Auxiliary cementing material with high chloride ion corrosion resistance and preparation method thereof
A technology for assisting cementitious materials and chloride ions, applied in the field of building materials, can solve problems such as emphasis on a single factor, few studies on nanomaterials and mineral admixtures, etc., to improve the curing rate, the preparation method is simple and easy to operate, The effect of reducing internal raw defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
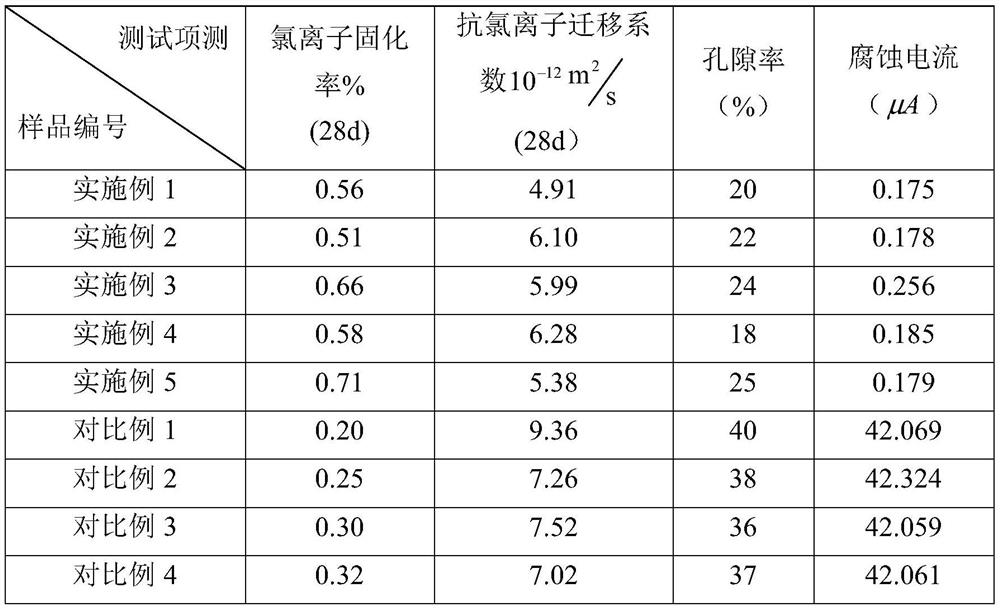
Embodiment 1
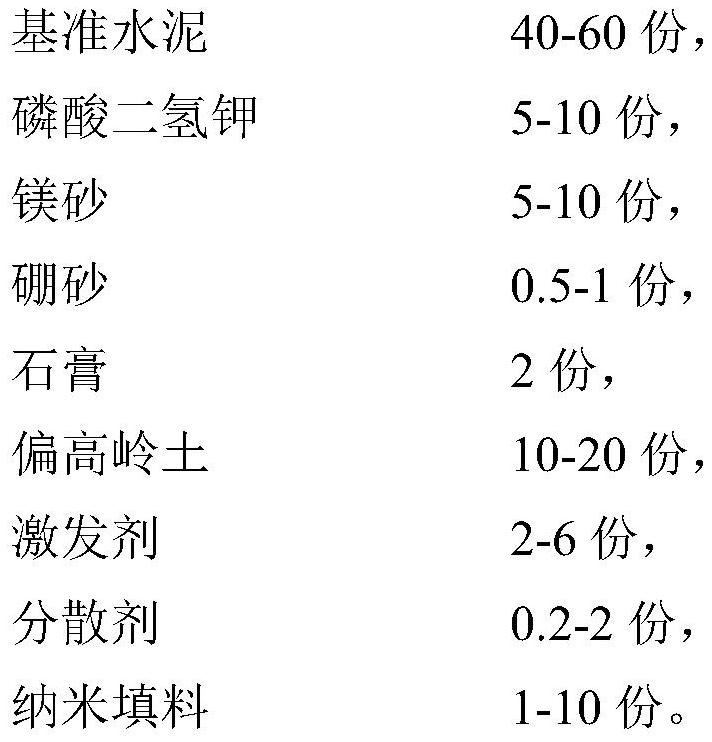
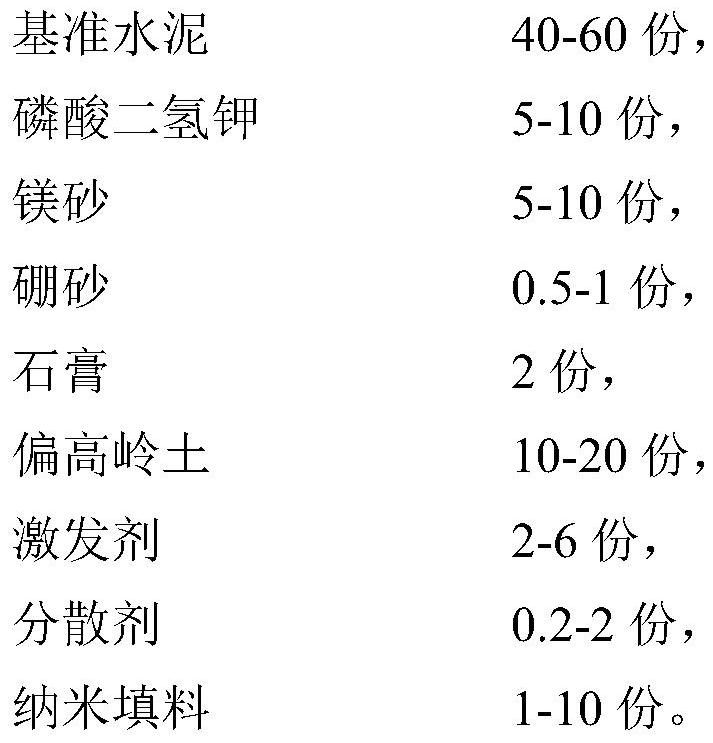
[0025] An auxiliary gelling material with high resistance to chloride ion erosion, made of the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0026] 43 parts of benchmark cement, 2 parts of gypsum, 7.5 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 7.5 parts of magnesia, 0.71 parts of borax, 15 parts of metakaolin, 5 parts of graphene, 3 parts of activator, and 1 part of dispersant.
[0027] The preparation method of the auxiliary gelling material with high resistance to chloride ion erosion is as follows:
[0028] 1) Nano-filler pretreatment: dissolving the dispersant in 17.8 parts by weight of water, then adding graphene, mixing and stirring, and then performing ultrasonic treatment for 30 minutes to obtain a surface-treated nano-filler suspension;
[0029] 2) Preparation of cementitious material: Weigh the reference cement, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, magnesia, borax, gypsum, metakaolin, activator and surface-treated nano-filler according to the above proportions, and mix them...
Embodiment 2
[0031] A high resistance to chloride ion erosion auxiliary gelling material, the difference from Example 1 is that the raw material composition and parts by weight are:
[0032] 43 parts of benchmark cement, 2 parts of gypsum, 9.5 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 9.5 parts of magnesia, 0.95 parts of borax, 15 parts of metakaolin, 5 parts of graphene, 3 parts of activator, and 1 part of dispersant.
[0033] Its preparation method is identical with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0035] A high resistance to chloride ion erosion auxiliary gelling material, the difference from Example 1 is that the raw material composition and parts by weight are:
[0036] 48 parts of benchmark cement, 2 parts of gypsum, 9.5 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 9.5 parts of magnesia, 0.95 parts of borax, 20 parts of metakaolin, 5 parts of graphene, 3 parts of activator, and 1 part of dispersant.
[0037] Its preparation method is identical with embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com