Cell capture method based on micro-tube fluidic chip
A chip and cell technology, applied in the field of medical testing, can solve problems such as complicated operation, cumbersome steps, and expensive reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] This embodiment relates to the preparation operation of the micropipe fluidic chip, including:
[0036] 1) The polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) matrix is mixed evenly with the curing agent.
[0037] 2) Take the silicon plate, place the copper wire with a diameter of 100 μm, and keep the copper wire and the silicon plate at 0.34mm to tighten and fix the copper wire.
[0038] 3) Pouring PDMS to completely wrap the copper wire, and place it in a 60°C oven for two hours to cure.
[0039] 4) Take out the cured PDMS, and pull out the copper wire to obtain a PDMS microchannel fluidic chip with an inner diameter of 100 μm.
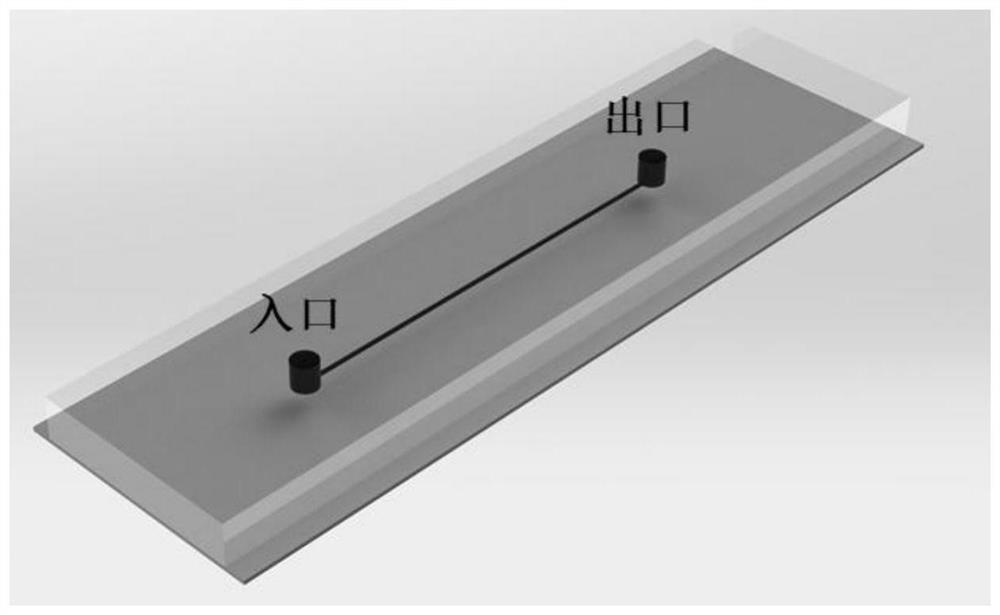
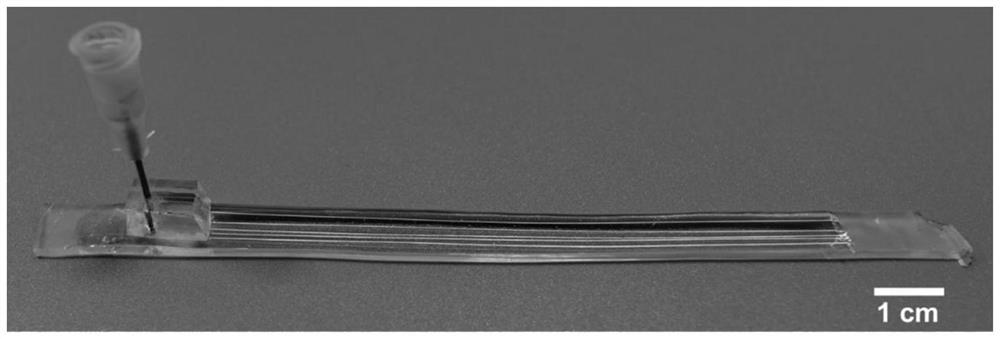
[0040] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, this embodiment relates to the microchannel fluidic chip prepared by the above method, that is, a PDMS plate including single or multiple circular channels.
[0041] This embodiment relates to the internal antibody modification and confirmation operations based on the above-mentioned microtubules, including:
...
Embodiment 2
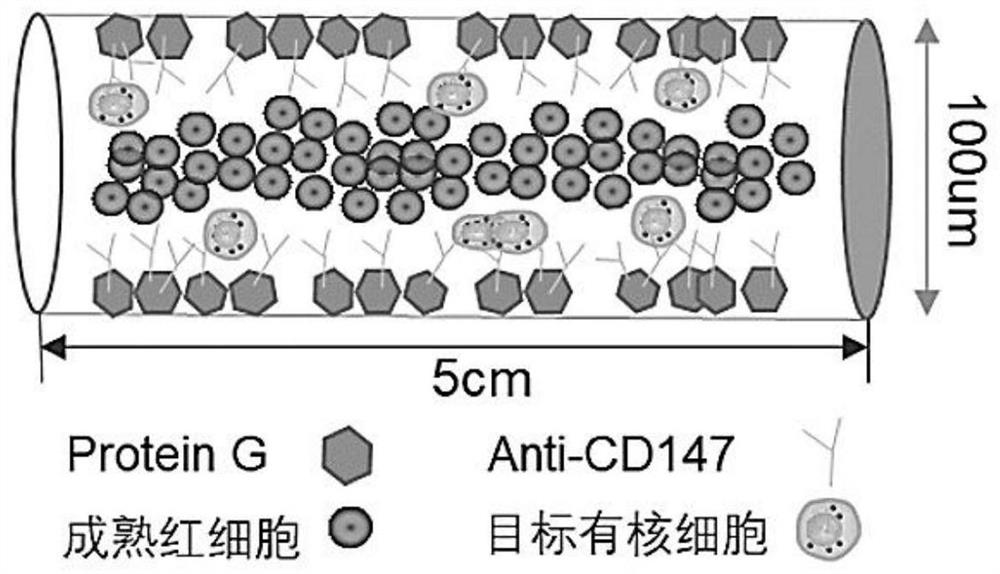
[0048] This embodiment relates to the fabrication of a microtube chip for nucleated red blood cells, and the specific steps are:
[0049] 1) Take the microtube chip prepared in Example 1, inject the IgG-conjugated CD147 antibody stock solution to fill the microtube, incubate overnight in a wet box at 4°C, and then wash the microtube with PBS to remove the unfirmly bound antibody.
[0050]2) In order to avoid non-specific adsorption of non-target cells, inject 2% fetal bovine serum albumin (BSA) to fill the microtubes, incubate in a humid box at room temperature for half an hour, and then rinse the microtubes with PBS; after the surface treatment of the microtubes, put them into 4°C refrigerator for standby to capture nucleated red blood cells.
[0051] This embodiment involves the sample processing and cell capture operation of the above-mentioned microtube chip, and the specific steps are:
[0052] 1) Pass 20 microliters of umbilical cord blood into the antibody-modified mic...
Embodiment 3
[0056] This embodiment relates to a method for in situ identification of fetal nucleated erythrocytes from umbilical cord blood in microtubes, and the specific steps are:
[0057] 1) Incubate with 0.05% glutaraldehyde to fix the cells, and wash the inner wall of the microtube with PBS after standing at room temperature for 10 minutes.
[0058] 2) Incubate with 0.01% Triton to perforate the cell membrane, and wash the inner wall of the microtube with PBS after standing at room temperature for 6 minutes.
[0059] 3) In order to avoid non-specific staining by the antibody, incubate with 2% BSA, let stand at room temperature for 6 minutes, and then wash the inner wall of the microtube with PBS.
[0060] 4) Incubate the HBF (hemoglobin F) + CD71 (PE) fluorescent antibody mixture, stain at 4°C overnight and wash the inner wall of the microtube with PBS to remove excess antibody in the tube.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com