Method for extracting and separating umbilical cord-derived skeletal stem cells
A separation method and stem cell technology, applied in the field of extraction and separation of umbilical cord-derived skeletal stem cells, can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining skeletal stem cells, large damage to the donor, and large secondary damage to the donor, etc., to shorten the primary culture time and increase the number and quality, less controversial effects of ethics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] A method for extracting umbilical cord derived bone stem cells, comprising the steps of:
[0059] S1. Primary isolation of human umbilical cord-derived stem cells (hUC-MSCs)
[0060] (1) After the human umbilical cord has undergone strict testing procedures (ABO / Rh blood type testing, HLA typing testing, syphilis antibody testing, HIV immune testing, CMV antibody testing, hepatitis B antigen antibody testing, etc.) to determine the safety, take a 20cm umbilical cord Put it into a collection bottle of PBS buffer containing double antibodies (final concentration of penicillin is 100U / mL and final concentration of streptomycin is 0.1mg / mL), seal and send to a sterile ultra-clean bench for processing;
[0061] (2) Disinfect the outer wall of the collection bottle with 75% alcohol, take out the umbilical cord tissue with sterile tweezers (big long tweezers) and transfer it to a petri dish, and wash it with double antibodies (final concentration of penicillin is 100U / mL and s...
Embodiment 2
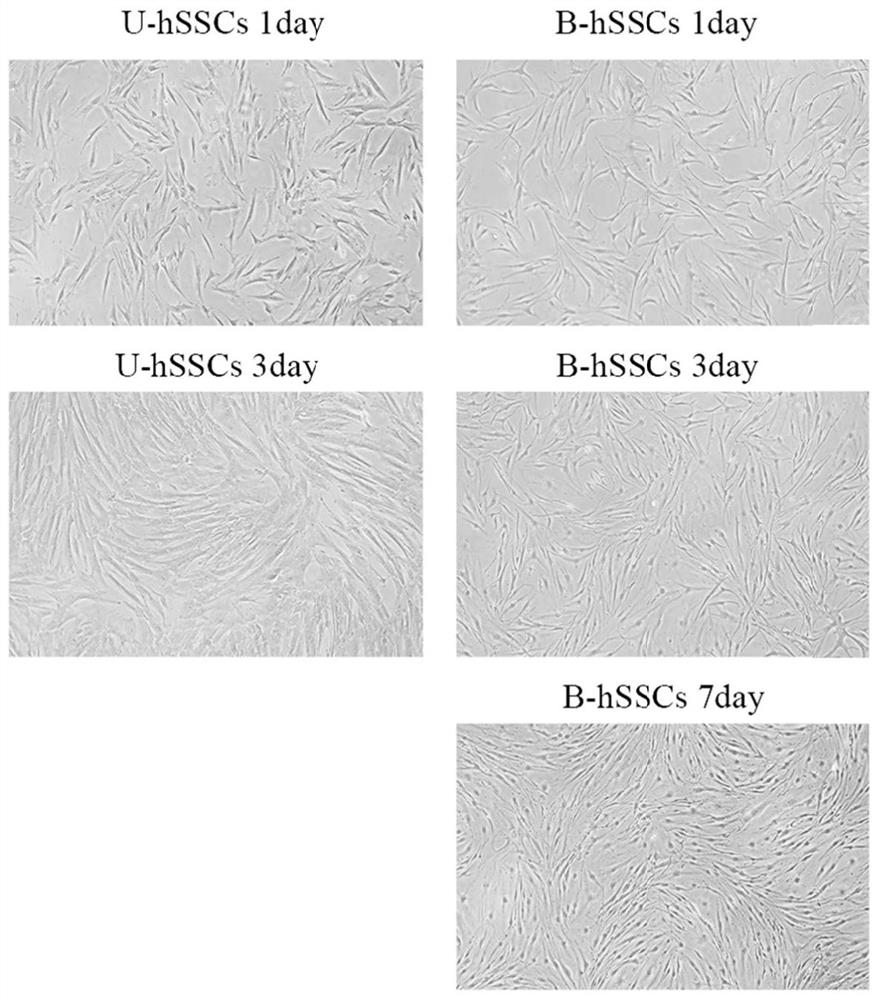
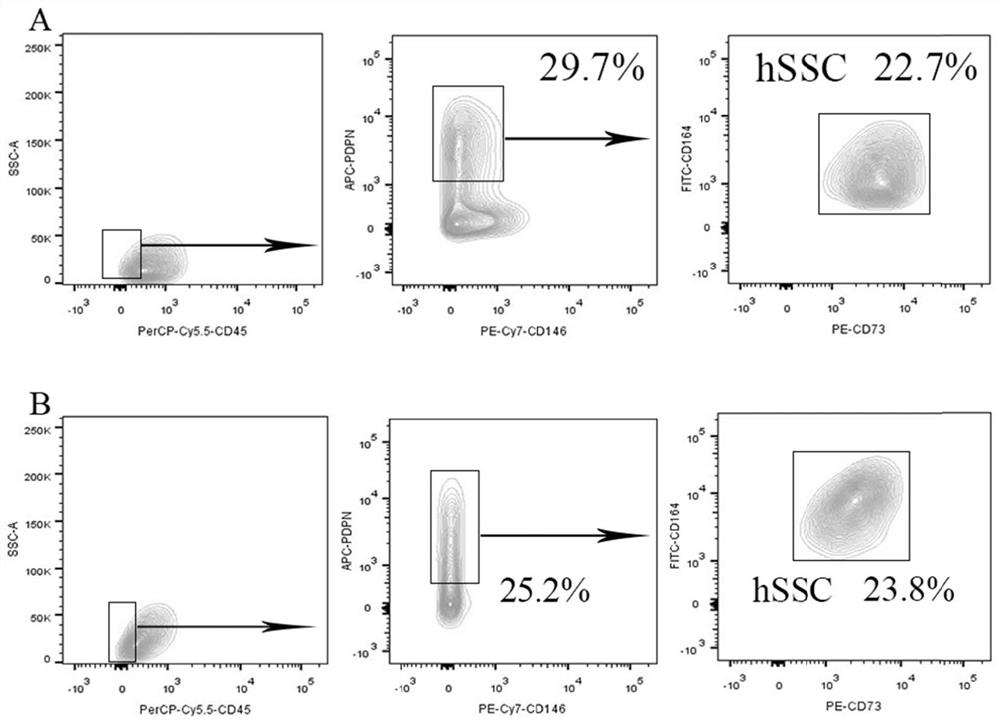
[0095] Example 2 Cell culture of umbilical cord-derived skeletal stem cells (U-hSSCs) and bone marrow-derived skeletal stem cells (B-hSSCs)
[0096] The U-hSSCs prepared in Example 1 and the B-hSSCs prepared in Comparative Example 1 were respectively inoculated into T25 cell culture flasks containing complete medium, and placed in CO 2 Culture in an incubator with a concentration of 5%, a humidity of 95%, and a temperature of 37°C; replace the medium every 48 hours, and wash the cells twice with PBS when the cell confluence reaches 80% to 90%; discard the PBS , add 1mL of digestion solution (trypsin-EDTA digestion solution (0.25%) containing phenol red, Solarbio, Cat#T1320), and put it in the incubator for digestion for 1min; discard the digestion solution, and stop the digestion with complete medium immediately; Transfer the cell suspension to a 15mL centrifuge tube and centrifuge at 800rpm for 5min; discard the supernatant, resuspend the cells with complete culture, and inoc...
Embodiment 3
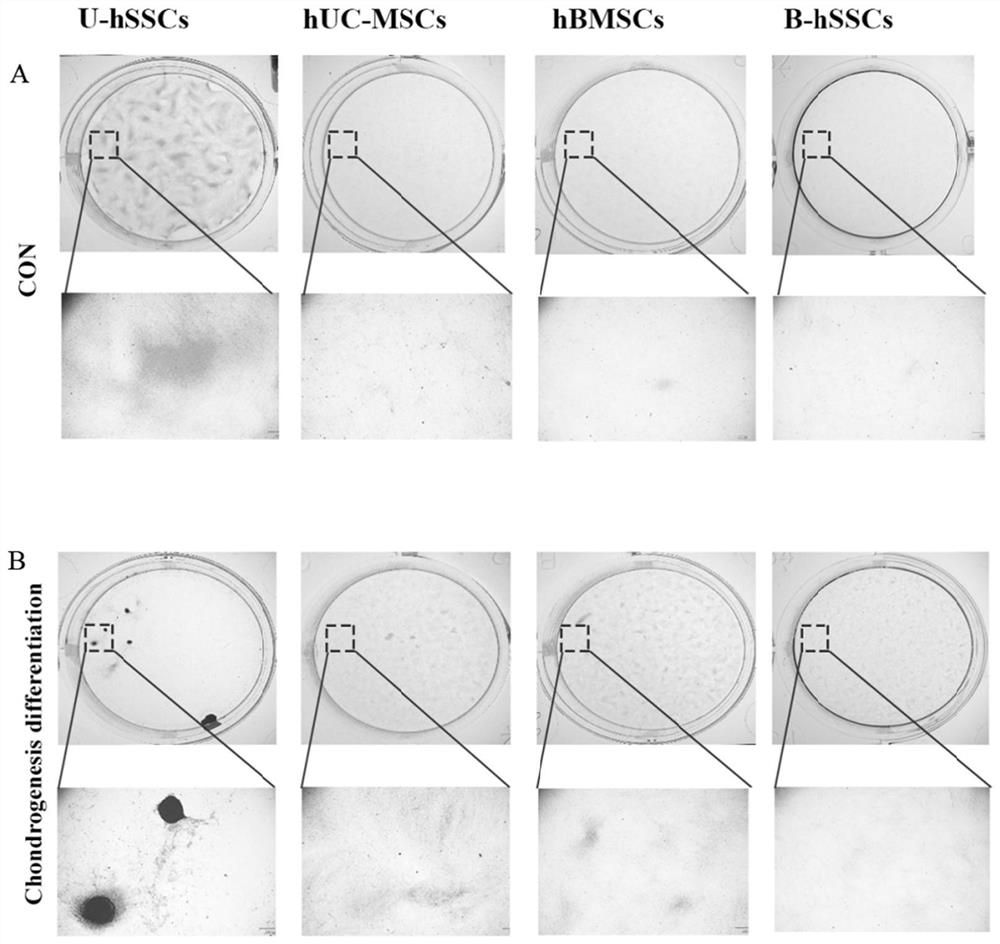
[0098] Cartilage differentiation of hSSCs derived from the umbilical cord of embodiment 3
[0099] Umbilical cord-derived skeletal stem cells (U-hSSCs), human umbilical cord stem cells (hUC-MSCs) (produced in Example 1), human bone marrow stromal stem cells (hBMSCs) and human bone marrow-derived skeletal stem cells (B- hSSCs) (prepared in Comparative Example 1) were inoculated in 12-well plates, with 2 wells for each type of cell, about 100,000 cells in each well, added 2 mL of complete medium, and placed at 37 ° C, 5% CO 2 Culture in the incubator until it was overgrown; the medium in the 12-well plate was aspirated and discarded, and 1 mL of chondrogenic differentiation medium (50% StemPro chondrogenic differentiation reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) was added to one well of each cell. TM , Cat#A1007101, 50% MEM Alpha (1×) medium)) for chondrogenic induction and differentiation, another well was added with the same volume of complete medium as a blank control; after the 4t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com