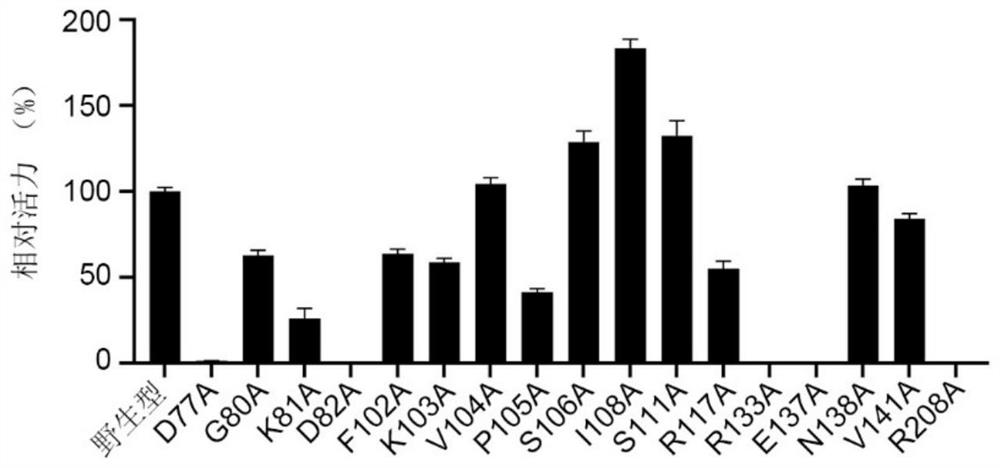
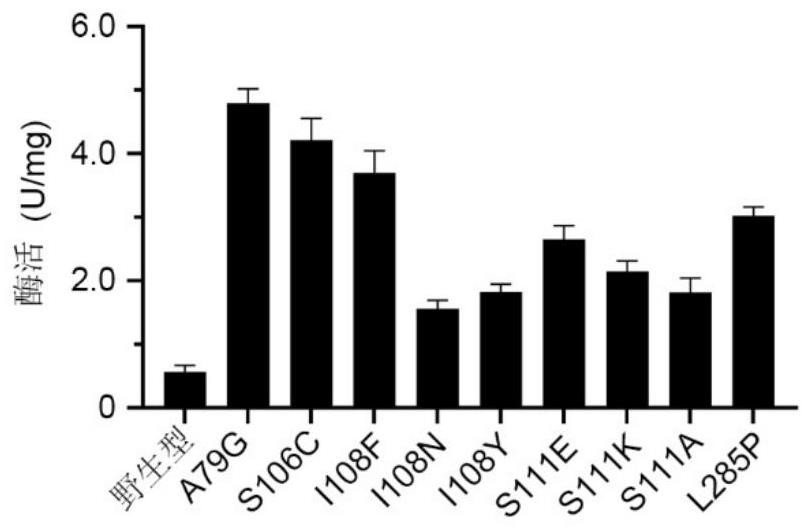
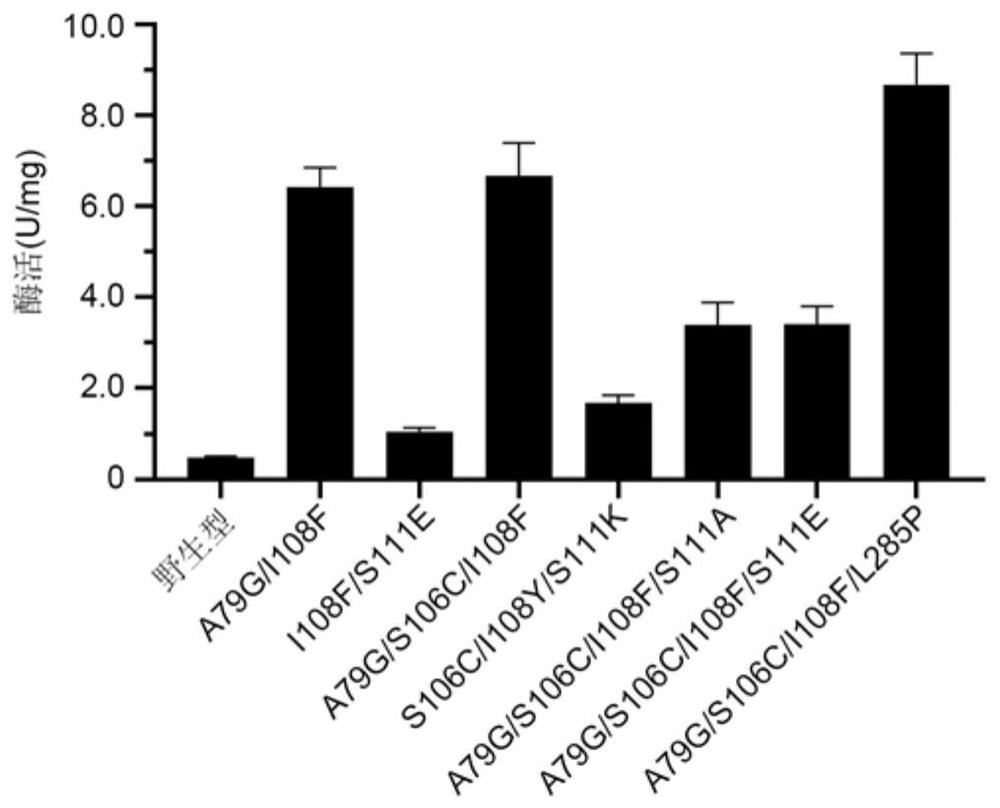
Polyphosphokinase mutant, engineering bacterium and application thereof
A polyphosphate kinase, mutant technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, enzyme and other directions, to achieve the effect of broad industrial application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Construction of wild-type Ecoli.BL21(DE3)-ChPPK
[0035] According to the PPK protein sequence (ChPPK, GenBank number: ABG57400.1) from Cytophaga hutchinsonii in GenBank, it was optimized for the codon preference of Escherichia coli, and a 6His tag was fused to the C-terminus of the sequence, provided by Beijing Qing Kebio Company (Beijing, China) synthesized a recombinant gene ChPPK sequence with a length of 930bp, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2.
[0036] The recombinant gene ChPPK was inserted under the T7 promoter of pET-28a(+) to obtain the expression plasmid pET28-ChPPK. Transform the expression plasmid into Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3), smear it on an LB plate containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin resistance, cultivate it at 37°C for 8-12 hours, and pick positive clones, which are wild Type Ecoli.BL21(DE3)-ChPPK for expression of recombinant ChPPK.
[0037] SEQ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Induced expression of wild-type Ecoli.BL21(DE3)-ChPPK and extraction of wild-type polyphosphate kinase
[0042] (1) Crude enzyme solution: Inoculate the wild-type Ecoli.BL21(DE3)-ChPPK obtained in Example 1 into LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin resistance, culture at 37°C for 12 hours at 200 rpm, and then Inoculate 1% (v / v) inoculum into fresh LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin resistance, cultivate at 37°C and 150 rpm until the OD600 of the bacteria = 0.6, and add a final concentration of 0.1 mM IPTG, induced at 28°C for 12h, centrifuged at 4°C, 8000rpm for 10min, discarded the supernatant, collected the precipitate, and obtained the wet cells expressing the recombinant ChPPK. The collected wet bacteria were resuspended in 50mM potassium phosphate buffer (PBS) with a pH of 7.2 in an amount of 40g / L to form a bacterial suspension, and crushed using an ultrasonic cell pulverizer with a crushing power of 50W, each working for 1s, and i...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: the mensuration of enzyme activity
[0045] The crude enzyme liquid prepared by 0.4mg embodiment 2 method or the polyphosphoric acid (PPA) of 0.05mg pure enzyme, final concentration 1.6g / L, the adenosine phosphate (AMP) of final concentration 2.25mM, the MgCl of final concentration 10mM 2 Added to 10mL of 50mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH7.5). The reaction solution was incubated at 37° C. for 5 min, and then 10 mL of 0.2 M phosphoric acid aqueous solution was added to terminate the reaction. The ATP content in the final solution was determined by HPLC method.
[0046] The instrument used for HPLC is Agilent 1260 Infinity II (Agilent Technologies Co., Ltd., USA), equipped with Agilent 2414 UV detector, Agilent 1525 pump, and Agilent 717 injector. The chromatographic column is XBridge C18column (C18, 5μm, 4.6×250mm, Waters, California, USA). The mobile phase rate was 1 mL / min, the UV detection wavelength was 254 nm, the mobile phase was potassium phosph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com