Printing and dyeing wastewater regenerant as well as preparation method and use method thereof
A technology for printing and dyeing wastewater and regenerant, applied in the field of textile printing and dyeing, can solve the problems of high equipment and operation requirements, secondary pollution, low recycling rate, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing chroma and shortening the process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031]Based on the above regenerative agent, the present application also provides a method of preparing an active dye staining wastewater regenerant, including the following steps:
[0032] According to the quality percentage, the following raw materials were weighed: the complex dispersant of the active dye cluster is 0.1-2%, and the active dye targets the positioning of 0.1-20%, pH regulator 0.1-3%, and deionized water is 75%. -99.7%, the content of the above components is 100%;
[0033] After mixing the complex dispersant and the dissociation of the oxidant, it was mixed with a deionized water of 25-40 ° C, and the pH conditioner was mixed well, stirred and uniform, and then stirred and uniform.
[0034] The active dye printing wastewater regeneration according to the present invention is quite different from conventional wastewater regenerative agents. Specifically, the conventional wastewater regenerant is added to the wastewater treatment process to remove the colored subst...
Embodiment 1
[0037] The preparation process of the active dye staining wastewater regeneration is specifically:
[0038] The above raw materials are weighed in accordance with the components name 1 of Embodiment 1 of Table 1 and the respective components of the components of Embodiment 1 in Table 2.
[0039] The weighing deionized water temperature is adjusted to 20-40 ° C;
[0040] Sodium phenolic condensate, sodium phenolic acid, sodium sulfate is sequentially added to 20-40 ° C deionized water, stirred is mixed, and sodium acetate is mixed, and then stirred again and uniformly to obtain a regenerative dye.
Embodiment 2-28
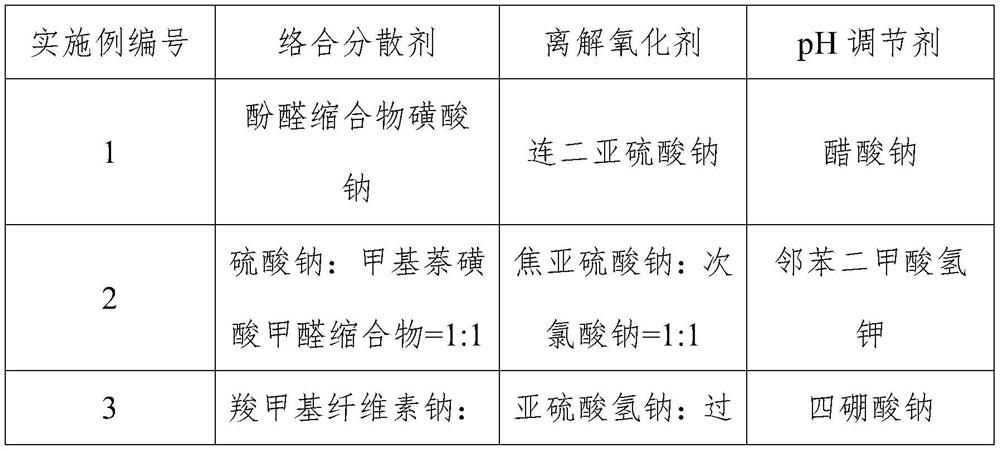
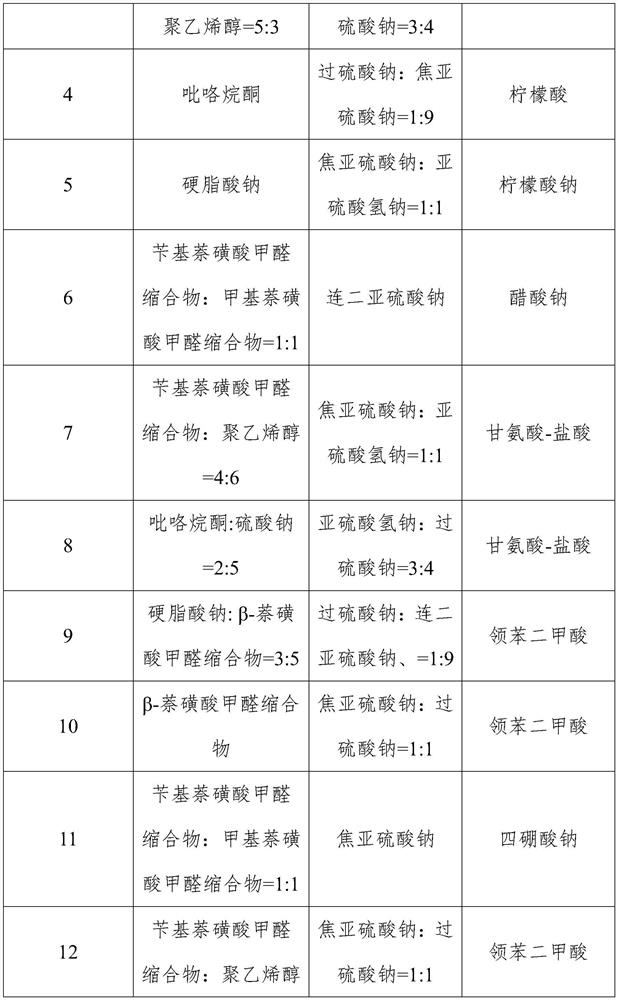
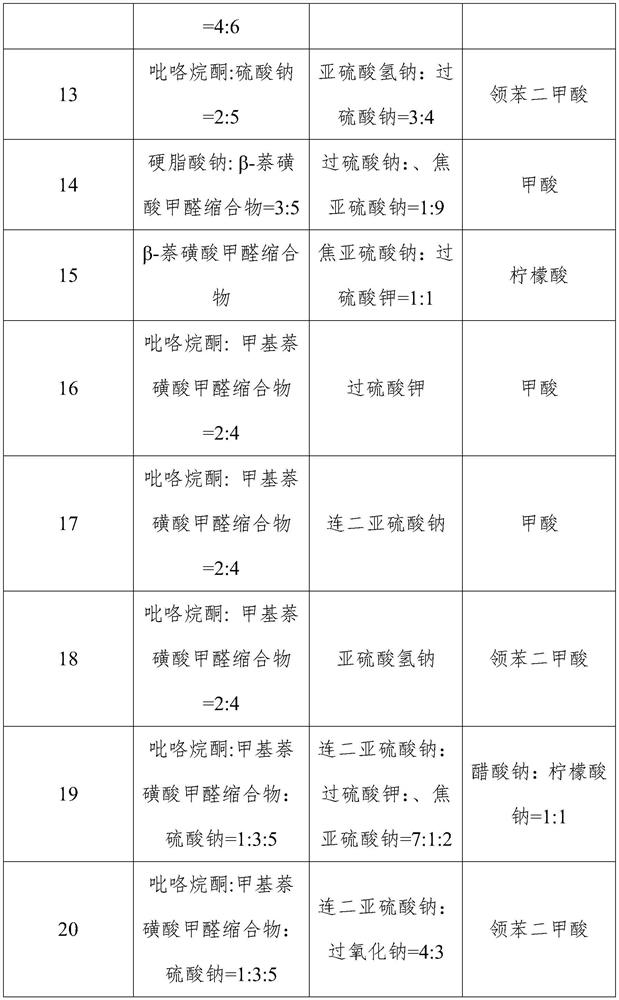
[0042] Embodiment 2-28 The preparation process of Example 2 is identical, and the specific formulation (chemical name and content of each component), respectively, see the components 2-28 in Table 1, respectively, in Table 2 Embodiment No. 2-28 corresponds to a mass percentage of mass.
[0043] Table 1 Structure information of compounds in Examples 1-28
[0044]
[0045]
[0046]
[0047]
[0048]
[0049] Table 2 Example 1-28 Additives Composition ratio
[0050]
[0051]
[0052] In the above embodiment, the structural information of A, B, and C is shown in Table 2.
[0053] In use, the amount of wastewater regeneration is added in accordance with 3-5% of the mass of the soap.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com