Precipitation strengthening type implantable magnesium alloy and preparation process thereof
A technology of precipitation strengthening and preparation process, which is applied in the field of precipitation-enhanced biomedical implantable magnesium alloy materials and its preparation process, which can solve problems such as poor bonding, increased instrument maintenance costs, and high cost, and achieve improved mechanical properties and corrosion resistance The effect of high stability, simple and easy preparation technology, and easy availability of raw materials and equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
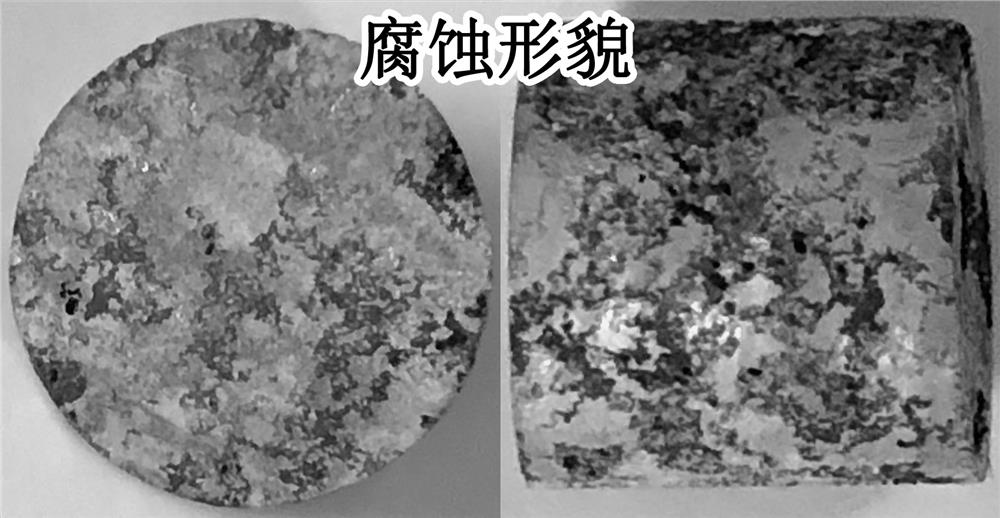
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The components and weight percentages of the magnesium alloy in this example are: Zn5.8%, Yb2.0%, Zr0.5%, and the rest is Mg.
[0025] The preparation process of the precipitation-strengthened implantable magnesium alloy includes three steps of smelting, solid solution and aging:
[0026] 1) The smelting is: in SF 6 +CO 2 The alloy ingot was prepared by melting Zn5.8%, Yb2.0%, Zr0.5% and the rest being Mg in the gas protection. The melting temperature was 770 ºC. , then poured out of the oven and cooled naturally to room temperature;
[0027] 2) The solid solution is: heat preservation at 400 °C for 24 hours in an environment filled with argon, so that the second phase distributed along the grain boundary can be fully redissolved into the matrix to ensure that the billet is not oxidized during solid solution, and then water-cooled to room temperature;
[0028] 3) The aging is as follows: heat the billet after solid solution treatment to 200 °C for 16 h in an argon e...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The components and weight percentages of the magnesium alloy in this example are: Zn6.0%, Yb1.0%, Zr0.5%, and the rest is Mg; submicron second phases are dispersed in the magnesium matrix.
[0033] The preparation process of the precipitation-strengthened implantable magnesium alloy includes three steps of smelting, solid solution and aging (such as figure 1 shown):
[0034] 1) The smelting is: in SF 6 +CO 2 In the gas protection, the alloy ingot was prepared by melting Zn6.0%, Yb1.0%, Zr0.5% and the rest being Mg. The melting temperature was 770 ºC. After fully melting, it was kept at 720 ºC for 20 minutes to remove slag. Then it was poured out of the oven and cooled to room temperature naturally;
[0035] 2) The solid solution is: heat preservation at 400 °C for 36 h in an environment filled with argon, so that the second phase distributed along the grain boundary can be fully redissolved into the matrix to ensure that the billet is not oxidized during solid solution...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com