Injectable decellularized scaffold for cartilage repair as well as preparation method and application of injectable decellularized scaffold
A decellularized scaffold and cartilage repair technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of inability to simulate the multi-layer structure of cartilage tissue, poor fixation, slow release, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
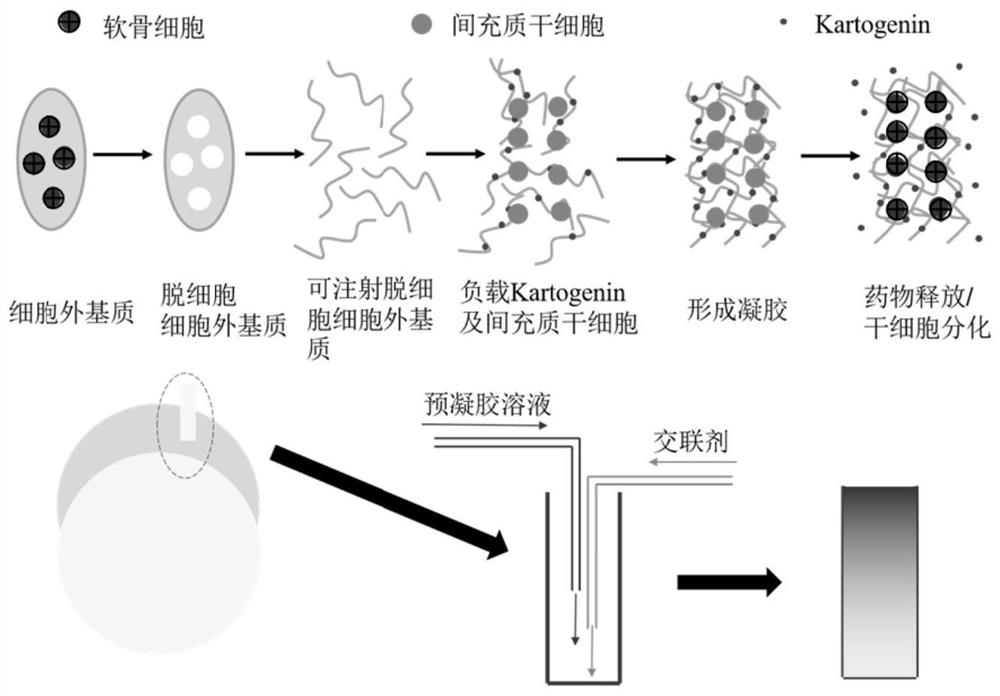
[0068] Step 1: Cartilage tissue was cut into 0.5mm thick slices, frozen at -80°C and ground into coarse powder. The powder was placed in a buffer solution of 1% emulsifier and stirred for 24 hours. Subsequently, the sample was placed in a mixed solution of DNase and RNase and stirred for 8 hours. Place it again in a buffer solution of 1% emulsifier and stir for 72 hours, and then soak in a large amount of deionized water overnight to remove residual chemical substances. Freeze at -80°C and continue to lyophilize, then grind into fine powder, and add to 15mg / mL pepsin / 0.01mol / L HCl solution. The mass ratio of pepsin to fine powder is 1:10. The resulting suspension was stirred at room temperature for 48 h for complete digestion. The resulting viscous solution was adjusted to neutrality using 0.1mol / L NaOH solution and 10×PBS in an ice-water bath to obtain injectable dECM;
[0069] Step 2: The synthesis of mesoporous silica was prepared by the improved Stober method adding po...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Step 1: Cartilage tissue was cut into 0.7mm thick slices, frozen at -80°C and ground into coarse powder. The powder was placed in a buffer solution of 1.5% emulsifier and stirred for 24 hours. Subsequently, the sample was placed in a mixed solution of DNase and RNase and stirred for 8 hours. Place it again in a buffer solution of 1% emulsifier and stir for 48 hours, and then soak in a large amount of deionized water overnight to remove residual chemical substances. Finally, the resulting dECM was frozen at -80°C and further lyophilized, then ground into a fine powder and added to a 15 mg / mL pepsin / 0.01 mol / L HCl solution. The mass ratio of pepsin to substrate is 1:2. The resulting suspension was stirred at room temperature for 48 h for complete digestion. The viscous solution was adjusted to neutrality using 0.1mol / L NaOH solution and 10×PBS in an ice-water bath to obtain injectable dECM;
[0076]Step 2: The synthesis of mesoporous silica was prepared by the improve...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Step 1: Cartilage tissue was cut into 0.7mm thick slices, frozen at -80°C and ground into coarse powder. The powder was placed in a buffer solution of 3% emulsifier and stirred for 24 hours. Subsequently, the sample was placed in a mixed solution of DNase and RNase and stirred for 12 hours. Place it again in a buffer solution of 3% emulsifier and stir for 48 hours, and then soak in a large amount of deionized water overnight to remove residual chemical substances. Finally, the resulting dECM was frozen at -80°C and further lyophilized, then ground into a fine powder and added to a 15 mg / mL pepsin / 0.01 mol / L HCl solution. The mass ratio of pepsin to substrate is 1:50. The resulting suspension was stirred at room temperature for 48 h for complete digestion. The viscous solution was adjusted to neutrality using 0.1mol / L NaOH solution and 10×PBS in an ice-water bath to obtain injectable dECM;
[0083] Step 2: The synthesis of mesoporous silica was prepared by the improv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com