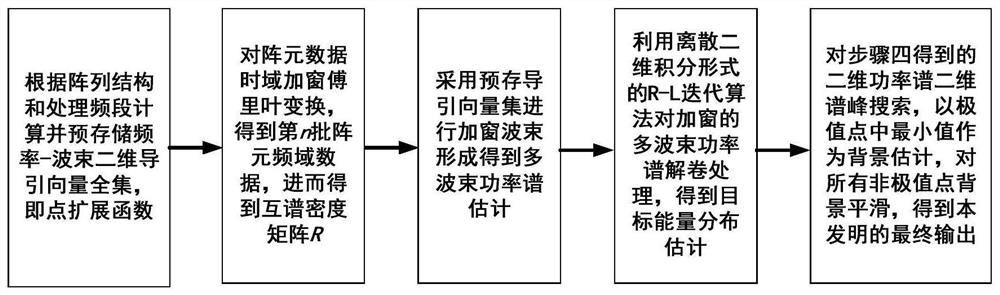
Windowing two-dimensional unrolling multi-beam power spectrum estimation algorithm
A power spectrum estimation and multi-beam technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, instrumentation, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem that iterative calculations cannot effectively detect 45° targets, cannot distinguish between 93° and 98° targets, and sacrifice spatial resolution efficiency and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving the actual performance, strengthening the significance of engineering practice, and suppressing interference energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
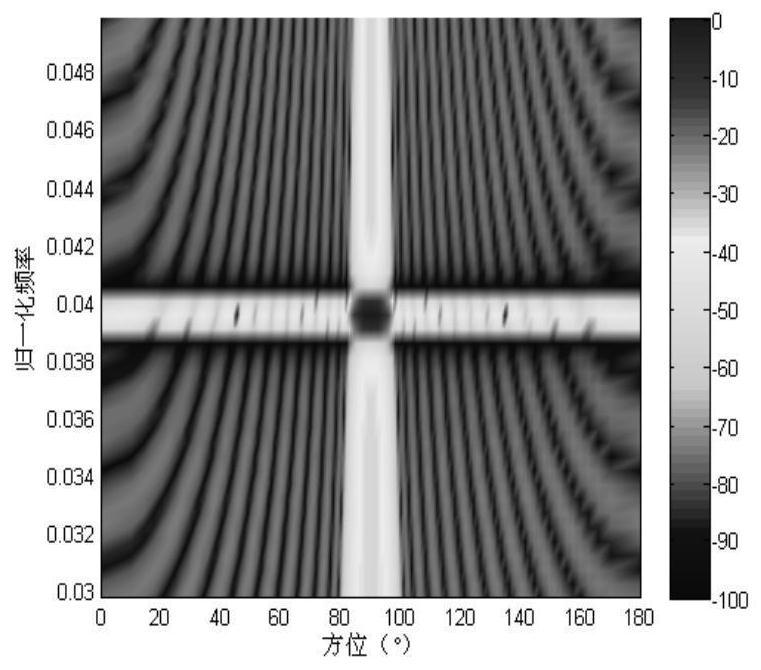
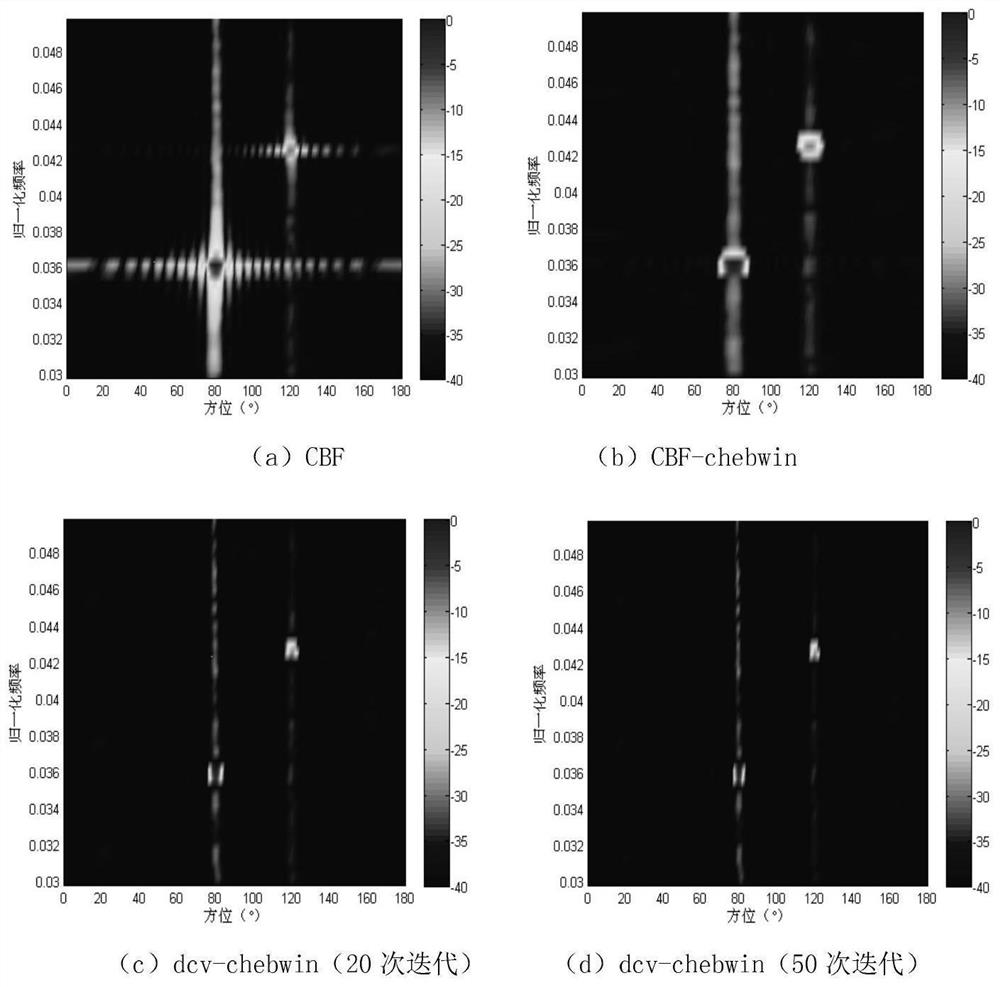
[0083]According to the flow process of step 1 to step 5, the performance of the present invention is investigated by simulation. A uniform line array with 32 elements is used to verify the performance of the proposed algorithm. The array element spacing is the half-wavelength corresponding to the highest processing frequency, and the range of the processing frequency band is [0.03,0.05] after normalization with the sampling frequency. Two independent signals in space are incident to the array, and the noise is Gaussian white noise independent between the array elements. The target spectral structure includes broadband continuum and line spectrum features covering the entire processing frequency band, where the incident direction of interference is 80°, interference The noise ratio is 10dB, contains a line spectrum component 15dB above the continuum background, and the normalized line spectrum frequency is 0.036. The incident direction of the target is 120°, the signal-to-nois...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com