Method for catalytically degrading waste polyester material by using zinc catalyst
A waste polyester and zinc catalyst technology, applied in the field of polyester degradation, can solve the problems of low material universality and low catalytic efficiency, and achieve the effect of simple production process, high catalytic efficiency and less by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: the reaction process of PET waste degradation in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0028]
[0029] Specifically, it is achieved through the following steps:
[0030] Step 1: Clean the discarded PET packaging box with deionized water, dry it fully in an oven at 60°C, and cut it into square pieces with a side length of about 5 mm (5±0.5 mm) to obtain polymer pieces.
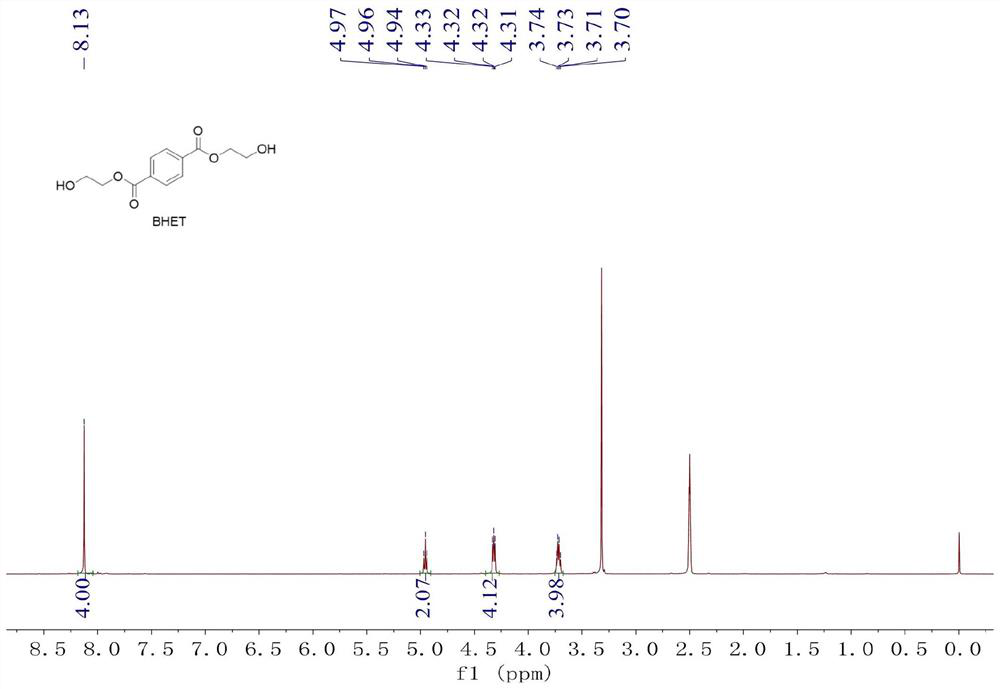
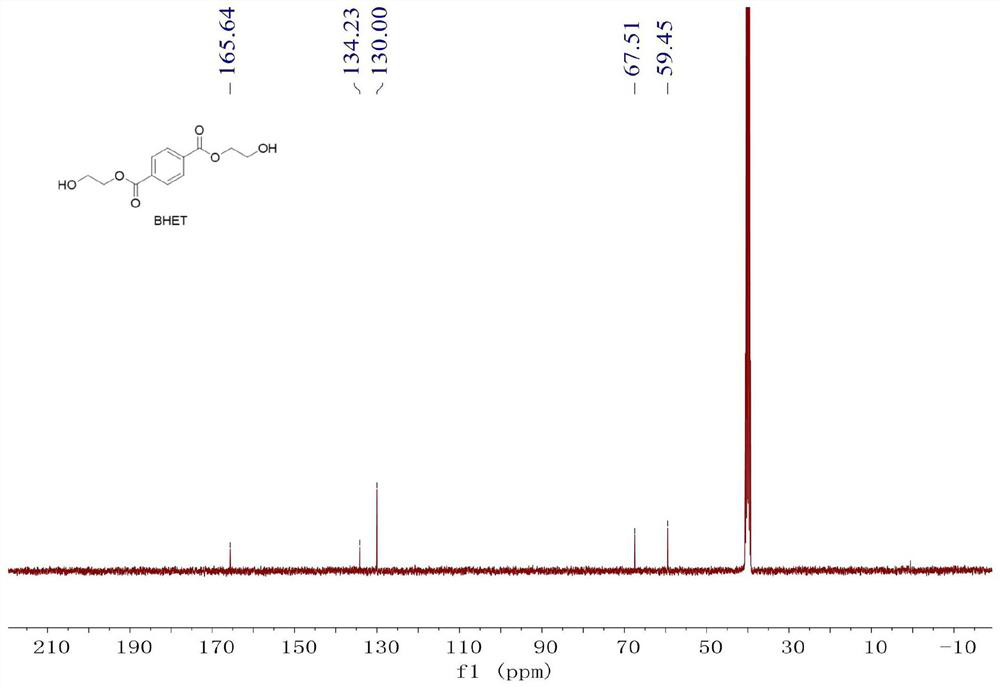
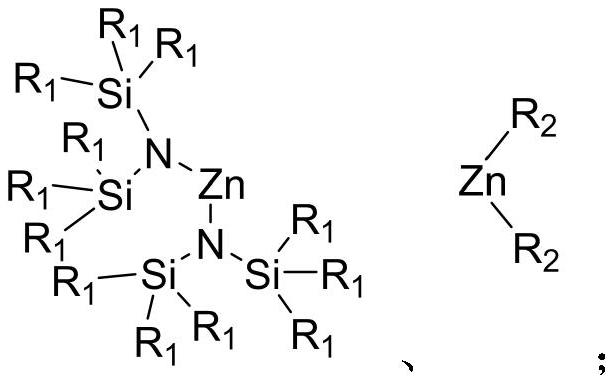
[0031] Step 2: Get a 5mL Schlenk bottle, vacuumize and replace the argon, then place it in the glove box, add 50mg (5mol% relative to the polymer unit) of Zn[N(SiMe 3 ) 2 ] 2 Catalyst, add 2mL of ethylene glycol, and then add 500mg of polymer fragments, stir and react at 180°C for 2 hours, the polymer fragments dissolve, nuclear magnetic monitoring polymer depolymerization is complete, and a crude product is obtained.
[0032] Step 3: Cool the crude product to room temperature, add 100 mL of deionized water, stir for 30 minutes, and then filter.
[0033] Step 4. Then take the trans...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: the reaction process of PET waste degradation in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0035]
[0036] Specifically, it is achieved through the following steps:
[0037] Step 1: Clean the discarded PET packaging box with deionized water, dry it fully in an oven at 60° C., and cut it into square pieces with a side length of about 5 mm (5±0.2 mm) to obtain polymer pieces.
[0038] Step 2: Get a 5mL Schlenk bottle, vacuumize and replace the argon, then place it in the glove box, add 20mg (2mol% relative to the polymer unit) of Zn[N(SiMe 3 ) 2 ] 2 Catalyst, add 2mL of ethylene glycol, and then add 500mg of polymer fragments. After stirring and reacting at 180°C for 5 hours, the polymer fragments dissolve, and the depolymerization of the polymer is monitored by NMR to obtain a crude product.
[0039] Step 3: Cool the crude product to room temperature, add 100 mL of deionized water, stir for 30 minutes, and then filter.
[0040] Step 4. Then take the tr...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: the reaction process of PET waste degradation in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0042]
[0043] Specifically, it is achieved through the following steps:
[0044] Step 1. Clean the discarded PET mineral water bottle with deionized water, dry it fully in an oven at 60° C., and cut it into square fragments with a side length of about 5 mm (5±0.1 mm) to obtain polymer fragments.
[0045] Step 2: Get a 5mL Schlenk bottle, vacuumize and replace the argon, then place it in the glove box, add 50mg (5mol% relative to the polymer unit) of Zn[N(SiMe 3 ) 2 ] 2 Catalyst, add 2mL of ethylene glycol, and then add 500mg of polymer fragments, stir and react at 180°C for 2 hours, the polymer fragments dissolve, nuclear magnetic monitoring polymer depolymerization is complete, and a crude product is obtained.
[0046] Step 3: Cool the crude product to room temperature, add 100 mL of deionized water, stir for 30 minutes, and then filter.
[0047]Step 4. Then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com