Thermo-sensitive embolism microsphere and preparation method thereof
A technology for embolizing microspheres and temperature sensitivity, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of poor suspension, low shrinkage rate, inability to embolize microspheres, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] The embodiment of the present application also provides a method for preparing the above-mentioned temperature-sensitive embolic microspheres, which includes the following steps:
[0044] (1) Prepare the oil phase system: add the oil-soluble dispersant to the oil phase solvent, stir and dissolve to form a uniform oil phase system.
[0045] Wherein, the oil-soluble dispersant is at least one of Span 20, Span 80, Tween 20, Tween 80, cellulose acetate, and cellulose acetate butyrate; the oil-soluble solvent is liquid paraffin, n-heptane, acetic acid At least one of ethyl ester and butyl acetate; the mass percentage of the oil-soluble dispersant in the oil phase is 1%-2%.
[0046] (2) Prepare the water phase system: first prepare the water-soluble polymer into a certain concentration of polymer aqueous solution; then dissolve the water-soluble monomer, cross-linking agent, and initiator in water to prepare a monomer aqueous solution; The aqueous solution and the monomer aq...
Embodiment 1
[0058] This example provides a series of temperature-sensitive embolic microspheres, which are prepared by reverse suspension polymerization. The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0059] (1) Preparation of oil phase system
[0060] Add 300mL of liquid paraffin into the four-necked bottle, measure 5mL of Span 80 into the four-necked bottle, stir and mix the liquid paraffin and Span 80 until a uniform oil phase system is formed.
[0061] (2) Preparation of water phase
[0062] First, prepare a 12% polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution (containing about 12 g of polyvinyl alcohol) with a mass fraction of 12% under the condition of heating in a constant temperature water bath at 80°C; another 2 g of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid (AMPS) was weighed , 3g of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), 0.02g of N,N-methylenebisacrylamide, 0.35mL of aminoacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal, 0.02g of ammonium persulfate, 0.04mL Tetramethylethylenediamine was added into 5mL of deionized...
Embodiment 2-5
[0077] This example provides a thermosensitive embolic microsphere respectively, the difference between the preparation method and Example 1 is that the mass percentage of NIPAM to the total amount of monomers is different, that is, the amount of NIPAM is different.
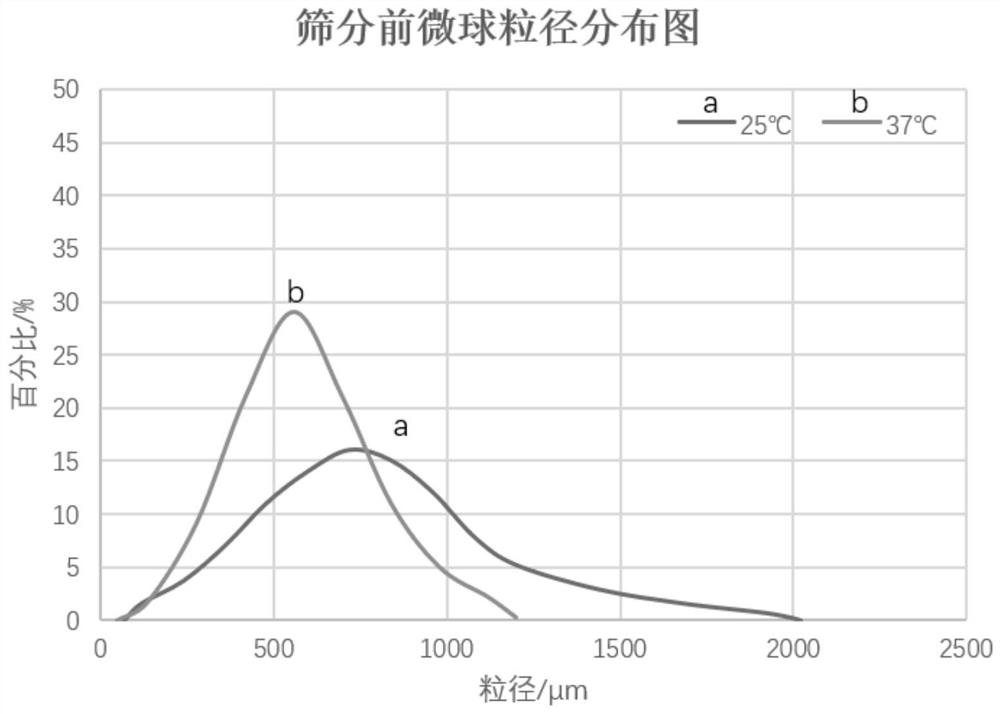
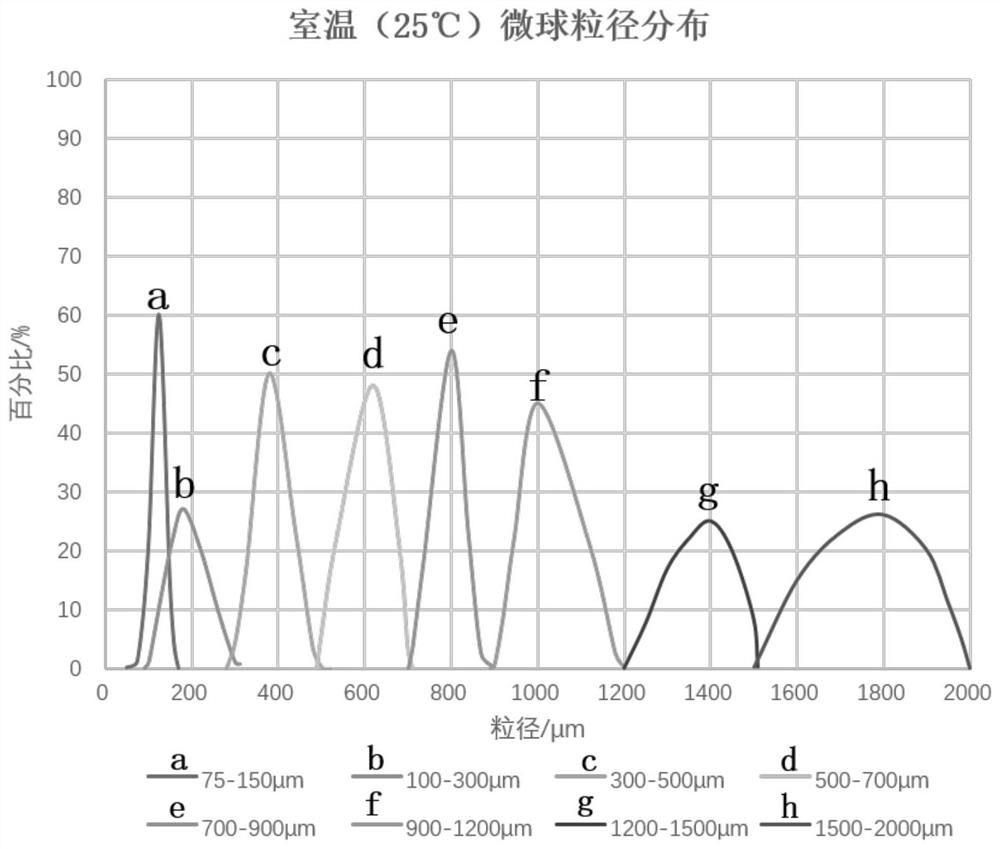
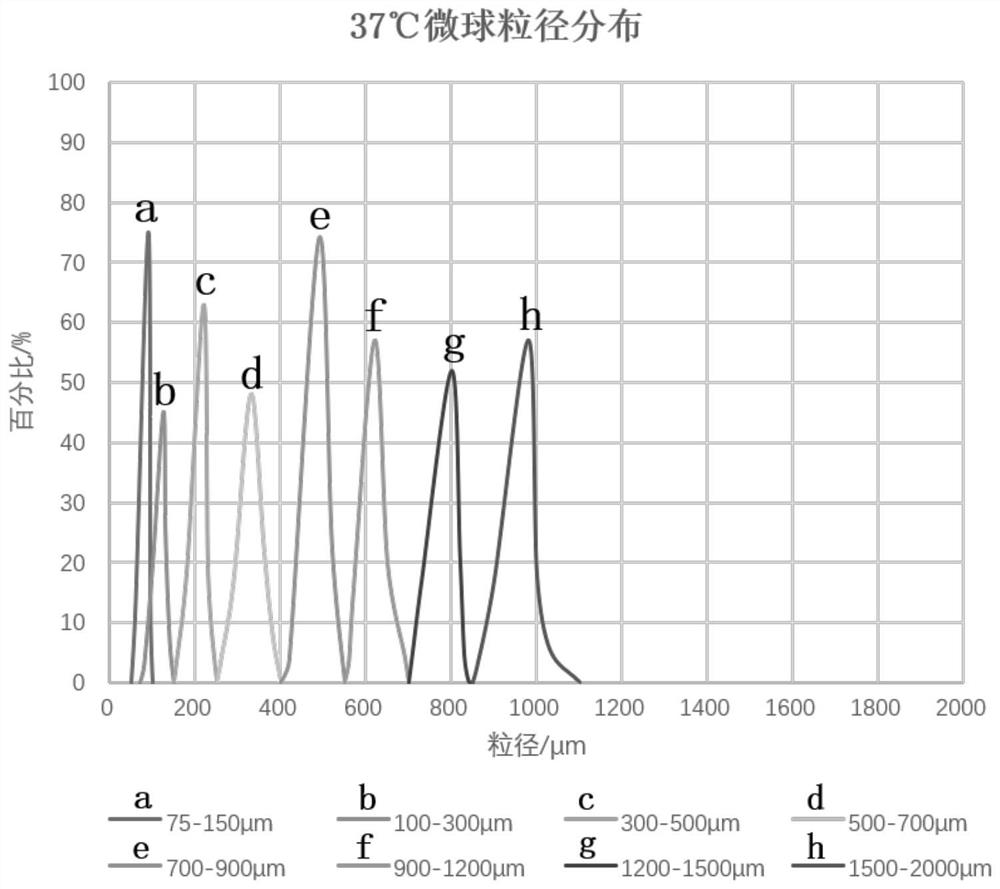
[0078] Test the particle size distribution width of the 300-500 μm embolic microspheres obtained by sieving in Example 2-5 at 37°C, and the particle size shrinkage relative to 25°C, the results are as follows Figure 4 and shown in Table 2.
[0079] Table 2 Effect of NIPAM dosage on particle size distribution of 300-500 μm embolic microspheres
[0080] group Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Example 5 Dosage of NIPAM 5% 10% 20% 30% Particle size distribution width W / μm 140 95 67 36 Average particle size shrinkage rate R / % 14.2 37.3 51.9 64.3
[0081] NIPAM dosage: the mass percentage of NIPAM in the total amount of monomers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com