Method for electrochemically detecting exosome
An exosome and electrochemical technology, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of inability to conduct a large amount of analysis, cumbersome and complicated, and inability to detect biochemical components, and achieve the effects of fast speed, wide detection range, and improved detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
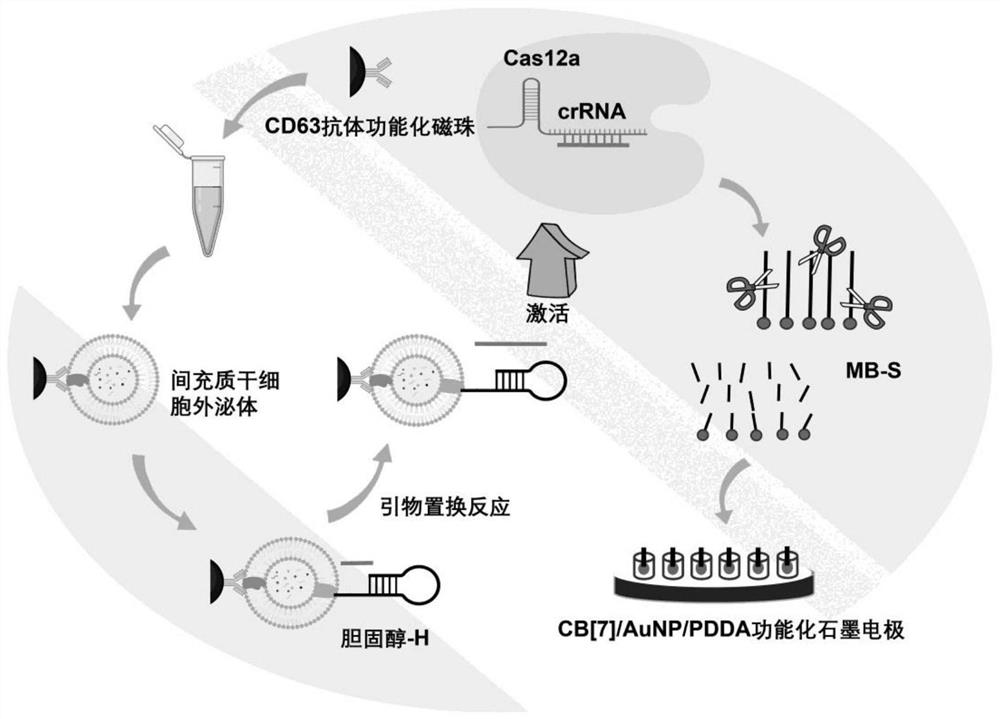
[0043] Example 1 Capture of exosomes
[0044] (a) First, take 100 μL-150 μL of carboxyl-functionalized magnetic beads and wash three times with pH 7.4 phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and then resuspend in PBS after magnetic separation, and then add 500 μL to 600 μL of 0.22 to 0.23 M 1 to the solution. -Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide / N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDC / NHS) solution, incubate at room temperature for 30 to 40 minutes to activate the bead surface the carboxyl group;
[0045] (b) After further washing with PBS and magnetic separation, add 10 μL to 15 μL of CD63 antibody to the magnetic bead solution, and react at room temperature for 1.5 to 2 hours, thereby preparing immunomagnetic beads functionalized with CD63 antibody through amino-carboxyl reaction , and finally, remove the antibody that is not bound to the magnetic beads after magnetic separation, and resuspend in PBS solution for later use;
[0046] (c) Take the CD63 antibody-functionalized immunomagn...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 CRISPR-Cas12a-assisted signal amplification
[0050] (a) Primer replacement reaction in 50-60 μL of reaction buffer (1.5-2 mM Tris-HCl, 1-1.5 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 1mM KCl, 1.2~1.5mM MgSO 4 and 0.01% TritonX-100) at 30-37°C for 1.5-2 hours. It contains the desired H chain inserted into the exosome membrane, 10~15 μM primer P chain, 0.8~1 unit μL -1 Bst DNA polymerase and 100-150 μM dNTPs (dCTP, dTTP and dATP).
[0051] (b) 200-300 nM crRNA, 600-800 nM methylene blue-labeled DNA (MB-S) and 200-300 nM Cas12a were added to the above solution, and DEPC water was added to make the final volume 100-150 μL. Finally, Cas12a catalyzed degradation by reacting at 30-37 °C for 10-15 min, and heating at 65-70 °C for 10-15 min to inactivate the enzyme.
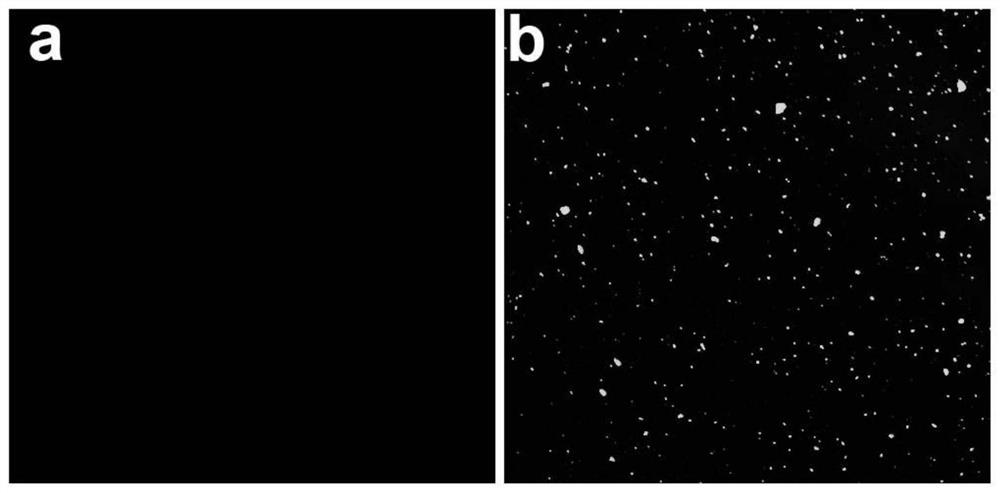
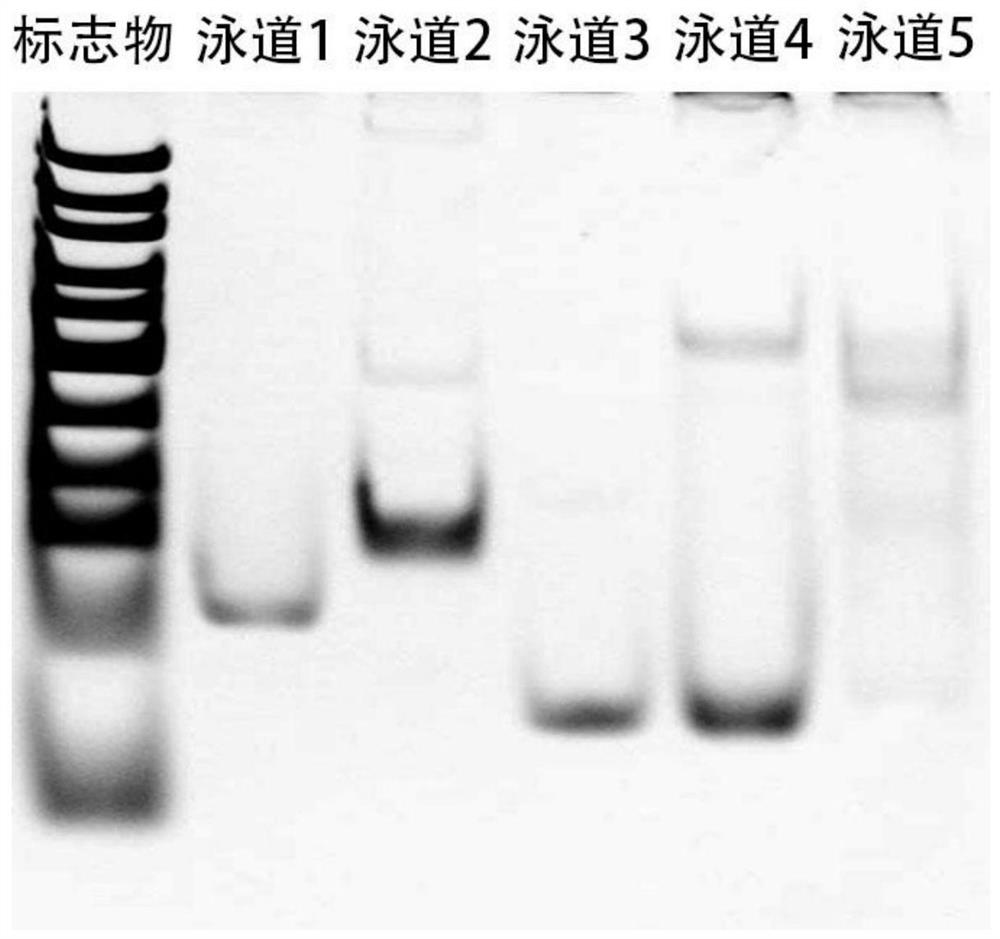
[0052] (c) Each sample was mixed with 1-2 μL of 6x loading buffer and loaded onto a 15% native polyacrylamide gel. After electrophoresis at 120V for 70-80 minutes in 1×Tris-borate-EDTA buffer, + The System Gel Imager ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3 Electrochemical detection of exosomes
[0060] (a) CD63 antibody-functionalized immunomagnetic beads (100-150 μL) were incubated with mesenchymal stem cell exosomes for 1.5-2 h at room temperature, and washed twice with PBS to remove exosomes that were not bound to the magnetic beads. Then, the captured exosomes were incubated with cholesterol-labeled catalytic hairpin DNA (cholesterol-H) for 45–50 min at room temperature, and washed twice with PBS to remove H chains that were not intercalated into the exosome membrane.
[0061] (b) Primer replacement reaction in 50-60 μL of reaction buffer (1.5-2 mM Tris-HCl, 1-1.5 mM (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 1mM KCl, 1.2~1.5mM MgSO 4 and 0.01% TritonX-100) at 30-37°C for 1.5-2 hours. It contains the desired exosomes inserted with cholesterol-H chain, 10-15 μM primer P chain, 0.8-1 unit μL-1Bst DNA polymerase and 100-150 μM dNTPs (dCTP, dTTP and dATP).
[0062] (c) 200-300 nM crRNA, 600-800 nM methylene blue-labeled DNA (MB-S) a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com