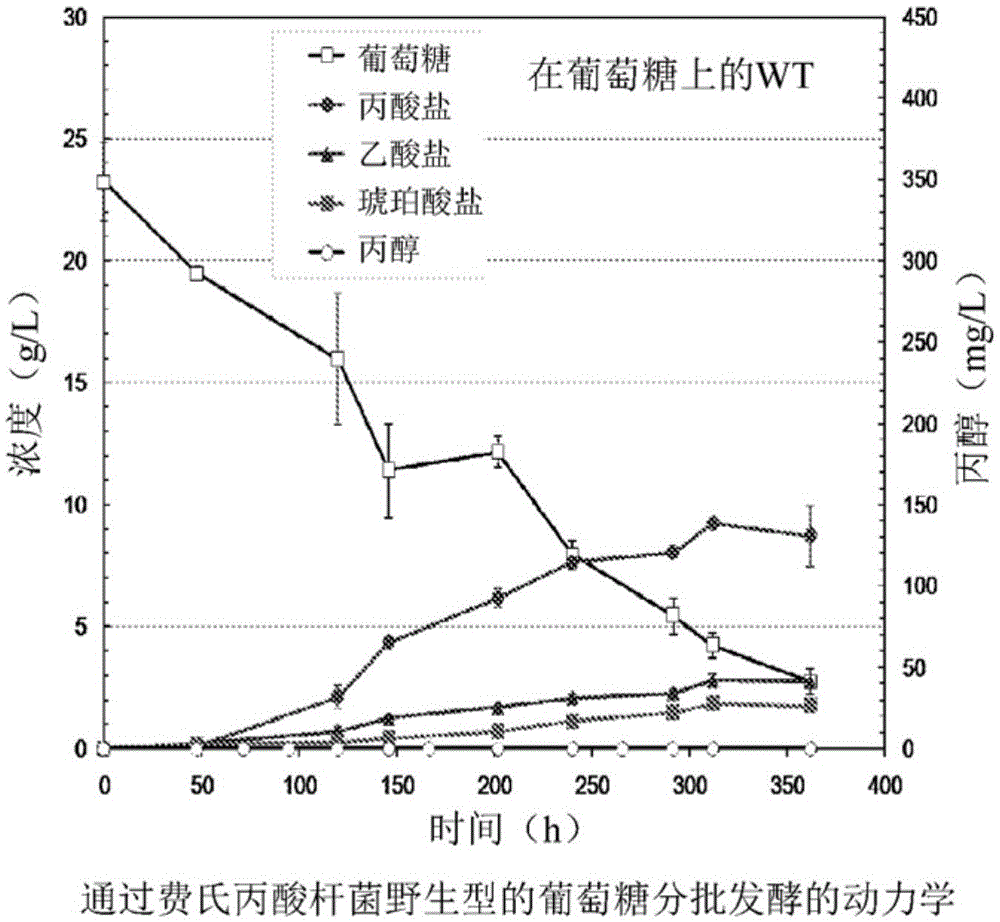
Process for producing n-propanol and propionic acid using metabolically engineered propionibacteria
A metabolically engineered propionibacteria, genomically modified to express a bifunctional aldehyde / alcohol dehydrogenase identified as GenBank Gene ID: 6062148; GI: 170080868, having activity on propionyl-CoA, is prepared and used in a fermentative process to biosynthetically prepare n-propanol, propionic acid, or a combination thereof.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
Diaryl propionyl-N-methyl hydroxamic acid type urease inhibitor and synthesis and application thereof
The invention relates to diaryl propionyl-N-methyl hydroxamic acid compounds which have a structural general formula shown in the specification. The diaryl propionyl-N-methyl hydroxamic acid compounds have a good function of inhibiting urease, and can be used for preparing medicaments for resisting gastritis, gastric ulcer, lithangiuria and the like. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the diaryl propionyl-N-methyl hydroxamic acid compounds.
Owner:党晓琴
Method for treating intermittent claudication comprising the administration of propionyl L-carnitine and a concomitant physical training
ActiveUS7560485B2Improve the quality of lifeBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseIntermittent claudication
The present invention discloses a method for treating a subject suffering from intermittent claudication (IC) wherein said subject takes an effective dose of propionyl L-carnitine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and also engaging in a concomitant physical training program. The method is particular effective for patients with intermittent claudication at class II of the Leriche-Fontaine's classification. The method provides a relief from peripheral arterial disease symptoms, as shown by claudication-limited exercise tolerance, while also improving quality of life.
Owner:ALFASIGMA SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com