Biomarker for diagnosing esophageal squamous carcinoma and detection kit
A biomarker, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma technology, applied in the field of medicine and biology, can solve the problems of poor prognosis, limited treatment methods, and 5-year survival rate of less than 20%, and achieve good diagnostic and differentiation effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Using human proteome chips to screen markers for the diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
[0039] 1. Experimental sample:
[0040] The sera of 30 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma group) and 24 normal subjects (normal control group) were collected from the specimen bank of the Henan Provincial Key Laboratory of Cancer Epidemiology; among them, the serum of 30 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma confirmed by pathology without any treatment; 24 normal human serums were obtained from healthy subjects, and the inclusion criteria for healthy subjects were: no cardiovascular, respiratory, liver, kidney, gastrointestinal tract , endocrine, blood, mental, or nervous system diseases and the history of the above diseases, no acute or chronic diseases, no autoimmune diseases, no evidence of any tumor-related; moreover, 30 patients with esophageal ...
Embodiment 2
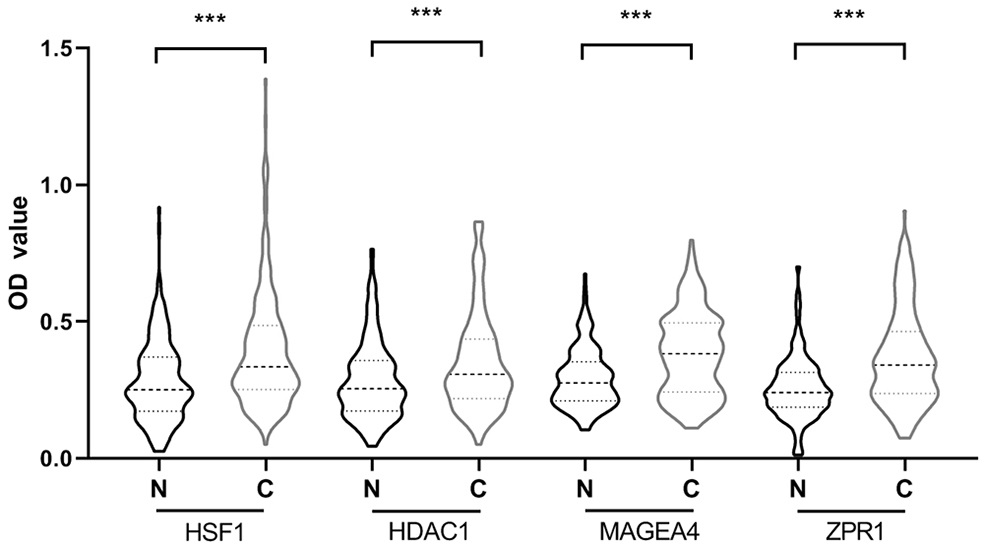
[0060] Example 2: ELISA detection of serum expression levels of anti-tumor-associated antigens ZPR1, HSF1, MAGEA4, HDAC1 autoantibodies
[0061] The expression levels of the four anti-tumor-associated antigen autoantibodies screened in Example 1 in human serum were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
[0062] 1. Experimental sample:
[0063] The samples of 229 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma group) and 229 normal controls (normal control group) included in this study were all obtained from the specimen bank of the Key Laboratory of Cancer Epidemiology in Henan Province; among them, 229 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Serum from patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma confirmed by pathology without any treatment; 229 normal human serum from healthy subjects, the inclusion criteria of healthy subjects are: no cardiovascular, respiratory, liver, kidney , gastrointestinal tract, endo...
Embodiment 3
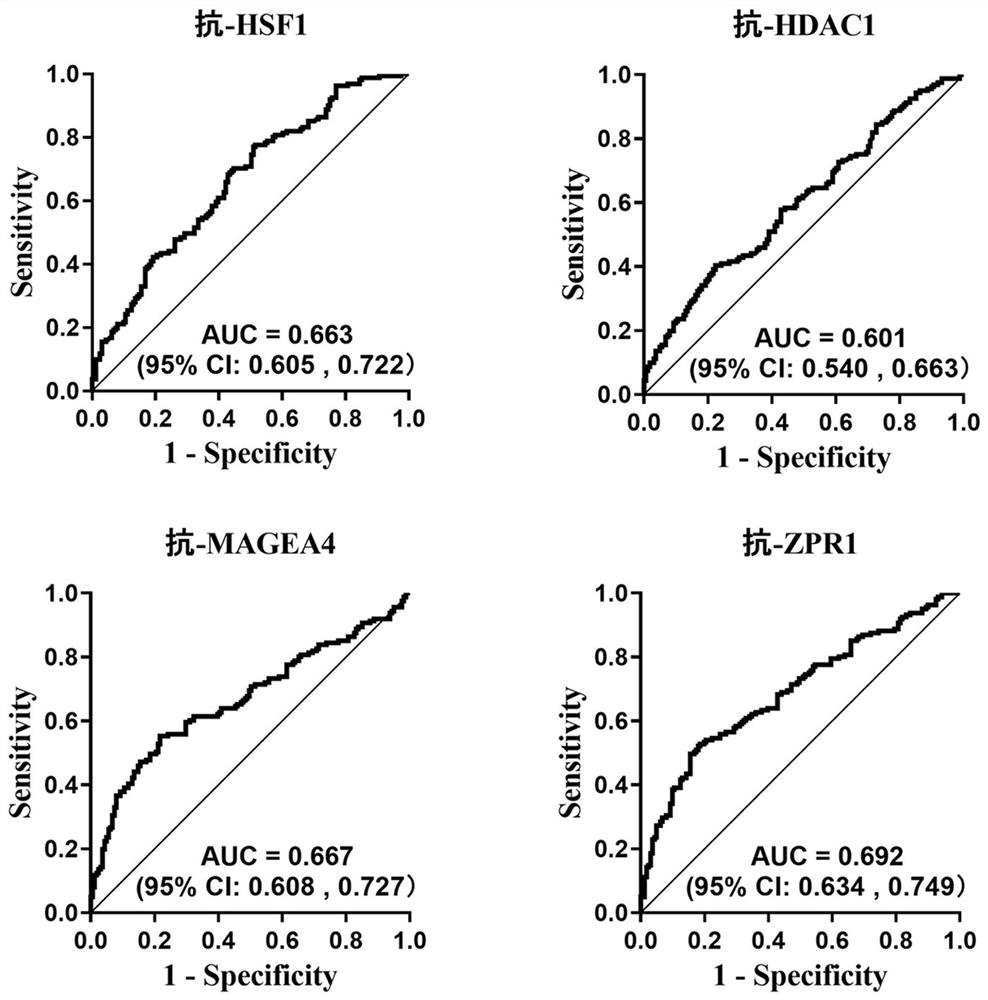
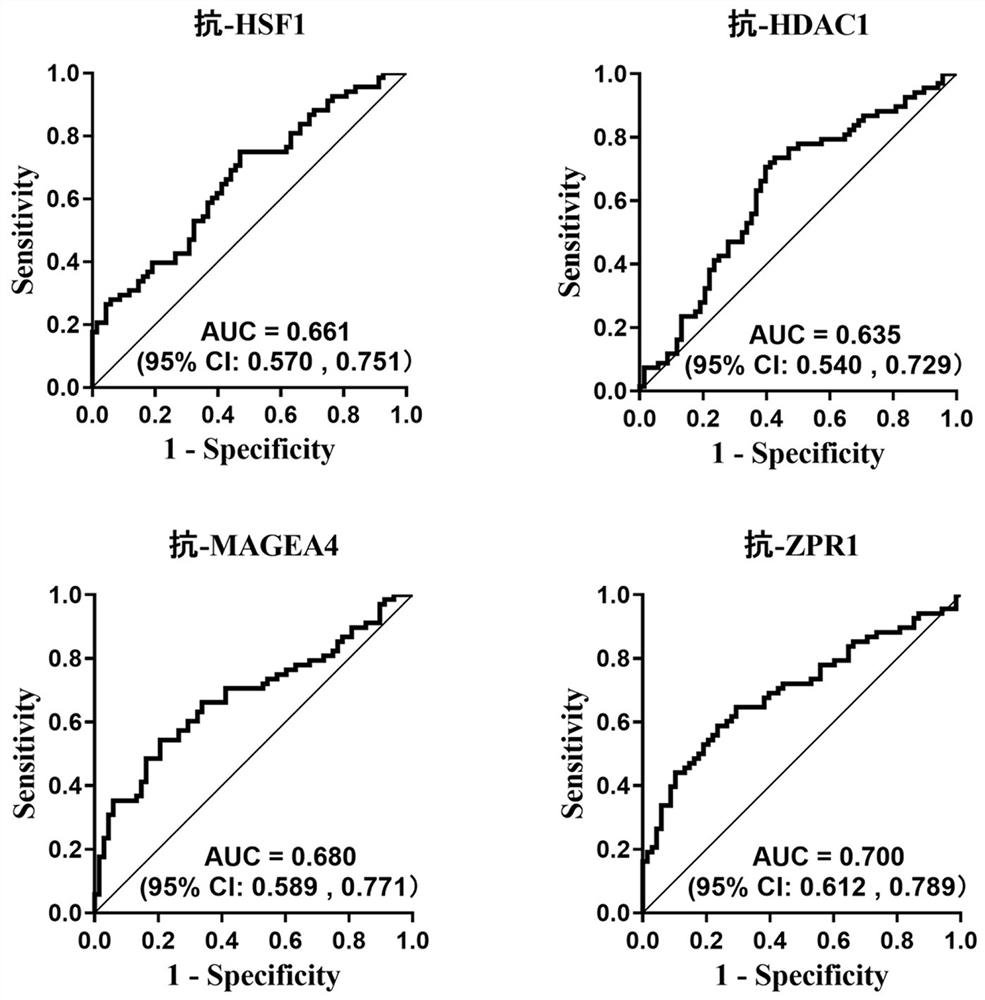
[0098] Example 3: Assessment of the ability of 4 autoantibodies against tumor-associated antigens to diagnose esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
[0099] 1. Experimental sample:
[0100] The serum of 229 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and the serum of 229 normal controls included in Example 2 are randomly divided into a training set and a verification set in a ratio of 7:3; 161 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (referred to as esophageal squamous cell carcinoma) in the training set 161 cases of normal control serum (denoted as normal control group); 68 cases of serum from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients and 68 cases of normal control serum in the validation set. Then according to the results of the expression levels of anti-tumor-associated antigens ZPR1, HSF1, MAGEA4, and HDAC1 autoantibodies in the training set and verification set detected by ELISA in Example 2, GraphPad Prism8.0 was used to draw ROC curves to analyze the four an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com