Screening method of sulfate reducing bacteria capable of degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
A screening method and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon technology, applied in the field of environmental microorganisms, can solve the problem of effective degradation of PAHs in anaerobic areas, low potential sensitivity, and restrict the further development of PAHs-contaminated soil and groundwater anaerobic bioremediation technology in anaerobic areas and application research to achieve the effect of overcoming the low enough environmental oxidation-reduction potential, simple operation, and wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
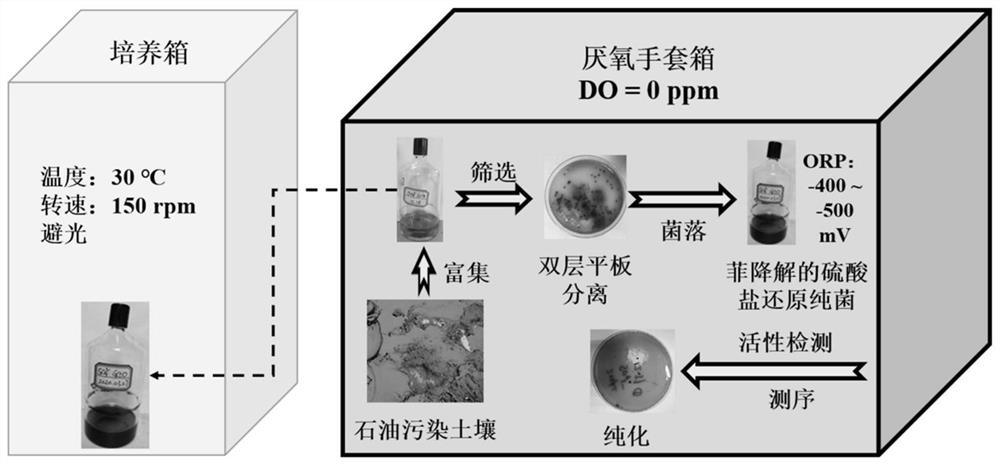
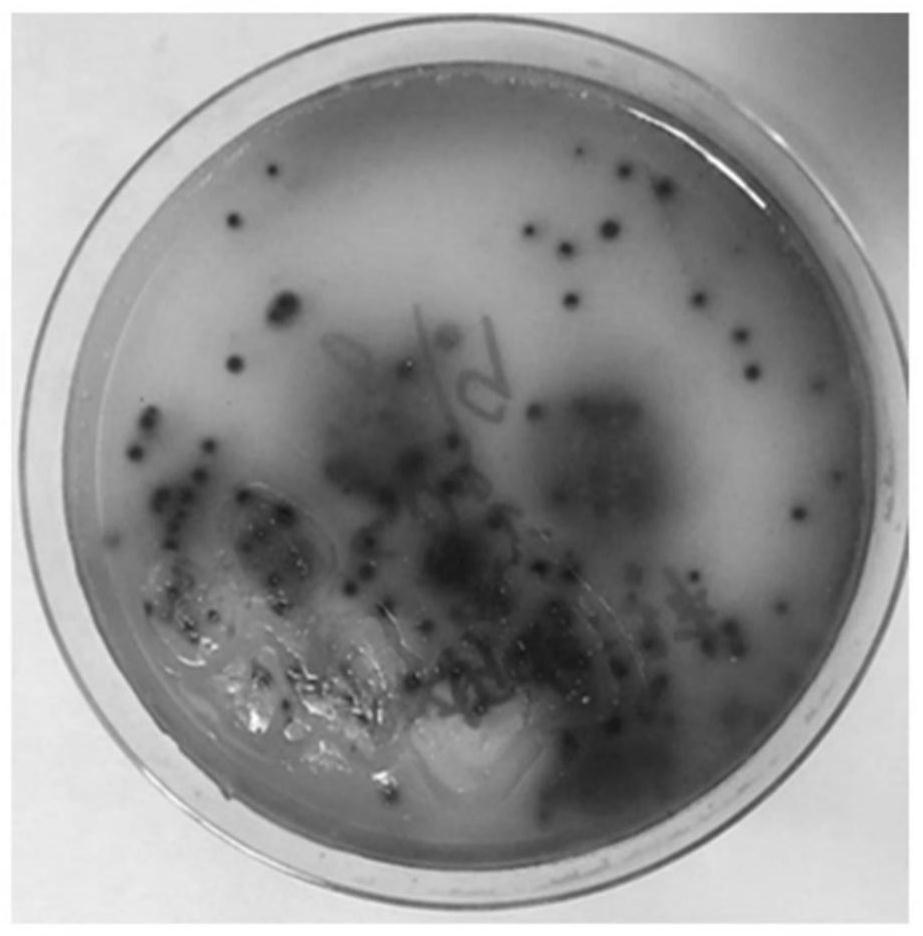
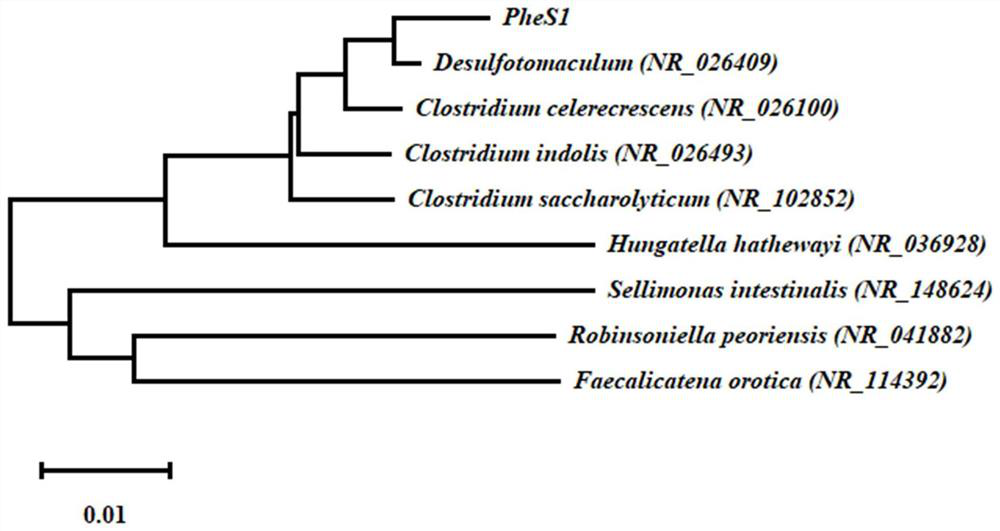
[0054] Such as figure 1 As shown, the screening method for sulfate-reducing bacteria that can anaerobically degrade phenanthrene includes: enrichment of sulfate-reducing bacteria for anaerobic biodegradation of phenanthrene, dilution coating of strains-anaerobic glove box and stacked dish sandwich method combined screening , Separation and purification of bacterial strains, determination of the ability of degrading phenanthrene and reducing sulfate radicals obtained by screening obtained pure sulfate-reducing bacteria, and preservation of strains.
[0055] Enrichment of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria for Anaerobic Biodegradation of Phenanthrene:
[0056] Add 50mL of basal medium into a small-mouth anaerobic bottle with a volume of 300mL, then vacuumize for 1min, expose to high-purity nitrogen for 15min, seal the anaerobic bottle with a butyl rubber stopper, and sterilize at 121°C and high pressure for 20min. Transfer the anaerobic bottle to an anaerobic glove box, remove the butyl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com