Method for extracting microbial DNA from sample
A technology in microorganisms and samples, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, DNA preparation, etc., and can solve the problems of difficult removal, unclear precipitation and separation, and low purity of nucleic acid products.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
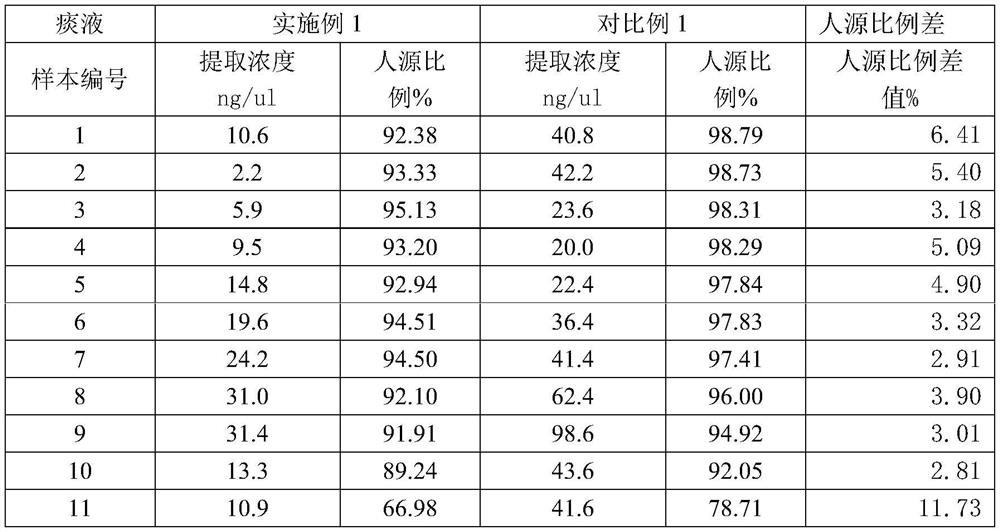
[0021] Example 1 - Sputum sample
[0022] In order to better illustrate that the simultaneous addition of liquefaction reagent and Benzonase nuclease can not only reduce the viscosity of the sample to make it more homogeneous, but also reduce the proportion of human DNA in the sample, comparative example 1 is specially set up, that is, there is no Benzonase nuclease in comparative example 1 Add to.
[0023] In Example 1: In the ultra-clean workbench, directly add 5 times the volume of 30% methanol solution and the prepared DTT solution to the sputum sample box, and the addition ratio is 10:1 (such as 1000ul methanol+100ulDTT) ; After sealing the membrane, shake the sample until there is no viscous substance visible to the naked eye, and put it into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube; add 1ul Benzonase enzyme and 10x Benzonase buffer to the 1.5ml sample to a final concentration of 1x. Benzonase buffer includes Tris-Hcl and Mgcl.
[0024] Incubate at 37°C for half an hour, then add EDTA ...
Embodiment 2-
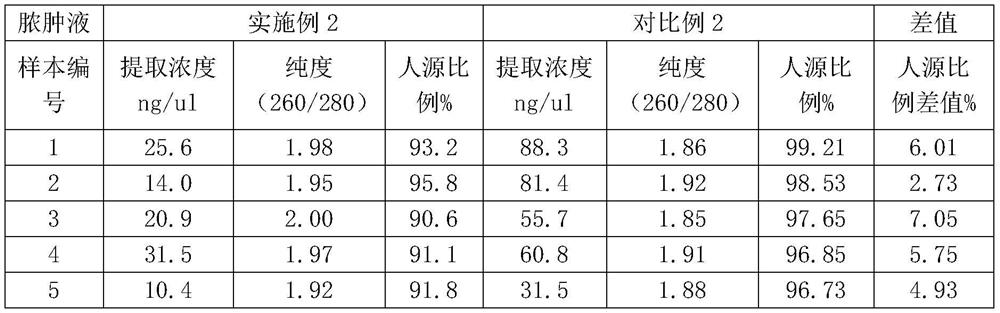
[0033] Example 2 - abscess fluid
[0034] In order to better illustrate that the simultaneous addition of liquefaction reagent and Benzonase nuclease can not only make the separation of abscess fluid supernatant and sediment more obvious, but also reduce the proportion of human DNA in the sample, comparative example 2 is specially set up, that is, there is no Benzonase nuclease added.
Embodiment 2
[0035]In Example 2: In the ultra-clean workbench, add 4 times the volume of 30% methanol solution and the DTT solution prepared in the tube for collecting the abscess fluid, and the addition ratio is 12:1 (such as 1200ul methanol+100ulDTT) ; After sealing the membrane, shake the sample until there is no viscous substance visible to the naked eye, and put it into a 2.0ml centrifuge tube; add 1ul Benzonase enzyme (250U) and 10x Benzonase buffer to the 1.5ml sample to a final concentration of 1x; Benzonase buffer includes Tris-Hcl and Mgcl.
[0036] Incubate at 37°C for half an hour, then add EDTA (final concentration 5mM, pH 8.0) and NaCl (final concentration 150mM) into the tube to quench the reaction; shake fully and centrifuge at 8000g for 10min, discard the supernatant, add 1ml of PBS to wash, centrifuge at 8000g for 10min and discard the supernatant Clear, add 500ulPBS;
[0037] Wrap the parafilm, clamp the explosion-proof clamp and incubate at 95°C for 10 minutes; transfe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com