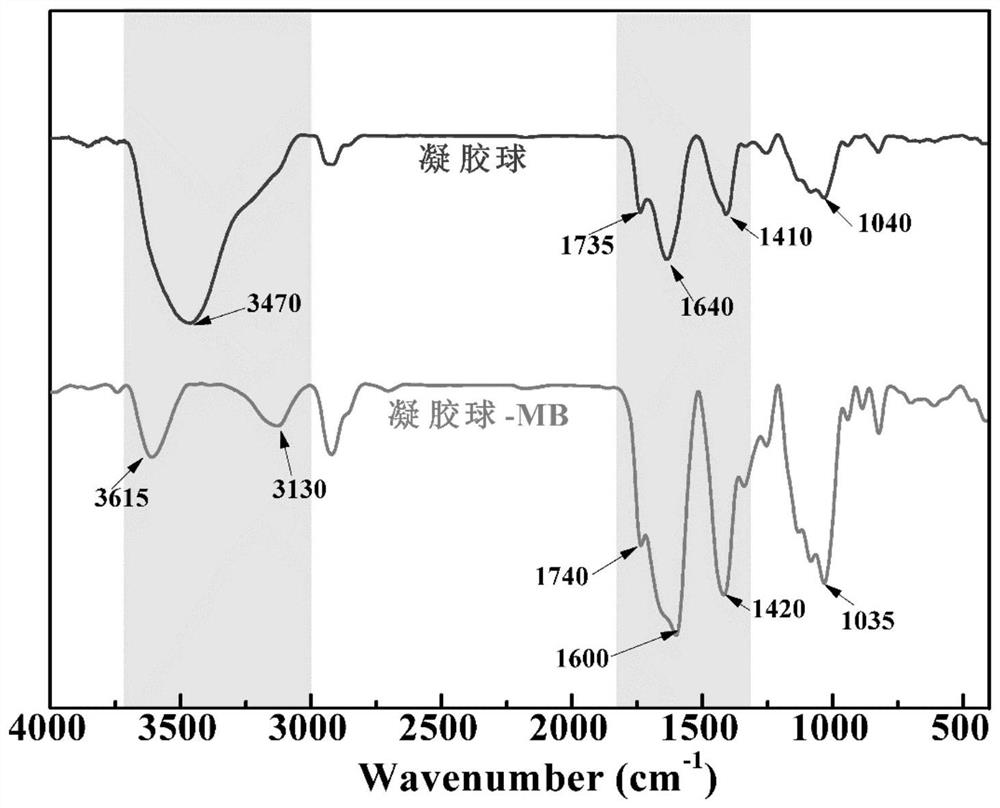
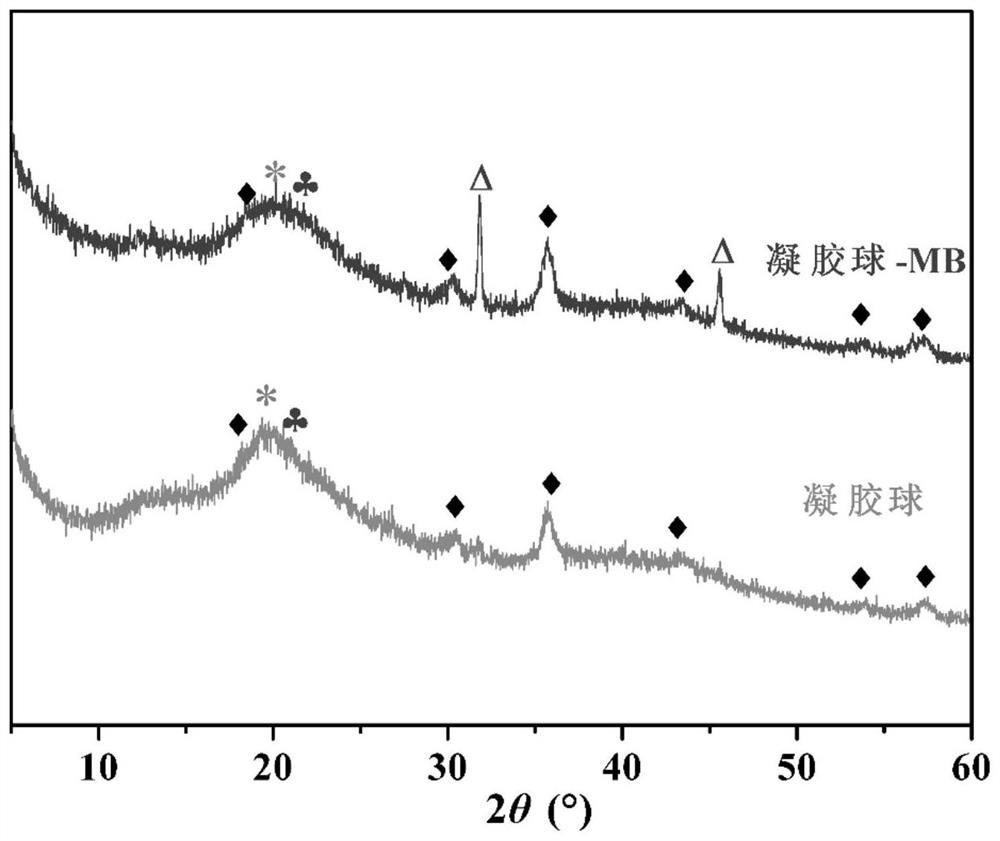
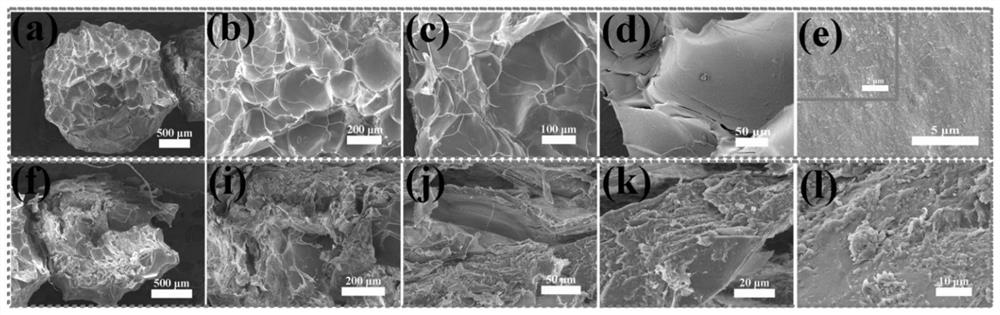
Method for removing organic dyestuff in wastewater
A technology for organic dyes and wastewater, applied in material preparation and environmental science and fields, can solve the problems of poor treatment quality, high preparation process requirements, and low adsorption efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Preparation of magnetic adsorption material:
[0033] After heating 50 g of deionized water to 85° C., 1 g of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and 2.5 g of ferric chloride hexahydrate were added into the deionized water, stirred and mixed evenly. Then add 5g of 25% ammonia water and 0.5g of potassium humate into the mixture, continue stirring for 1 hour, stop heating, cool to room temperature, and filter to obtain a black precipitate. The black precipitate was washed three times with water and ethanol, and dried in vacuum at 40° C. for 8 hours to obtain a magnetic dopant.
[0034] 10% polyvinyl alcohol solution, 3% sodium alginate solution, 1% magnetic dopant water dispersion solution, 5% boric acid solution and 4% calcium chloride solution were respectively prepared in mass fraction. 5% boric acid solution and 4% calcium chloride solution are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:1 to prepare borate calcium chloride solution.
[0035] Mix 10g of 10% polyvinyl alcohol s...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Preparation of magnetic adsorption material:
[0044]After heating 75 g of deionized water to 90° C., 1.5 g of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and 3.8 g of ferric chloride hexahydrate were added into the deionized water, and stirred and mixed evenly. Then 7.5g of 25% ammonia water and 0.75g of potassium humate were added to the mixture, and after stirring for 2 hours, the heating was stopped, cooled to room temperature, and filtered to obtain a black precipitate. The black precipitate was washed 4 times with water and ethanol, and dried in vacuum at 50° C. for 10 h to obtain a magnetic dopant.
[0045] 10% polyvinyl alcohol solution, 3% sodium alginate solution, 3% magnetic dopant water dispersion solution, 6.5% boric acid solution and 5% calcium chloride solution were prepared respectively. Then, 6.5% boric acid solution and 5% calcium chloride solution were mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:1 to prepare borate calcium chloride solution.
[0046] 15g of 10% polyvi...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Preparation of magnetic adsorption material:
[0056] After heating 100 g of deionized water to 95° C., 2 g of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate and 5.2 g of ferric chloride hexahydrate were added into the deionized water, stirred and mixed evenly. Then, 10 g of 25% ammonia water and 1 g of potassium humate were added to the mixture, and after stirring for 3 hours, the heating was stopped, cooled to room temperature, and filtered to obtain a black precipitate. The black precipitate was washed 5 times with water and ethanol, and dried in vacuum at 60° C. for 12 hours to obtain a magnetic dopant.
[0057] Prepare 10% polyvinyl alcohol solution, 3% sodium alginate solution, 5% magnetic dopant aqueous dispersion solution, 8% boric acid solution and 6% calcium chloride solution. Then, 8% boric acid solution and 6% calcium chloride were mixed according to a mass ratio of 1:1 to prepare boric acid calcium chloride solution.
[0058] 20g of 10% polyvinyl alcohol solution and 20g ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com