Molecular marker system for identifying authenticity of sugarcane hybrid and development method of molecular marker system
A technology of molecular markers and authenticity, applied in the fields of bioinformatics and molecular genetic breeding, can solve the problems of limited number of markers, missed screening, and small number of markers, etc., achieve stable amplification effect, facilitate popularization and application, and reduce missed detection rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
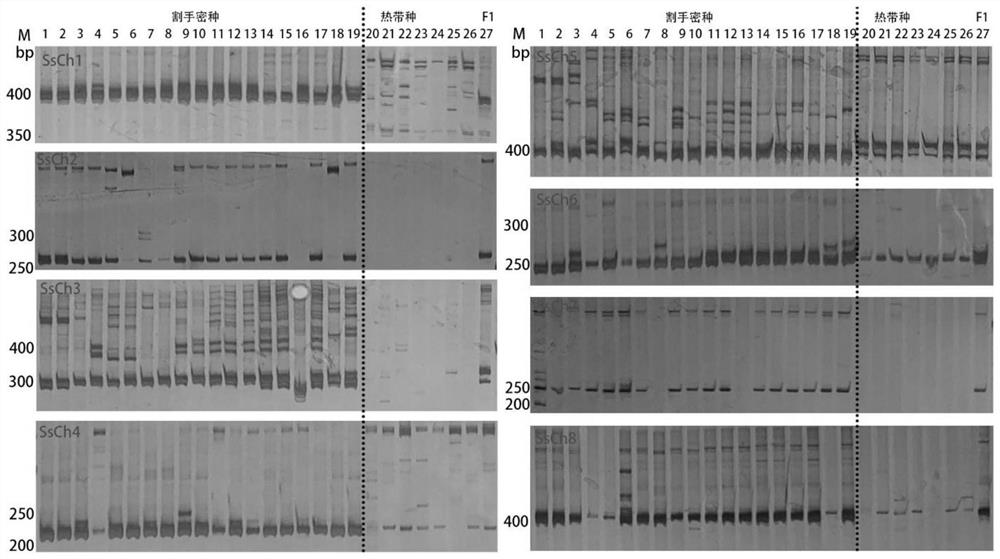
[0023] Example 1: Homologous differential DNA sequence acquisition of tropical species and cut hands dense species
[0024] Use the RepeatMasker software to filter the repetitive sequences in the genomes of tropical species and cut-hand dense species, and then break the genome into 50bp DNA sequences at intervals of 5 bases, and paste these short sequences into the genome to further verify the sequence Genome source. The method of BLAST sequence alignment of short sequences from two genome sources is compared with each other to obtain homologous and differential DNA sequences.
[0025] The invention uses whole genome sequence information, uses RepeatMasker software to filter repeated sequences, and obtains difference DNA sequence information at the whole genome level between two sugarcane species through mutual comparison.
[0026] It should be noted that the RepeatMasker software used here for filtering repetitive sequences and BLAST sequence alignment is a prior art, and it...
Embodiment 2
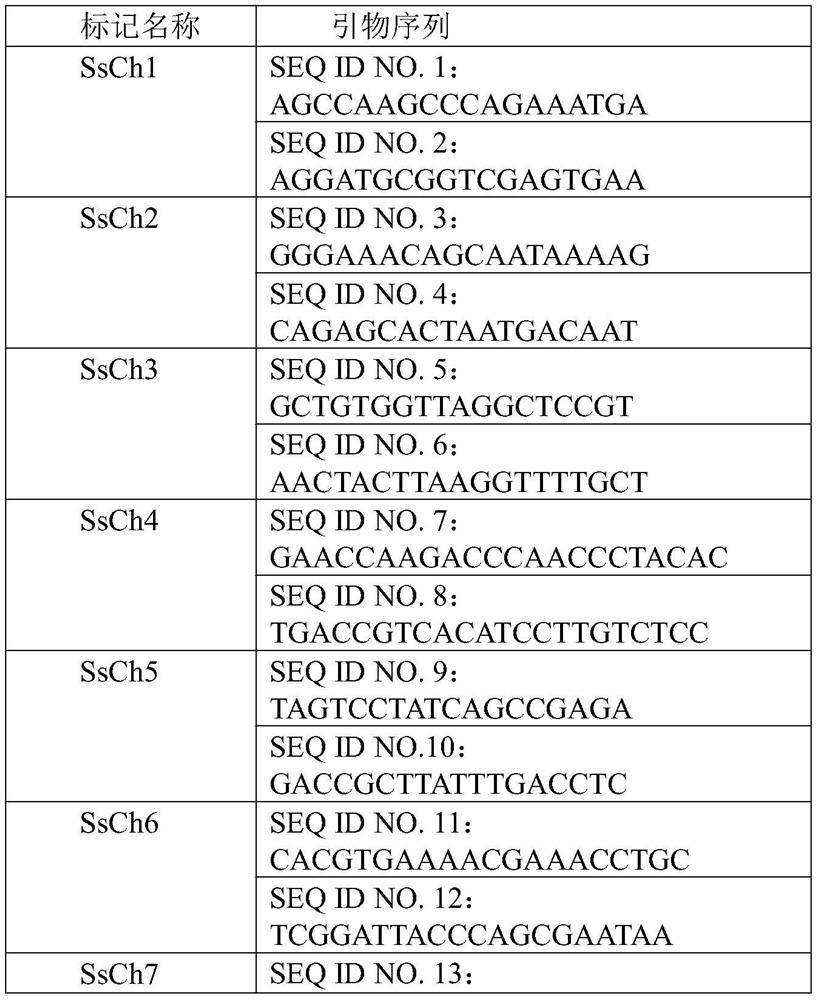
[0027] Example 2: Primer Design and PCR Amplification of Differential DNA Sequences
[0028] The primer design software Primer Premier 5.0 was used to design primers for the differential DNA sequences. The length of the primers was required to be 20 ± 5 bp when designing the primers, and the primers should be designed in the conserved regions at both ends of the differential sequences.
[0029] The reaction system of PCR is: 0.25 μL each of primers, 2 μL of DNA template, 5 μL of PCRMix, and finally add ddH2O to make up the total volume to 10 μL.
[0030] The conditions of PCR amplification were: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 min; denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 61°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 60 s, 28 cycles, and final extension at 72°C for 10 min.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3: the electrophoresis detection of PCR product
[0032] The electrophoresis that the present invention adopts is polyacrylamide electrophoresis, and flow process is:
[0033] 1. After installing the glue tank, configure polyacrylamide gel working solution (8% polyacrylamide, 300ul10% AP, 60ul TEMED), and pour it into the glue tank.
[0034] 2. After the gel is solidified, add 1×TBE electrophoresis buffer (10.8g Tris, 5.5g boric acid, 4mL EDTA (0.5M, pH 8.0), 80ml ultrapure water, dilute to 100mL).
[0035] 3. Add 2ul of the PCR product into the loading buffer, and take 1ul and put it into the prepared gel spotting well.
[0036] 4. Use 180v constant voltage for electrophoresis for 100 minutes.
[0037] 5. End the electrophoresis, remove the gel and put it into the dye solution (1L of pure water is dissolved by adding 1g of silver nitrate), and rotate horizontally on the shaker for 15min.
[0038] 6. Wash the gel twice with ultrapure water, 30s each time. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com