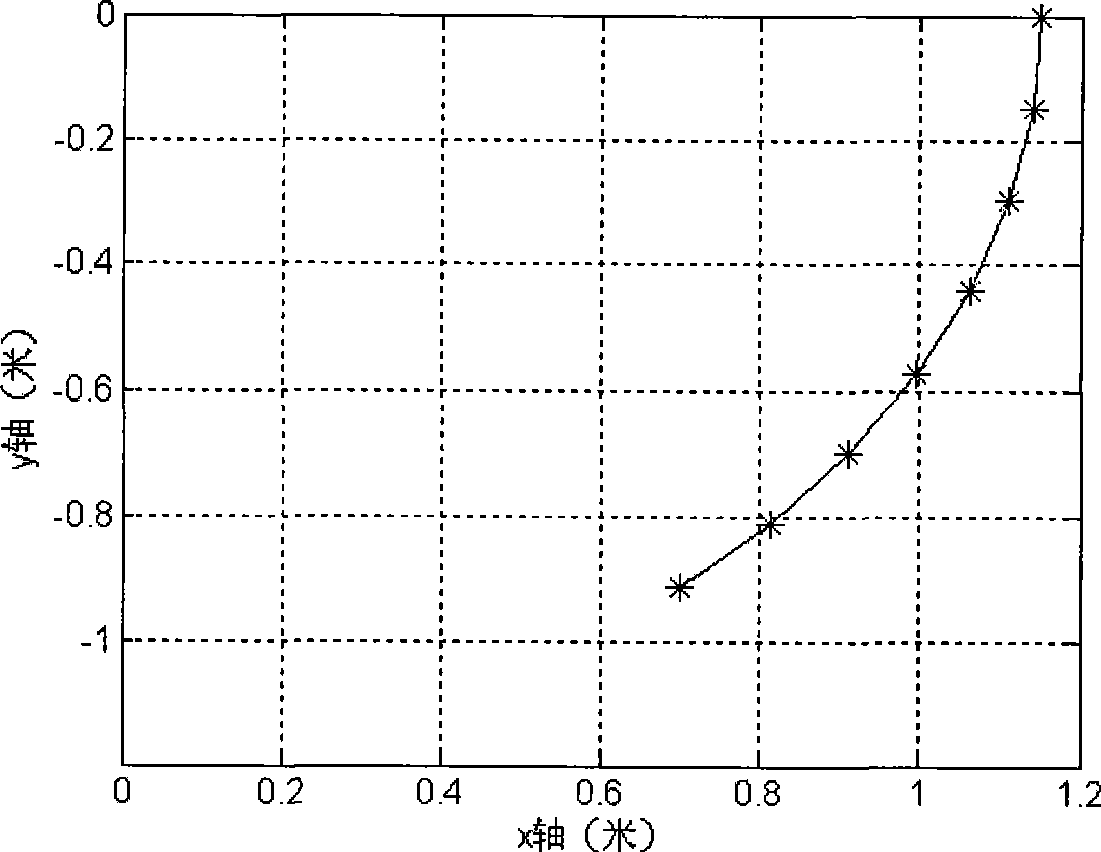
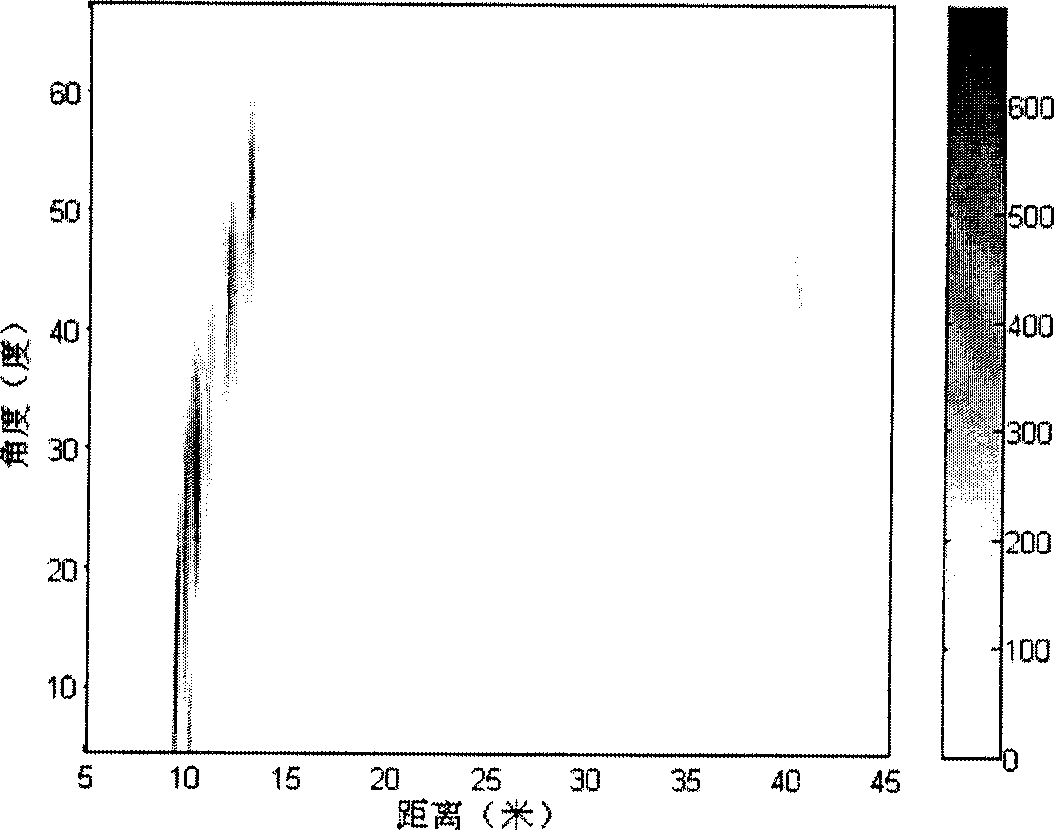
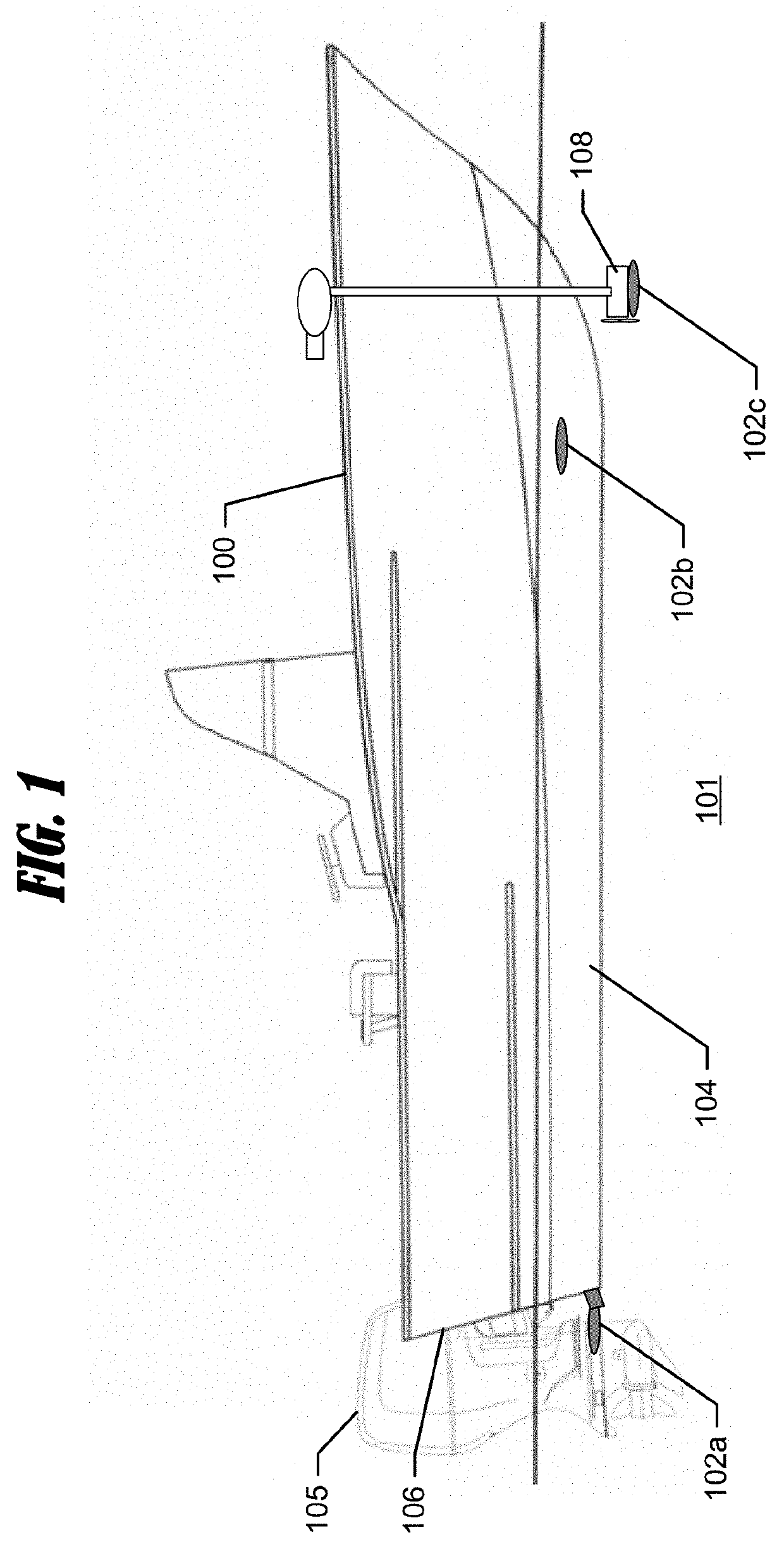
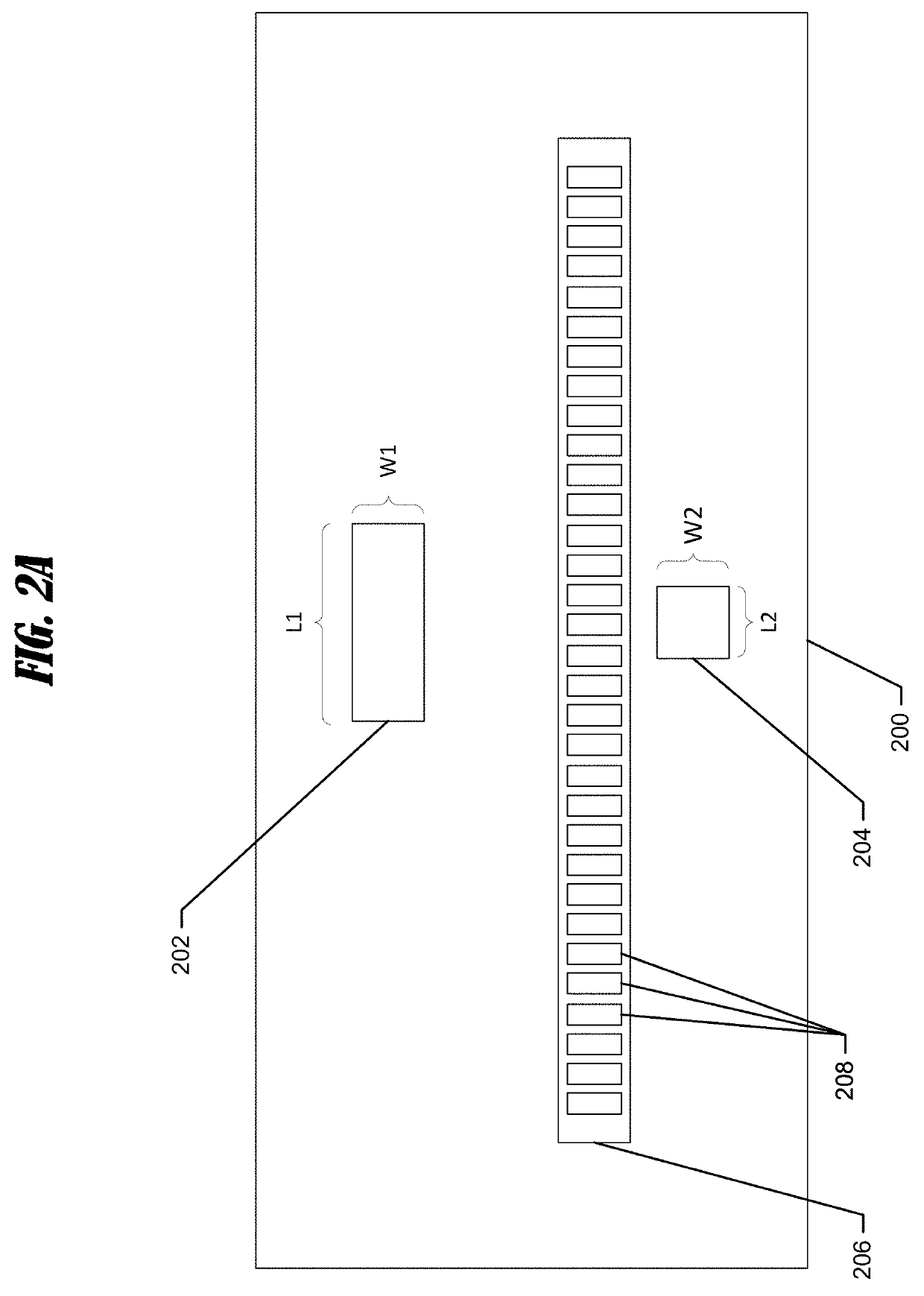
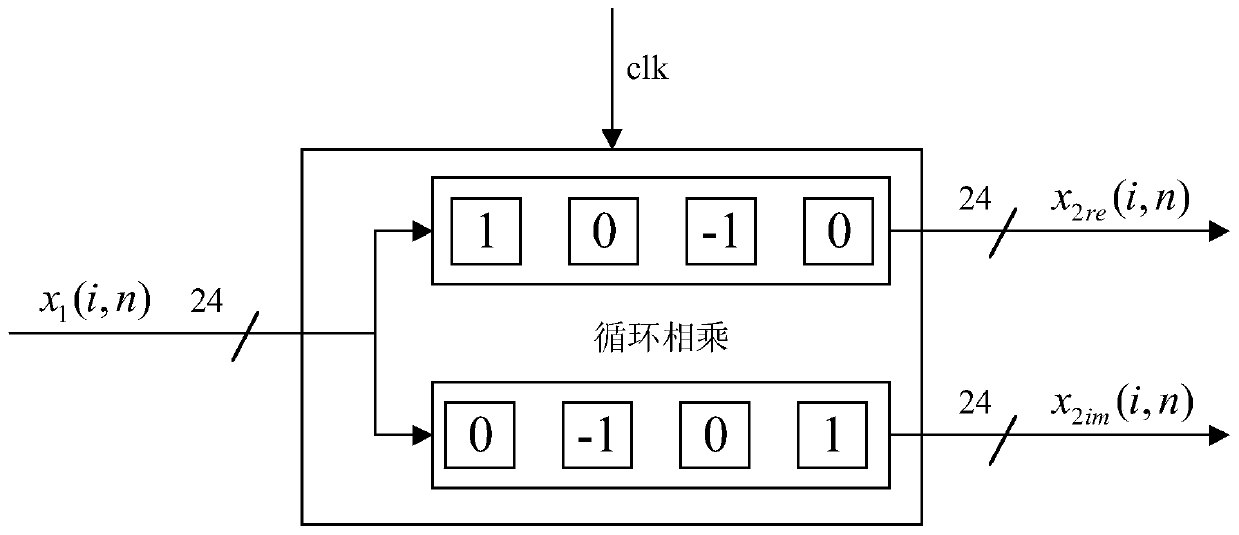
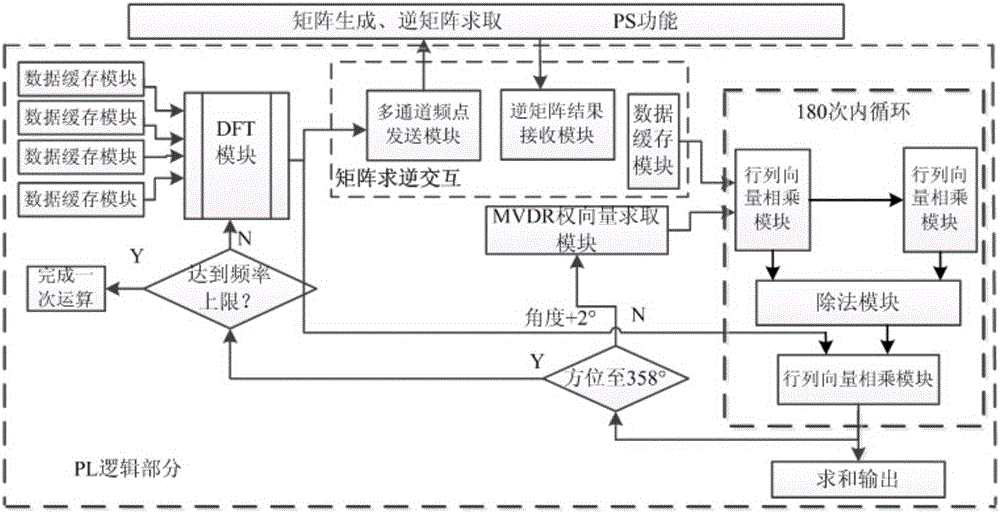
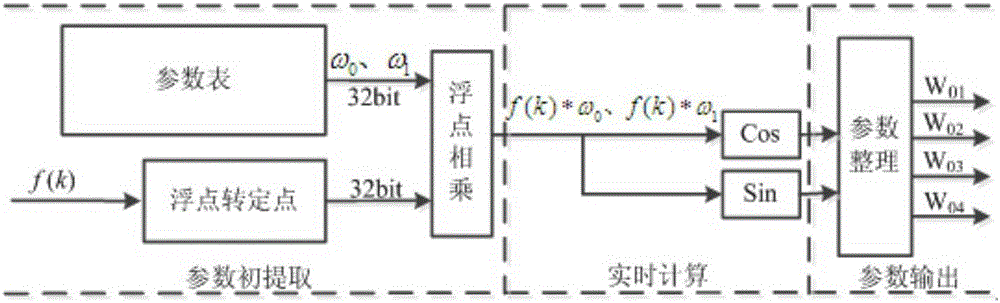
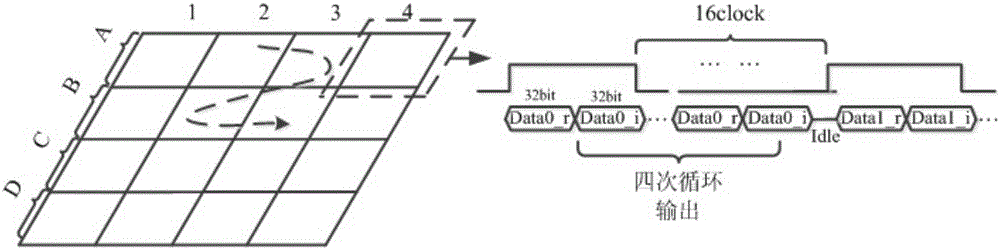
Patents
Literature
83 results about "Sonar signal processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
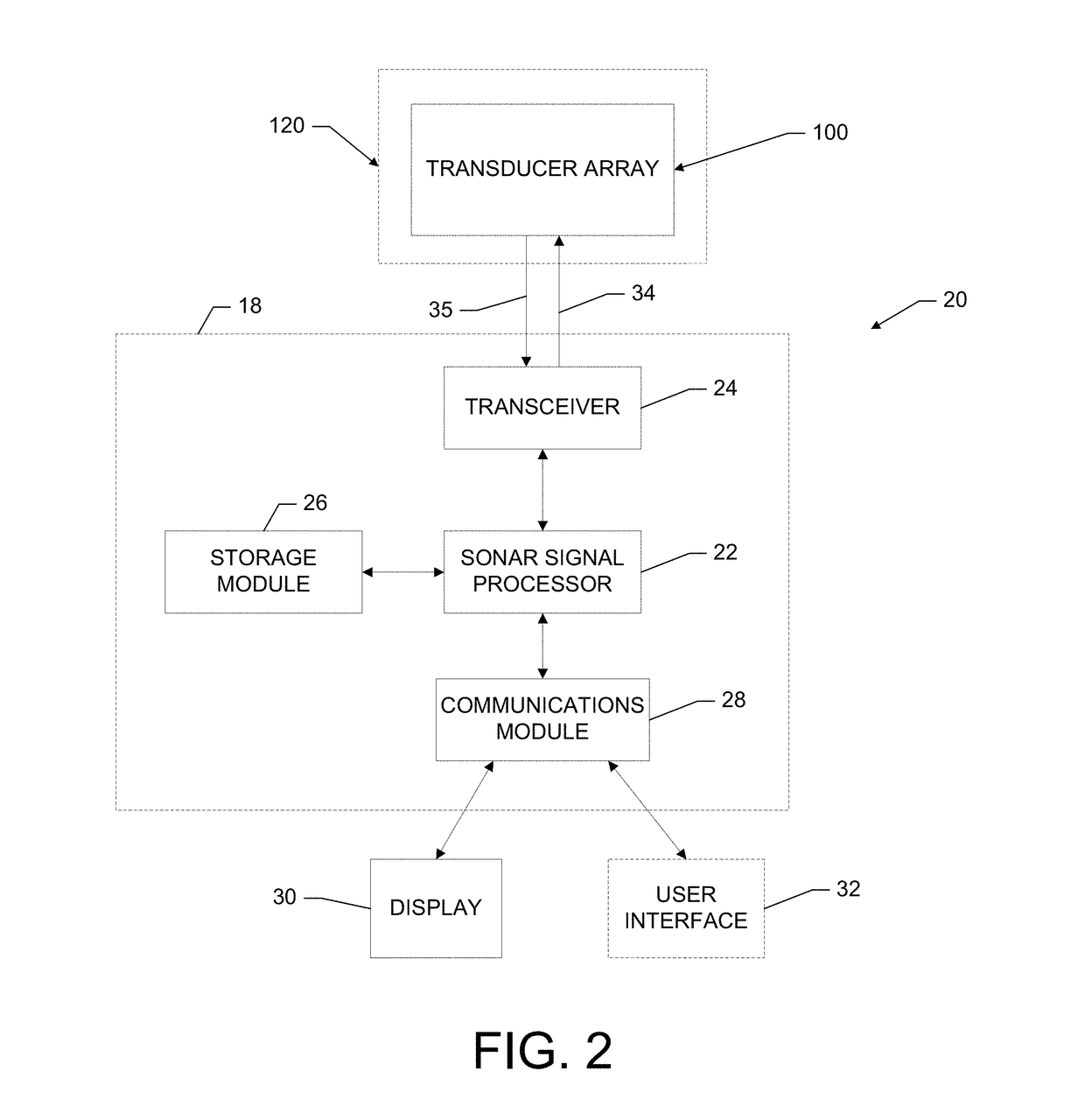
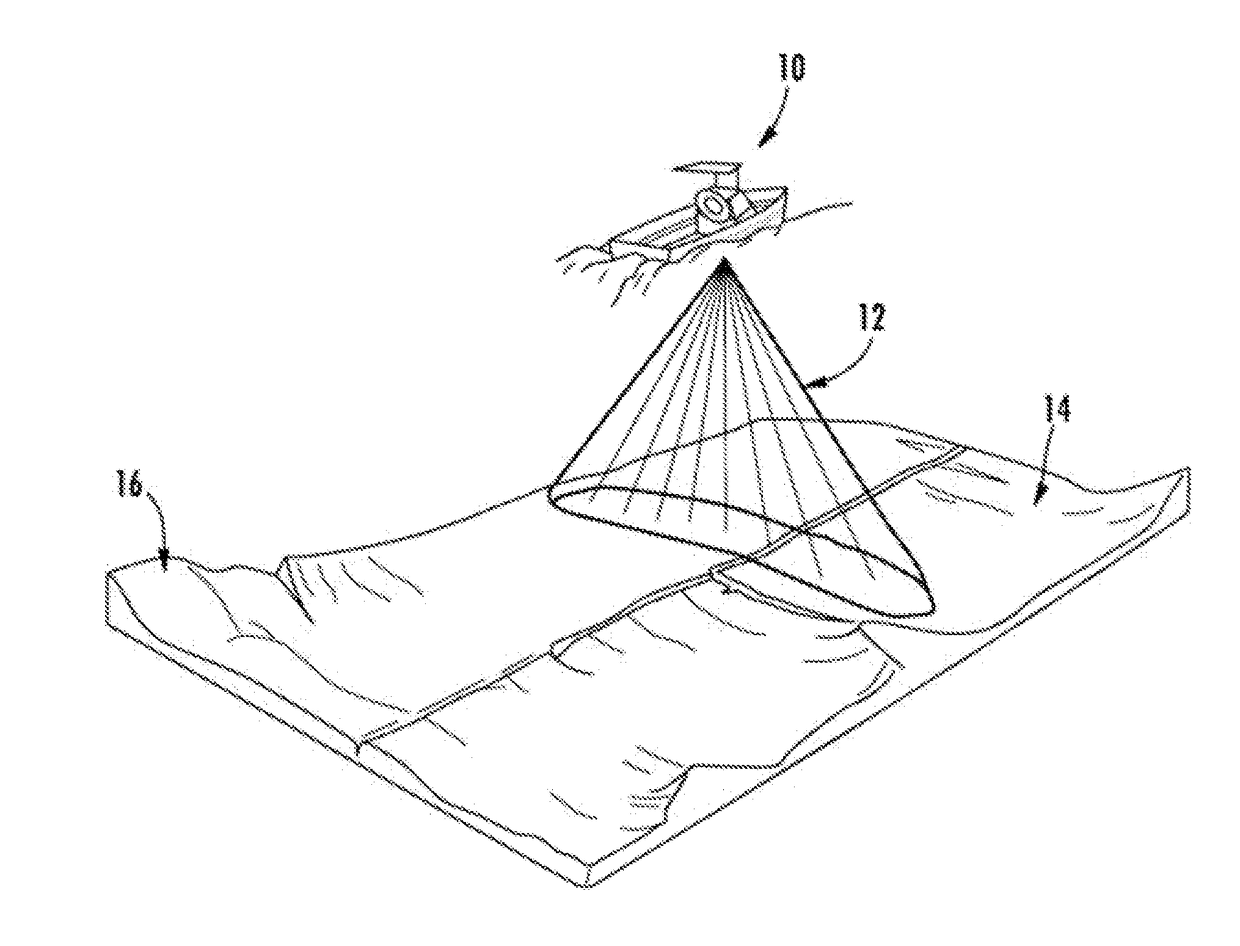
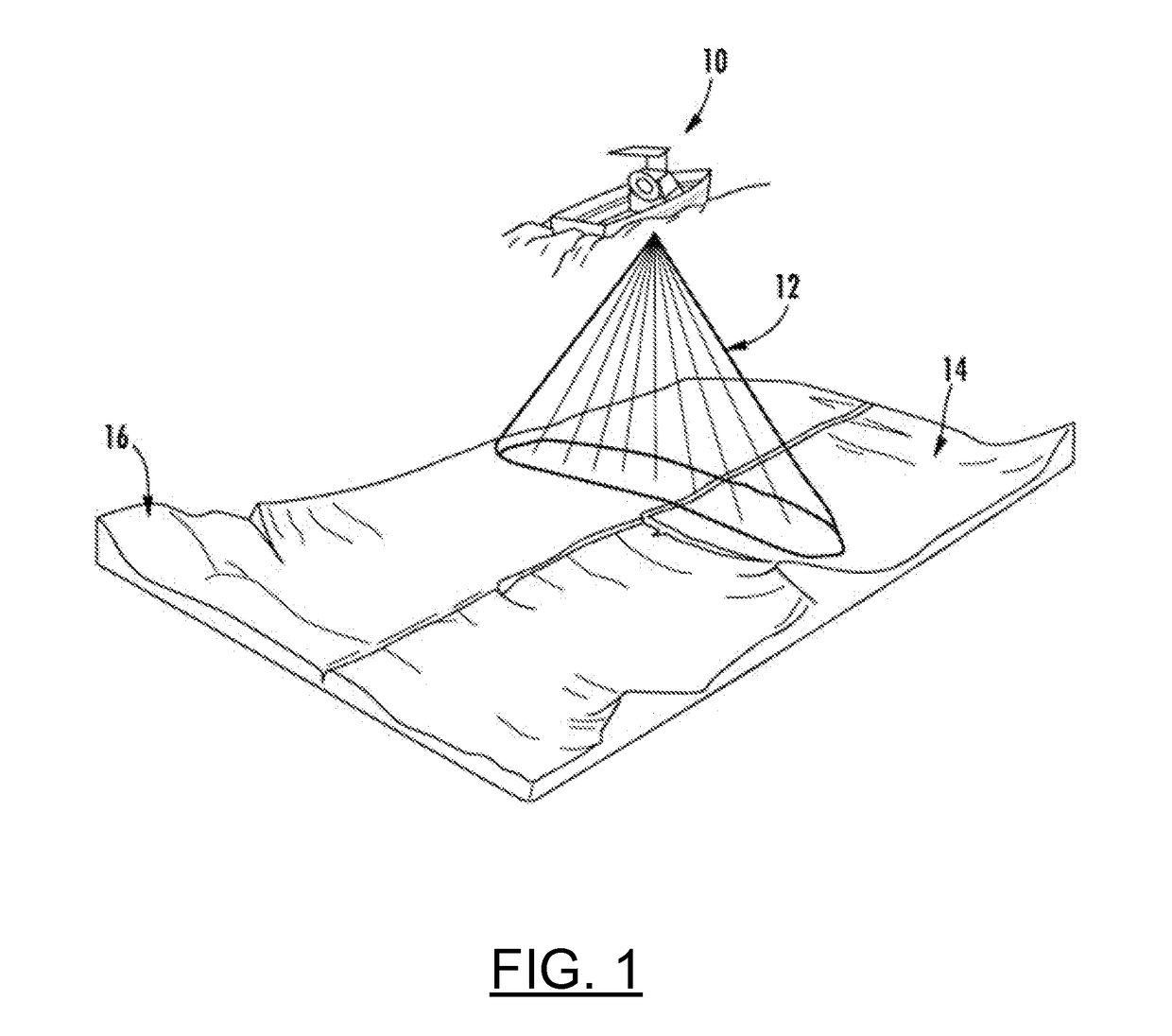
Sonar systems are generally used underwater for range finding and detection. Active sonar emits an acoustic signal, or pulse of sound, into the water. The sound bounces off the target object and returns an “echo” to the sonar transducer. Unlike active sonar, passive sonar does not emit its own signal, which is an advantage for military vessels. But passive sonar cannot measure the range of an object unless it is used in conjunction with other passive listening devices. Multiple passive sonar devices must be used for triangulation of a sound source. No matter whether active sonar or passive sonar, the information included in the reflected signal can not be used without technical signal processing. To extract the useful information from the mixed signal, some steps are taken to transfer the raw acoustic data.
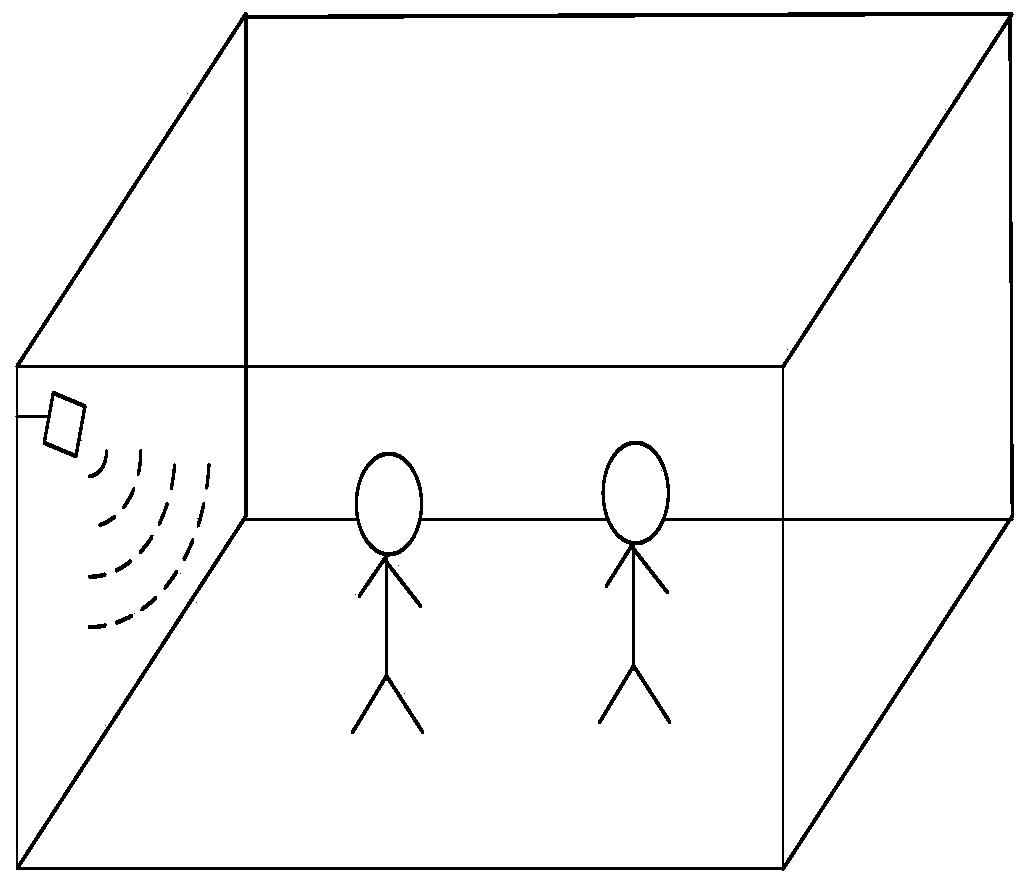
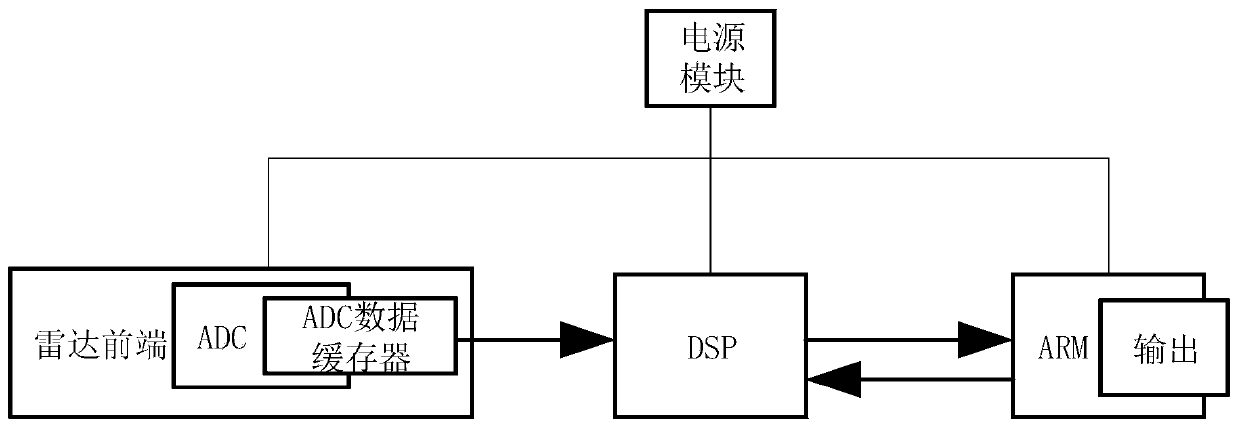
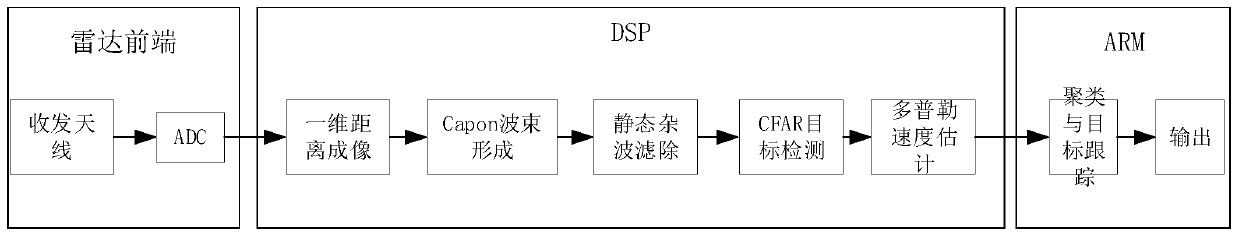
Personnel detection and counting system based on millimeter wave radar
ActiveCN110118966AEasy to detectAchieve countRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingData set
The invention provides a personnel detection and counting system based on a millimeter wave radar, wherein the millimeter wave radar is installed at a set position of a monitoring area, the millimeterwave radar transmits millimeter wave band radio frequency signals to the monitoring area through a multi-transmitting and multi-receiving antenna of the millimeter wave radar and receives echo signals at the same time, the echo signals are subjected to frequency mixing with the transmitted signals and then subjected to down-conversion to obtain beat intermediate frequency signals, and the beat intermediate frequency signals are sampled to obtain an echo sampling sequence. A digital signal processor reads the echo sampling sequence and performs signal processing to obtain a detected point cloud data set. An ARM processor reads the point cloud data set, meanwhile, Kalman filtering tracking is carried out on the point cloud data, continuous observation of states and the number of a pluralityof human body moving targets is achieved, the positions and the number of people in the monitoring area are obtained, and the number of people in the monitoring area is counted. The personnel detection and counting system based on the millimeter wave radar can track at least 20 targets simultaneously, provide the position and speed information of the targets, effectively judge the state of the targets and give early warning in time.
Owner:长沙莫之比智能科技有限公司
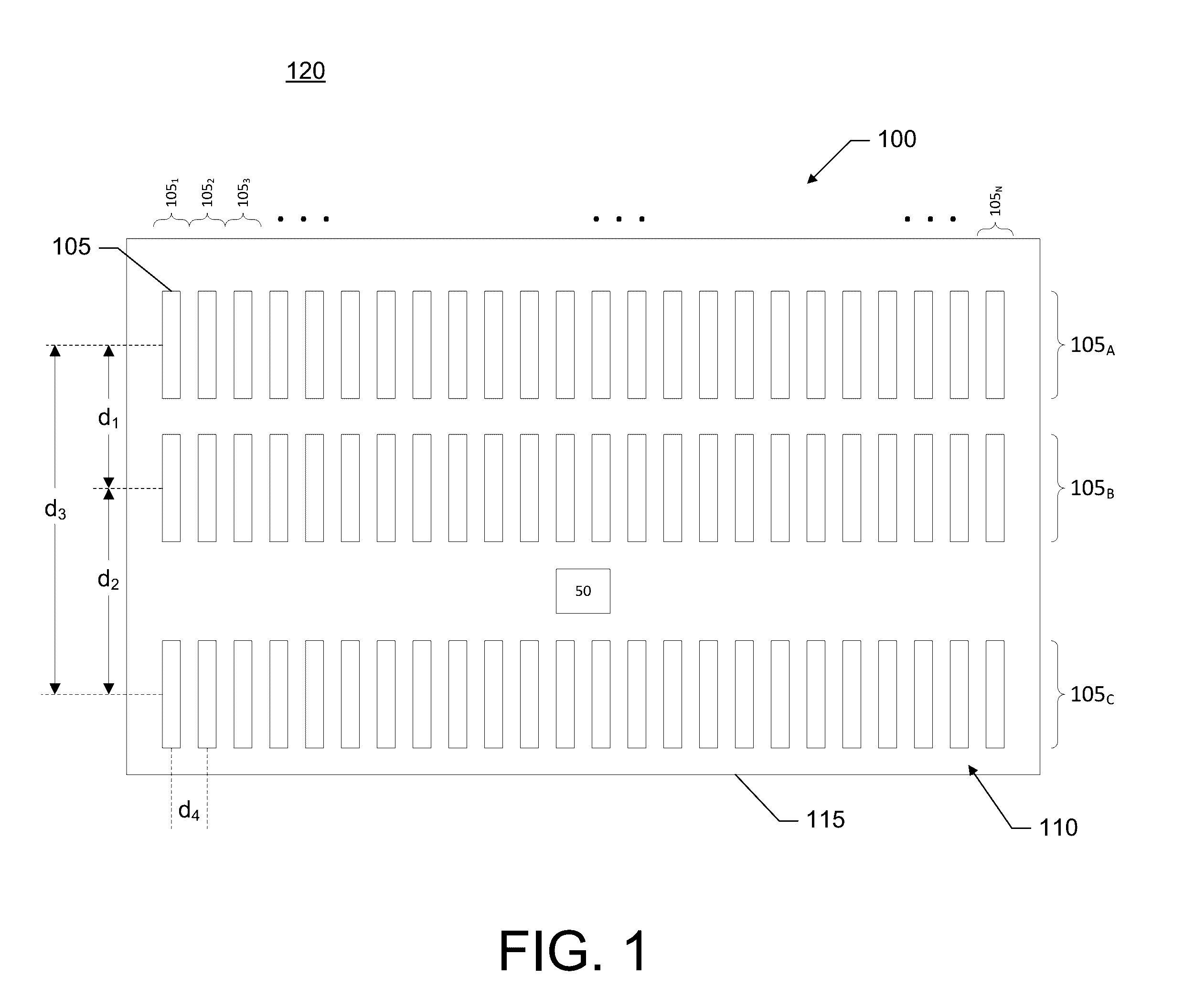
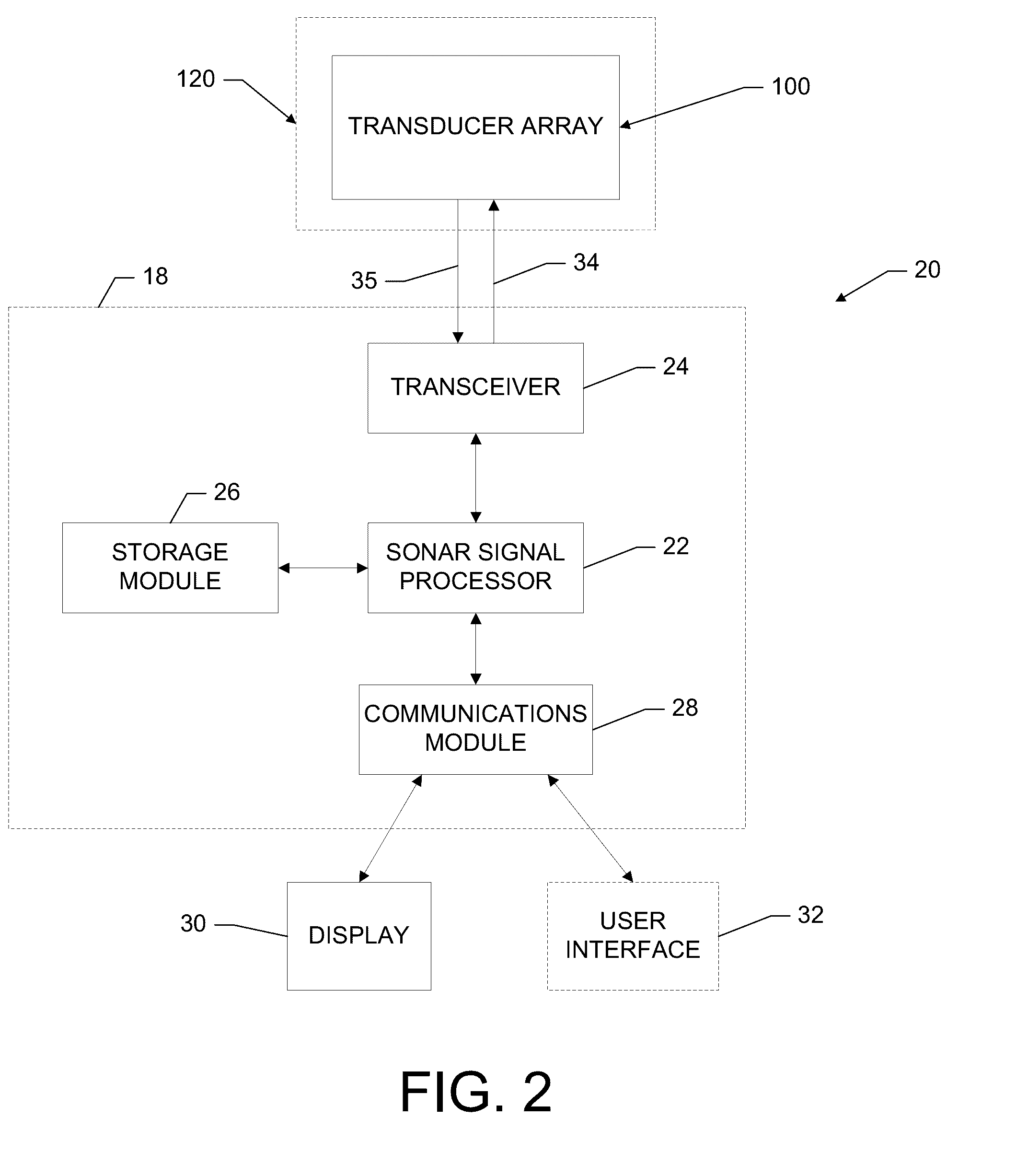
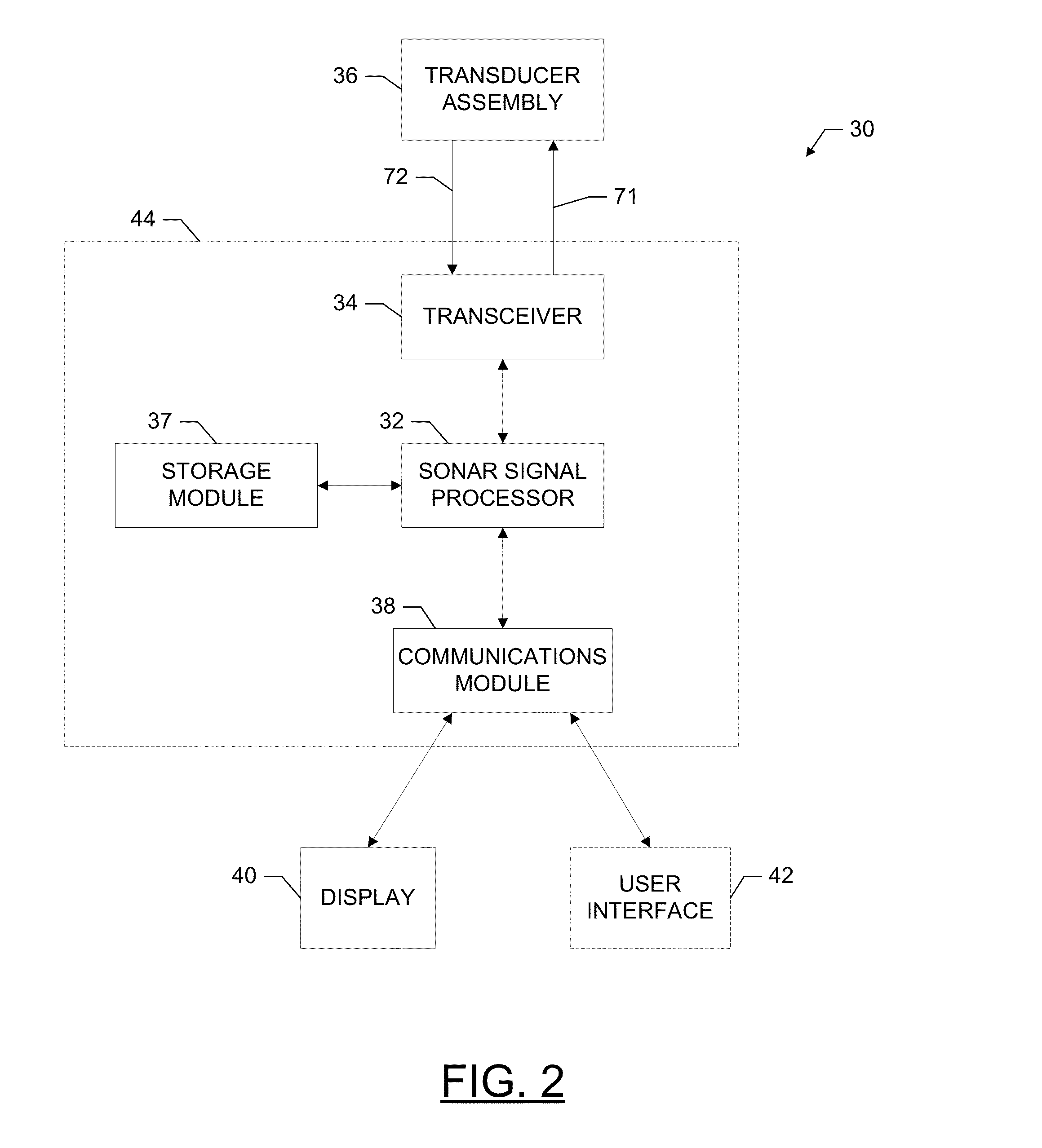
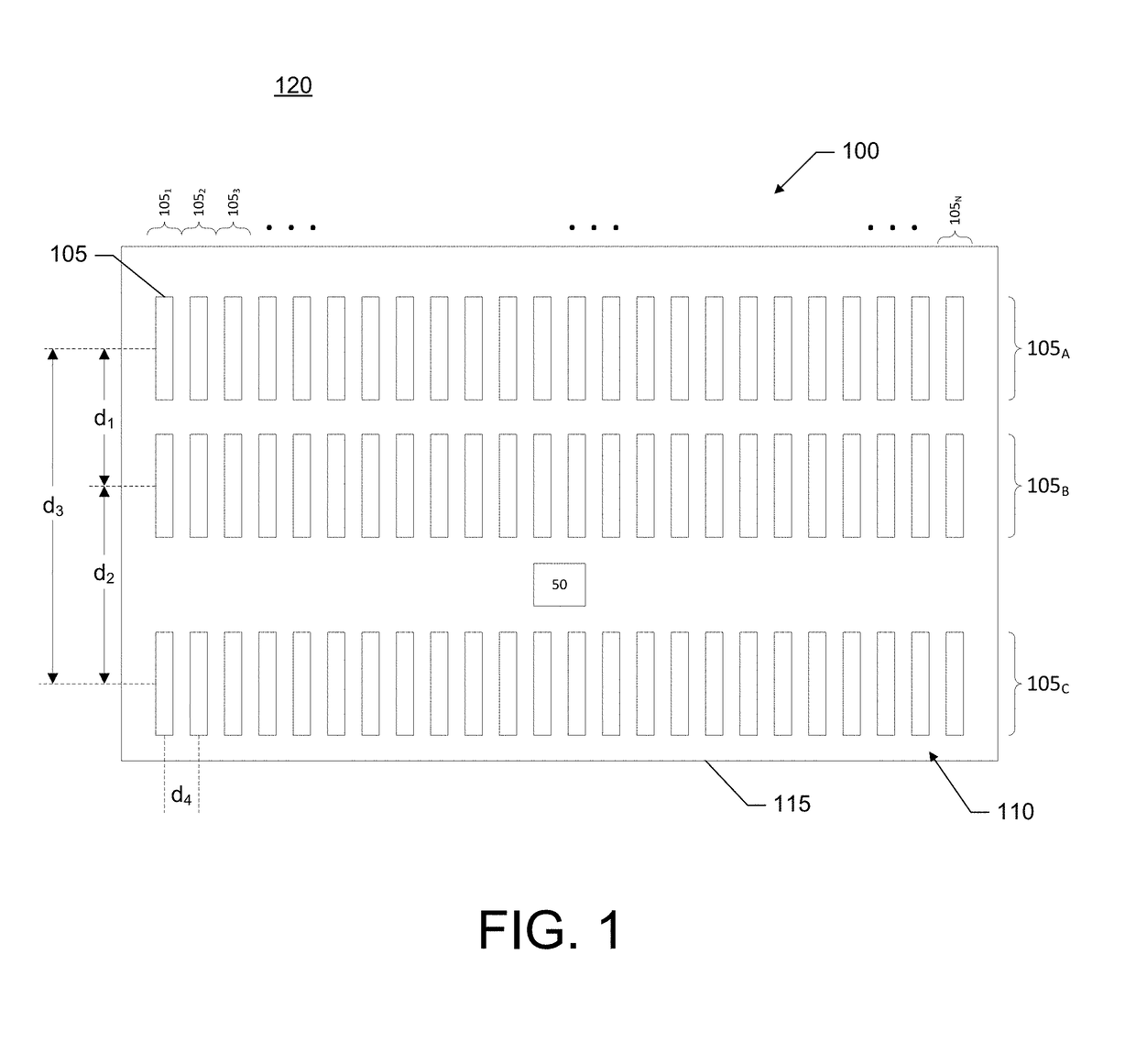
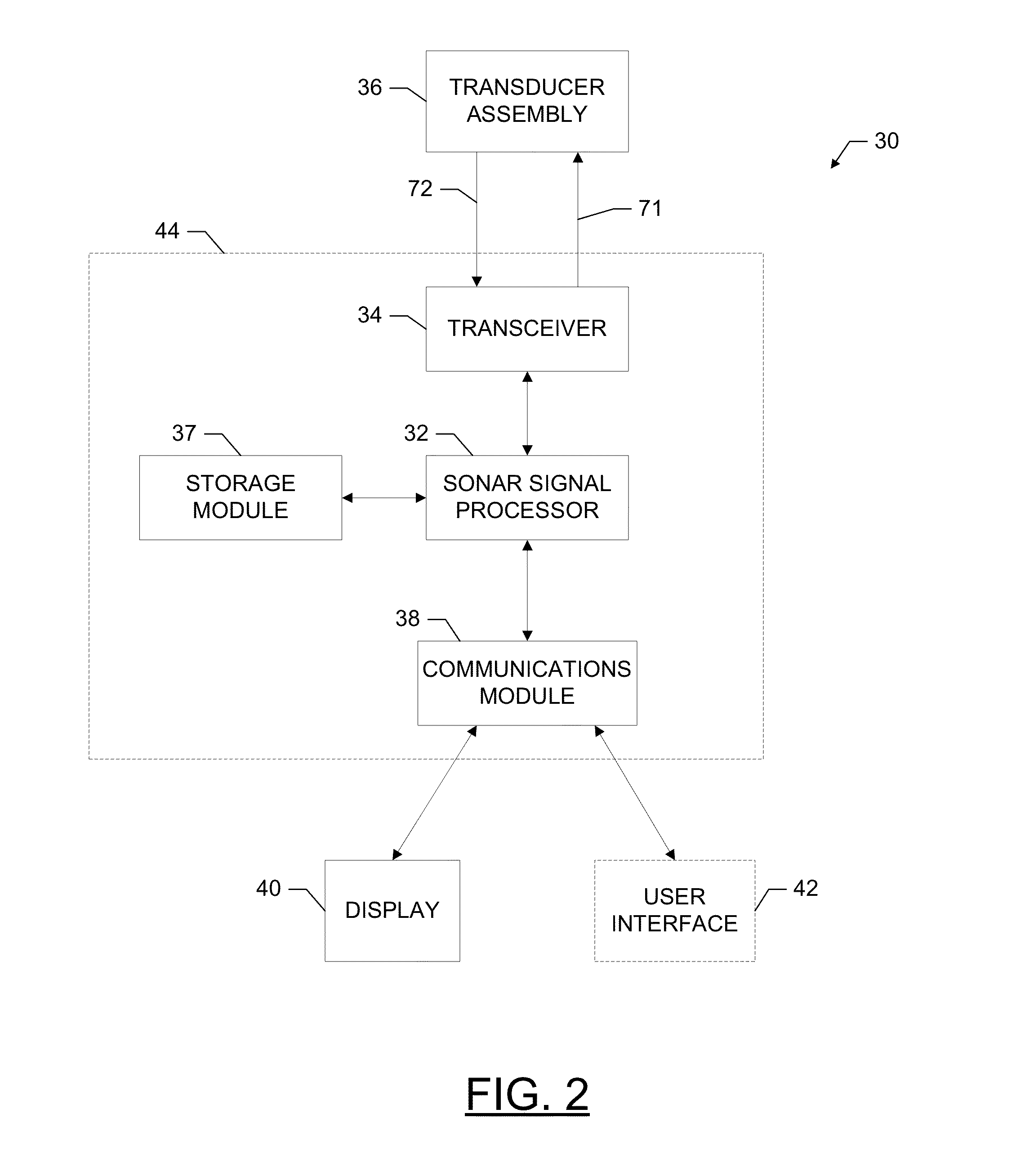
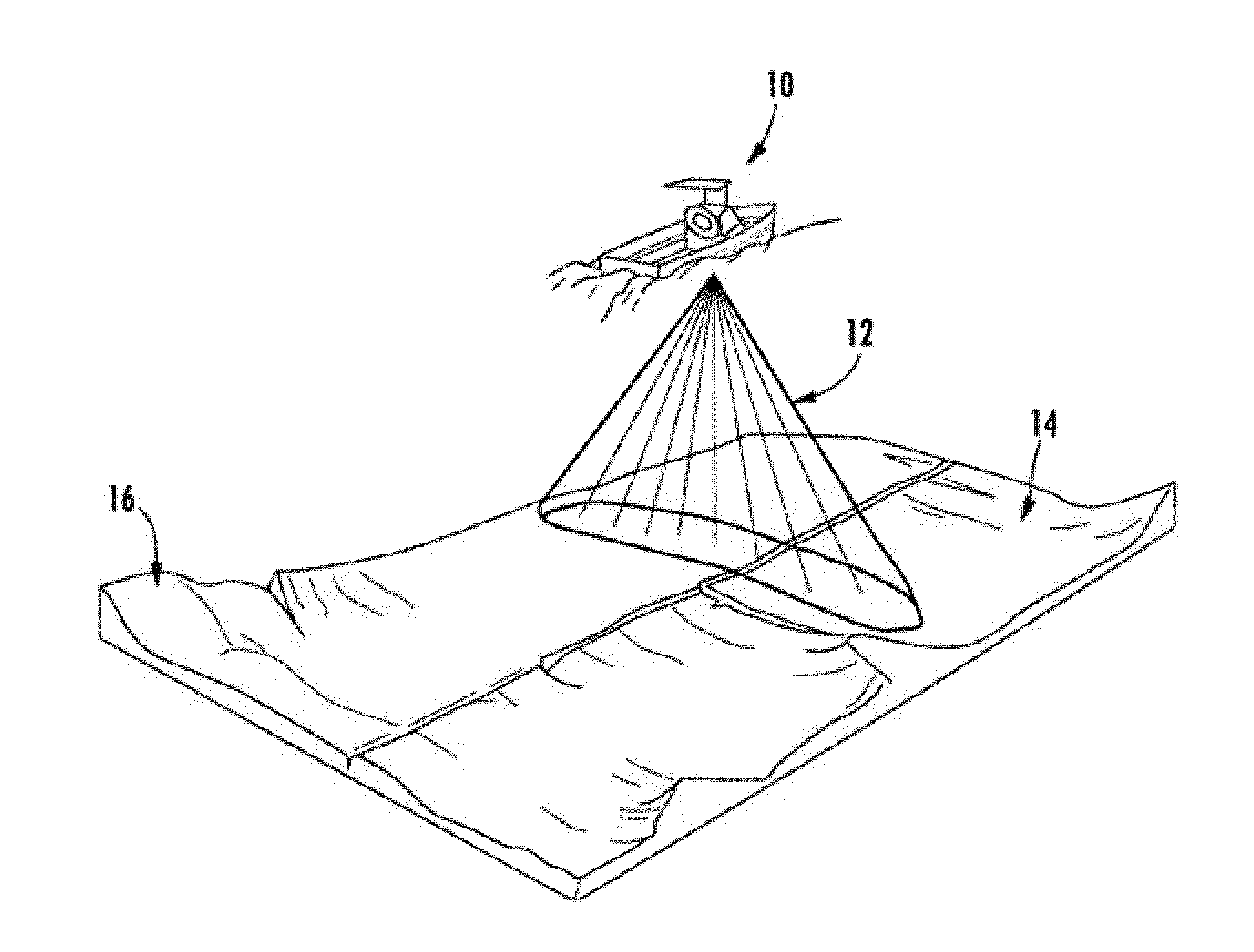
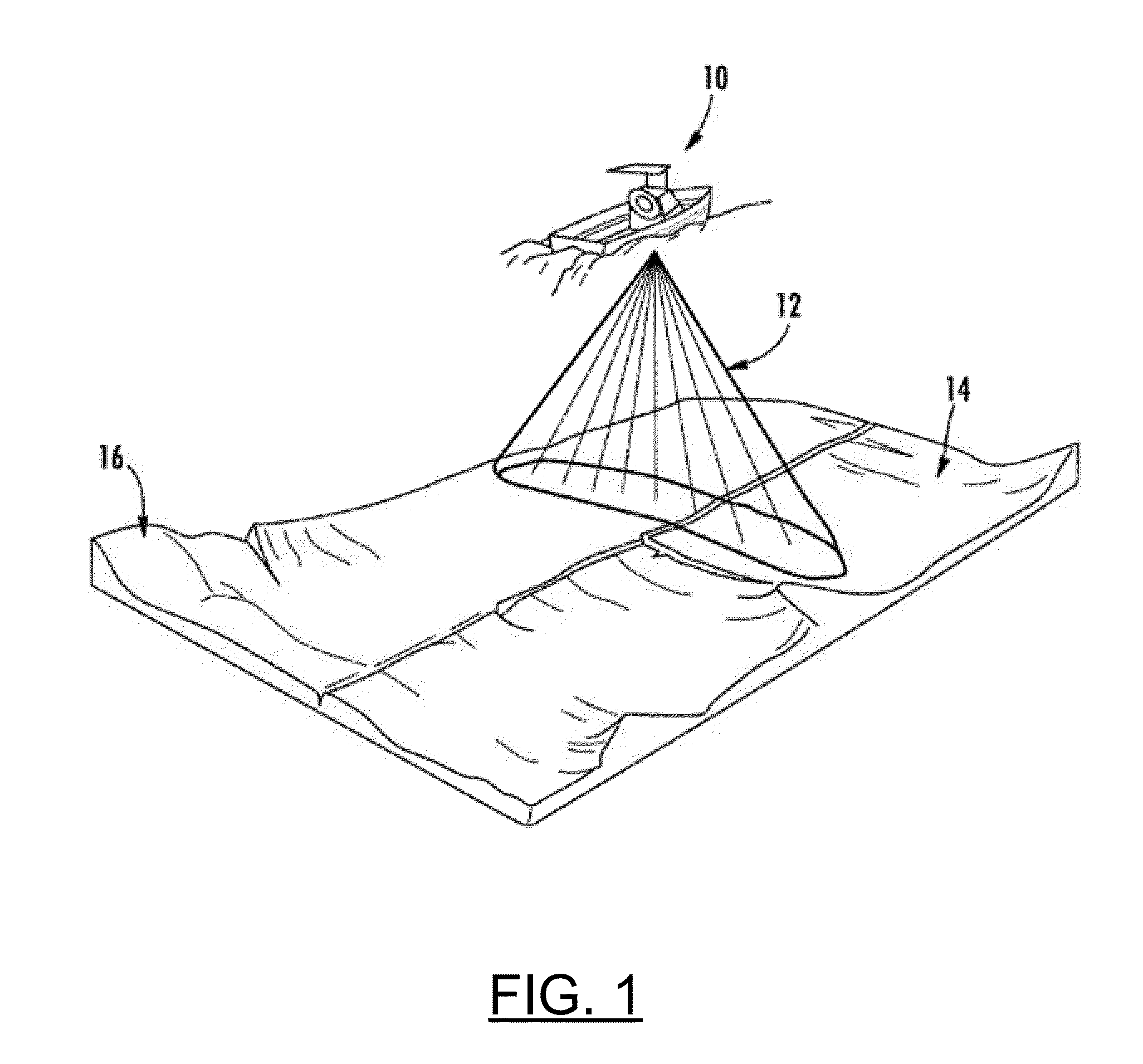
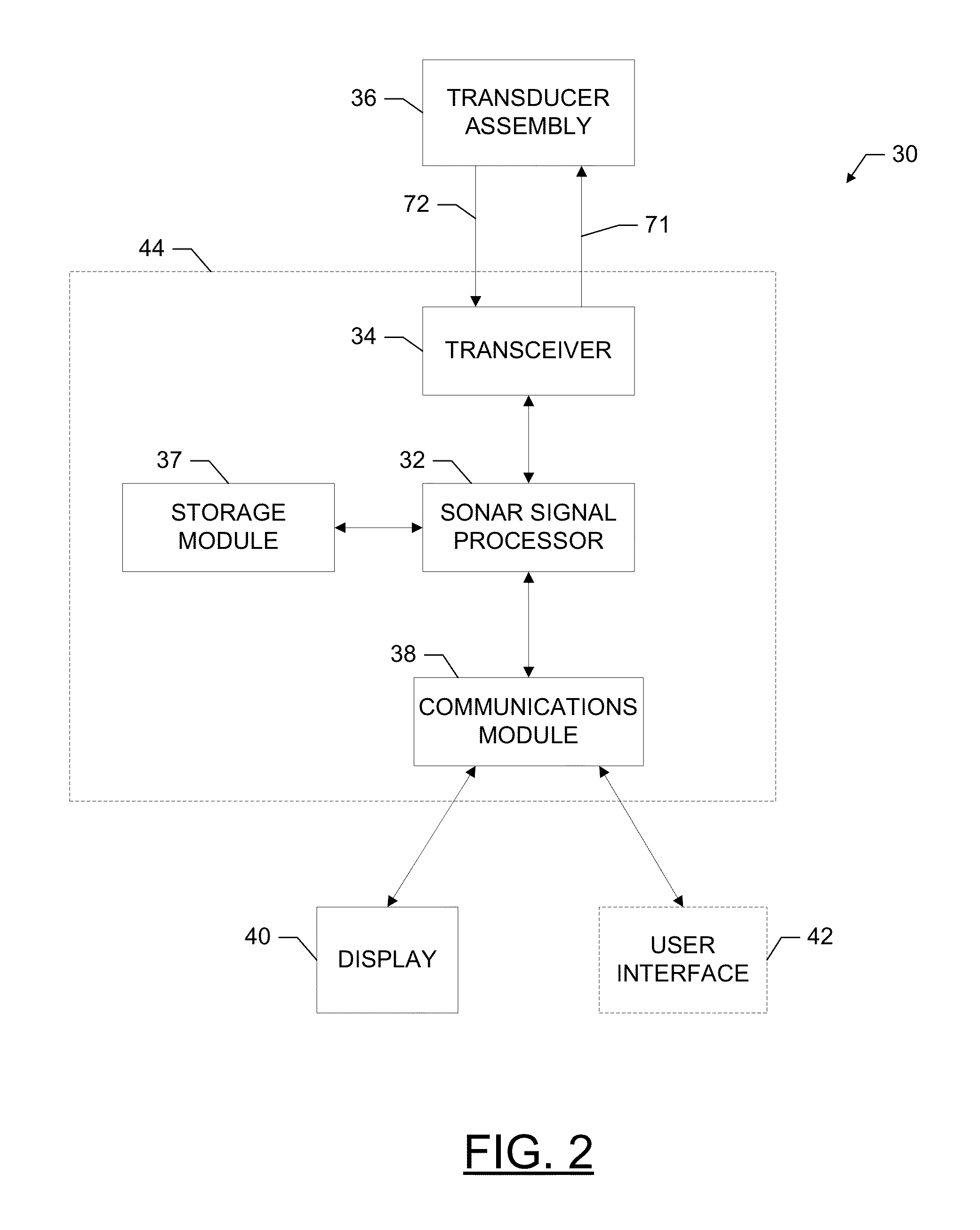
Sonar systems and methods using interferometry and/or beamforming for 3D imaging
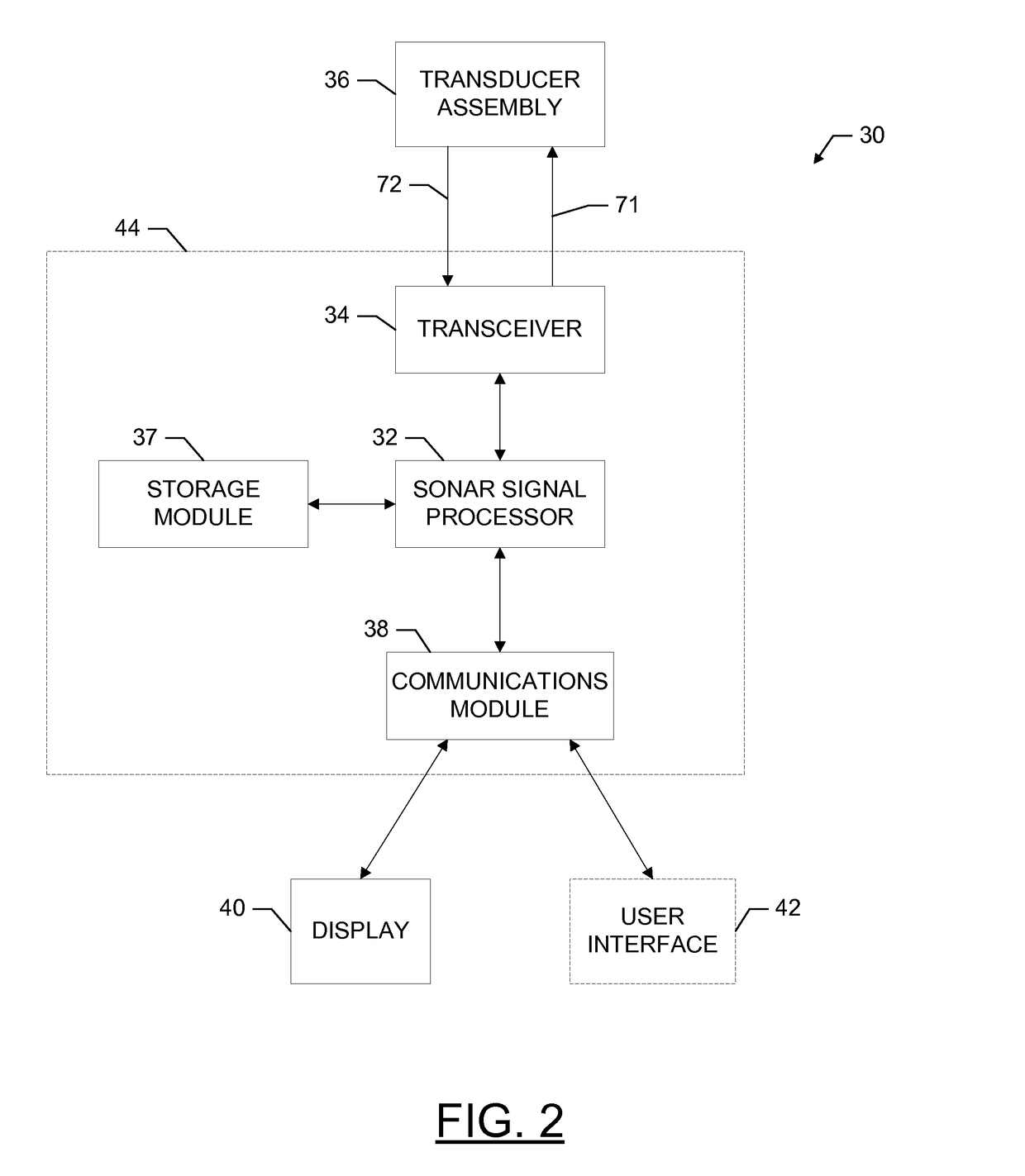
Provided are a sonar system, transducer assembly, and method for imaging an underwater environment. The sonar system may include a housing having a transducer array defining first and second rows of transducer elements positioned at a predetermined distance. The first row of transducer elements may include at least first and second transducer elements configured to convert sound energy into first and second sonar return data. The second row of transducer elements may include at least third and fourth transducer elements configured to convert sound energy into third and fourth sonar return data. A sonar signal processor may be configured to process the first and second sonar return data and third and fourth sonar return data to generate respective first and second array sonar return data corresponding to a plurality of first and second receive beams and generate 3D sonar return data by correlating the angles associated with the receive beams.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
Systems and associated methods for producing a 3D sonar image
Provided are a sonar system and transducer assembly for producing a 3D image of an underwater environment. The sonar system may include a housing mountable to a watercraft having a transmit transducer that may transmit sonar pulses into the water. The system may include at least one sidescan transducer array in the housing that receives first and second sonar returns with first and second transducer elements and converts the first and second returns into first and second sonar return data. A sonar signal processor may then generate a 3D mesh data using the first and second sonar return data and at least a predetermined distance between the transducer elements. An associated method of using the sonar system is also provided.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
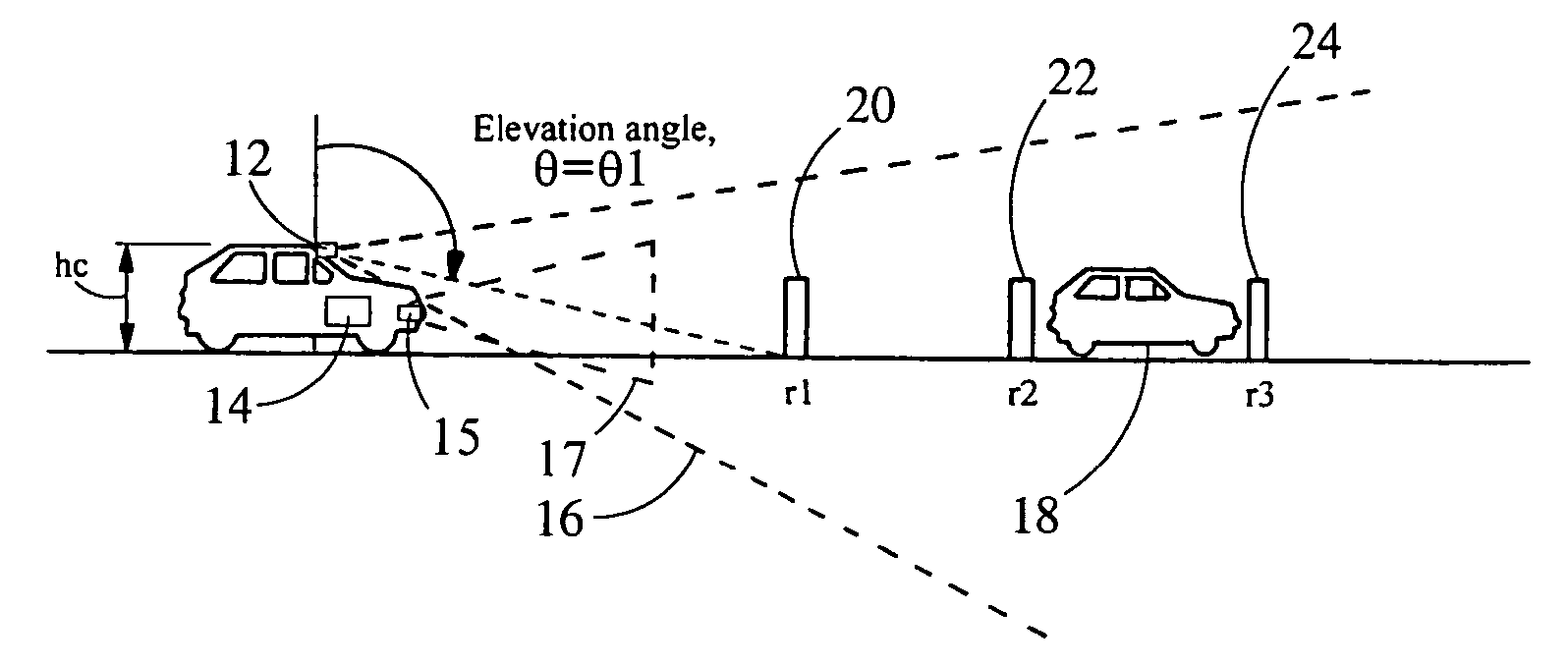
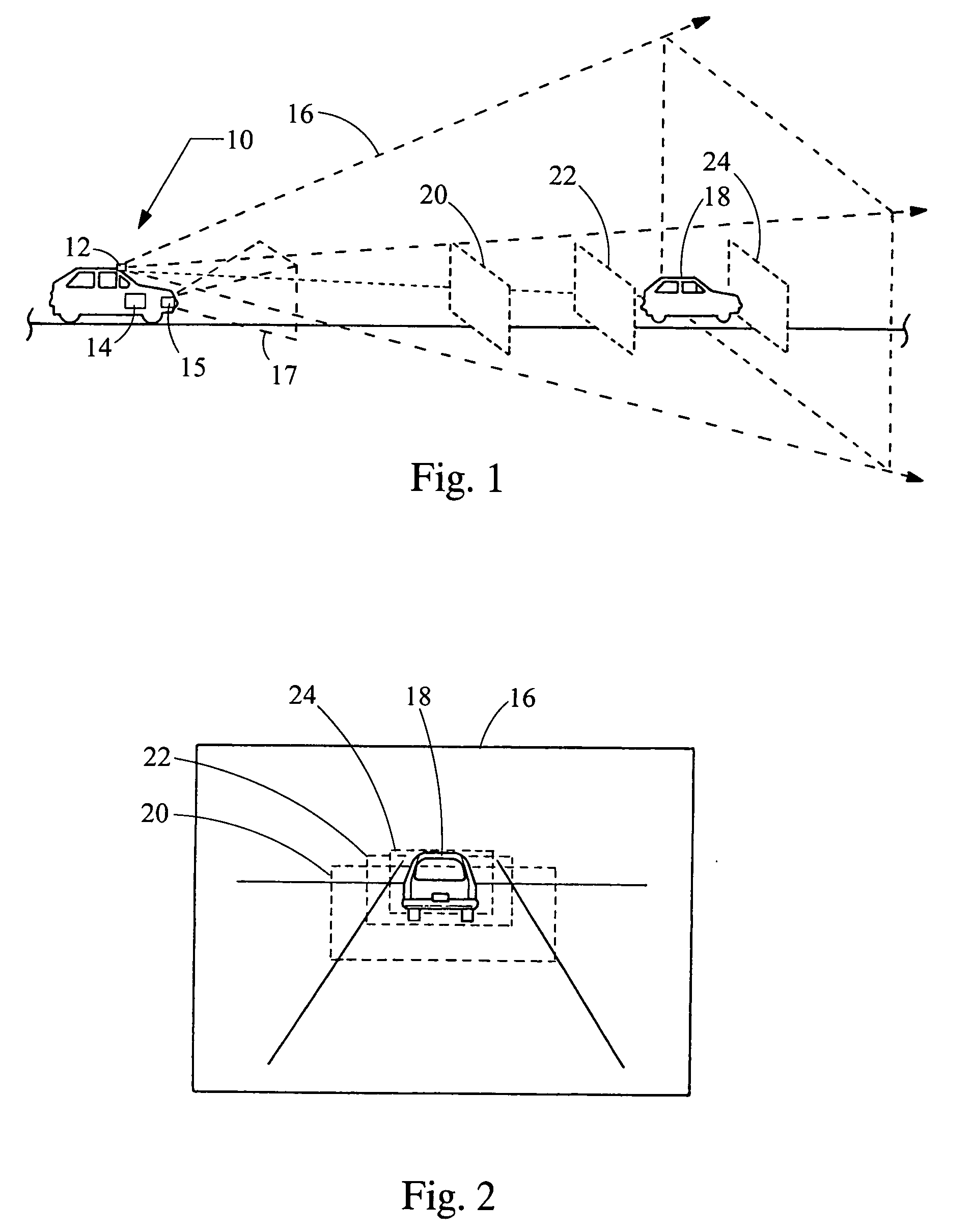
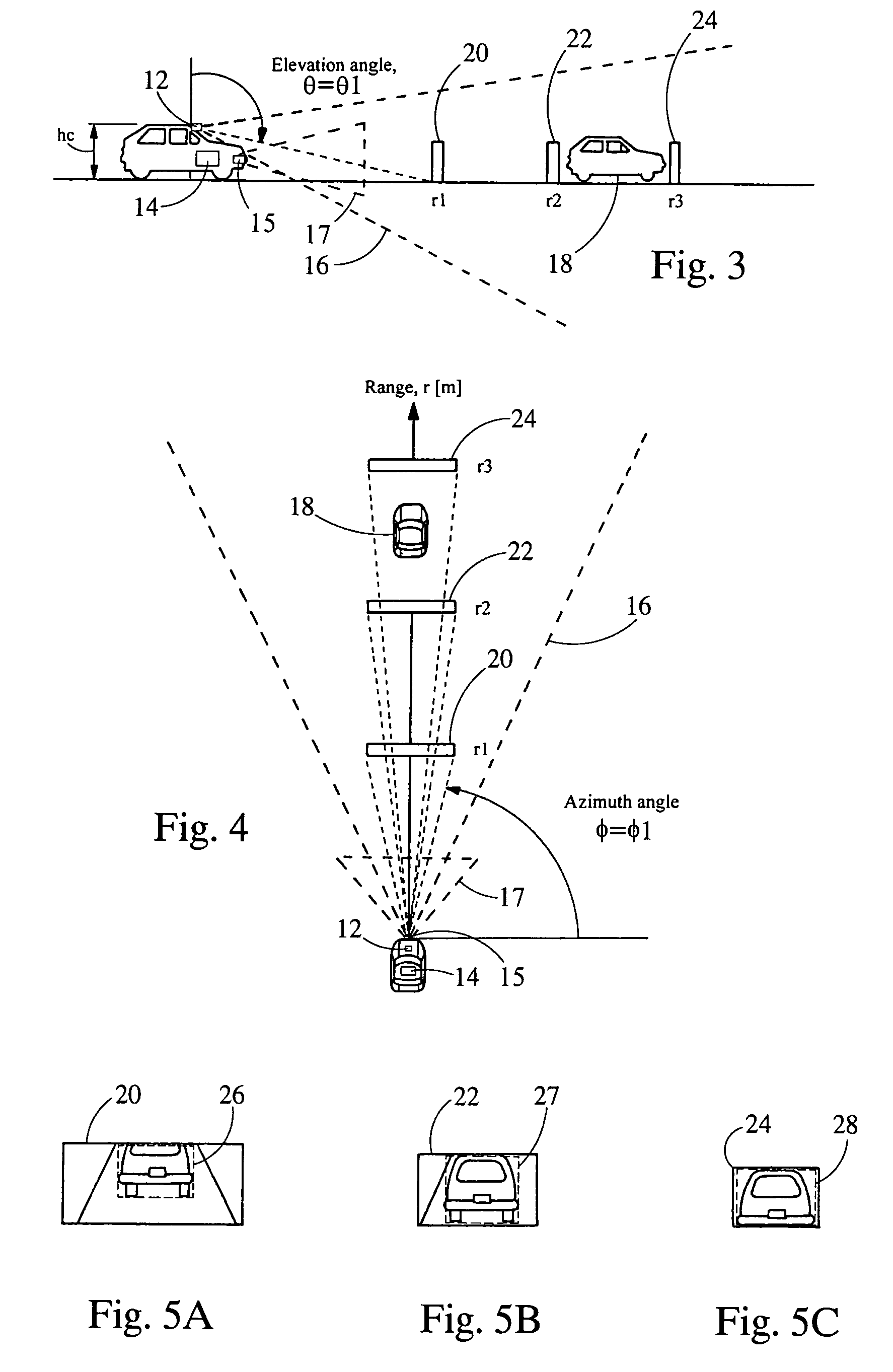
Single camera system and method for range and lateral position measurement of a preceding vehicle
A system for determining range and lateral position of a vehicle is provided. The system includes a camera, a sonar and a processor. The camera is configured to view a long range region of interest and generate an electrical image of the region. The sonar is configured to view a short range region of interest an output a sonar signal. The processor is in electrical communication with the camera and the sonar to receive the electrical image and the sonar signal. The processor analyzes the image and the sonar signal in order to determine the range of an object.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
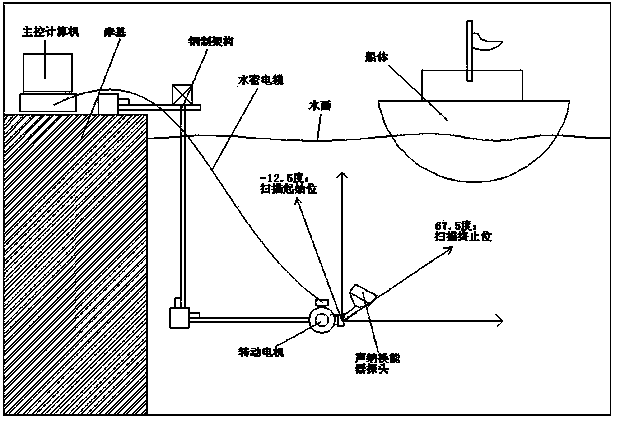
Automatic ship draught detection system based on multi-beam side-scan sonar technology
ActiveCN103675823AThe measurement process is simple and efficientHigh measurement accuracyVessel stability improvementMovement controllersDigital signal processingComputer module
The invention relates to an automatic ship draught detection system based on the multi-beam side-scan sonar technology. The automatic ship draught detection system comprises an underwater sonar scanning subsystem, a sonar signal processing subsystem and a master control subsystem. The underwater sonar scanning subsystem comprises a sonar transducer and a rotating motor, wherein the sonar transducer is provided with a 360-degree rotating shaft, and the rotating motor is used for driving the sonar transducer to rotate. The sonar signal processing subsystem comprises a watertight electronic cabin and a digital signal processing module located in the watertight electronic cabin, and data and command transmission between the sonar signal processing subsystem and the master control subsystem is carried out through a watertight cable. The rotating motor of the underwater sonar scanning subsystem is fixed in the watertight electronic cabin and connected with the digital signal processing module. The master control subsystem comprises a master control computer and a power supply unit, and display and control software of the automatic ship draught detection system operates on the master control computer. The automatic ship draught detection system has the advantages of being small in investment, easy to install and maintain and high in measuring accuracy, and the measurement process is convenient and fast to carry out and efficient.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
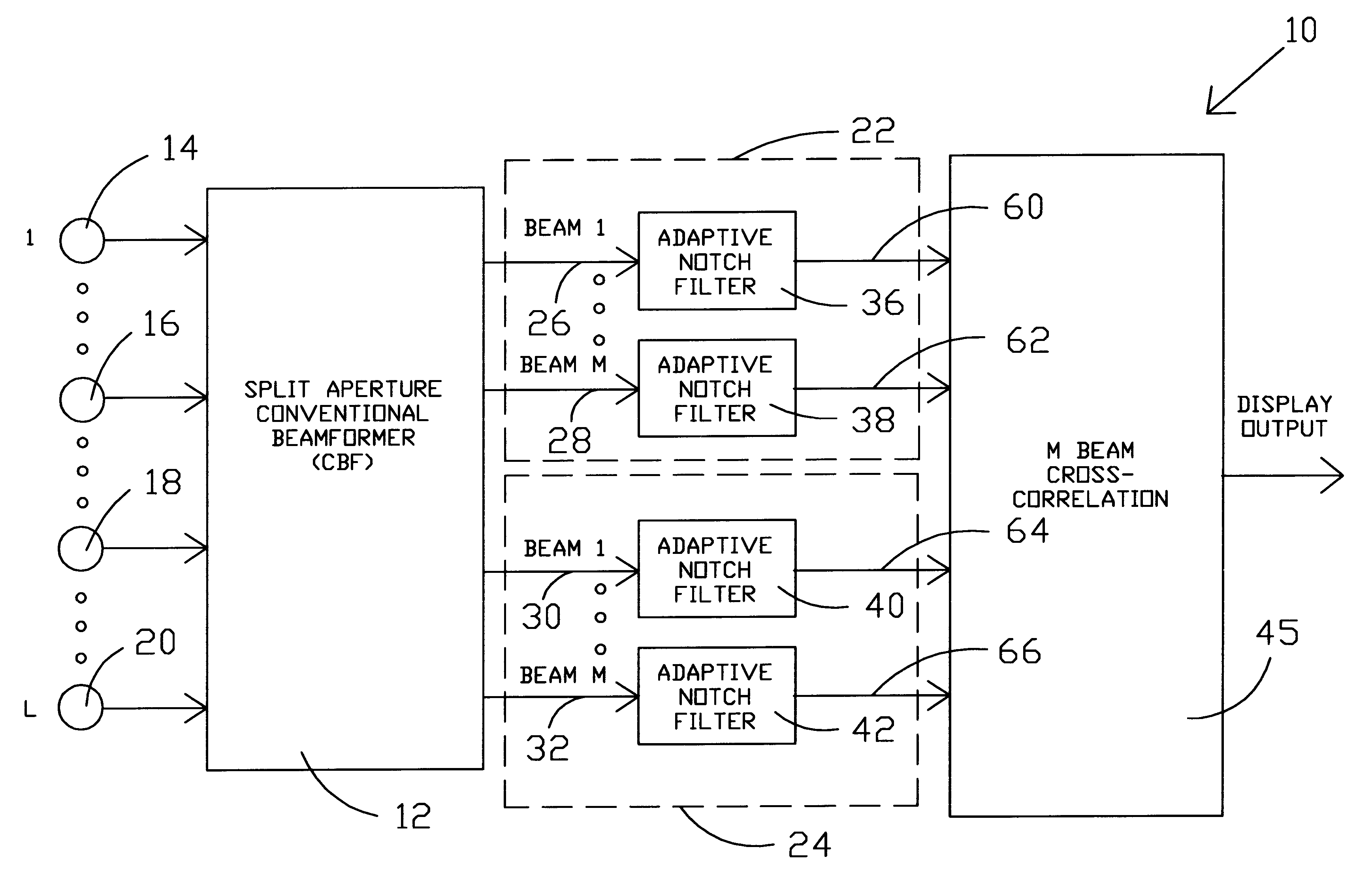
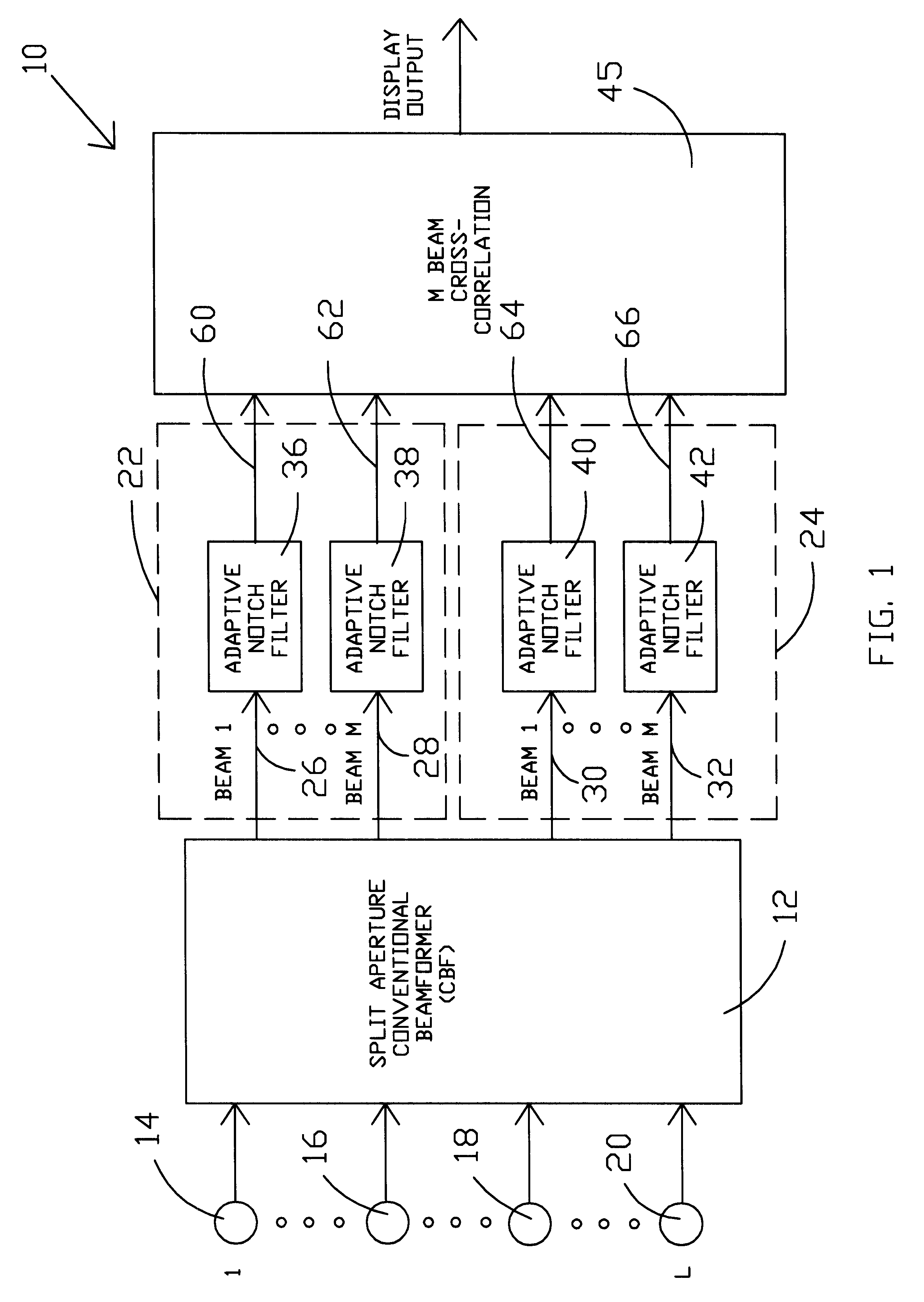
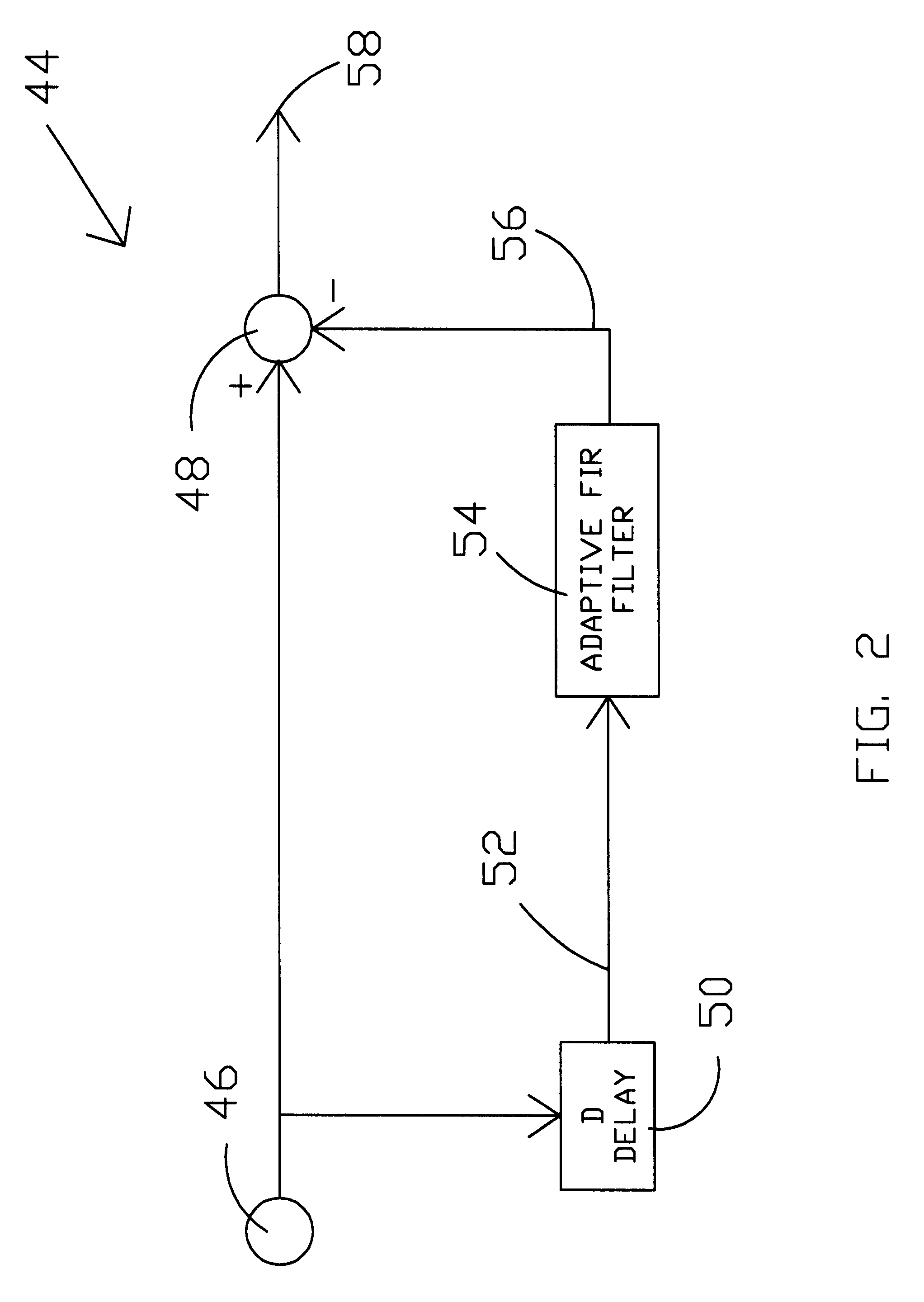
Adaptive cross correlator
InactiveUS6590833B1Direction/deviation determination systemsAcoustic wave reradiationFinite impulse responseSonar signal processing
A system and method are provided for an adaptive filter that is especially useful for sonar signal processing. The beam outputs of a conventional beamformer are provided as inputs to adaptive notch filters in accord with the present invention. The outputs of the plurality of adaptive notch filters are applied to a standard cross correlation process. In each of the adaptive notch filters, the beam outputs are split into two paths and in one path are applied directly to a signal combiner. In the second path, the beam outputs are delayed. The delayed beam outputs are applied to an adaptive finite impulse response filter, the output of which is an estimate of the narrowband interference contained within the beam output. The narrowband interference is then suppressed in the signal combiner prior to application to the standard cross correlation process.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
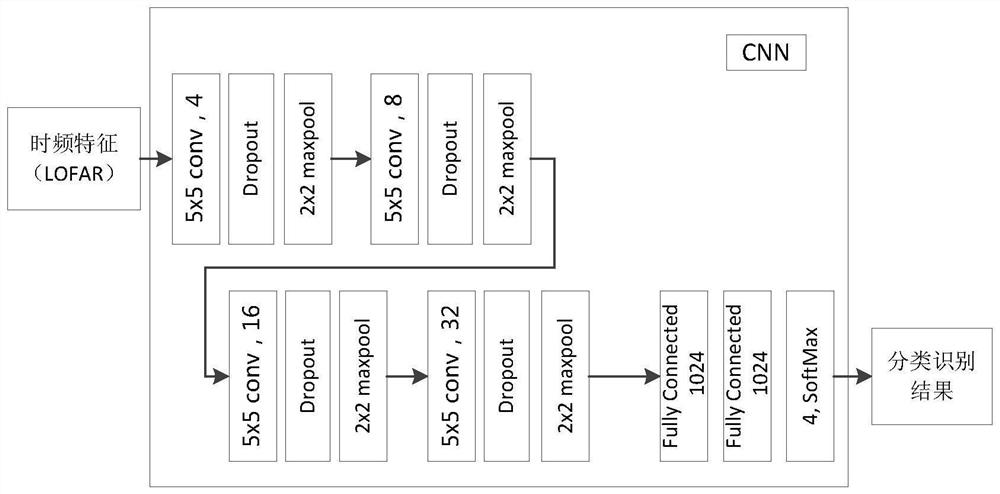
Underwater acoustic target recognition method based on signal processing and deep-shallow network multi-model fusion
ActiveCN112364779ATo achieve the purpose of classification and identificationHigh degree of automationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAlgorithmTarget signal
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic target recognition method based on signal processing and deep-shallow network multi-model fusion, and belongs to the technical field of underwater acoustic target passive reconnaissance. According to the method, target signal data acquired by a passive reconnaissance array are preprocessed by using a signal processing method, interference is filteredout, target features are extracted, then a multi-model recognition architecture is constructed by using a convolutional neural network and a residual network, and finally a voting decision mechanism is introduced to realize classification and recognition of maneuvering targets in water. Sonar signal processing is used as preprocessing to solve the problem that clean samples are difficult to obtainunder complex sea conditions; multi-dimensional features are adopted as training samples to improve adaptive capacity and recognition accuracy under different sea conditions and working conditions; the recognition accuracy and robustness of the method are improved based on fusion recognition of a multi-neural-network model.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Automatic detection system of ship draught depth based on single-beam sonar array scanning technique
InactiveCN103661836AThe measurement process is simple and efficientHigh measurement accuracyVessel stability improvementMovement controllersSoftware systemShore
The invention relates to an automatic detection system of a ship draught depth based on the single-beam sonar array scanning technique. The automatic detection system comprises a single-beam sonar primitive array, a sonar signal processor and a back stage master control system. The single-beam sonar primitive array is installed on an approach channel cross section so as to form a draught depth detection door device. The single-beam sonar primitive array is a combination of a set of single-beam transducers. The sonar signal processor is used for performing sequence collecting, signal amplifying, filtering, analog-digital conversion and DSP processing on all the transducers, and a formed digital signal is transmitted to the back stage master control system through the RS485 protocol. The single-beam sonar primitive array is connected with the sonar signal processor arranged on the shore through a watertight cable. The back stage master control system comprises a master control computer and a power supply unit. An upper computer software system is operated on the master control computer. The automatic detection system of the ship draught depth based on the single-beam sonar array scanning technique has the advantages of being small in investment, easy to install and maintain, simple, fast and efficient in measuring process and high in measuring precision.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
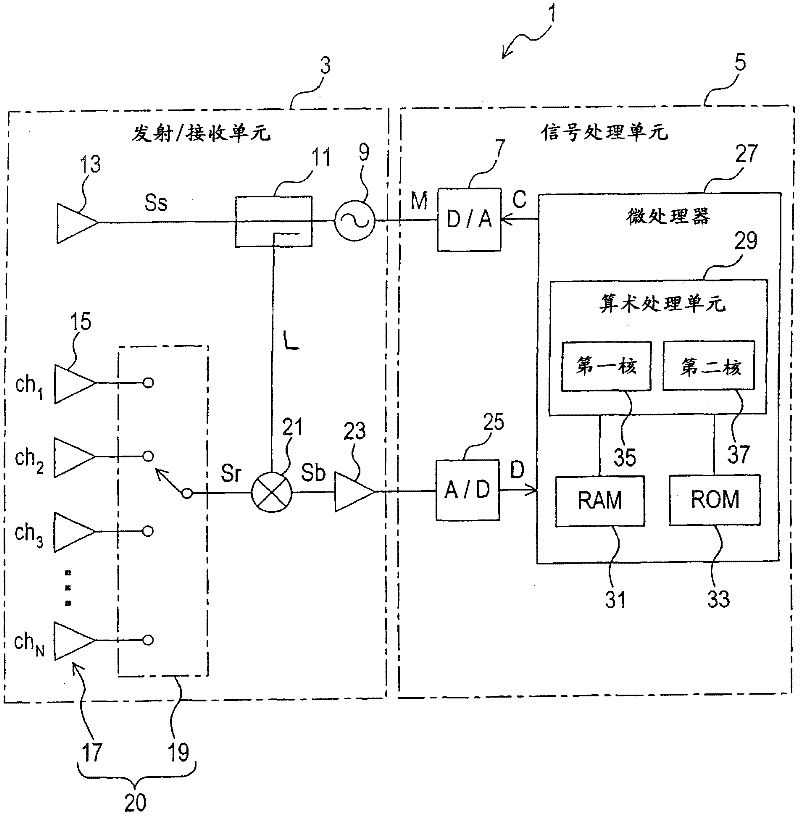
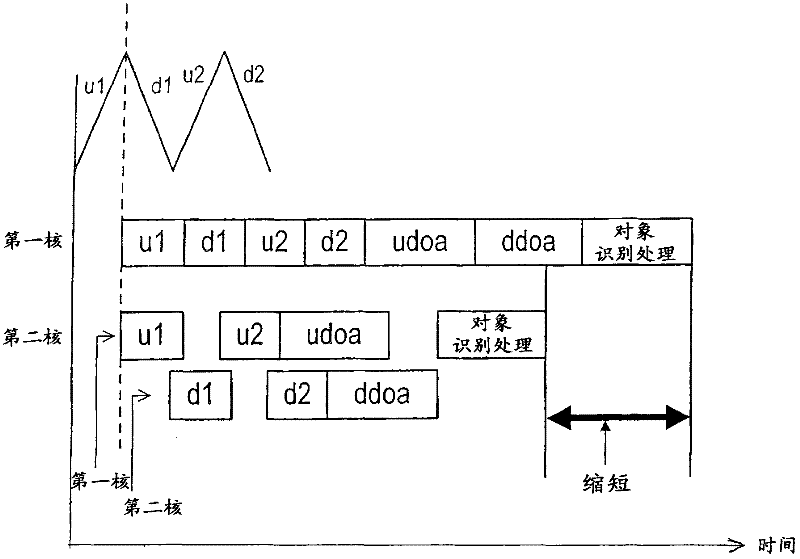
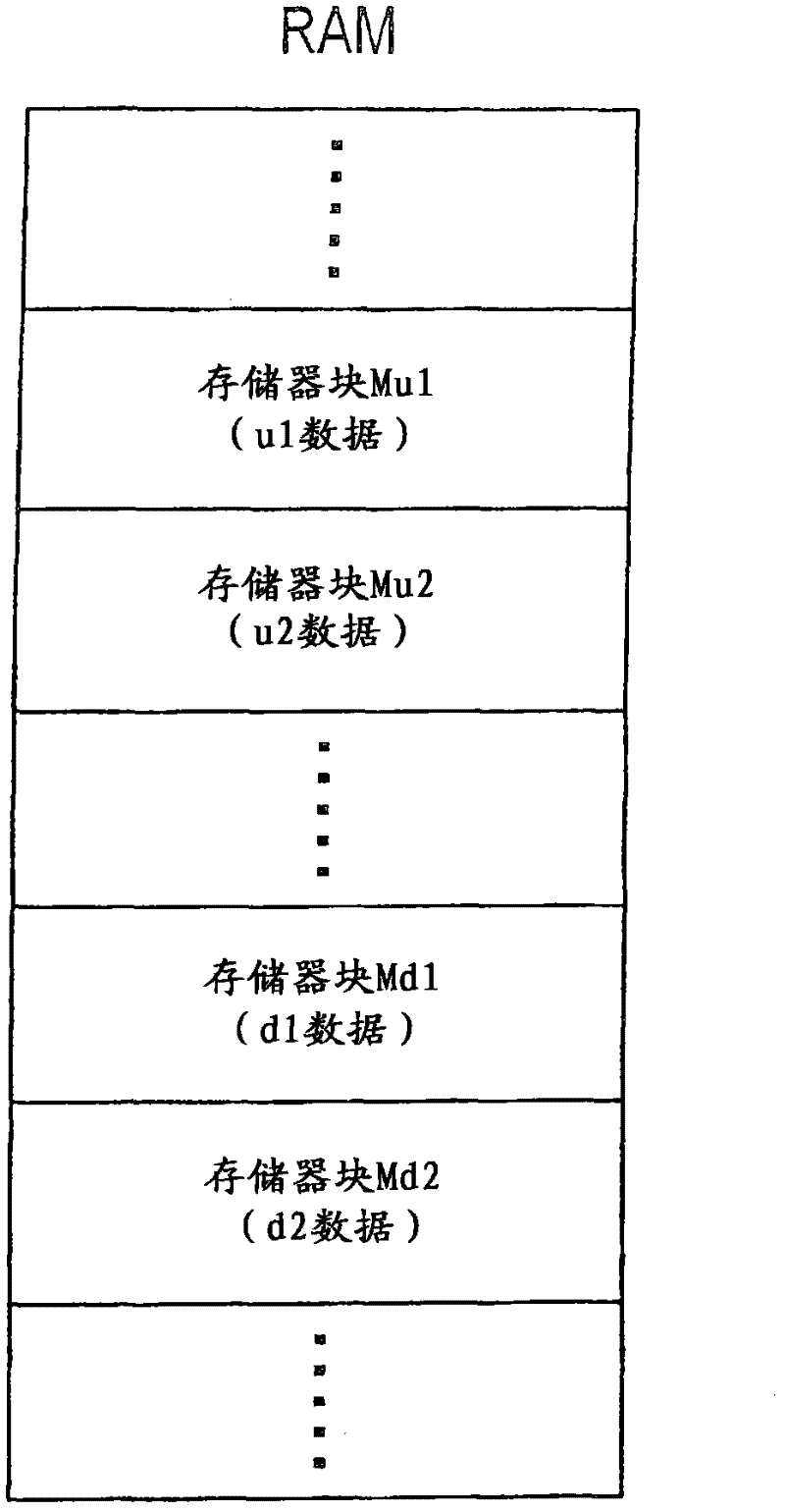
Fmcw radar apparatus having a plurality of processor cores used for signal processing
InactiveCN102540190AMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionObject basedRadar
The invention provides a FMCW radar apparatus having a plurality of processor cores used for signal processing. The FMCW radar apparatus obtaining information about a target object includes: a transmitter generating a transmission signal of which frequency is modulated based on the FMCW method, the receiver receiving the radar waves reflected at the object, a mixer that generates a beat signal from a mixed signal of the received signal and the transmission signal, and a signal processing unit processing the beat signal to obtain the information including a distance between the own vehicle and the target object, and a relative velocity of the target object. The signal processing unit includes first calculating means and second calculating means, which operate in parallel each other to calculate the information about the object based on the beat signal from an upward-modulation period when the frequency is modulated to be increased and from a downward-modulation period when the frequency is modulated to be decreased respectively.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Sonar systems and methods using interferometry and/or beamforming for 3D imaging
Provided are a sonar system, transducer assembly, and method for imaging an underwater environment. The sonar system may include a housing having a transducer array defining first and second rows of transducer elements positioned at a predetermined distance. The first row of transducer elements may include at least first and second transducer elements configured to convert sound energy into first and second sonar return data. The second row of transducer elements may include at least third and fourth transducer elements configured to convert sound energy into third and fourth sonar return data. A sonar signal processor may be configured to process the first and second sonar return data and third and fourth sonar return data to generate respective first and second array sonar return data corresponding to a plurality of first and second receive beams and generate 3D sonar return data by correlating the angles associated with the receive beams.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
Systems and associated methods for producing a 3D sonar image
Provided are a sonar system and transducer assembly for producing a 3D image of an underwater environment. The sonar system may include a housing mountable to a watercraft having at least one transducer array. The transducer array may include a transmit / receive element configured to transmit sonar pulses and a second transducer element. The transmit / receive element and the second transducer element may receive first and second sonar returns convert the first and second returns into first and second sonar return data. A sonar signal processor may then generate a 3D mesh data using the first and second sonar return data and at least a predetermined distance between the transducer elements. An associated method of using the sonar system is also provided.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
Passive target tracking method based on interactive multiple model(s)
ActiveCN109188443ASolve association problemsSolve multi-objective intersection problemsAcoustic wave reradiationModel methodSonar signal processing
The present invention discloses a passive target tracking method based on interactive multiple model(s), pertaining to the technical field of passive sonar signal processing and passive target tracking. The problems of tracking loss and false tracking are prone to occur in tracking due to false alarm and multi-target crossing, and the tracking method based on a target motion model involves the linear solution of nonlinear equation(s), so that the difficulty is relatively high. The algorithm can realize data association in the tracking by using the interactive multiple model method, all the models do not involve the nonlinear equation(s), the problem of measurement loss is solved by using a prediction method, and thus the purpose of track maintenance in the tracking is realized. The algorithm can be applied to the single-array bearing-only passive target tracking and is not constrained by scanning beams and the detection method, the real-time tracking can be performed, and thus the method has relatively extensive adaptation.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
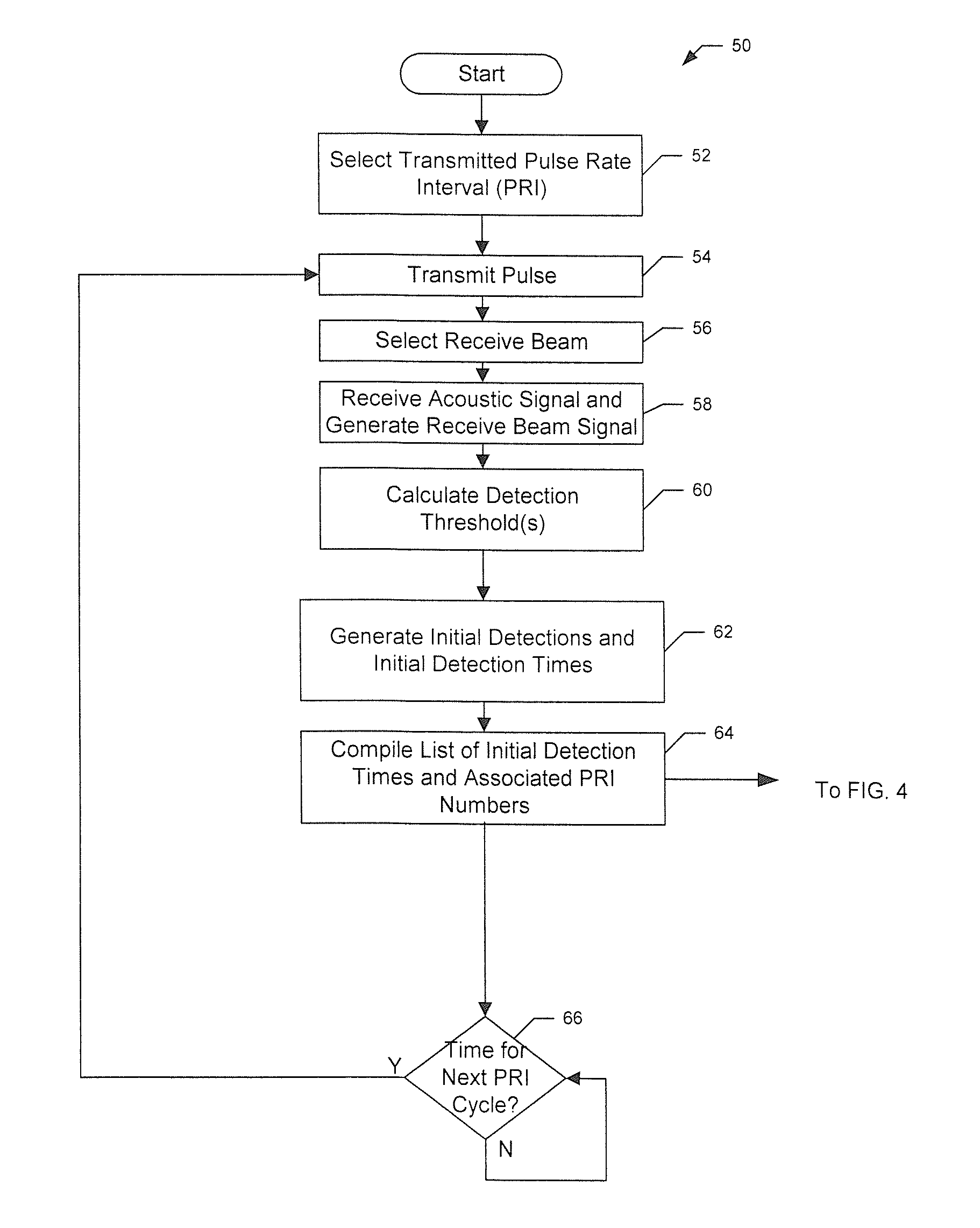
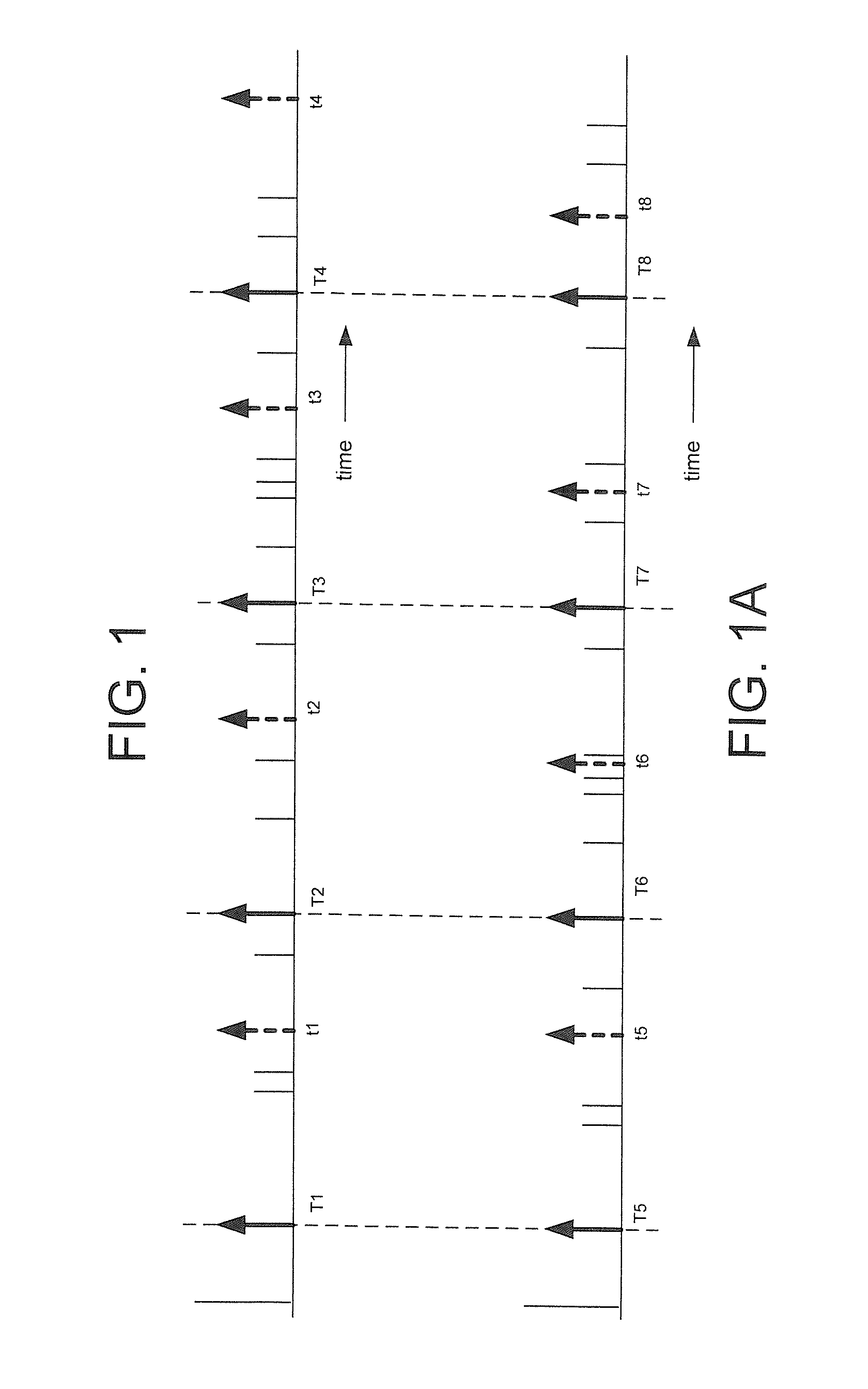
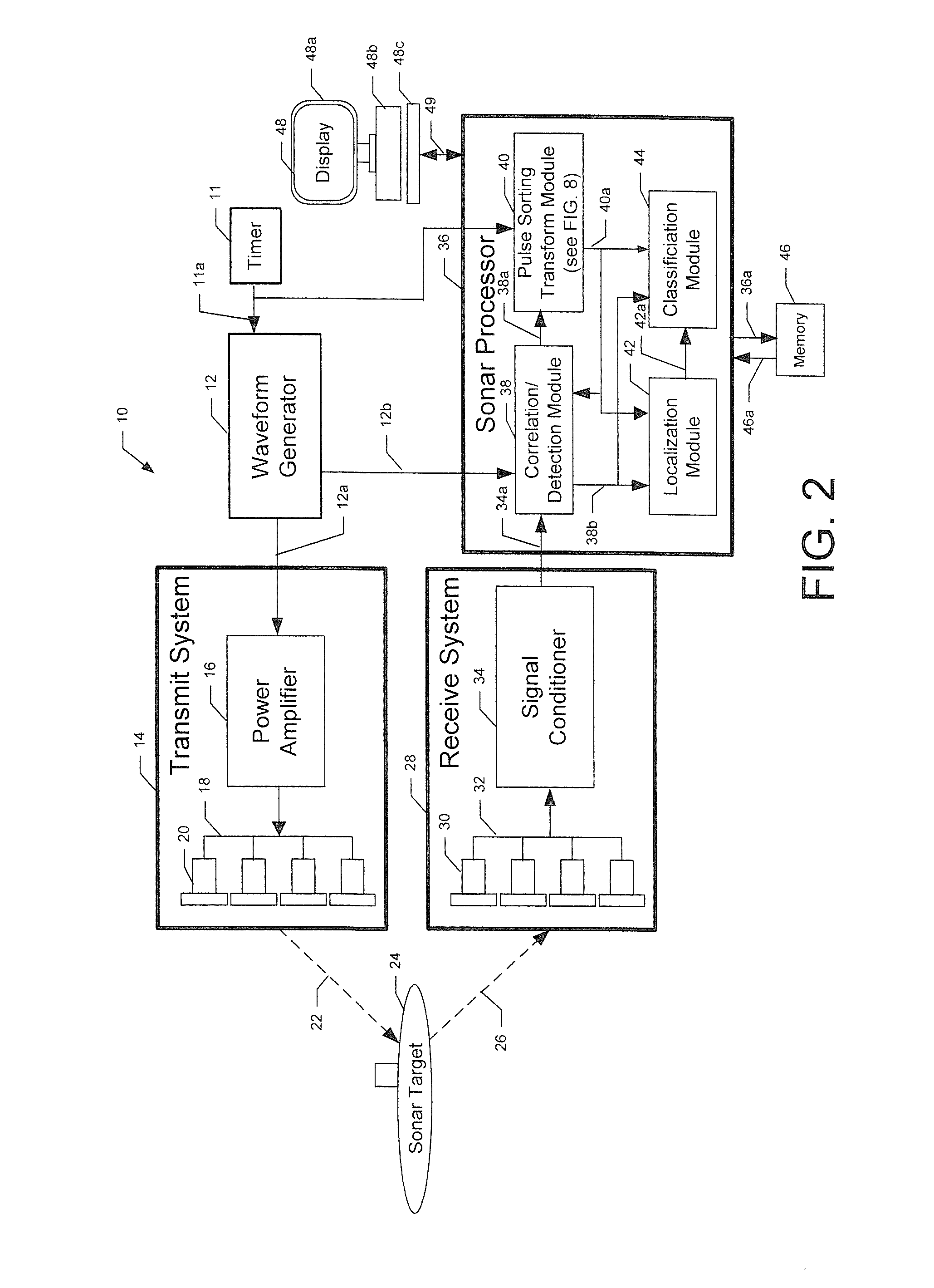
Active sonar system and active sonar method using a pulse sorting transform
ActiveUS20110242939A1Easy to detectPromote localizationAcoustic wave reradiationSound productionSonar signal processing
An active sonar system, a method associated therewith, and a computer-readable medium associate therewith, each provide a method of sonar signal processing. The method includes receiving a plurality of initial detections of a target and associated initial detection times, associated with sound transmitted at a pulse rate interval (PRI), and associated with received sound including echoes from a target. The echoes result from the transmitted sound. The method also includes analyzing the plurality of initial detection times with a pulse sorting transform configured to identify periodic PST detection times within the plurality of initial detection times that are equally spaced in time and that are representative of the echoes from the target.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
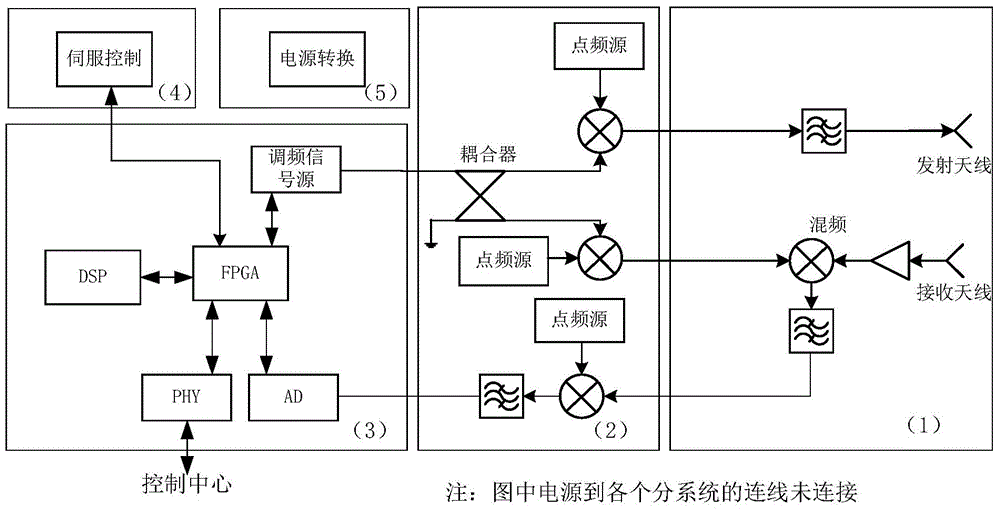
Scene foreign matter detecting system based on millimeter wave radar
InactiveCN105204075AHigh range resolutionLittle influence of weather factorsDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionForeign matterIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a scene foreign matter detecting system based on a millimeter wave radar. A millimeter wave integration receiving and transmitting subsystem is used for receiving a linear frequency modulation signal sent by an intermediate frequency subsystem and converting the linear frequency modulation signal into electromagnetic wavers for radiation; an echo signal is converted into an electric signal through the millimeter wave integration receiving and transmitting subsystem, and a first intermediate frequency signal is obtained after the echo signal and the linear frequency modulation signal are subjected to frequency mixing processing and is sent to the intermediate frequency subsystem; the intermediate frequency subsystem processes a source signal so that a needed linear frequency modulation signal can be obtained, and a second intermediate frequency signal is acquired after variable-frequency processing is performed on the first intermediate frequency signal and is input to a signal processing subsystem; the signal processing subsystem is used for performing signal processing on the second intermediate frequency signal so that the relative distance between foreign matter and the radar can be acquired; then the current antenna direction of the radar is acquired in real time through a servo subsystem; finally, the relation position between the foreign matter and the radar is acquired; the servo subsystem performs servo control for a rotating table where the radar is located. The system can emit a large-bandwidth signal and improve the range resolution.
Owner:北京理工雷科电子信息技术有限公司
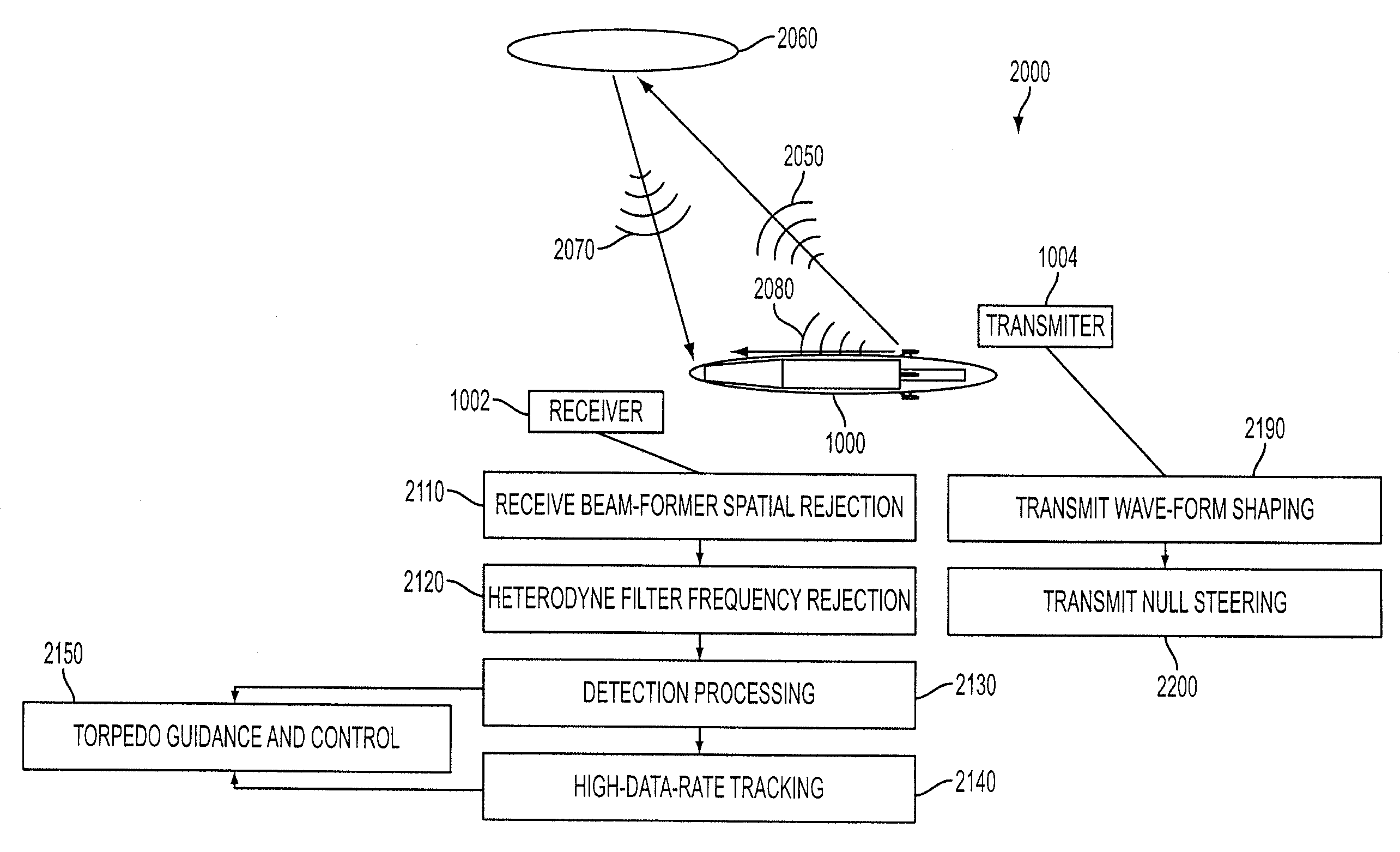
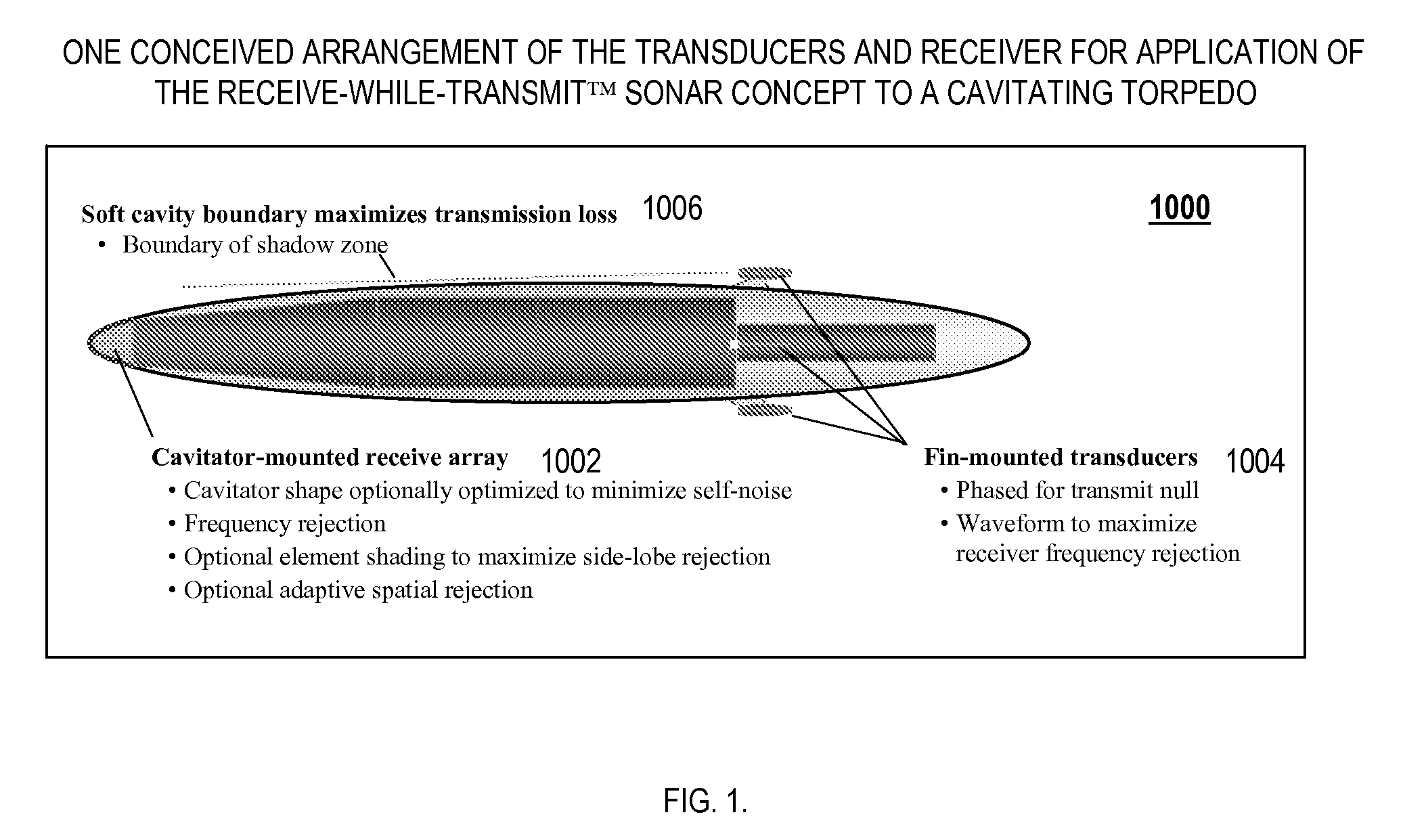
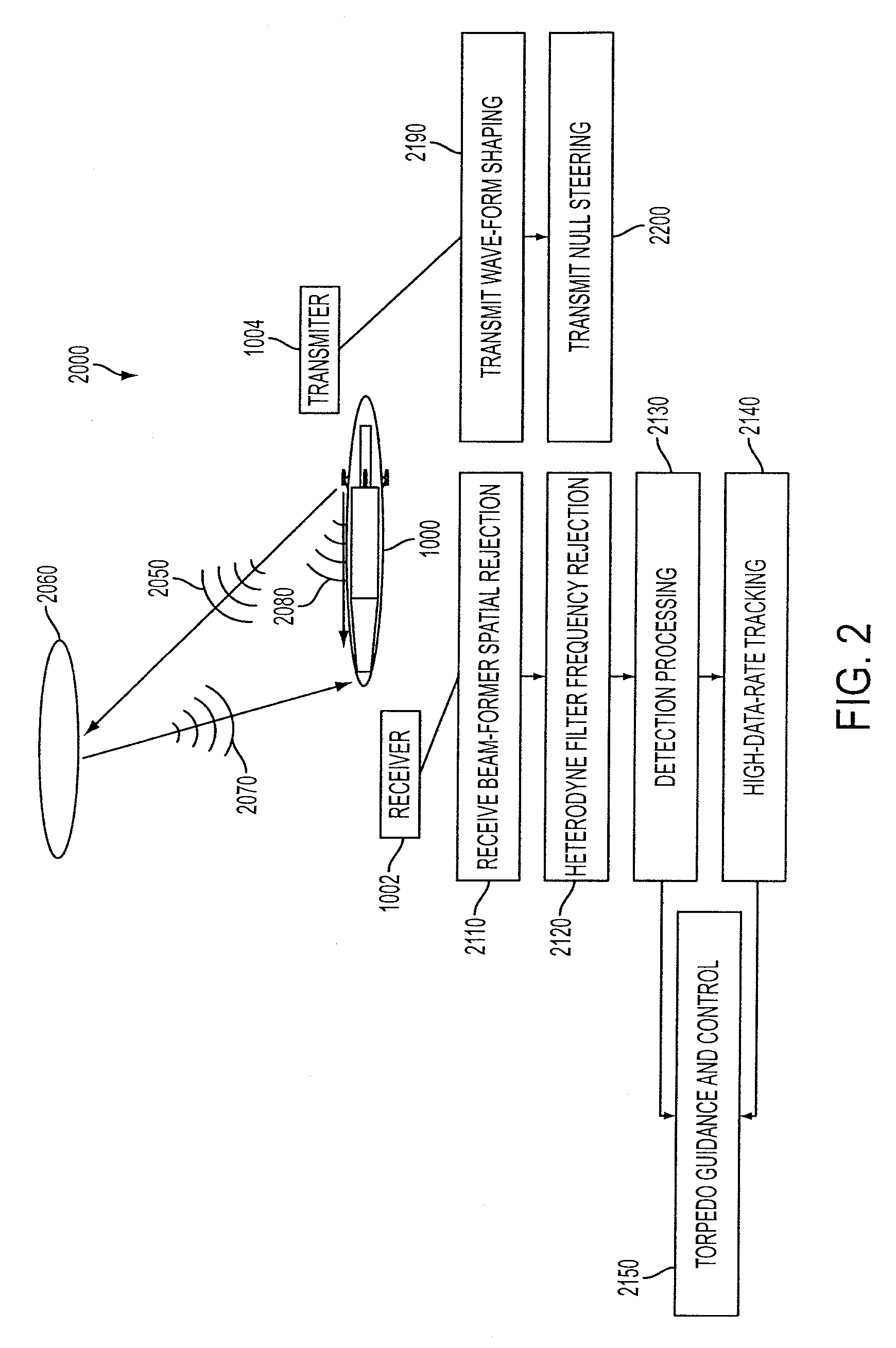
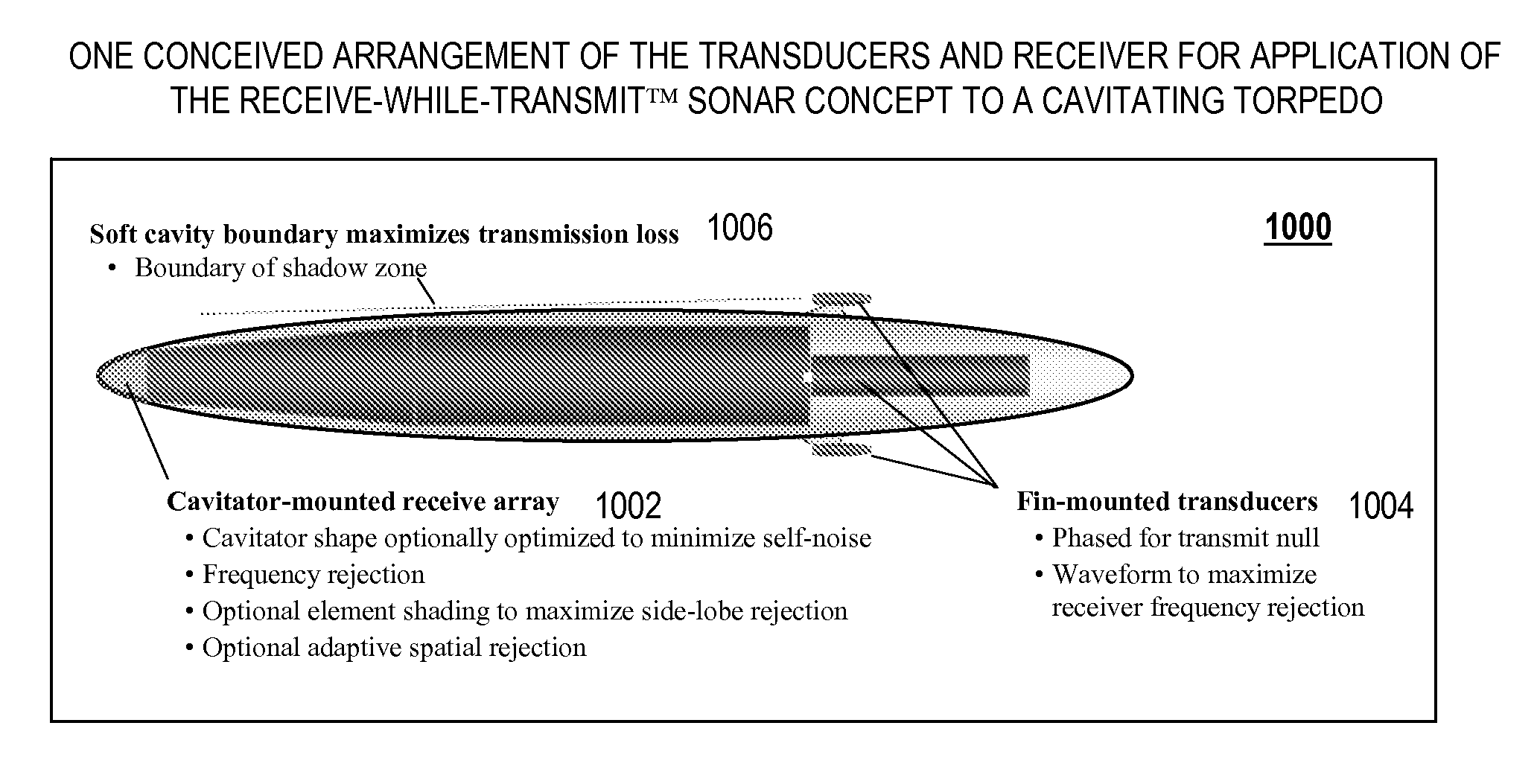
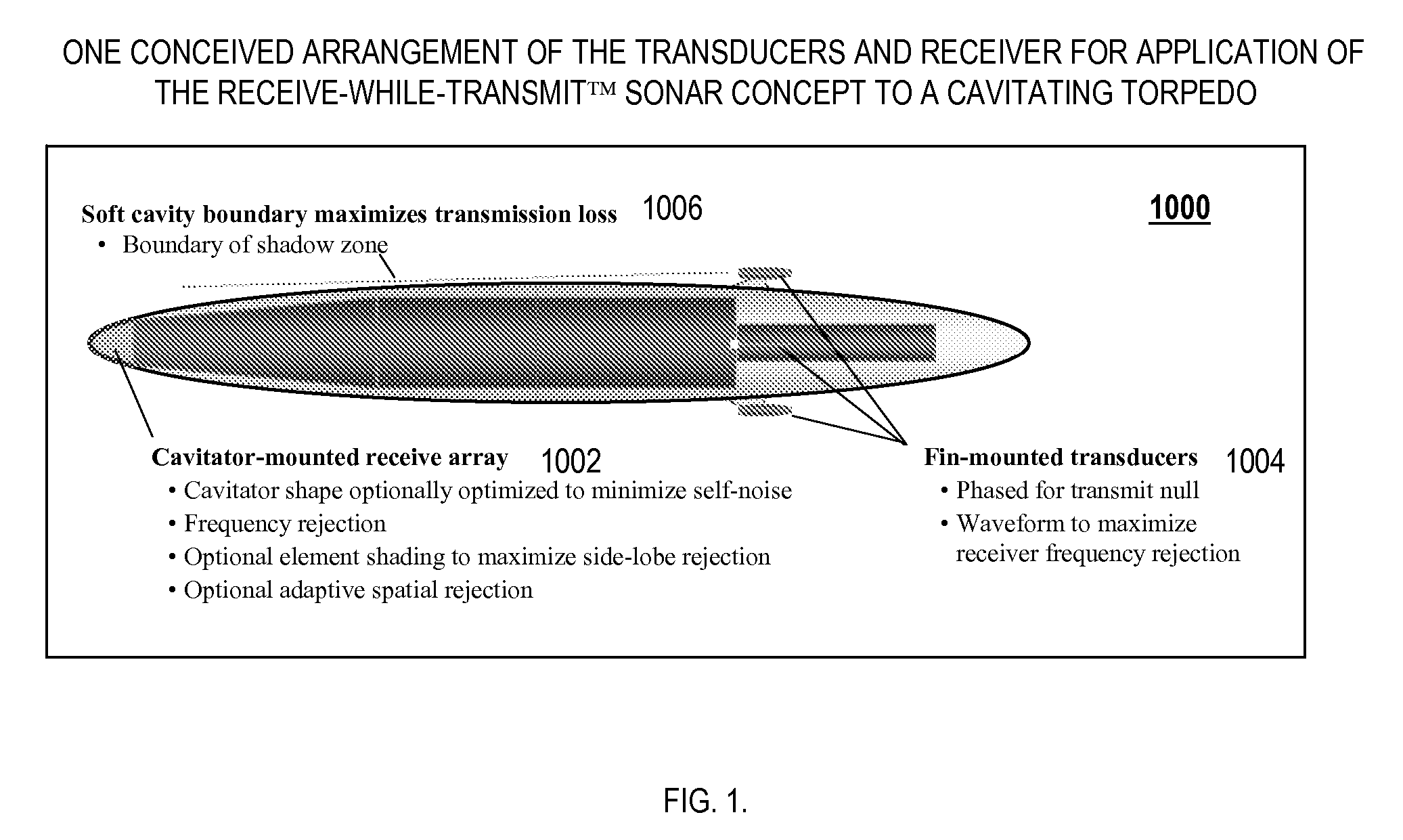
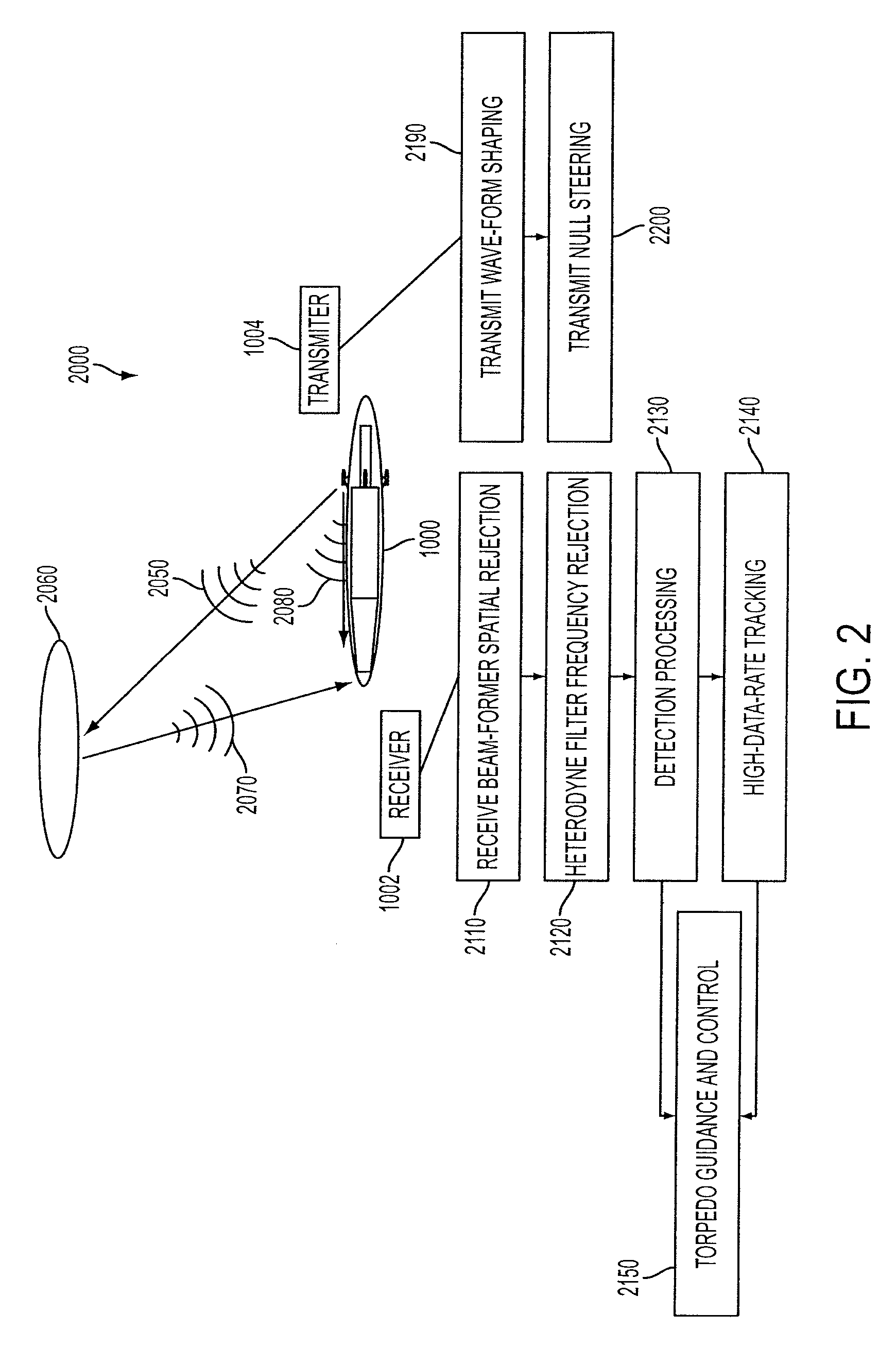
Cavitating Body Sonar System and Process
InactiveUS20080002526A1Improved sonar system performanceImprove performanceAcoustic wave reradiationTransducerWave form
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention may include a cavitating body sonar system and method. The method may include, in an exemplary embodiment: applying a receiving-while-transmitting sonar signal processing to at least one cavitating body, over an entire range of achievable sonar operating frequencies; applying transmit wave-form shaping to a RWT sonar system employed on the cavitating body; applying heterodyne filter frequency rejection to the RWT sonar system employed on the cavitating body; applying detection processing techniques to the RWT sonar system employed on the cavitating body; employing at least one transducer as an acoustical transmitter near a scattering body comprising the cavitating body, wherein the at least one transducer is strategically located with respect to said cavitating body, at least one target, and a receiver, wherein the receiver lies in a shadow zone of the body, but the at least one target does not; and, employing at least one transducer as an acoustical transmitter near a scattering body comprising the cavitating body, wherein the at least one transducer is strategically located with respect to a cavity, at least one target, and a receiver, wherein direct propagation of a transmitted signal along the outside of the cavity to the receiver is inhibited, and reflected propagation from the acoustical transmitter to the target and thence reflected to the receiver is not inhibited.
Owner:GEN DYNAMICS INFORMATION TECH
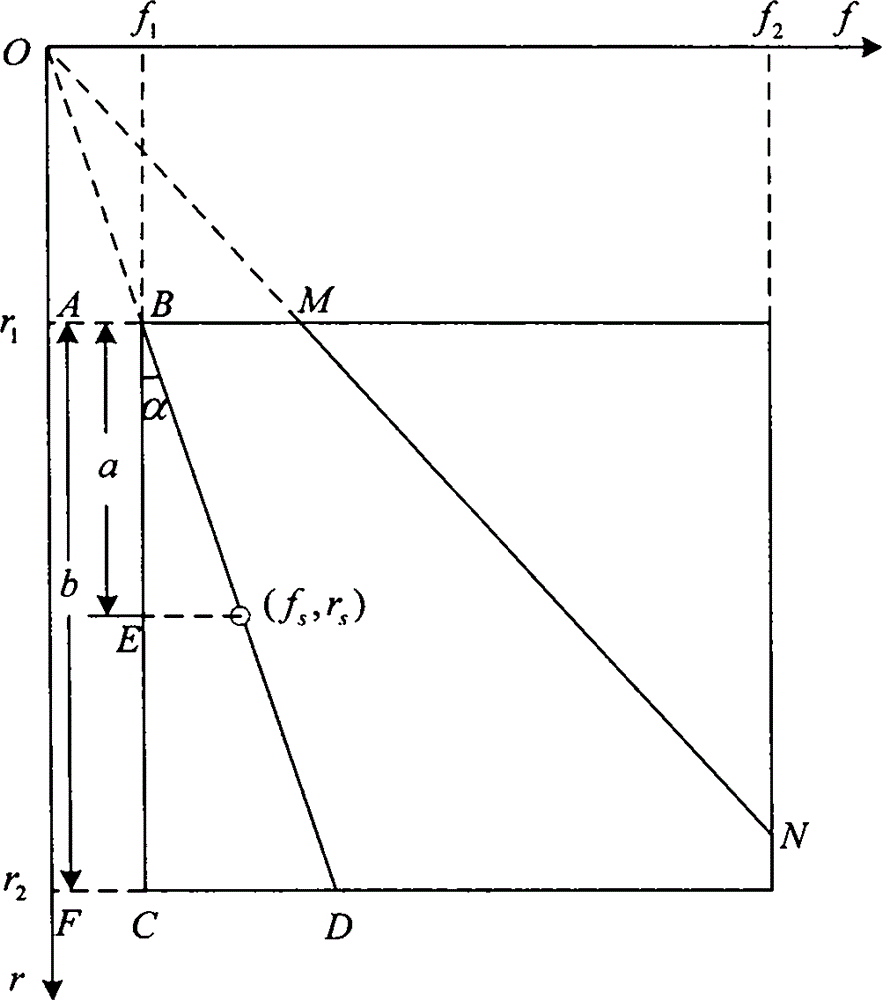
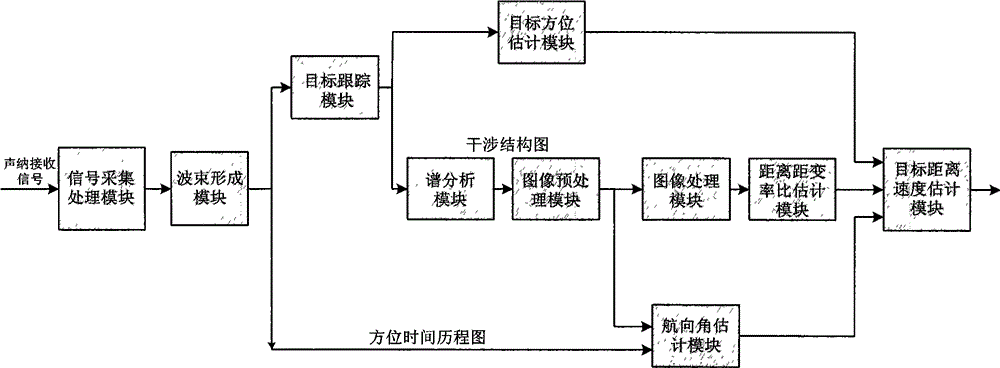
Single horizontal array passive speed measurement and distance measurement device based on sound field interference fringe and method
The present invention relates to a single horizontal array passive speed measurement and distance measurement method based on sound field interference fringe, belonging to the field of underwater acoustic engineering and sonar signal processing. The method comprises a step of carrying out condition processing and collection on the signal received by each array element of a sonar, a step of carrying out beam formation on the collected signals and obtaining an azimuth time journey map after accumulation, a step of tracking an interested object, taking a tracking beam as object azimuth estimation, carrying out short-time Fourier transform spectrum analysis on the output of the tracking beam, obtaining the interference structural map of the interested object, selecting two equal time intervals of a single horizontal array in a motion process, forming interference structural maps, carrying out preprocessing and Radon transform on the two interference structural maps, and estimating an object heading angle with the combination of the waveguide invariant theory, and a step of realizing the estimation of the distance and speed of the interested object. According to the method, the physical nature of an underwater sound field is fully dug, the prior knowledge of a marine environment is not needed, the algorithm is simple and easy and is convenient and flexible to use, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:中国人民解放军92232部队
Multiple beam section sonar signal processing device
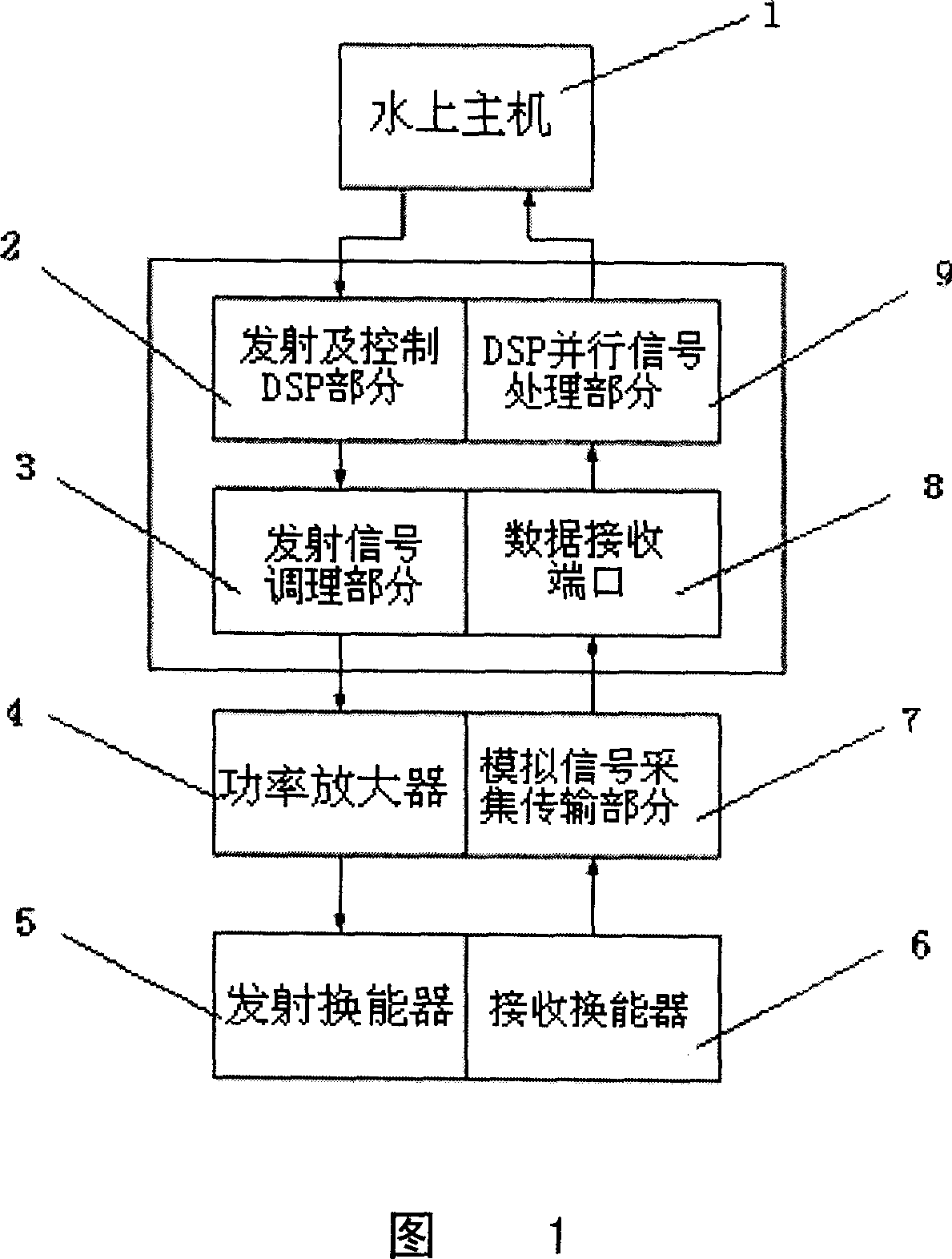
InactiveCN101055311ASmall sizeReduce weightSpecial data processing applicationsAcoustic wave reradiationLine tubingSignal conditioning
The invention relates to a multi-beam profile sonar signal processing device, characterized in comprising a host computer above water, an emission and control DSP part disposed on the underwater robot, an emission signal conditioning part, a power amplifier, an emission transducer, a, an analog signal acquisition transmitting part, a data receiving port and a DSP parallel signal processing part. The emission and control DSP part connected with the water host computer by cable receives command of water host computer, the emission signal conditioning part amplifies, filters and isolates the analog signal produced by the emission and control DSP part, and then amplified by the power amplifier, the emission transducer emits the signal underwater after electrical / mechanical conversion; the reception transducer receives the echo which is converted to digital signal by the analog signal acquisition transmitting part after performing mechanical / electrical conversion, and transmitted to the data reception port, then transmitted to the water host computer by cable after processing by the DSP parallel signal processing part. The invention can be applied widely in the process of detecting azimuth of undersea oil pipeline.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Systems and associated methods for producing a 3D sonar image
Provided are a sonar system and transducer assembly for producing a 3D image of an underwater environment. The sonar system may include a housing having a transmit transducer that may transmit sonar pulses into the water. The system may include at least one sidescan transducer array in the housing that receives first and second sonar returns with first and second transducer elements and converts the first and second returns into first and second sonar return data. The first sidescan element may also transmit second sonar pulses, and at least one of the sidescan elements may receive the second sonar pulses to generate sidescan sonar return data. A sonar signal processor may then generate a 3D mesh data and sidescan image data and generate a 3D image data based on the 3D mesh data and sidescan image data. An associated method of using the sonar system is also provided.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
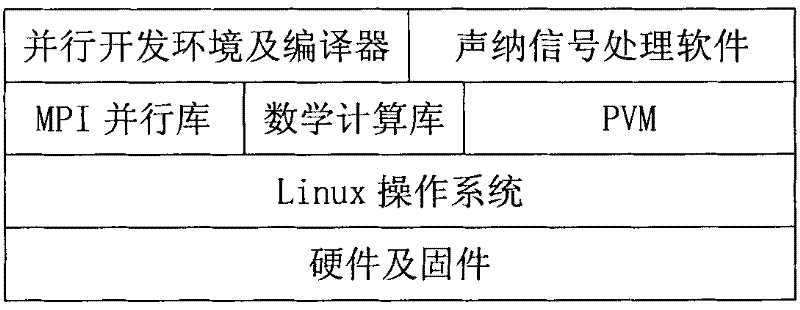
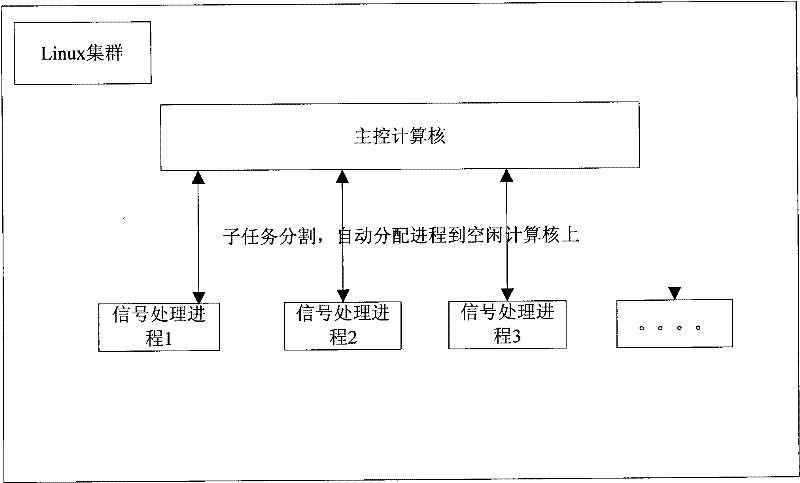
Method for implementing sonar real-time signal processing based on Linux group
ActiveCN102183759ALow costEasy to buildWave based measurement systemsMultiprogramming arrangementsOperational systemNetwork communication
The invention relates to a method for implementing sonar real-time signal processing based on a Linux group. In the method, two parts, namely a sonar base array signal real-time simulator and sonar real-time signal processing, are involved. By the method, a parallel processing design idea is introduced into the sonar signal processing, a signal processing task is divided into various independent sub tasks, allocation of hardware resources and data links are automatically realized by the Linux group, the various sub tasks are automatically allocated and run on various calculation cores, a datastream and a control stream are automatically realized by a network communication method, and human intervention is not required. The method has the advantages that: the Linux group is adopted in a signal processing hardware platform; as the Linux group is low in cost and easy in construction, the expandibility is higher and the calculation capability is strong. By adoption of a Linux operating system, a hardware platform and a software platform are separated and the signal processing programming is executed in a universal exploitation environment, so the difficulty of signal processing software is simplified. Due to adoption of a message passing interface (MPI) base for parallel program exploitation, the parallel calculation capability of the group is developed fully.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
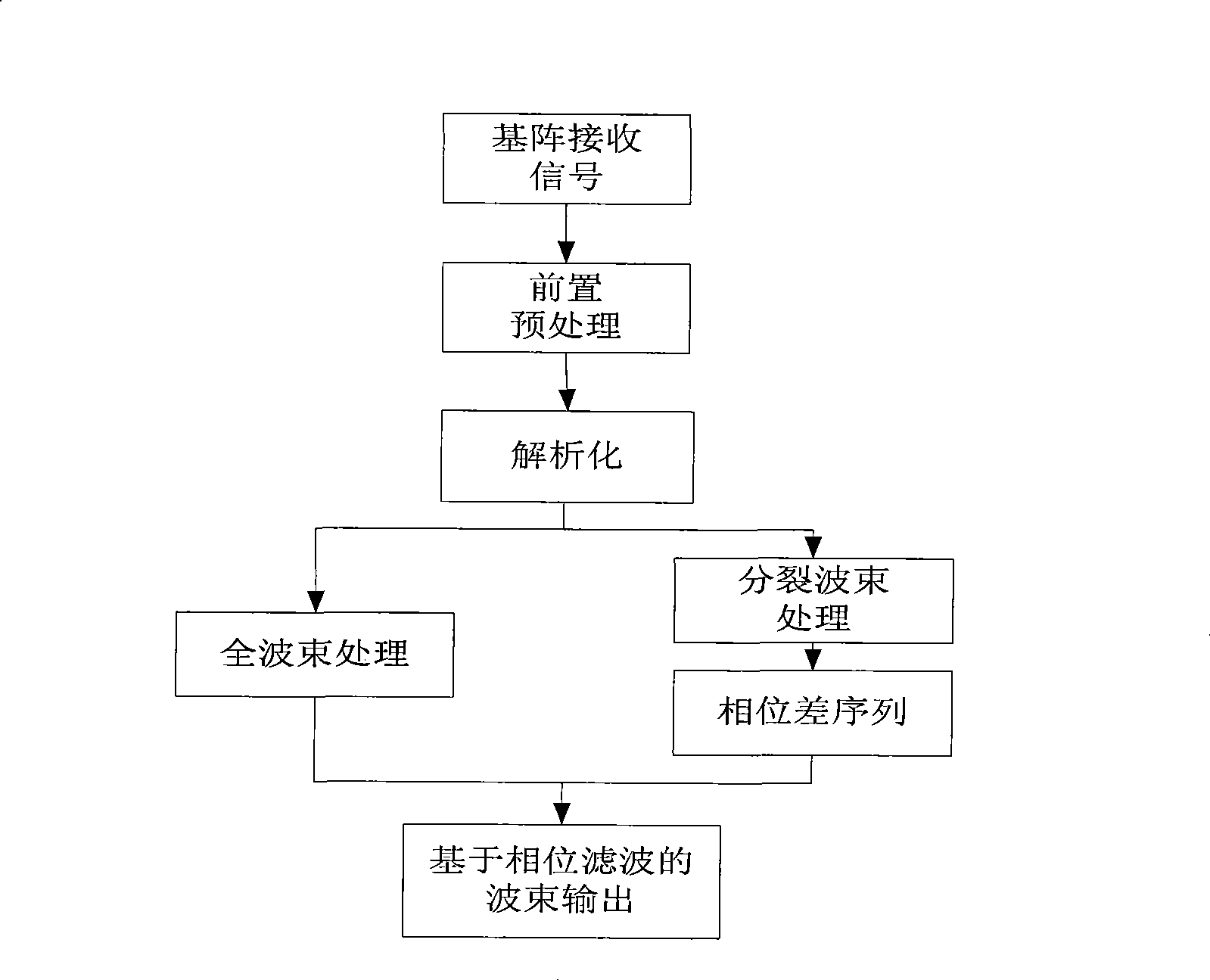
Phase filtering based beam forming method
ActiveCN101504458ASuppresses reverberant echo signalsCalculation method is simpleWave based measurement systemsFiltrationPhase difference
The invention relates to the field of sonar signal processing, in particular to a phase filtration-based beam forming method. In the method, the result of beam forming is subjected to phase filtration according to a phase difference sequence of split beams so as to form a phase filtration-based beam forming output. The novel phase filtration-based beam forming method provided by the invention has the advantages of making full use of phase information, narrowing the major lobes of beams, suppressing reverberation return signals in directions excluding the directions of the main axes of the beams as much as possible, improving the precision of the estimation of the time of arrival (TOA) of following waves, along with simple calculation method, small calculated amount and easy implementation.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Sonar transducer having geometric elements
ActiveUS20190265354A1Reduce detailsLimit resultSound producing devicesAcoustic wave reradiationTransducerLight beam
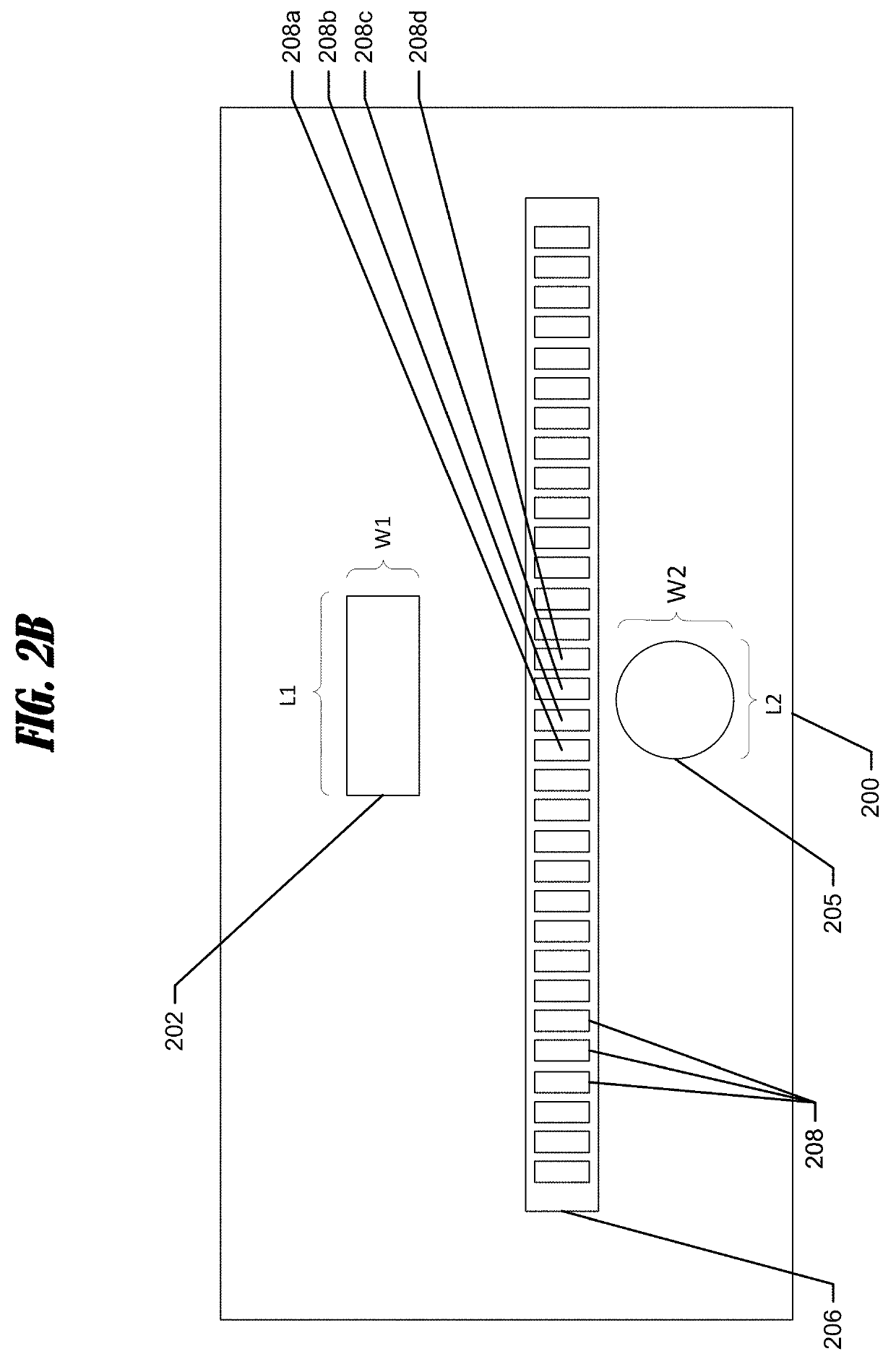
A system is provided for imaging an underwater environment. The system includes a transducer assembly with at least one transmit transducer element and an array of receive transducer elements. Each receive transducer element is configured to receive sonar returns and form sonar return data. A sonar signal processor is configured to receive the sonar return data from each receive transducer element and generate sonar image data. The sonar return data from all of the receive transducer elements may be summed and used to form a high-definition 1D (e.g., time-based) sonar image. The sonar return data from only a subgroup may be summed and used to form a lower-definition 1D sonar image. In some systems, an array of series-connected transmit transducer elements can be used. The orientation of the emitting faces of the array may vary slightly to mimic a curved surface for increased beam coverage.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
Systems and associated methods for producing a 3D sonar image
Provided are a sonar system and transducer assembly for producing a 3D image of an underwater environment. The sonar system may include a housing mountable to a watercraft having a transmit transducer that may transmit sonar pulses into the water. The system may include at least one sidescan transducer array in the housing that receives first and second sonar returns with first and second transducer elements and converts the first and second returns into first and second sonar return data. A sonar signal processor may then generate a 3D mesh data using the first and second sonar return data and at least a predetermined distance between the transducer elements. An associated method of using the sonar system is also provided.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
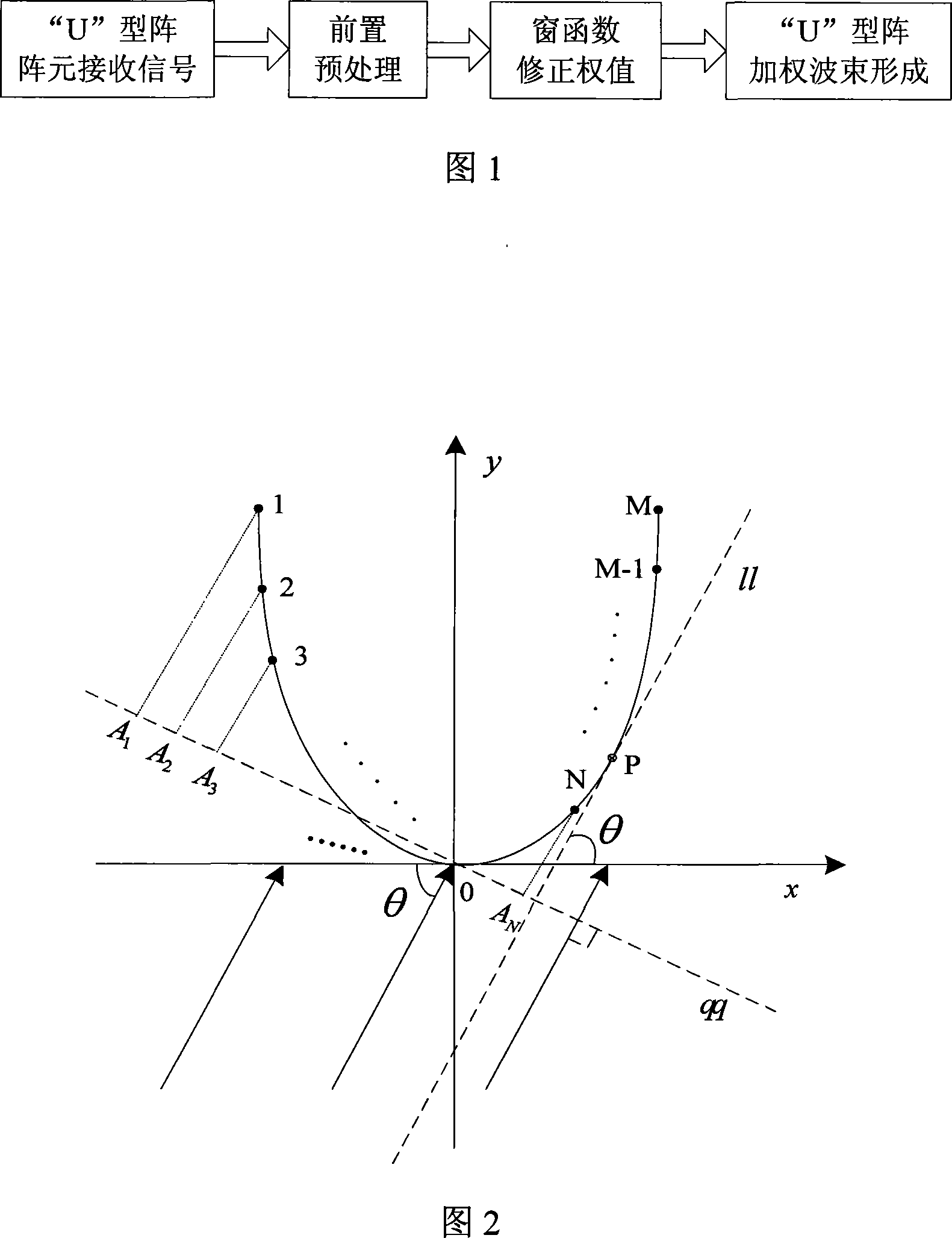
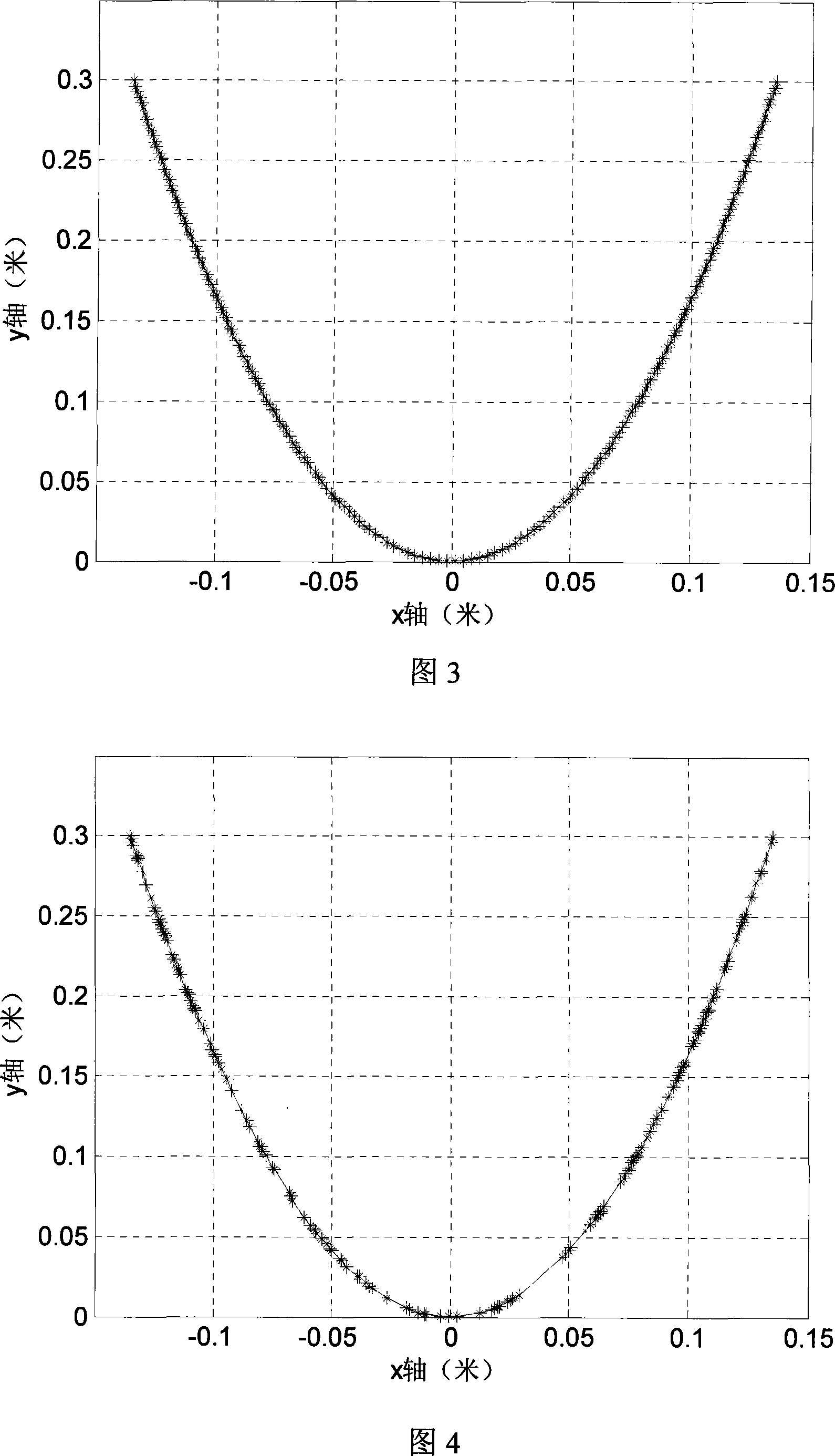
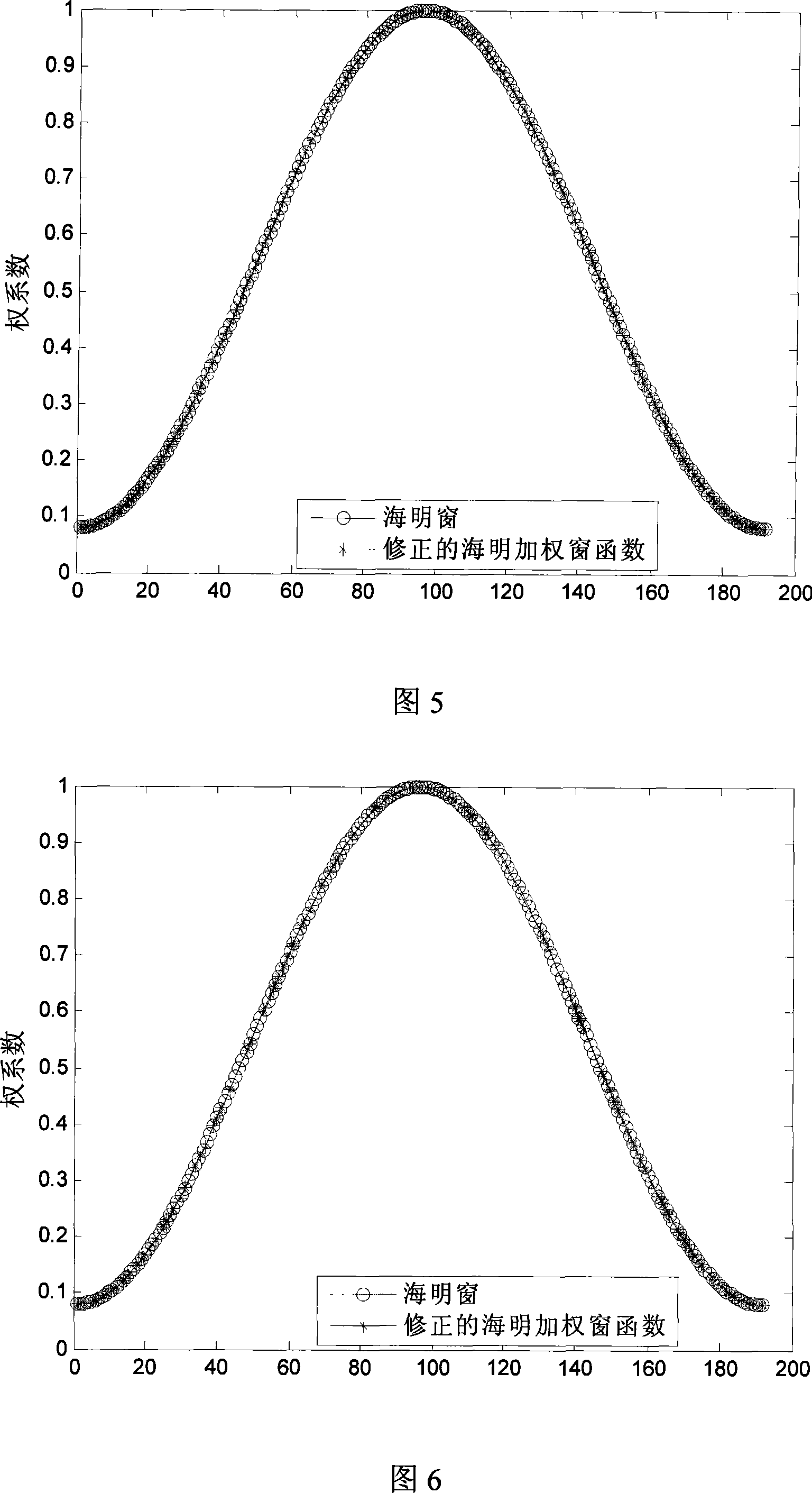
U-shaped array beam forming weighting method
ActiveCN101149435AEasy to implement forming weighting methodImprove performanceAcoustic wave reradiationSide lobeSonar signal processing
This invention relates to the sonar signal processor field, it is main a kind of U array wave-packet formation weighted method, confirms the interpolation point according to the projection coordinate ubiety of the U array component in the wave array surface direction which is upright with the wave-packet pre-produced direction, calculates the modified window function value matched the U array component location. This invention provides a new U array wave-packet formation weighted method, extends the window function weight based on uniform array to non-uniform array weight, restrains side-lobe effectively, and improves the ability of the array wave-packet formation.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
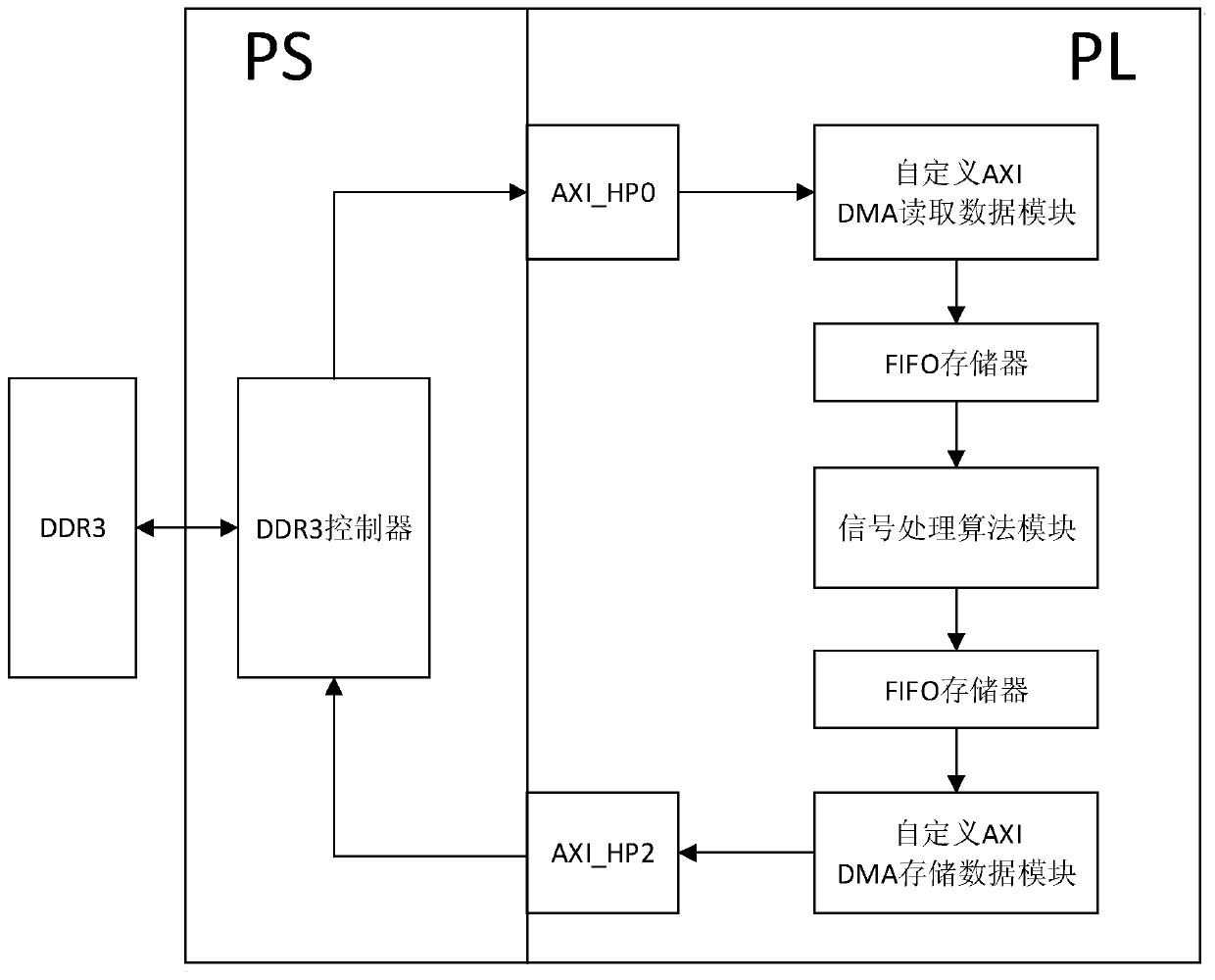
Side-scan sonar signal processing method based on ZYNQ
ActiveCN110244304AFast operationAcoustic wave reradiationQuadrature demodulationSonar signal processing
The invention discloses a side-scan sonar signal processing method based on ZYNQ. The method comprises the following steps of 1) reading AD original acquisition data in a DDR3 shared memory outside a PS end at a PL end by utilizing a FIFO memory, a self-defined DMA reading data module, EMIO and a logic unit of an AXI-HP interface; 2) carrying out digital quadrature demodulation, low-pass filtering downsampling and matched filtering processing on the AD original acquisition data in the step 1) by utilizing an FIR IP core, a Block RAM IP core, a multiplier IP core and a CORDIC IP core; and 3) storing a processing result in the step 2) into the DDR3 shared memory outside the PS end at the PL end by utilizing the FIFO memory, the self-defined DMA reading data module, a PL-PS interrupt and the logic unit of the AXI-HP interface. According to the method, the speed and precision of the side-scanning sonar signal processing can be effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Sonar signal processing method based on ZYNQ-7000 platform
The present invention discloses a sonar signal processing method based on a ZYNQ-7000 platform. The ZYNQ-7000 platform comprises a dual-core processor and a FPGA which perform data interaction through an AXI bus protocol; prior to the sonar signal processing, the FGPA source of the ZYNQ-7000 platform is estimated; the MVDR direction finding algorithm is divided into a main body algorithm and an auxiliary algorithm based on the estimation result and the MVDR direction finding algorithm; the main body algorithm is realized on the FPGA, and the auxiliary algorithm is realized on the dual-core processor; and when the sonar signal processing is performed, the sonar signals are received, and the main body algorithm and the auxiliary algorithm are called to obtain the processing results. The sonar signal processing method based on a ZYNQ-7000 platform is able to perform modularization division of the MVDR direction finding algorithm, divided modules are operated in the dual-core processor and the FPGA of the platform, and the processing speed is fast and the logic source of the FPGA is saved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hyper-beam forming method based on near-field focusing
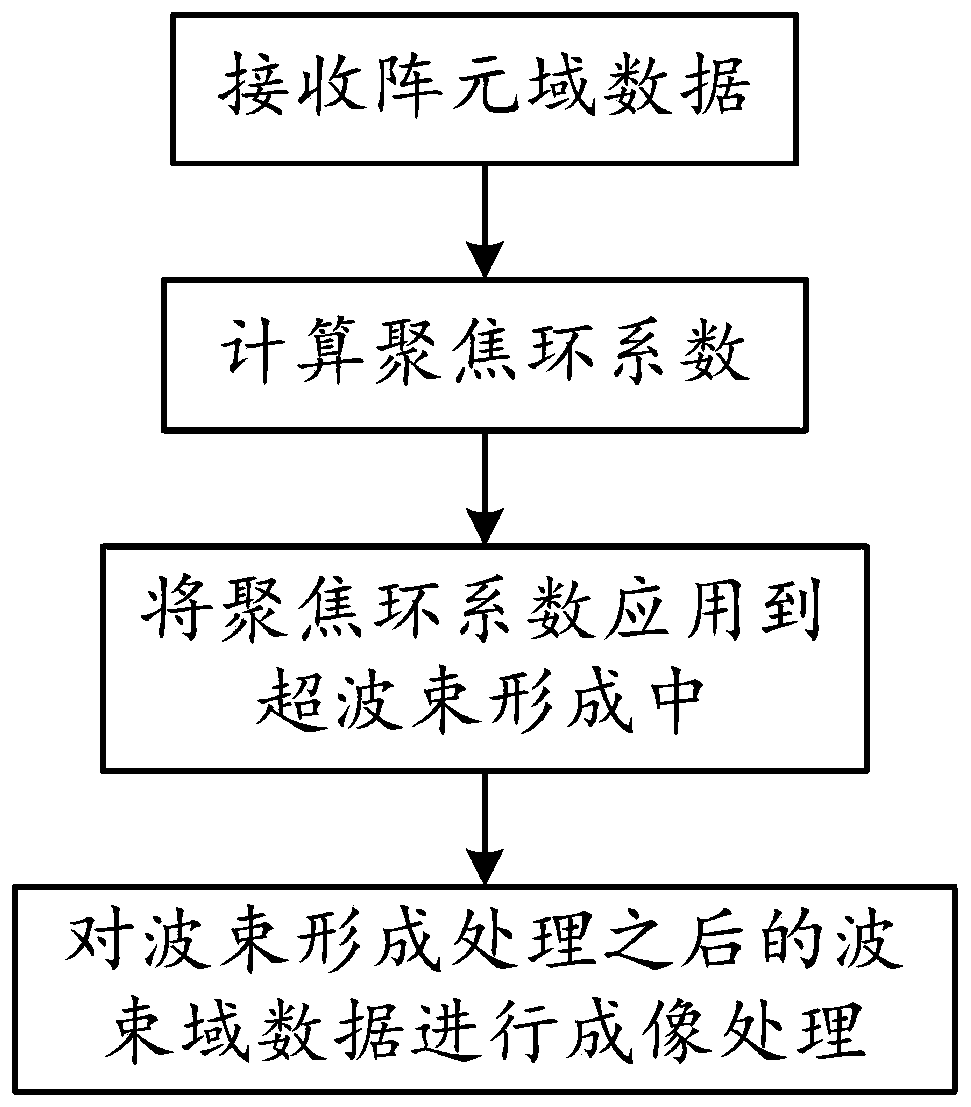
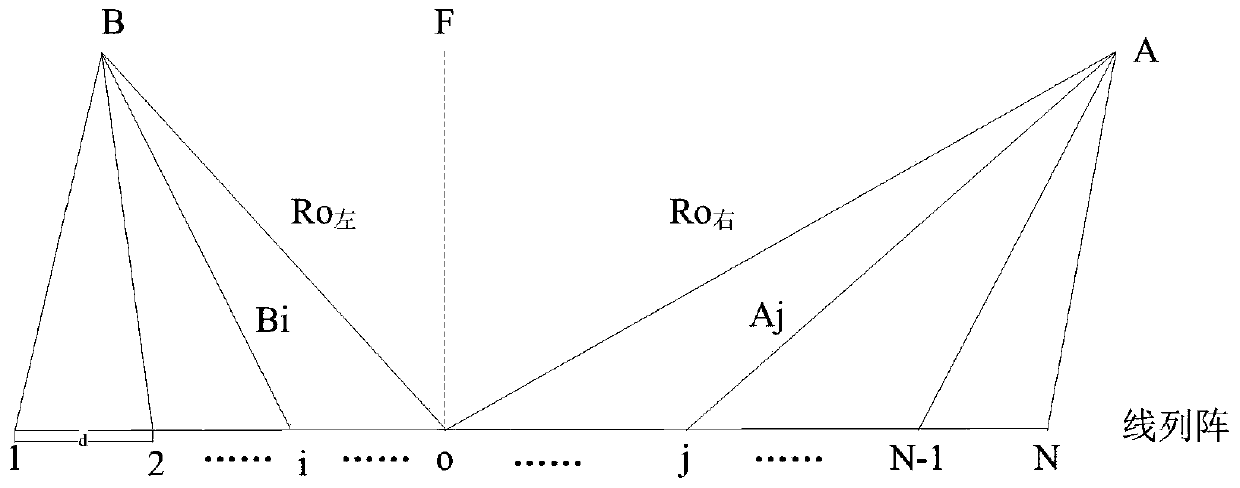
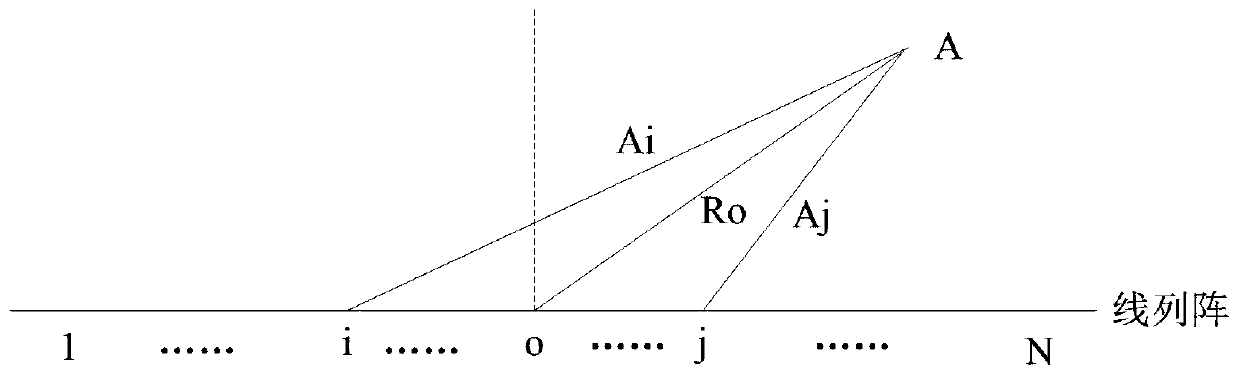
PendingCN110687538AEasy to detectImprove estimation accuracyAcoustic wave reradiationImaging processingSide lobe
The invention belongs to the technical field of sonar signal processing, and discloses a hyper-beam forming method based on near-field focusing. The method comprises the following steps: receiving element space data; calculating a focusing ring coefficient; applying the focusing ring coefficient in hyper-beam forming; and carrying out imaging processing on beam space data obtained after beam forming processing. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that a hyper-beam achieves a narrow main lobe and a low sidelobe, so that the detection performance of a sonar system can be effectively improved, the false alarm probability can be reduced, and the estimation precision for a target orientation can be increased; and the segment focusing hyper-beam forming technology is adoptedfor phase focusing compensation within a near-field range, so that the problem of image blurring caused by phase mismatching can be solved.
Owner:HAIYING ENTERPRISE GROUP
Secondary wave arrival direction estimution sonar signal processing method
InactiveCN101051083APhase correctionImprove estimation accuracyAcoustic wave reradiationFeature vectorImage resolution
A method for processing sonar signal of 2-D wave direction estimation includes revising phase outputted by base element; calculating correlation function estimation value of sonar array, carrying out character decomposition on said function estimation value; calculating first sub-array and correlation function estimation value of sub-array pair; carrying out character decomposition on said value of sub-array pair; calculating character vector estimation value of all sub-array pair, field angle estimation value of each object to sonar array two directions, etc and selecting two field angle estimation value corresponding to minimum variance estimation.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Active sonar single frequency tracking method
ActiveCN109444898AContinuous and stable target trackingStable single-frequency tracking Doppler information output resultsAcoustic wave reradiationSignal onSonar signal processing
The invention relates to the field of sonar signal processing, specifically relates to the field of the target tracking of sonar, and mainly discloses an active sonar single frequency tracking method.The combined signal based active sonar single frequency tracking method can be constructed by utilizing the continuously stable and high-precision tracking characteristics of a broadband frequency modulation signal on suspected targets, so that stable, accurate single frequency tracking doppler information output results can be obtained; and the method is simple in engineering implementation andgood in effect.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
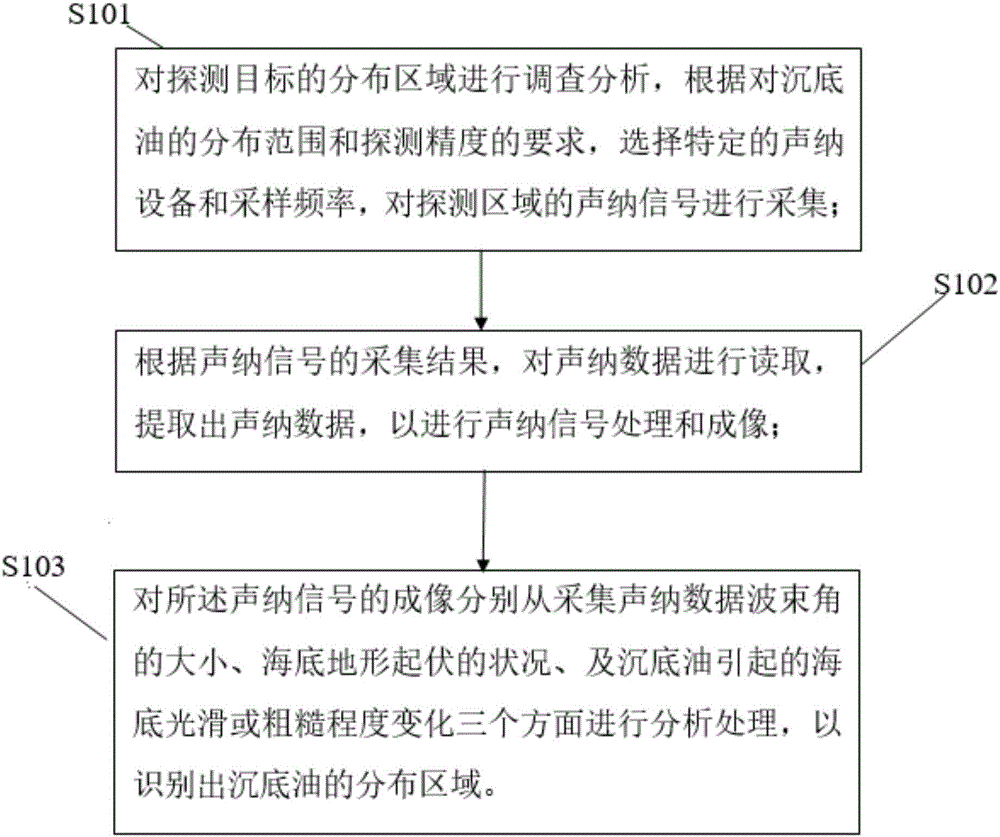
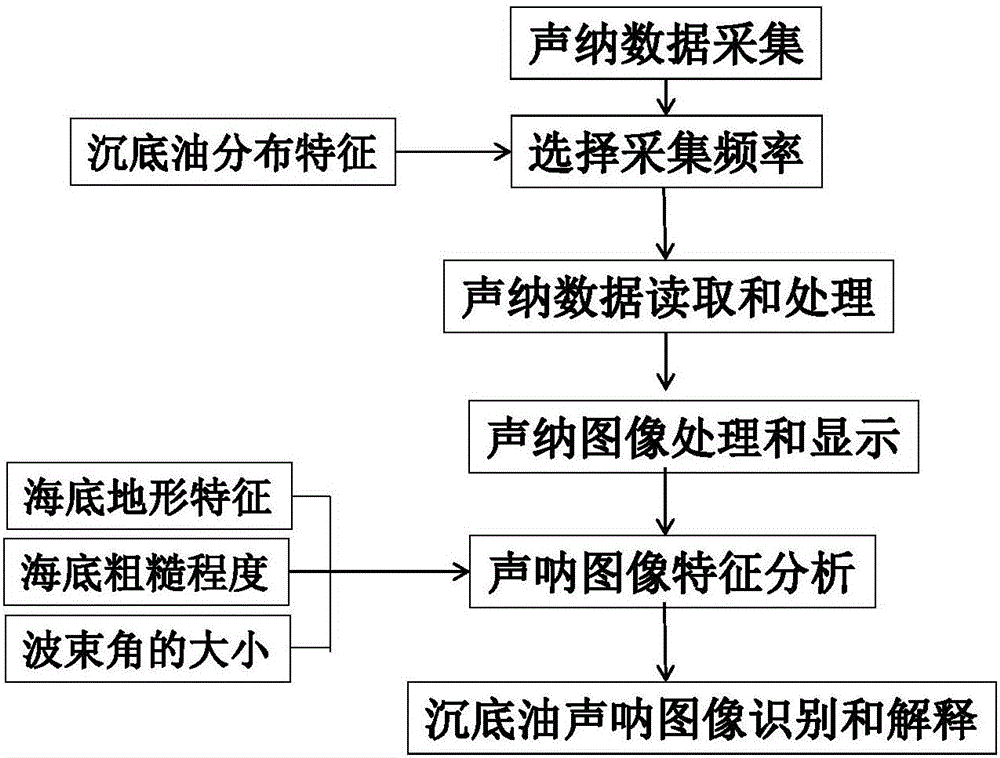
Sinking-to-bottom oil identification method and system based on sonar image characteristics
InactiveCN106802419AAccurate identificationCorrect identificationAcoustic wave reradiationOcean bottomSonar signal processing
The application discloses a sinking-to-bottom oil identification method and system based on sonar image characteristics. The method includes the following steps: investigating and analyzing a distribution area of a detection target, and according to requirements on the distribution range and detection precision of sinking-to-bottom oil, selecting specific sonar equipment and sampling frequency to collect sonar signals of a detection region; according to a collection result of the sonar signals, reading sonar data, and extracting the sonar data to perform sonar signal processing and imaging; analyzing and processing imaging of the sonar signals in three aspects of collecting the size of a sonar data beam angle, the condition of seabed topographic relief and the seabed smooth or roughness degree caused by sinking-to-bottom oil, so as to identify a distribution region of the sinking-to-bottom oil. The sinking-to-bottom oil identification method based on sonar image characteristics has the advantages that the correct identification and accurate description of the sinking-to-bottom oil can be effectively realized, the method has the characteristics of accurate identification and convenient operation, and has huge application potential and wide application prospects in later cleaning of spilled oil.
Owner:中海石油环保服务(天津)有限公司
Cavitating body sonar system and process
InactiveUS7453769B2Improve performanceImprove system performanceAcoustic wave reradiationWave formTransducer
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention may include a cavitating body sonar system and method. The method may include, in an exemplary embodiment: applying a receiving-while-transmitting sonar signal processing to at least one cavitating body, over an entire range of achievable sonar operating frequencies; applying transmit wave-form shaping to a RWT sonar system employed on the cavitating body; applying heterodyne filter frequency rejection to the RWT sonar system employed on the cavitating body; applying detection processing techniques to the RWT sonar system employed on the cavitating body; employing at least one transducer as an acoustical transmitter near a scattering body comprising the cavitating body, wherein the at least one transducer is strategically located with respect to said cavitating body, at least one target, and a receiver, wherein the receiver lies in a shadow zone of the body, but the at least one target does not; and, employing at least one transducer as an acoustical transmitter near a scattering body comprising the cavitating body, wherein the at least one transducer is strategically located with respect to a cavity, at least one target, and a receiver, wherein direct propagation of a transmitted signal along the outside of the cavity to the receiver is inhibited, and reflected propagation from the acoustical transmitter to the target and thence reflected to the receiver is not inhibited.
Owner:GEN DYNAMICS INFORMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com