Degrading strain for bifenthrin insecticides and application thereof
A bifenthrin and insecticide technology, applied in the fields of environmental microorganisms and agriculture, can solve problems such as endangering ecological balance, human and animal health, environmental problems, and less research, achieving significant degradation effects and enriching the germplasm resource bank Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Isolation, screening and identification of degrading bacterial strain F2
[0032] 1. Enrichment culture, isolation and screening of bifenthrin-like insecticide-degrading bacteria:
[0033] 1.1 Enrichment culture of strains
[0034] The 2 parts of soil collected from the pesticide factory were domesticated for 40 days, and the culture solution obtained from the domestication was diluted to 10 -7 , and then spread them evenly on LB agar plates, culture at a constant temperature of 30°C for 5 days, pick single colonies with different colony shapes and colony colors, and streak culture again; repeat streak culture for more than five times, and obtain 13 different strains , numbered F2-13 in sequence, for the next experiment.
[0035] 1.2 Screening of strains
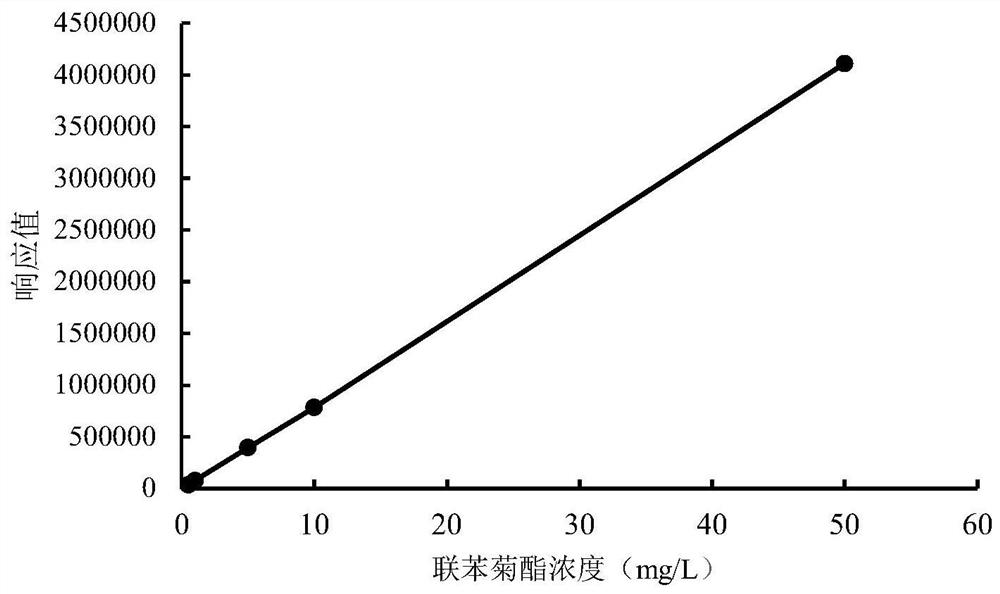
[0036] 1.2.1 Bifenthrin standard curve
[0037] Prepare 100mg / L bifenthrin mother solution with acetone, then dilute the mother solution with acetonitrile to form a series of standard sample solutions (0...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Degradability determination of embodiment 2 bacterial strain F2 to bifenthrin insecticides
[0065] 2.1 Optimization of strain F2 degradation conditions
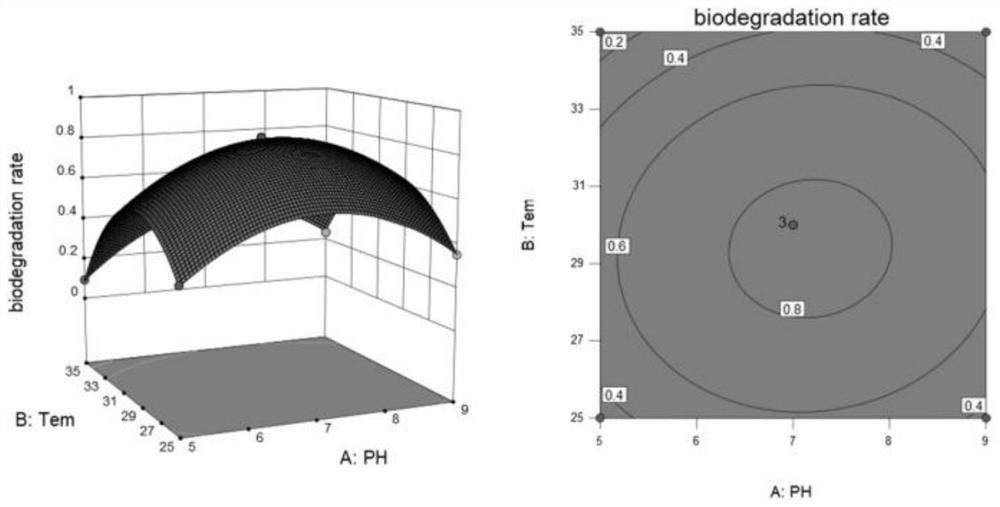
[0066] Using RSM, the pH(A 2 ), temperature (B 2 ) and inoculation volume (C 2 ) as the independent variable, with Y 3 (Bifenthrin degradation rate) is the response value, and is optimized by Box-Behnken design conditions. The results of the experimental design and responses are detailed in Table 6. By responding to the value Y 3 , that is, the degradation rate of bifenthrin is subjected to polynomial regression analysis, and a quadratic response regression model is established to obtain the degradation rate of bifenthrin (Y 3 ) of the quadratic polynomial response surface regression equation:
[0067] Y 3 =-14.9042+0.8173A 2 +0.7856B 2 +4.9663C 2 +2.96A 2 B 2 -0.0577A 2 C 2 -0.0142B 2 C 2 -0.061A 2 2 -0.0136B 2 2 -4.0235C 2 2
[0068] The variance analysis of the fitted model is shown in Table...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3 Soil remediation experiment of Acinetobacter schindleri (Acinetobacter schindleri) strain F2
[0089] 1. Soil sample for test
[0090] The topsoil (0-20cm) of the farmland was taken from the experimental field of the teaching farm of South China Agricultural University.
[0091] After the soil samples were retrieved, they were first placed in a cool and ventilated place to dry naturally, then ground after air drying, passed through a 2mm sieve, and a certain amount of bifenthrin was dissolved in acetone, and then soaked in diatomaceous earth to completely dissolve the bifenthrin. adsorption.
[0092] The soaked diatomaceous earth is placed in a fume hood to dry, and it is mixed into the soil so that the concentration of bifenthrin in the soil is about 50 mg / kg. Take 500g of each soil sample and cultivate it in a constant temperature and humidity incubator at 30°C. 7 The inoculation amount of CFU / g was inserted into the F2 degrading bacterial agent, and the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| correlation coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com