Red light semiconductor laser of aluminum-free active region and preparation method of red light semiconductor laser
An active region and semiconductor technology, applied in the field of optoelectronics, can solve the problems of high material growth requirements, easy formation of defects, affecting laser performance, etc., to reduce light absorption, reduce the formation of cavity surface defects, and improve the effect of burning resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
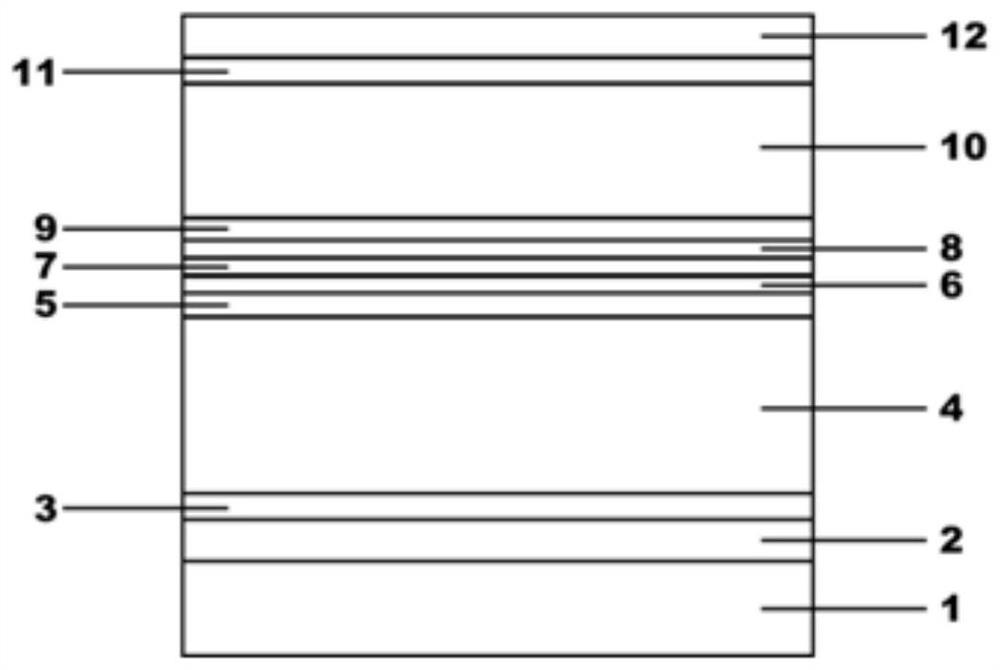
[0093] A red light semiconductor laser with no aluminum active region, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes GaAs substrate 1 , GaAs buffer layer 2 , GaAs x1 In 1-x1 P lower transition layer 3, AlGaInP lower confinement layer 4, Ga x5 In 1-x5 As y4 P 1-y4 Lower waveguide layer 5, Ga 1-x6 In x6 P lower barrier layer 6, Ga 1-x7 In x7 P quantum well 7, Ga 1-x8 In x8 P upper barrier layer 8, Ga x9 In 1-x9 As y5 P 1-y5 Upper waveguide layer 9, AlGaInP upper confinement layer 10, Ga 1-x12 In x12 P upper transition layer 11 and GaAs cap layer 12;
[0094] The AlGaInP lower confinement layer 4 includes (Al 1-x2 Ga x2 ) y1 In 1-y1 P lower confinement layer-1, (Al 1- x3 Ga x3 ) y2 In 1-y2 P lower confinement layer-2, (Al 1-x4 Ga x4 ) y3 In 1-y3 P lower limit layer -3;
[0095] The AlGaInP upper confinement layer 10 includes (Al 1-x10 Ga x10 ) y6 In 1-y6 P upper confinement layer-1, (Al 1-x11 Ga x11 ) y7 In 1-y7 P upper limit layer-2;
[0096] Amon...
Embodiment 2
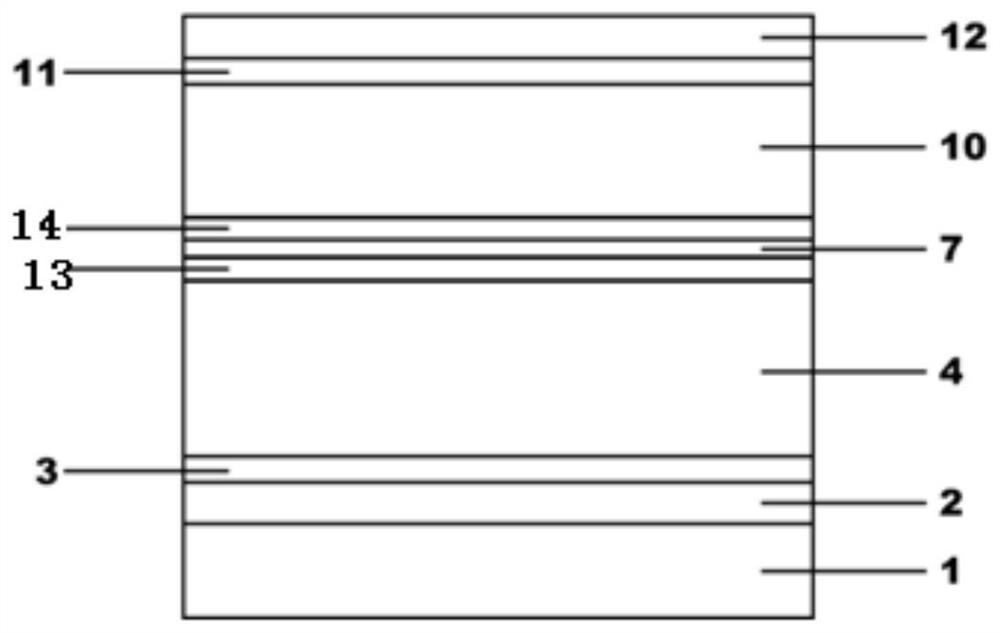
[0105] A red light semiconductor laser without aluminum active region according to Embodiment 1, the difference is: Ga x5 In 1- x5 As y4 P 1-y4 The thickness of the lower waveguide layer 5 is 0.1-0.3 μm, unintentionally doped; Ga x9 In 1-x9 As y5 P 1-y5 The thickness of the upper waveguide layer 9 is 0.1-0.3 μm, unintentionally doped; Ga 1-x7 In x7 The P quantum well 7 has a thickness of 5-10 nm and is unintentionally doped.
Embodiment 3
[0107] A red light semiconductor laser without an aluminum active region according to Embodiment 1, the difference is: x5=0.9, y4=0.8. Ga x5 In 1-x5 As y4 P 1-y4 The thickness of the lower waveguide layer 5 is 0.2 μm. x9=0.9, y5=0.8. Ga x9 In 1-x9 As y5 P 1-y5 The thickness of the upper waveguide layer 9 is 0.13 μm. x7=0.65. Ga x5 In 1-x5 As y4 P 1-y4 Lower waveguide layer 5, Ga x9 In 1-x9 As y5 P 1-y5 The value of the composition of the upper waveguide layer 9 is to adjust the band gap and lattice constant, while the Ga x5 In 1-x5 As y4 P 1-y4 Lower waveguide layer 5, Ga x9 In 1- x9 As y5 P 1-y5 The thickness of the upper waveguide layer 9 is different, the purpose is to control the shift of the light field in the light emitting area to the N side, and reduce the loss caused by the carrier to the light absorption.
[0108] Ga 1-x7 In x7 The thickness of the P quantum well 7 is 7 nm. Ga 1-x7 In x7 The P quantum well 7 has different components, d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com