Method for separating wood fiber components
A technology of lignocellulosic and lignocellulosic raw materials, which is applied in the fields of fiber raw material treatment, washing/replacing pulp treatment liquid, textiles and papermaking, etc. It can solve the problems of difficult large-scale industrial application, reduce the potential of high-value utilization of lignin, and the formation of lignin Difficult and stable problems, to achieve the effect of efficient utilization and solve the balance problem of degradation yield and reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
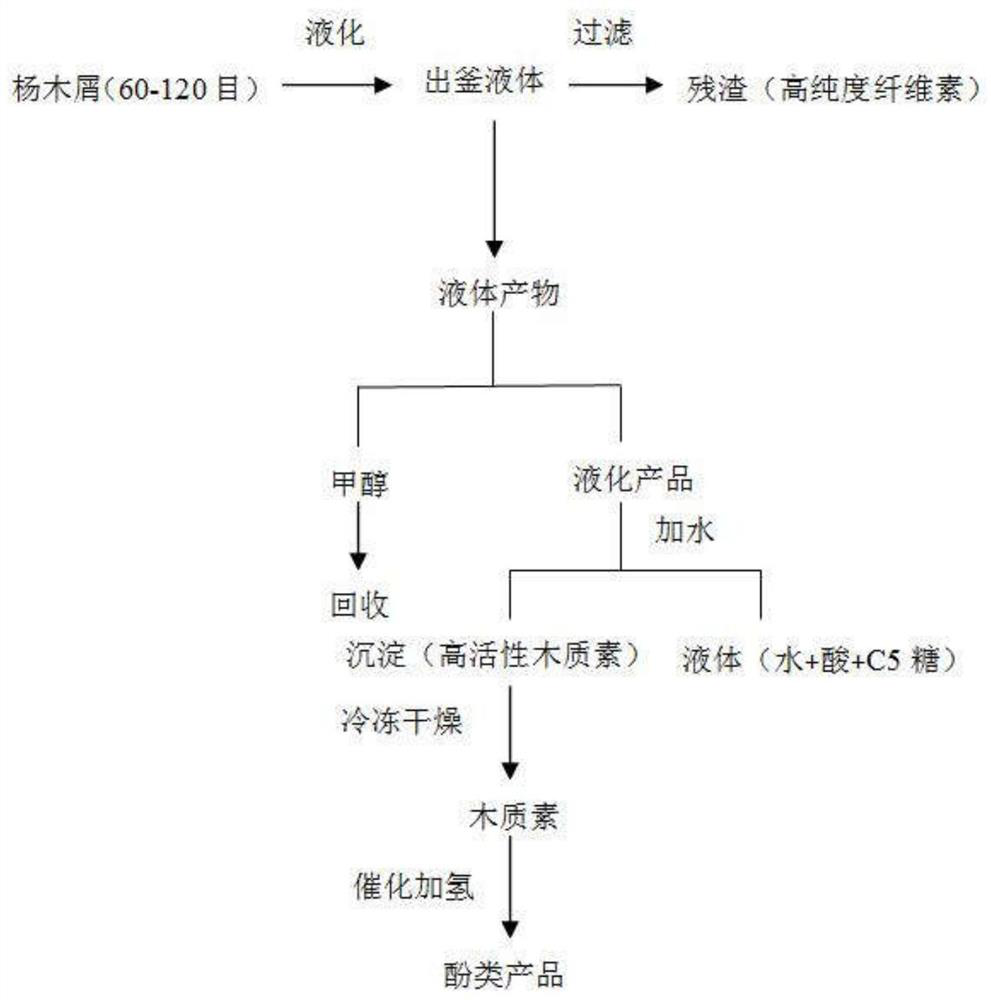
[0026] A method for the separation of lignocellulosic components, the flow chart is as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0027] (1) Weigh 3.0g of poplar sawdust, dissolve 18.0g of 4-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid hydrate (37.5wt.%) in 30.0g of methanol, add it into the reaction kettle, start stirring, and heat up to 60°C, temperature controlled reaction for 2h;
[0028] (2) After the reaction was completed, it was rapidly cooled to room temperature, filtered, and the residue was washed with water and dried at 105° C. to obtain 1.7 g of solid residue with a conversion rate of 42.8%. The contents of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the residue were 82.7%, 4.8% and 9.3%, respectively.
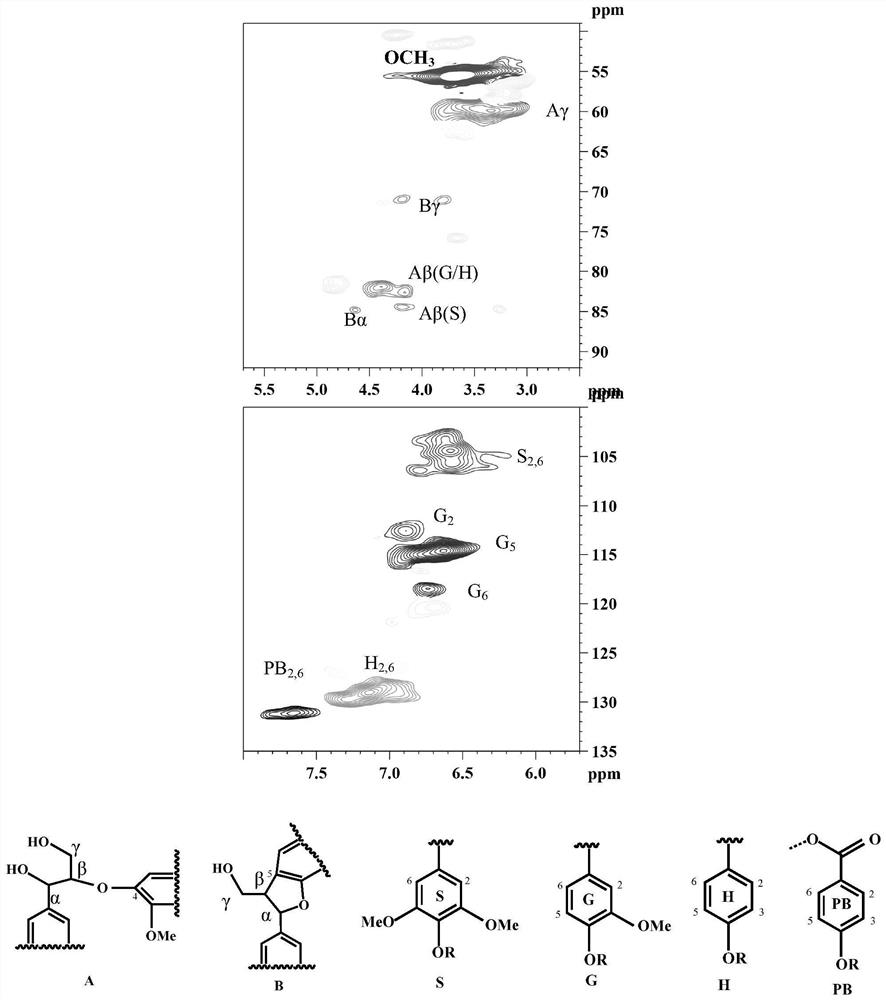
[0029] image 3 The 2D-HSQC delineated the two main cross-signaling regions of lignin, namely the side chain (δC / δH 40-90 / 2.5-5.5ppm) and aromatic (δC / δH 100-140 / 5.5-8.5ppm) regions; Signals in the compound region (δC / δH90-105 / 4.0-5.5ppm) were not detected in all lignin sampl...
Embodiment 2
[0031] A method for separating lignocellulosic components, comprising the steps of:
[0032] (1) Weigh 3.0g of poplar sawdust, dissolve 18.0g of 4-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid hydrate (37.5wt.%) in 30.0g of methanol, add it into the reaction kettle, start stirring, and heat up to 70°C, temperature controlled reaction for 2h;
[0033] (2) After the reaction was completed, it was rapidly cooled to room temperature, filtered, and the residue was washed with water and dried at 105° C. to obtain 1.6 g of solid residue with a conversion rate of 47.8%. The contents of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the residue were 88.9%, 2.9% and 5.7%, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0035] A method for separating lignocellulosic components, comprising the steps of:
[0036] (1) Weigh 3.0g of poplar sawdust, dissolve 18.0g of 4-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid hydrate (37.5wt.%) in 30.0g of methanol, add it to the reaction kettle, start stirring, and heat up to 80°C, temperature controlled reaction for 2h;
[0037] (2) After the reaction was completed, it was rapidly cooled to room temperature, filtered, and the residue was washed with water and dried at 105° C. to obtain 1.4 g of solid residue with a conversion rate of 53.5%. The contents of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the residue were 92.5%, 2.5% and 3.4%, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com