Beneficiation method for pegmatite type lithium polymetallic ore
A technology of polymetallic ore and beneficiation methods, applied in the direction of solid separation, etc., can solve the problems of low comprehensive resource utilization rate and single product structure, and achieve the effect of increasing the difference in floatability, efficient separation, and realizing no tailings discharge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
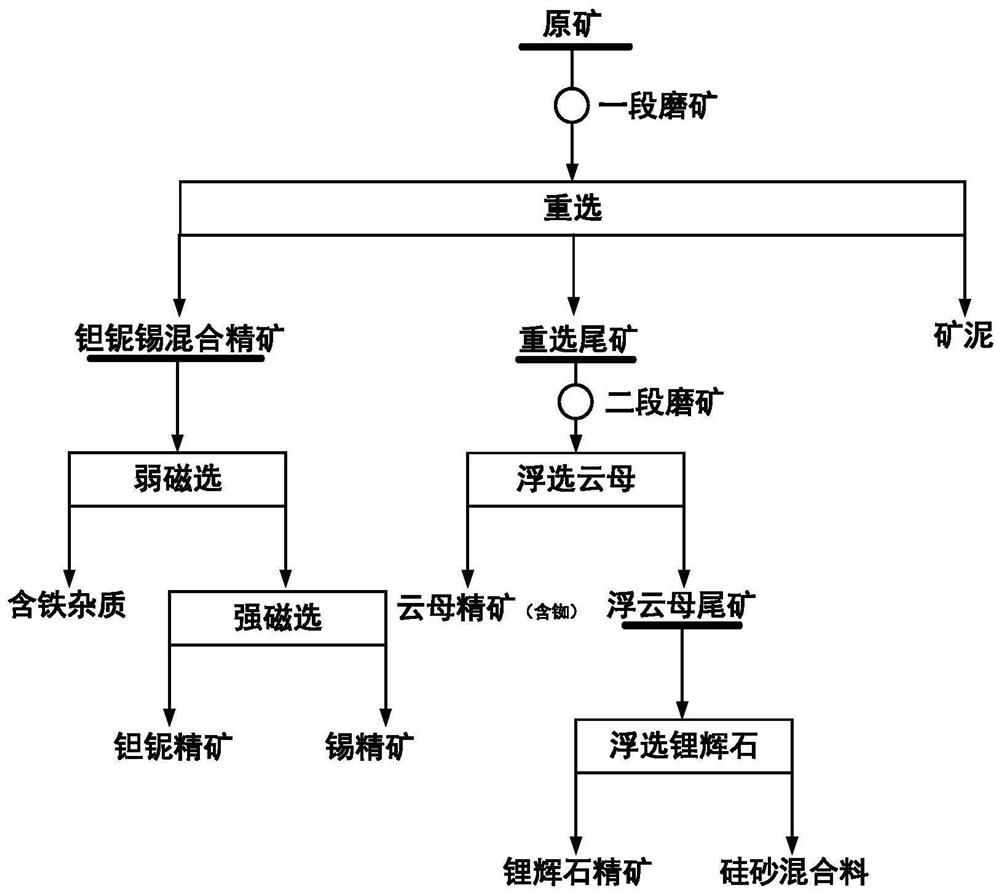
[0042] Schematic diagram of the comprehensive recovery process of lithium polymetallic ore figure 1 As shown, the specific process is:
[0043] S1: Grind the raw ore to -0.30mm;
[0044]S2: Gravity separation-magnetic separation: use spiral chute for rough separation, Nelson centrifugal separator for concentration (gravity acceleration 50G) to obtain mixed concentrate of tantalum, niobium and tin, gravity separation tailings and slime; then use weak magnetic separator Do weak magnetic separation on tantalum, niobium and tin mixed concentrate (background magnetic field strength is 0.15T) to obtain iron-containing impurities and weak magnetic tailings, and finally use high gradient strong magnetic separator (background magnetic field strength 0.80T) to separate weak magnetic tailings High-gradient strong magnetic separation to obtain tantalum-niobium concentrate and tin concentrate; 2 o 5 Grade 18.86%, recovery rate 62.41%, Nb 2 o 5 Grade 38.59%, recovery rate 64.48%, tin c...
Embodiment 2
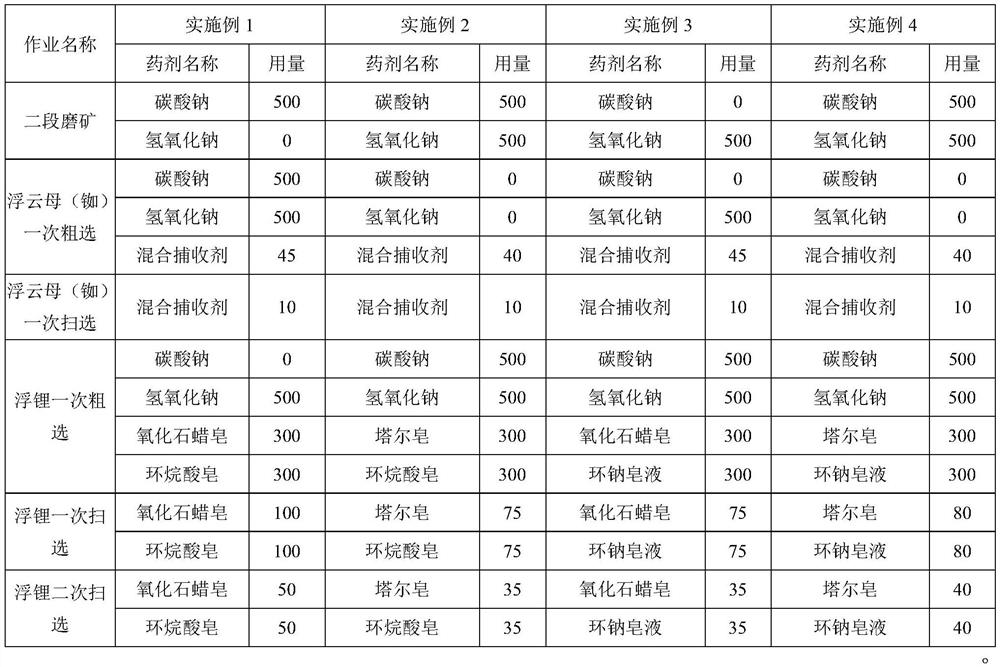
[0049] The raw ore sample that present embodiment uses is with embodiment 1. The specific comprehensive recovery process of lithium polymetallic ore is the same as that in Example 1, except that the gravity acceleration of step S2 Nelson centrifugal concentrator is 45G, and the background scene of high-gradient strong magnetic separation is 0.90T, and finally tantalum-niobium concentrate Ta 2 o 5 Grade 17.95%, recovery rate 63.01%, Nb 2 o 5 Grade 37.81%, recovery rate 65.18% and tin concentrate Sn grade 46.37%, recovery rate 72.79%; Steps S3, S4 and S5 are shown in Table 1 for the medicaments and their dosages; the final Rb 2 Rubidium-containing mica concentrate and pumice tailings with an O grade of 0.66% and a recovery rate of 27.85%, as well as Li 2 Spodumene concentrate and silica sand mixture with O grade of 5.70% and recovery rate of 85.38%.
Embodiment 3
[0051] The raw ore sample that this example uses is with example 1. The specific comprehensive recovery process of lithium polymetallic ore is the same as in Example 1, except that the background scene of step S2 high-gradient strong magnetic separation is 1.0T, and finally tantalum-niobium concentrate Ta 2 o 5 Grade 19.51%, Recovery 63.05%, Nb 2 o 5 Grade 39.99%, recovery rate 65.17% and tin concentrate Sn grade 48.94%, recovery rate 71.35%; Steps S3, S4 and S5 are shown in Table 1 for the medicaments and their dosages; the final Rb 2 Rubidium-containing mica concentrate and pumice tailings with O grade of 0.73% and recovery rate of 28.26%, and Li 2 Spodumene concentrate and silica sand mixture with O grade of 6.02% and recovery rate of 83.28%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com