Extracellular vesicles for inhalation
A technology of vesicles and cells, which is applied in the treatment of respiratory diseases, compositions containing vesicles, and the field of exosomes, which can solve problems such as the inability to obtain information about nebulized administration of exosomes, and the inability to solve mucus barriers or cell membrane barriers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0097] In order to facilitate the understanding of the invention, a specific embodiment and variants thereof will now be described by way of example with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
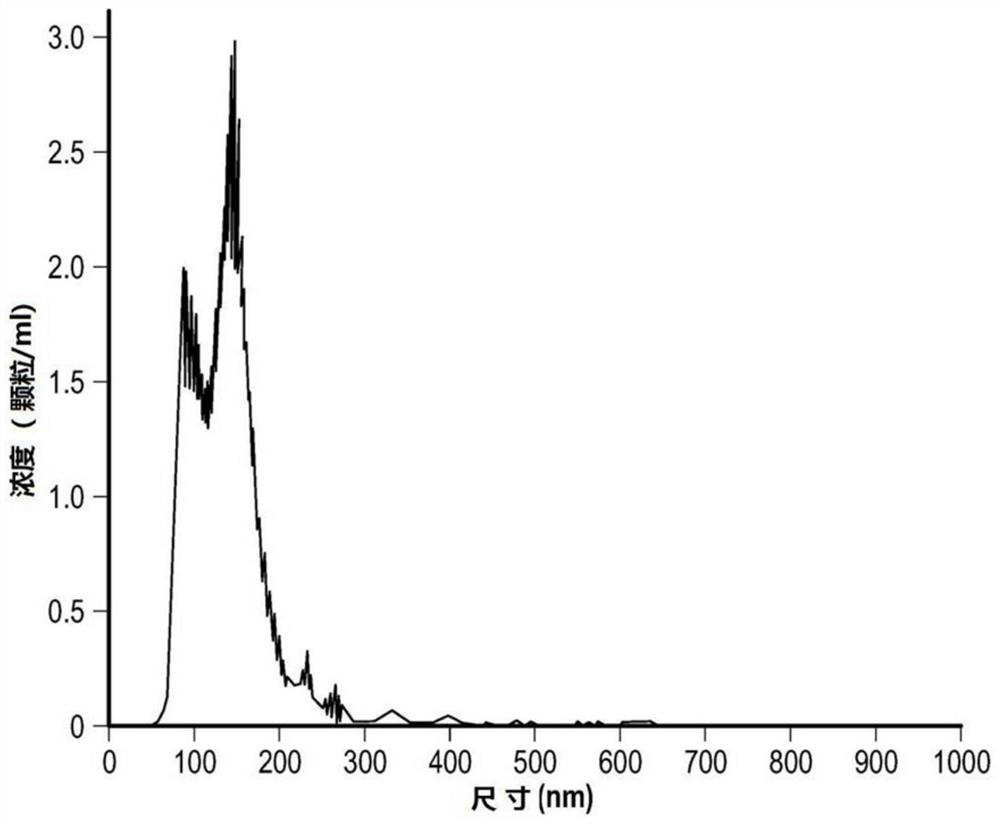
[0098] Figure 1A and 1B is a graph of the concentration and size of non-PEGylated exosomes and PEGylated exosomes using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA);
[0099] Figure 2A and 2B Zeta potential distributions of PEGylated exosomes and non-PEGylated exosomes are shown.
[0100] Figures 3A-3F is a series of transmission electron microscopy images of PEGylated and non-PEGylated exosomes.
[0101] Figures 4A-4E A series of flow cytometry images of MSCs and exosomes labeled with Far-Red dye.
[0102] Figures 5A-5C are confocal microscopy images of treated and untreated exosomes that have entered cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells, which first penetrated the mucus layer in air-liquid interface culture.
[0103] Figure 6a and 6b is the nanoparticle track...
Embodiment 1
[0127] The purpose of this example is to isolate exosomes from human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) and efficiently modify their surface with low molecular weight lipid-modified polyethylene glycol (lipid-PEG) to improve aerosolization and mucus penetration properties of exosomes.
[0128] Fluorescence labeling of hMSCs
[0129] Frozen bone marrow MSCs (donor #163) were thawed and directly inoculated into 15 T-175 cells in EV-depleted complete medium (CCM) containing 10 ng / ml human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). flasks (1 x 10 per flask 6 cells) were passaged when they reached 80-85% confluency. Cells were aggregated and resuspended in PBS before being pelleted and mixed with 2 μg far-infrared dye (excitation / emission ~630 / 661 nm) (cell tracking) / 1 × 10 6 Cells are incubated in the dark for 20 min (this will label the exosomes with a far-infrared dye-labeled cytosolic protein). After incubation, MSC medium was added to stop the reaction and incubated for an addit...
Embodiment 2
[0167]The purpose of this example is to show that the surface modification of exosomes can be effectively achieved, and a genetically engineered mesenchymal stem cell population of bioengineered cells overexpressing the CFTR gene can be successfully established.
[0168] BT-20 and hMSC cell line culture technology
[0169] will come from HTB-19 TM BT-20 cells as BT-20 human epithelial cells were cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS and 100 IU / ml penicillin / streptomycin as complete conditioned medium (CCM). Human mesenchymal stem cell donor No. 096 in Gibco MEM Alpha medium containing 10% FBS and 100 lU / ml penicillin / streptomycin and 1 ng / ml human basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) was used to cultivate.
[0170] Cells were fed 3 days per week using an aseptic technique in which spent media was removed from the culture flask with a pipette and added to a waste bottle, which was then replenished with an appropriate amount of fresh media (including suppleme...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com