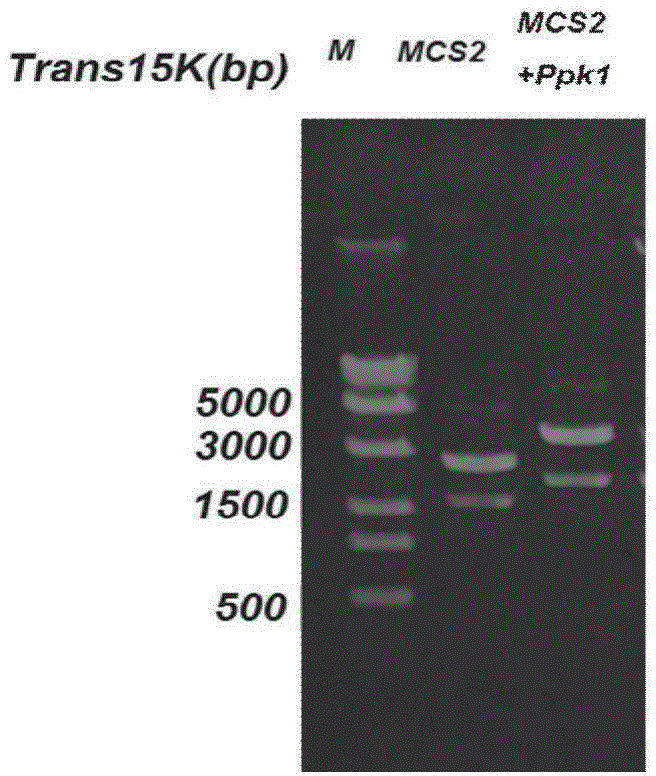
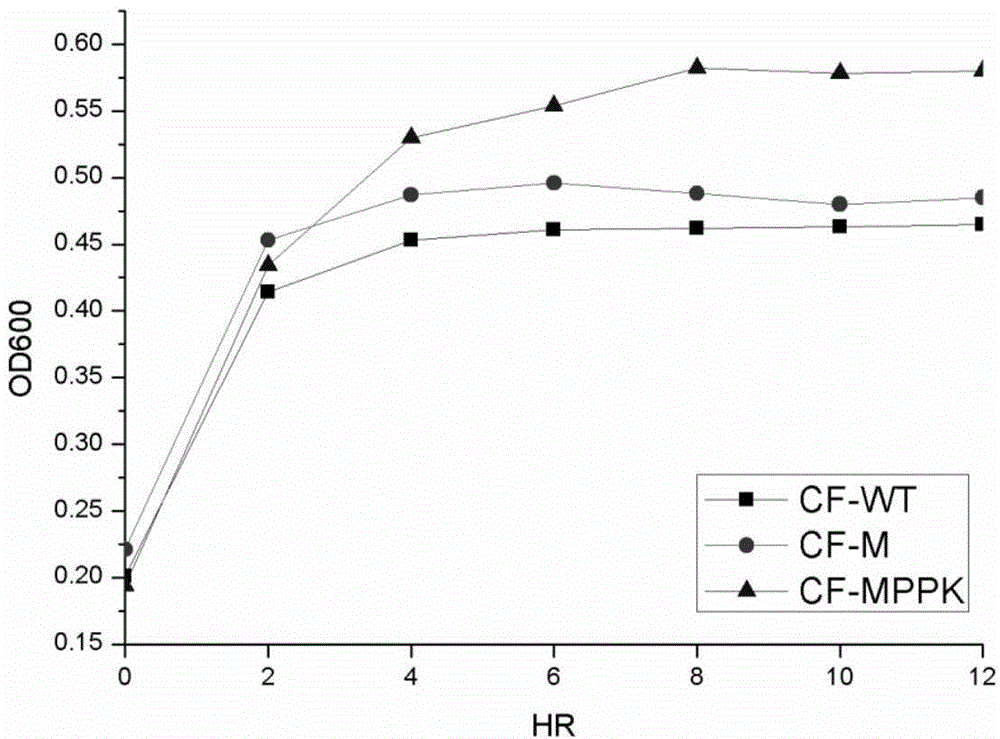
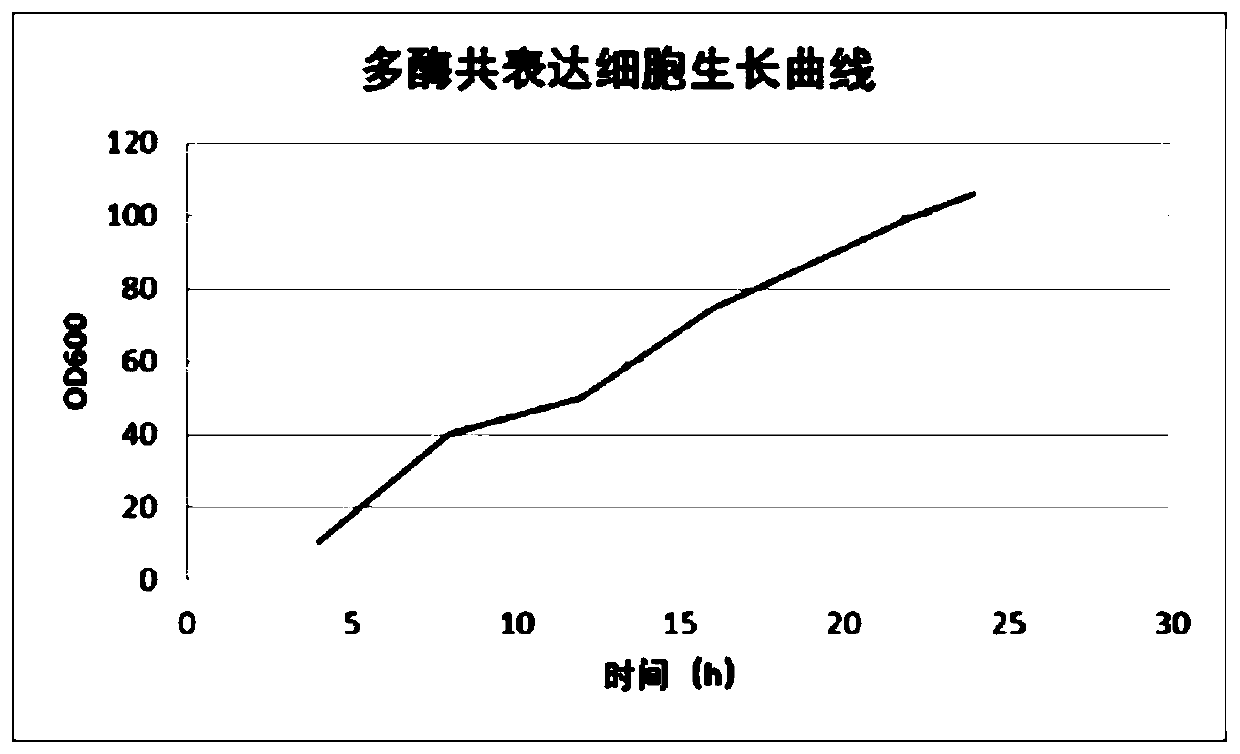
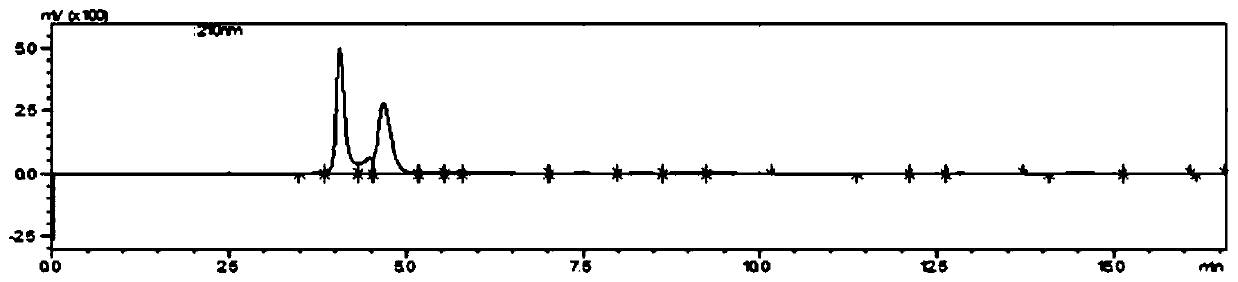
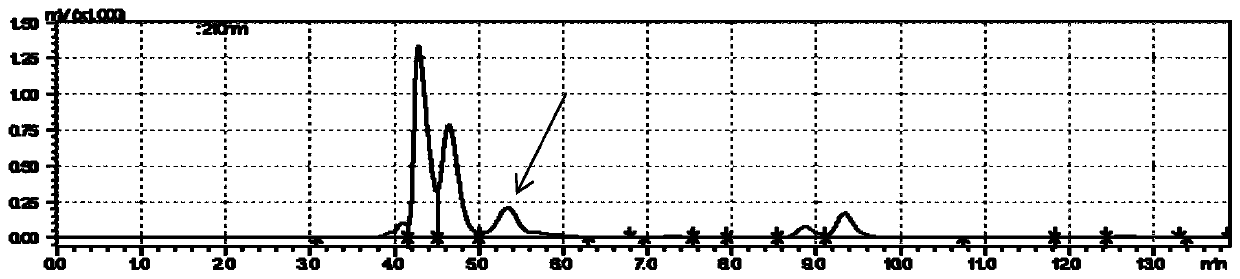
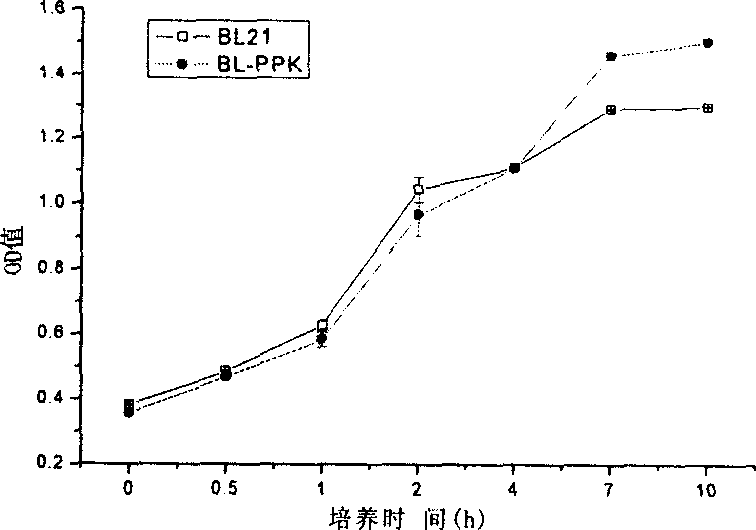
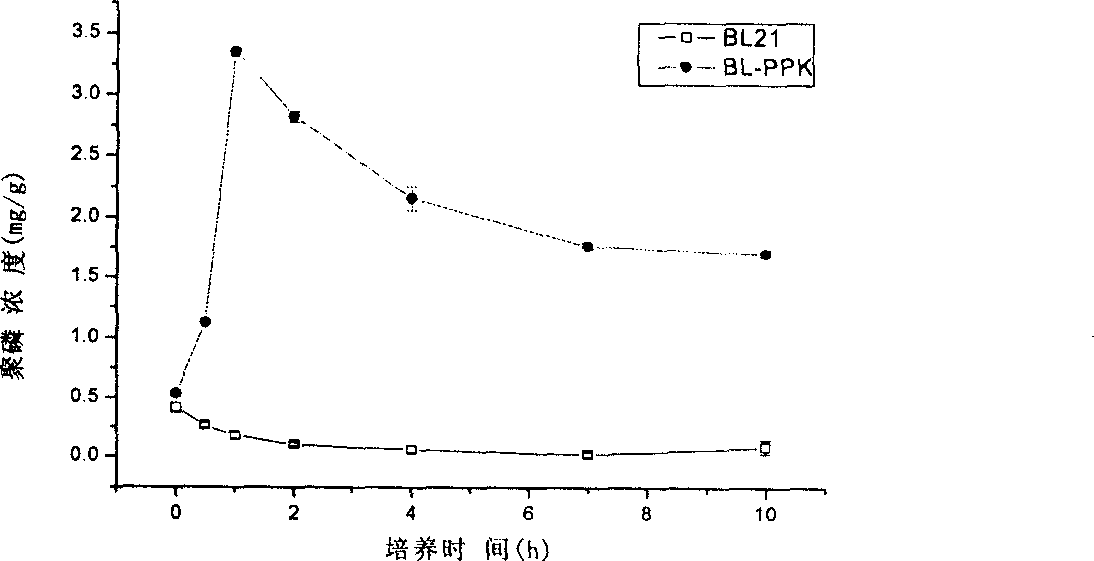
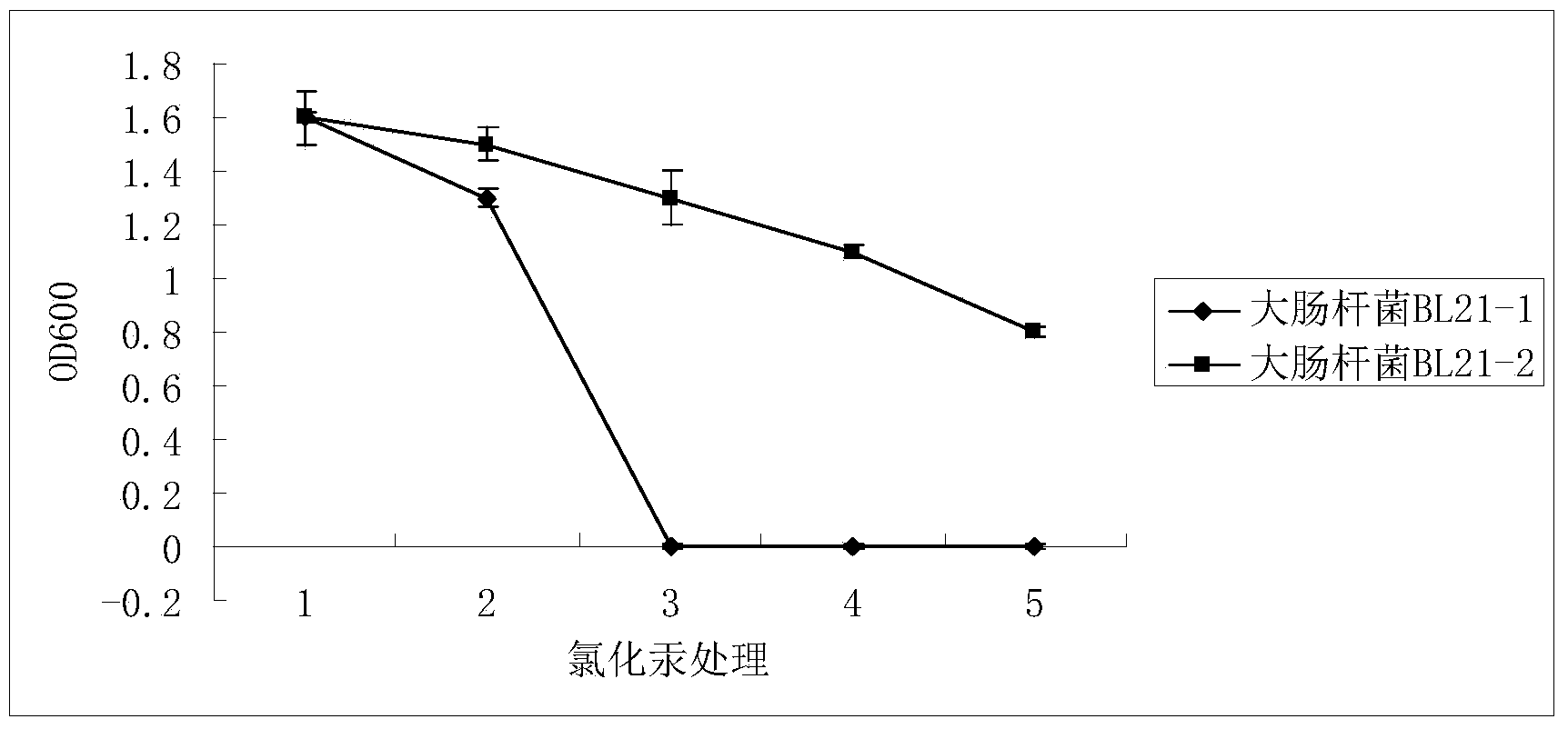
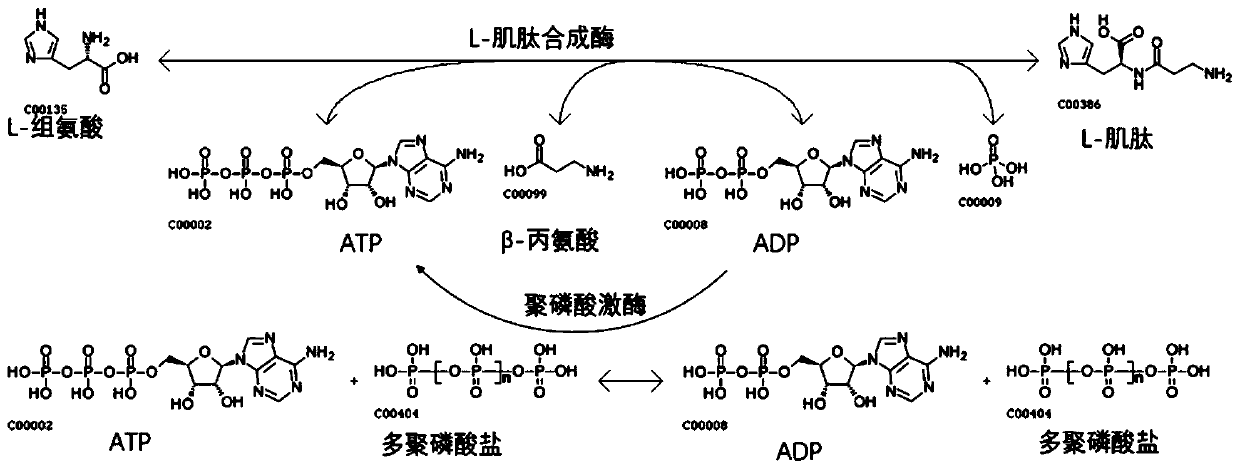
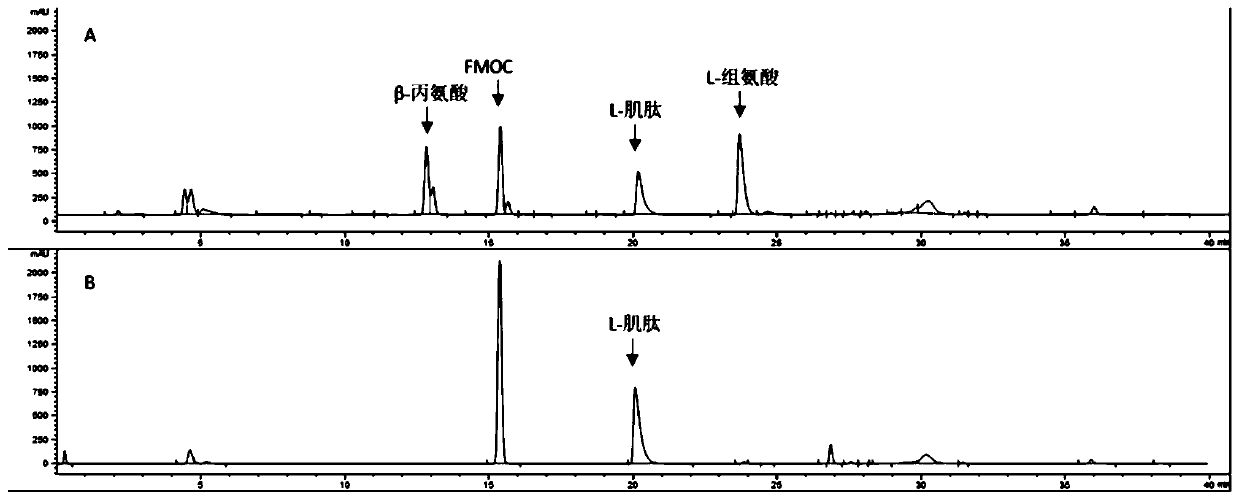
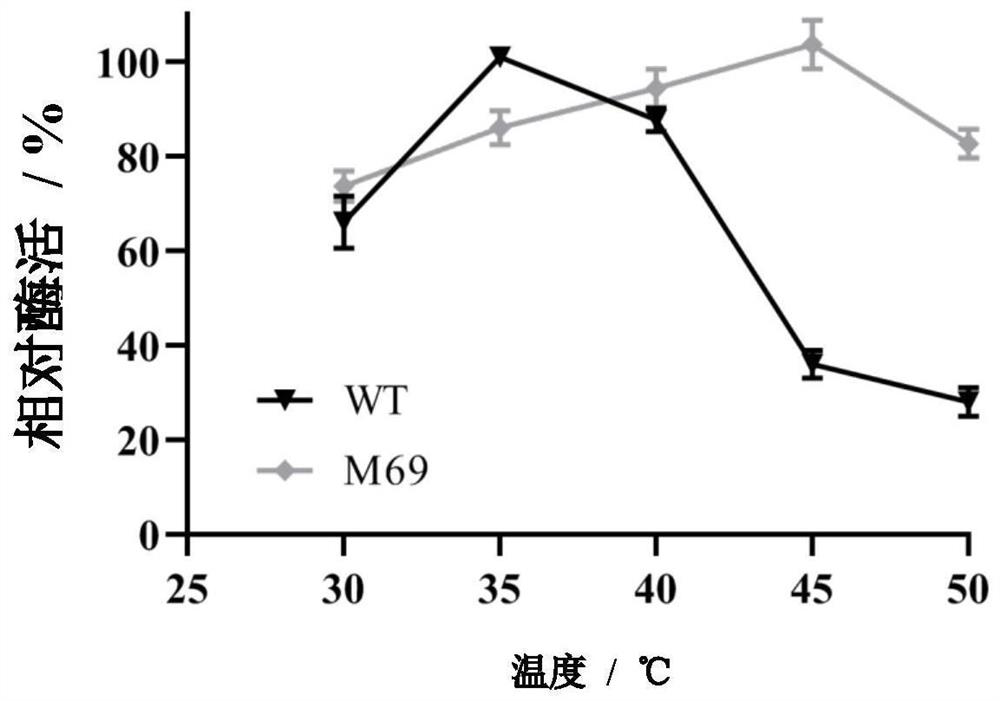
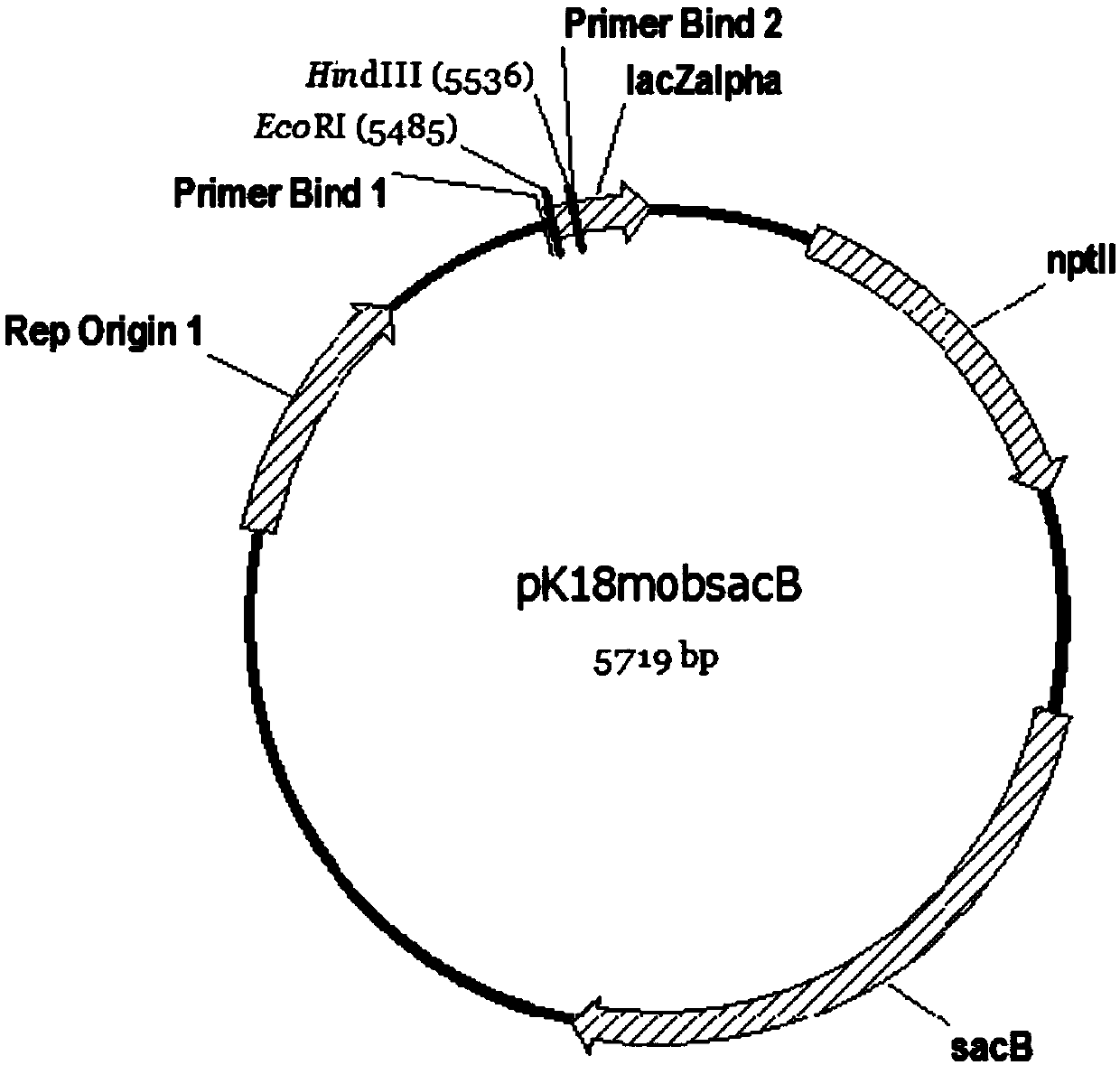
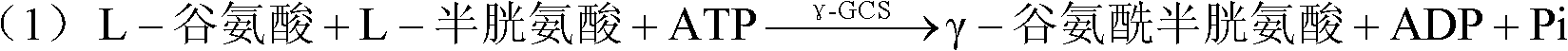Patents
Literature
62 results about "Polyphosphate kinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
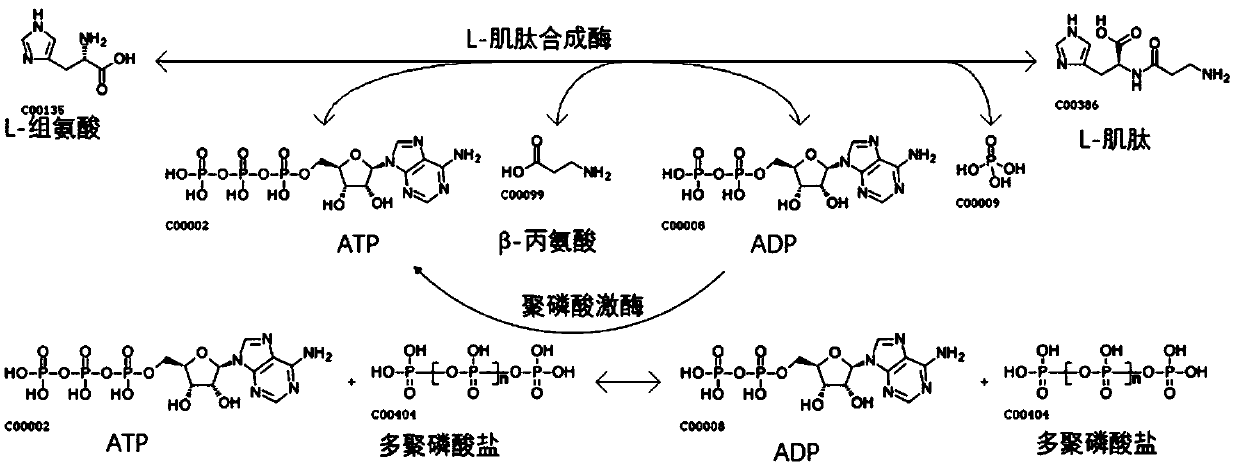
In enzymology, a polyphosphate kinase (EC 2.7.4.1), or polyphosphate polymerase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of polyphosphate from ATP, with chain lengths of up to a thousand or more orthophosphate moieties. ATP + (phosphate)ₙ ⇌ ADP + (phosphate)ₙ₊₁ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and polyphosphate [(phosphate)n], whereas its two products are ADP and polyphosphate extended by one phosphate moiety [(phosphate)n+1].
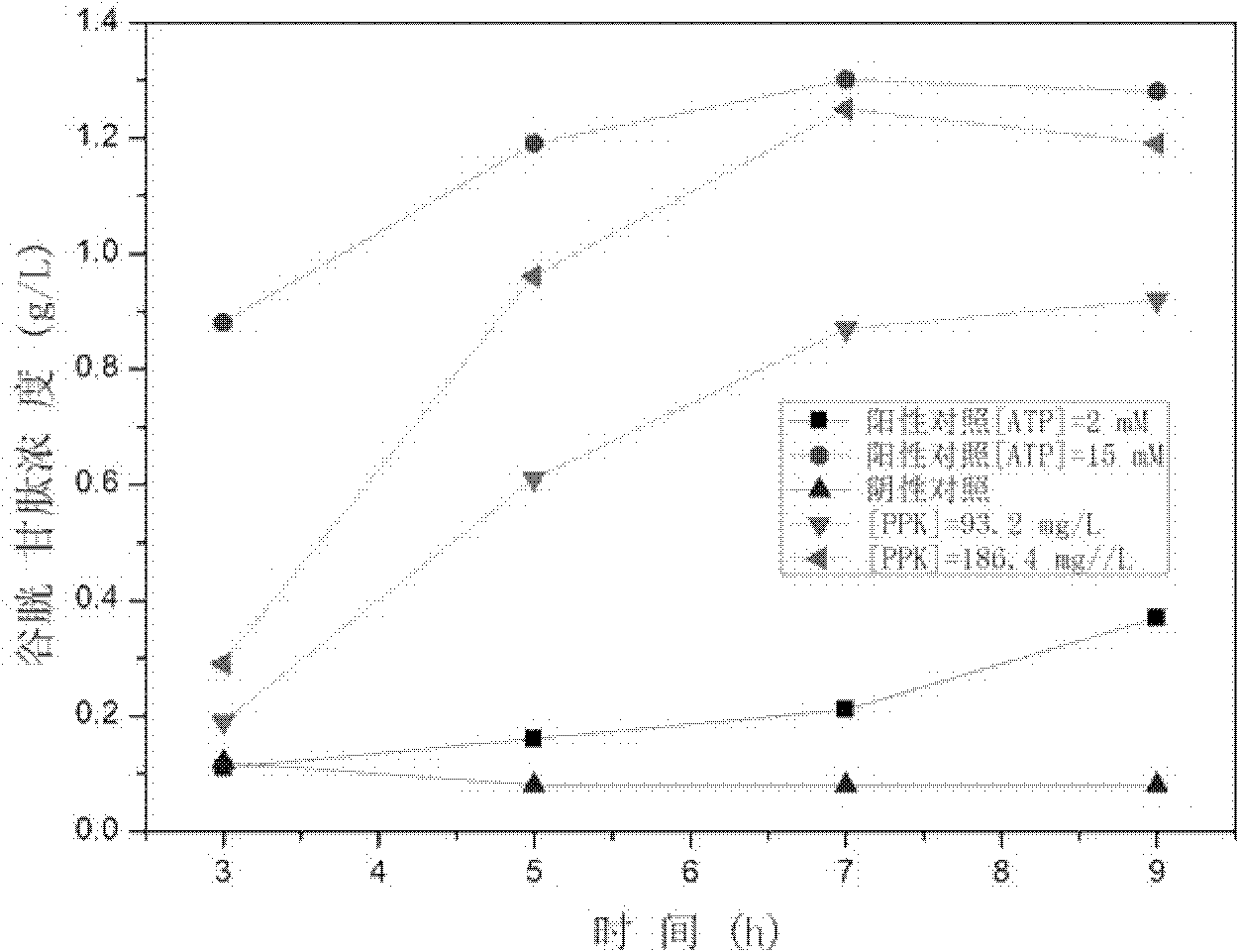
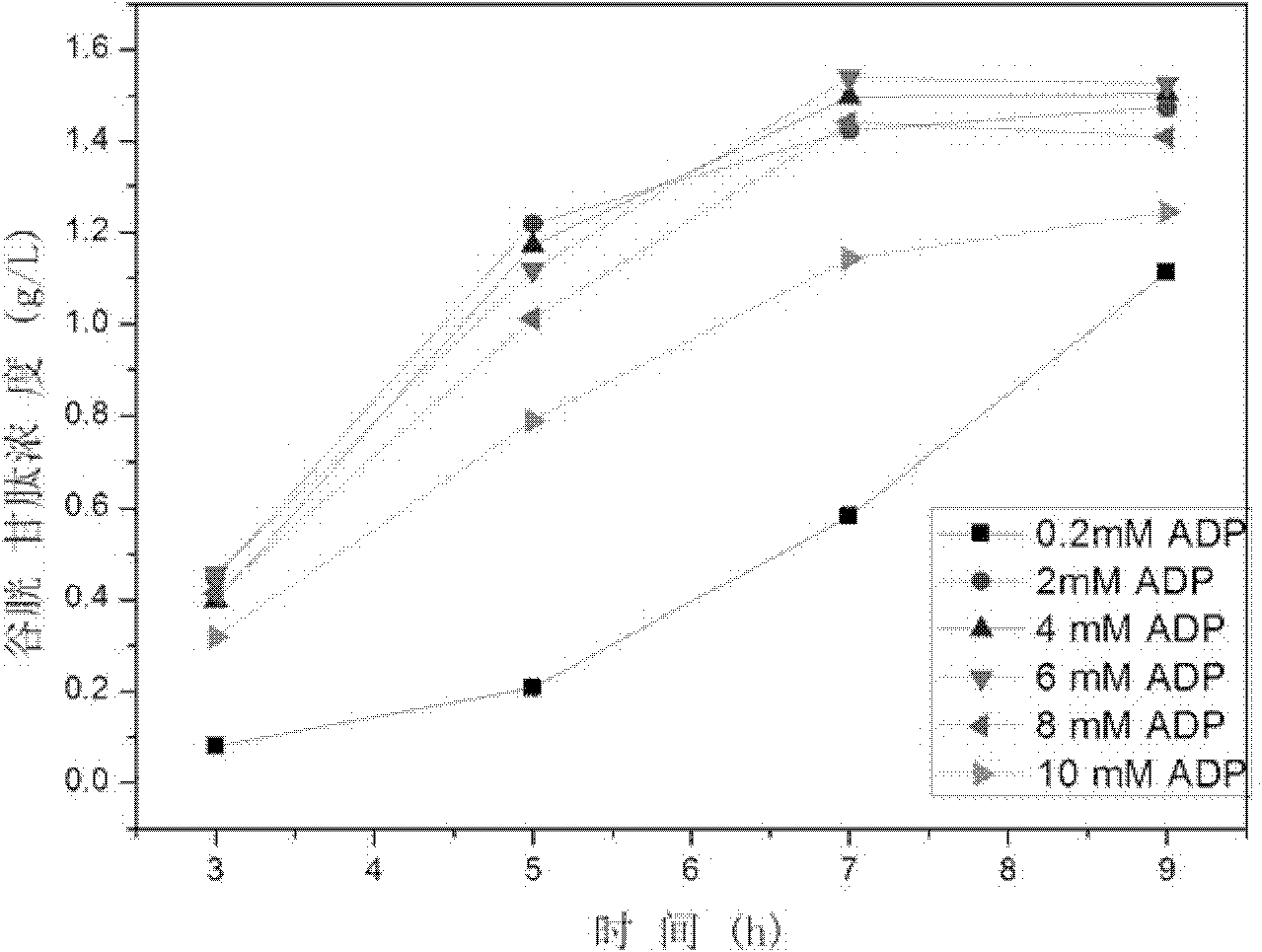
Method for synthesis of glutathione in vitro
ActiveCN102220400ALow costChemically stableFermentationGamma-Glutamylcysteine synthetaseAdenosine diphosphate
The invention relates to a method for synthesis of glutathione in vitro, comprising the step of: generating ATP (adenosine triphosphate) from ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and polyphosphoric acid compound under the catalysis of polyphosphate kinase; under the catalysis of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione synthetase, synthesizing glutathione in vitro by glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine with the energy provided by the ATP. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention can bring enzymes into complete contact with a substrate so as to improve the mass transfer efficiency and the utilization rate of enzymes. And the reaction system of the method is simple and strong in controllability. In addition, the method can solve the problem of great investment of ATP during production and reduce the production cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Inositol polyphosphate kinase genes and uses thereof
InactiveUS7067720B2Improve nutritional qualityReduce environmental impactSugar derivativesTransferasesNucleotidePhytic acid
This invention relates to newly identified polynucleotides and polypeptides in the phytic acid biosynthetic pathway, variants and derivatives of same; methods for making the polynucleotides, polypeptides, variants, derivatives and antagonists. In particular the invention relates to polynucleotides and polypeptides of the inositol polyphosphate kinase gene family. In particular this invention relates to using the newly identified polynucleotides and polypeptides to modulate the phytic acid biosynthesis in such a way as to decrease phytate and / or increase non-phytate phosphorous, especially in corn or soy animal feedstuffs.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Method for regenerating ATP(adenosine triphosphate) through enzyme method
InactiveCN105463043ALow costComply with temperature requirementsTransferasesFermentationPhosphoric acidHeterogeneous source
The invention relates to a method for regenerating ATP(adenosine triphosphate). A heterogeneous source is used for expressing polyphosphate kinase, and under catalyzing of polyphosphate kinase, polyphosphates with the low polymerization degree are used as phosphoric acid donors for regenerating ATP. Compared with an existing ATP regeneration method, adopted polyphosphate kinase is a normal-temperature enzyme, can be combined with multiple enzymes for promoting reaction coupling, and adopts a tripolyphosphate, a tetrapolyphosphate and a hexametaphosphate as the phosphoric acid donors, these polyphosphates are low in polymerization degree, common, easy to obtain and low in price, on the basis of simplifying the ATP regeneration process, feasibility of ATP regeneration is improved, and the ATP regeneration cost is reduced; activity of a PPK enzyme is not inhibited by polyphosphate concentration, and possibility is provided for industrialized large-scale production.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Citrobacter freundii with transformed phosphorus accumulating genes and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN104531599AEfficient removalConducive to survivalBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyBacteroides
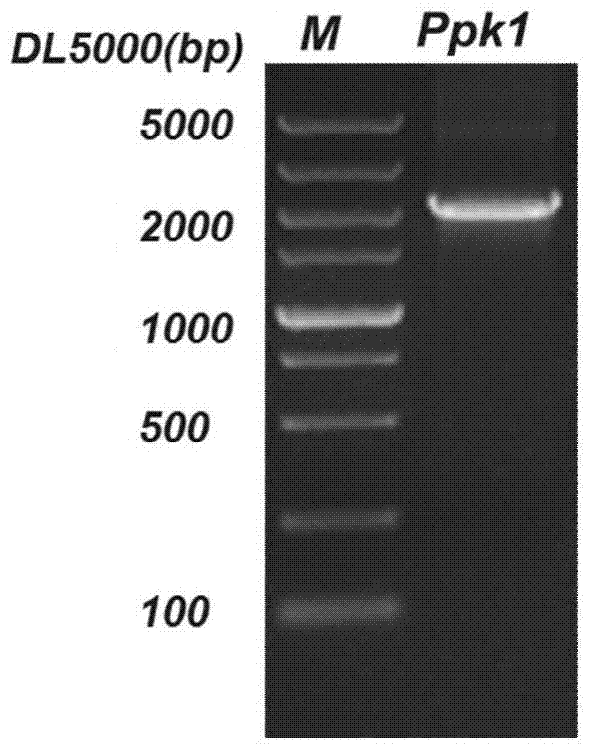
The invention discloses a Citrobacter freundii with transformed phosphorus accumulating genes. Polyphosphate kinase Ppk1 genes derived from the Citrobacter freundii are led into the Citrobacter freundii. The DNA of the Citrobacter freundii only contains Ppk1 genes, and the control way of the Ppk1 genes and Ppx genes is dual-cis-trans cotranscription. The phosphorus accumulation ability of bacteria with the characteristics can be improved by means of the Ppk1 with host bacteria as a receptor to express the source. The invention further discloses a construction method of the Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes and the application of the Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes in waste water dephosphorization. The Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes has the advantage of being high in dephosphorization ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for preparing sialyllactose
InactiveCN110396532ASimple ingredientsClear ingredientsFermentationSialyltransferaseCMP-Sialic Acid Synthetase
The invention discloses a method for preparing sialyllactose, and relates to the technical field of preparation of sialyllactose. The method for preparing sialyllactose disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of adding kinase to a reaction system containing a substrate, and performing an enzyme catalysis reaction to prepare the sialyllactose, wherein the kinase comprises CMP kinase, polyphosphate sialic acid synthase and sialytransferase; and the substrate comprises CMP, polyphosphate, sialic acid and lactose. The method adopts various kinase namely the CMP kinase, the polyphosphate kinase, the CMP-sialic acid synthetase and sialytransferase to catalyze the corresponding substrate to prepare the sialyllactose. The method has the characteristics of being high in yield, low in cost, short in cycle and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method of synthesizing L-carnosine using L-amino acid ligase by one-step method
ActiveCN109593805AAchieve recyclingWide variety of sourcesTransferasesNucleic acid vectorPhosphorylationL-Carnosine
The invention discloses a method of synthesizing L-carnosine using L-amino acid ligase by a one-step method. The method comprises the steps of taking beta-alanine, L-histidine, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and polyphosphate as raw materials, and MgCl2 as an activator, adding L-amino acid ligase and polyphosphate kinase, and synthesizing L-carnosine through an enzymatic reaction and coupled coupleunder conditions of a pH of 6.5-8.5 and a temperature of 30-45 DEG C. According to the method, a sequence optimized L-amino acid ligase gene is successfully expressed in escherichia coli, and beta alanine and L-histidine can be catalyzed to synthesize L-carnosine at one step. A substrate is not required to be methylated or subjected to group protection; ATP required by a catalytic reaction is continuously regenerated by allowing polyphosphate kinase to catalyze phosphorylation of ADP (adenosine diphosphate); cyclic regeneration of ATP can be achieved only by consuming a small amount of ADP; and a renewable raw material, sodium hexametaphosphate, is wide in source, low in cost, simple to operate and easy in large-scale production.
Owner:苏州百因诺生物科技有限公司
Construction method for polyphosphate kinase gene transformed Escherichia coli
InactiveCN1876809AProof of feasibilityEfficient removalBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBamHIGene clone
The invention discloses a construction approach for bacillus coli of transpolyphosphokinase gene, in which the said method includes gene-clone and carrier-construction; the clone includes extracting master DNA of bacillus coli; designing primers; augmenting ppk gene; restructuring the augmented object gene into clonic carrier pMD18-T and converting bacillus coli DH5 alpha; the construction includes adopting restriction enzymes of BamHI and HindIII bisenzyme to cut pMD18-T plasmid with ppk object gene and idle expression carrier pET-28a(+); directionally connecting the object gene by T4 to the expression carrier pET-28a(+), then converting the DH5 alpha; by the PCR and bisenzyme pressure methods screening and verifying the positive recon; extracting the recombination plasmid Pet28a-PPK and converting the acceptor strain BL21(DE3). The invention is of simple process and the obtained gene has efficient phosphorous removal ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof in production of L-glutamine
ActiveCN113684165AIncrease productionHigh glycosamine conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesBacterosiraGlutamic acid
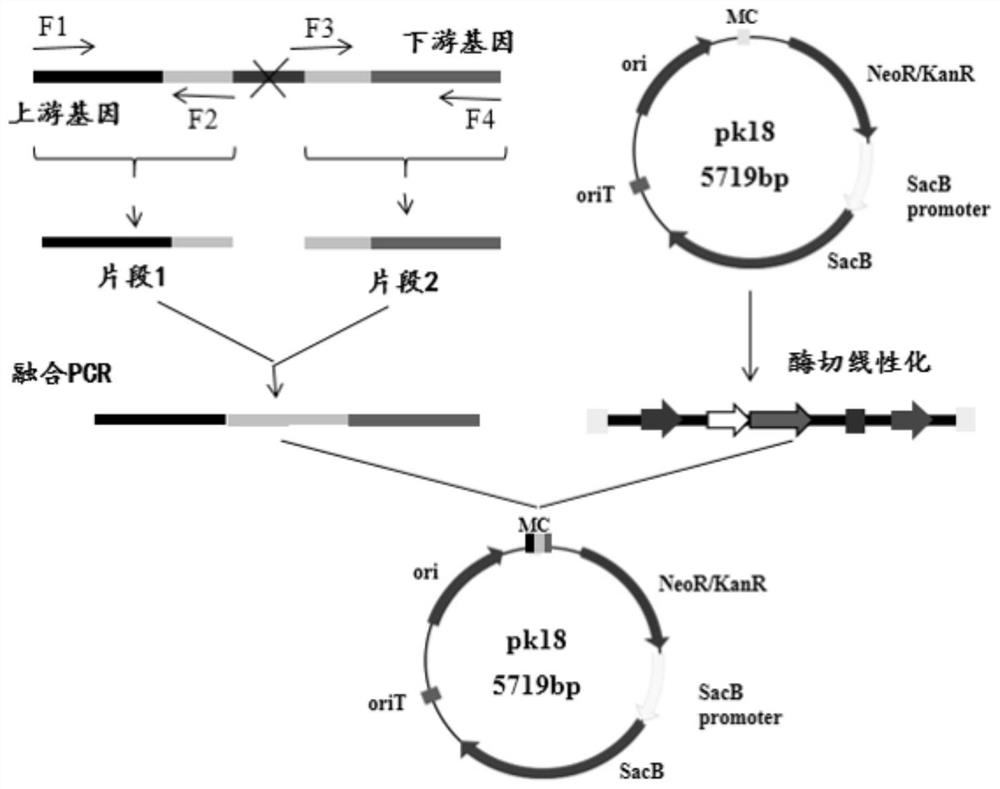
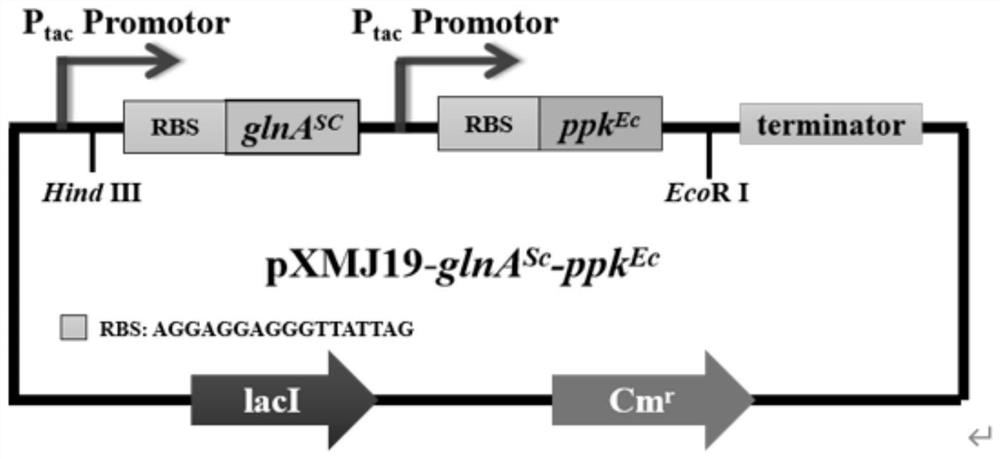
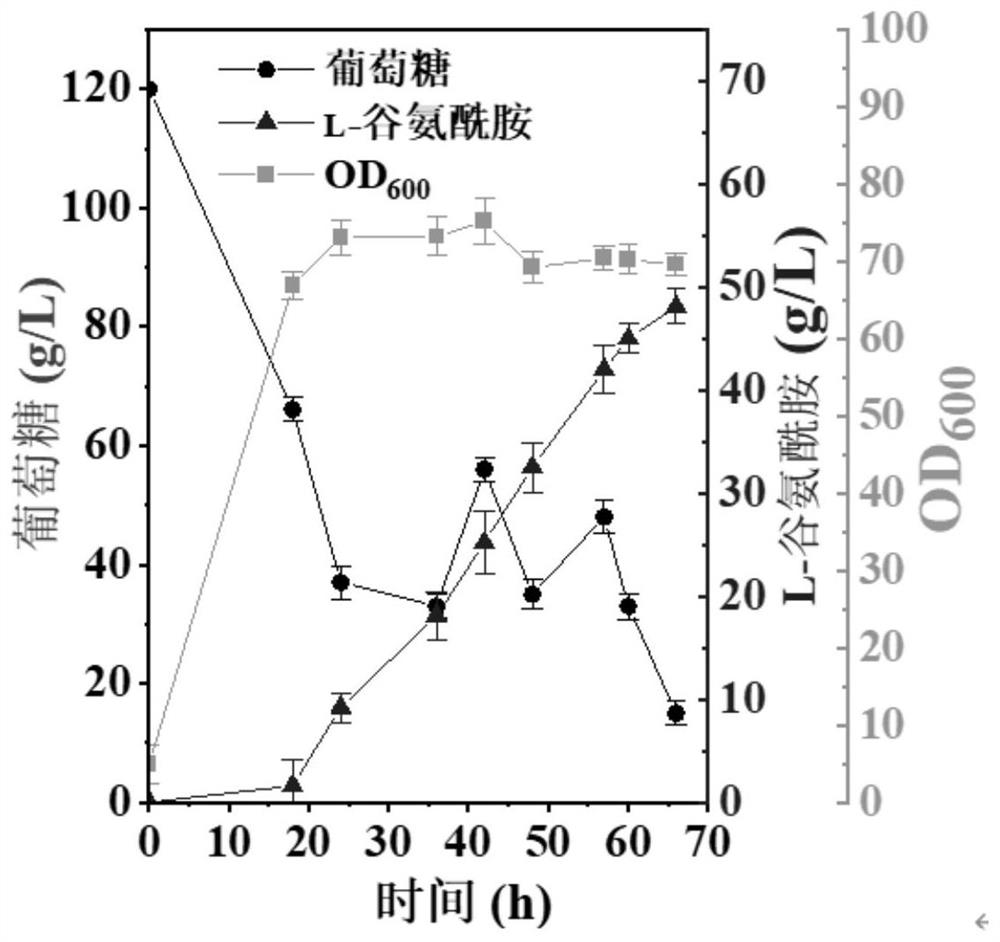
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof in production of L-glutamine, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The activity of gamma-glutamate kinase, glutamic acid secretion mechanical channel protein and adenosine acylase of glutamine synthetase in cells of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is lost, and plasmid pXMJ19 is used for co-expressing the glutamine synthetase from saccharomyces cerevisiae and polyphosphate kinase from escherichia coli. The invention provides the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum CGQ03 / pXMJ19-glnASc-ppkEc capable of producing the L-glutamine at high yield; the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is inoculated into a 5L fermentation tank and is fermented for 66h, so that the yield of the L-glutamine in fermentation liquid reaches 73.5 + / -3.1g / L and the conversion rate of glucosamine reaches 0.368 + / -0.034.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for regenerating ATP using rationally designed enzyme
ActiveCN105624238ALow costComply with temperature requirementsTransferasesFermentationPhosphoric acidTetra
The invention relates to a method for regenerating ATP using a rationally designed enzyme. Through rational design after sequence alignment, polyphosphate kinase from sinorhizobium meliloti is mutated and heterologously expressed; and under the catalysis of the polyphosphate kinase, the regeneration of ATP is realized by adopting polyphosphate with low polymerization degree as a phosphoric acid donor. Compared with existing ATP regeneration method, the polyphosphate kinase used in the invention is a normal-temperature enzyme which can react for coupling with multiple enzymes; the enzyme can take tetra-polyphosphate as a phosphoric acid donor; compared with phosphoric acid with high polymerization rate, the tetra-polyphosphoric acid is more common and easily available; and the feasibility of ATP regeneration is increased on the basis of simplifying the ATP regeneration process, and the cost of ATP regeneration is reduced. The activity of PPK enzyme is not inhibited by the polyphosphate concentration, and industrial large-scale production is possible.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
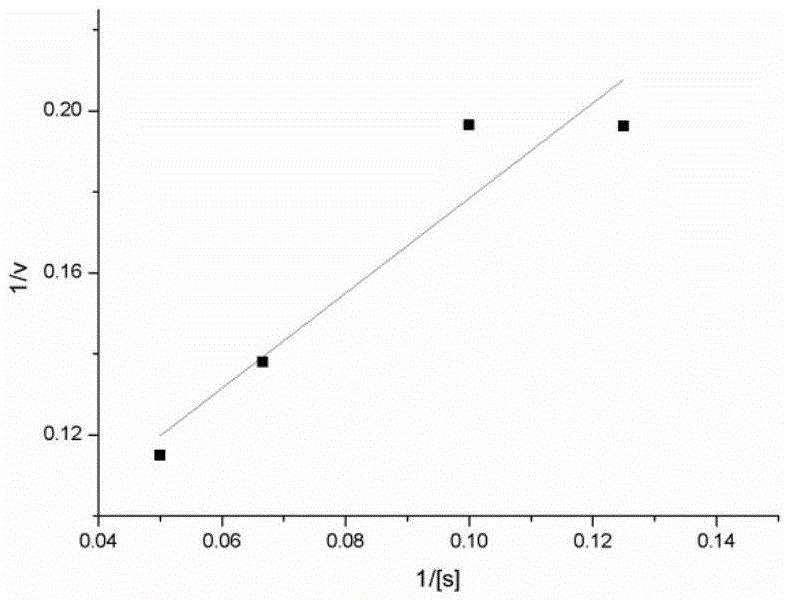
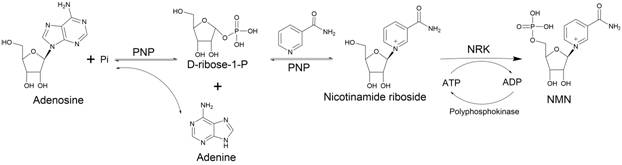
Enzymatic synthesis method of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide
ActiveCN112795606AImprove conversion rateLow costFermentationEnzymatic synthesisNicotinamide riboside
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses an enzymatic synthesis method of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide. According to the method, adenosine and phosphate serve as starting materials, D-ribose-1-phosphoric acid and nicotinamide ribose intermediates are generated under enzyme catalysis of an enzyme composition of PNP enzyme and NRK enzyme, NMN is obtained through an irreversible reaction finally, and the substrate conversion rate can be greatly increased; the whole reaction system only needs two enzymes to participate, and the by-product adenine can be recycled; meanwhile, only one molecule of ATP needs to be consumed while one molecule of NMN is generated, and ADP is regenerated into ATP by adding polyphosphate kinase, so that the cost of the whole process is greatly reduced.
Owner:珠海瑞德林生物有限公司
Use of transgenic terrestrial plants in eutrophic water restoration
InactiveCN102398990AReduce soluble phosphorus contentBiological water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationRosaceae
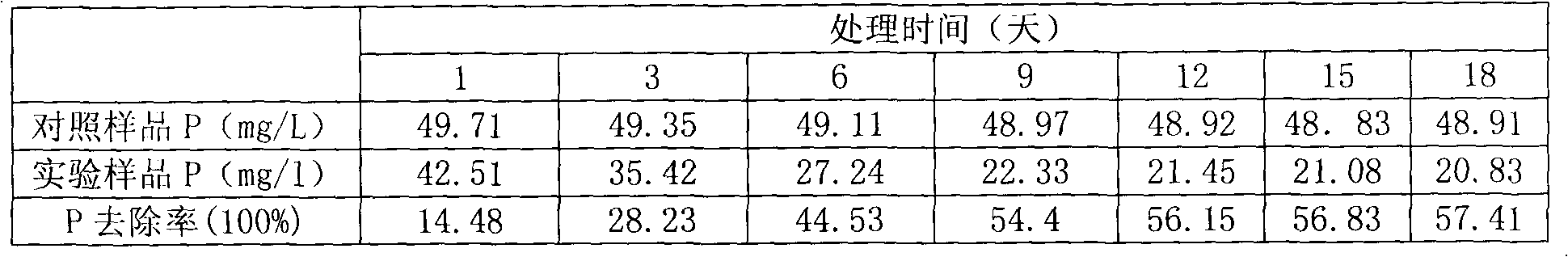
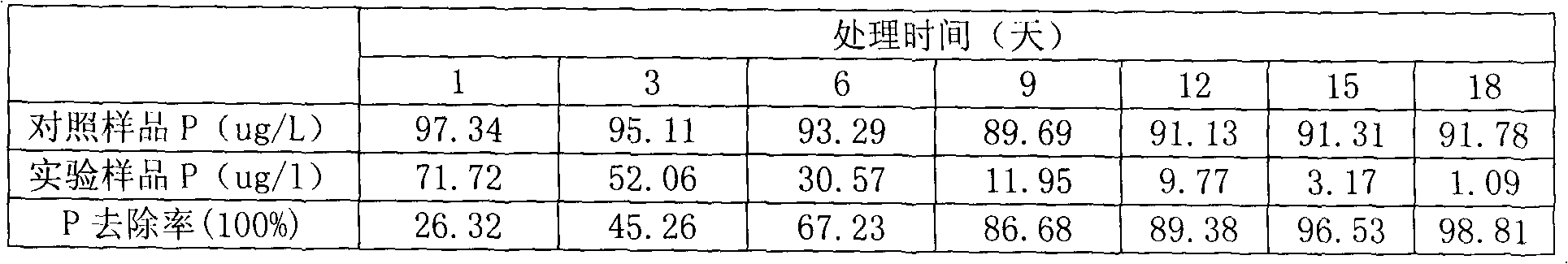
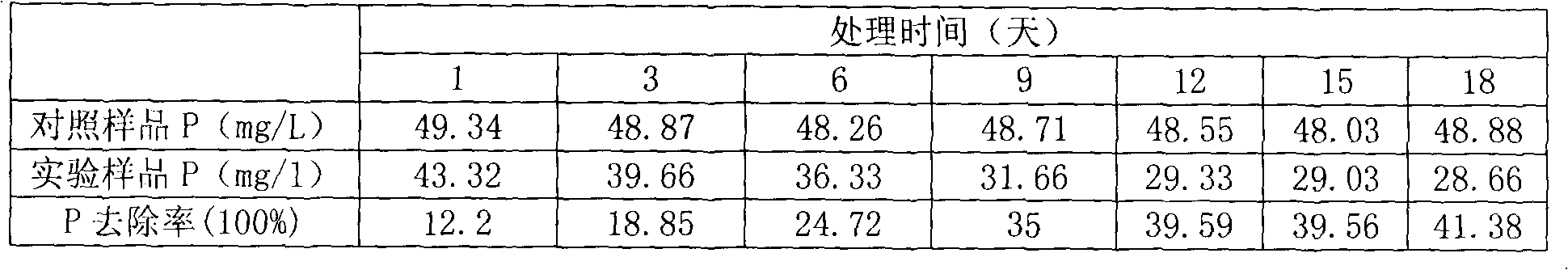
The invention belongs to the field of biological phosphorus accumulating technology, and relates to a method for removing soluble phosphorus from eutrophic water by using transgenic terrestrial plants. According to the present invention, the transgenic terrestrial plants comprise tobacco in Solanaceae and strawberry in Rosaceae, and the imported exogenous gene is polyphosphate kinase gene (ppk); after the transgenic plants are induced by water roots, a foam plate sealed with a nylon net is adopted to fix the transgenic plants, which float on the water surface; in the high concentration soluble phosphorus (50 mg / ml)-containing water, the maximum phosphorus removal rates of the transgenic tobacco and the transgenic strawberry are respectively 57.4% and 41.38%; in the low concentration soluble phosphorus (100 mug / ml)-containing water, the maximum phosphorus removal rates of the transgenic tobacco and the transgenic strawberry are respectively 98.8% and 94.3%. The method of the present invention is applicable for efficient biological removal of the phosphorus, biological treatment of the phosphorus-rich wastewater, biological restoration of the eutrophic water, and biological purification of the eutrophic water.
Owner:许雷
A strain of Citrobacter freundii transgenic for phosphorus accumulation gene and its construction method and application
ActiveCN104531599BEfficient removalConducive to survivalBacteriaWater contaminantsBacteroidesGemella
The invention discloses a Citrobacter freundii with transformed phosphorus accumulating genes. Polyphosphate kinase Ppk1 genes derived from the Citrobacter freundii are led into the Citrobacter freundii. The DNA of the Citrobacter freundii only contains Ppk1 genes, and the control way of the Ppk1 genes and Ppx genes is dual-cis-trans cotranscription. The phosphorus accumulation ability of bacteria with the characteristics can be improved by means of the Ppk1 with host bacteria as a receptor to express the source. The invention further discloses a construction method of the Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes and the application of the Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes in waste water dephosphorization. The Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes has the advantage of being high in dephosphorization ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Recombinant plasmid for eliminating industrial wastewater mercury pollution, construction method, recombinant engineering bacterium and application
InactiveCN103525849AImproved mercury toleranceImprove toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesConserved sequence
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid for eliminating industrial wastewater mercury pollution, a construction method, a recombinant engineering bacterium and an application. The recombinant plasmid is established by inserting tobacco chloroplast rrn16 gene strong promoter, ribosome binding site conserved sequence of 5'UTR sequence of escherichia coli T7 phage gene 10, 3'-end non-coding area of tobacco chloroplast rps16 gene, enterobacter aerogenes polyphosphate kinase gene ppk and pseudomonas K-62 strain on the basis of plasmid pET28a and by eliminating mer operon of merA and merG. Organic mercury and inorganic mercury in wastewater are transferred into bacterial cells through merT-merP, the organic mercury is degraded into divalent mercury through merB1 and merB2, the divalent mercury is chelated into the cells through ppk, the toxicity of mercury to the bacteria cells is reduced, mercury in the wastewater is accumulated inside the bacterial cells, and mercury pollution in the waster is eliminated through collecting the recombinant engineering bacteria.
Owner:舒海燕 +1
Method for synthetizing L-carnosine by one-step method and truncated L-carnosine synthetase
The invention discloses a method for synthetizing L-carnosine by a one-step method and truncated L-carnosine synthetase. According to the method, beta-alanine, L-histidine, ATP and polyphosphate are used as raw materials, MgCl2 is used as an activator, L-carnosine synthetase and polyphosphate kinase are added, and through an enzymatic reaction under the condition of pH being 6.5-8.5 and the temperature being 30-45 DEG C, the carnosine is coupled, catalyzed and synthetized. According to the method disclosed by the invention, escherichia coli is used for respectively expressing the truncated L-carnosine synthetase (of which the amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQID No.3) and the polyphosphate kinase, through purification, mixing is performed, a dual-enzyme coupling system is formed, and the L-carnosine synthetase in truncated expression can catalyze the L-carnosine synthetized from beta-alanine and L-histidine; besides, accompanied with ATP dephosphorylation, ADP is formed, the polyphosphate kinase catalyzes polyphosphate transphosphorylation groups, and ATP is formed for the ADP, so that circulation and regeneration of the ATP can be realized; and through the dual-enzyme couplingsystem, a reaction is performed under the appropriate reaction condition, so that carnosine is obtained. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the raw materials are low in cost, the enzymatic conversion time is short, the operation is simple and convenient, and the production cost is low.
Owner:苏州百因诺生物科技有限公司
Mutant of gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase, and encoding gene, amino acid sequence and application of mutant
ActiveCN113151198AImprove thermal stabilityHigh activityMicroorganism based processesLigasesTheanineCatalytic effect
The invention discloses a mutant of gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase, and an encoding gene, amino acid and application of the mutant to production of theanine. Specifically, the mutant of the gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase is obtained through a genetic engineering method. The optimum temperature of enzyme is increased by 10 DEG C while the thermal stability of the gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase is improved, the mutant can play a very good catalytic effect without being in a buffer salt solution, and meanwhile, the theanine is efficiently synthesized by utilizing the mutant through a method of coupling polyphosphate kinase; and according to the method, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) regeneration can be implemented while the theanine is synthesize by catalysis, and an effective way is provided for enzymatic industrial production of the theanine.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
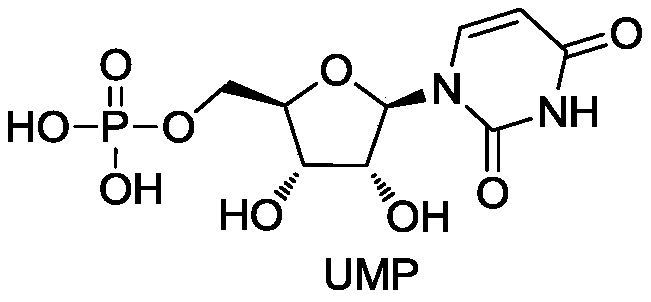
Method for preparing uridylic acid by enzyme method
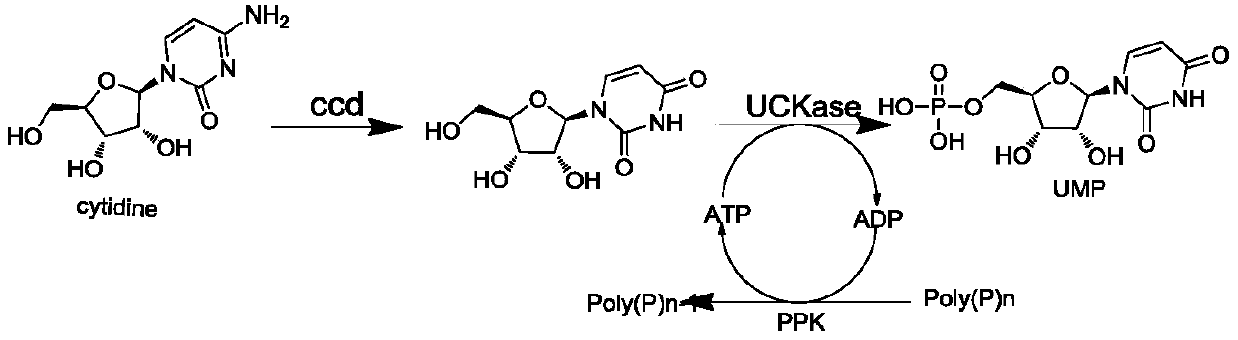
InactiveCN110885812APromote safe productionSafe preparationHydrolasesTransferasesKinaseCytidine deaminase
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy and biochemical engineering, discloses an enzyme composition for uridylic acid production and a method for preparing uridylicacid by an enzyme method. The enzyme composition is prepared by cytidine deaminase, polyphosphate kinase and uridine-cytidine kinase. The three enzymes are reasonably combined to efficiently catalyzeand prepare uridylic acid. The enzyme composition disclosed by the invention can be recycled and is low in cost; and energy-saving and environment-friendly effects are realized. According to the invention, the cytidine is used as a substrate and the enzyme composition for uridylic acid production is added, so that the uridylic acid is prepared with low cost and high safety and reliability; the cost of the existing route is reduced; and the large-scale production is realized. The application of uridylic acid in fields of biocatalysis and medicines is guaranteed.
Owner:杭州唯泰生物药业有限公司 +1
Method for producing hydrogen by bacterial fermentation
InactiveCN101597624AIncrease conversion rateReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismPhosphate ion
The invention discloses a method for producing hydrogen by bacterial fermentation, which is implemented by culturing hydrogen-producing microorganism in a basic culture medium added with phosphate radical ions to produce hydrogen under the conditions of (1) complete anaerobic culture and (2) culture with the concentration being 0.1-7.6% according to percent by volume, and then culture under complete anaerobic condition. The phosphate radical ions are H2PO4, HPO4, PO4, pyrophosphate radical or polyphosphate radical ions. The concentration of the phosphate radical ions is 0.01-0.15mol / L in respect to the basic culture medium. The hydrogen producing microorganism is enteroaerogen. The enteroaerogen is enteroaerogen or enteroaerogen expressing polyphosphate kinase. The hydrogen production method of the invention can improve the conversion yield of hydrogen and reduce production cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Production method for substance using atp
A method of producing a substance includes synthesizing a molecule at least by mixing substrates, a synthase, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a polyphosphate kinase 2, and a polyphosphoric acid mixture. The polyphosphoric acid mixture includes 50% or more of polyphosphoric acid with a degree of polymerization of not less than 15. Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is generated from the ATP during the synthesis. The synthesis is coupled with an ATP regeneration reaction in which the ATP is regenerated by the polyphosphate kinase 2 from the ADP and the polyphosphoric acid.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Recombinant genetically engineered bacterium for producing gastrodin, construction method and application
PendingCN113604414AImprove conversion rateIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationSucrose synthetaseEngineered genetic
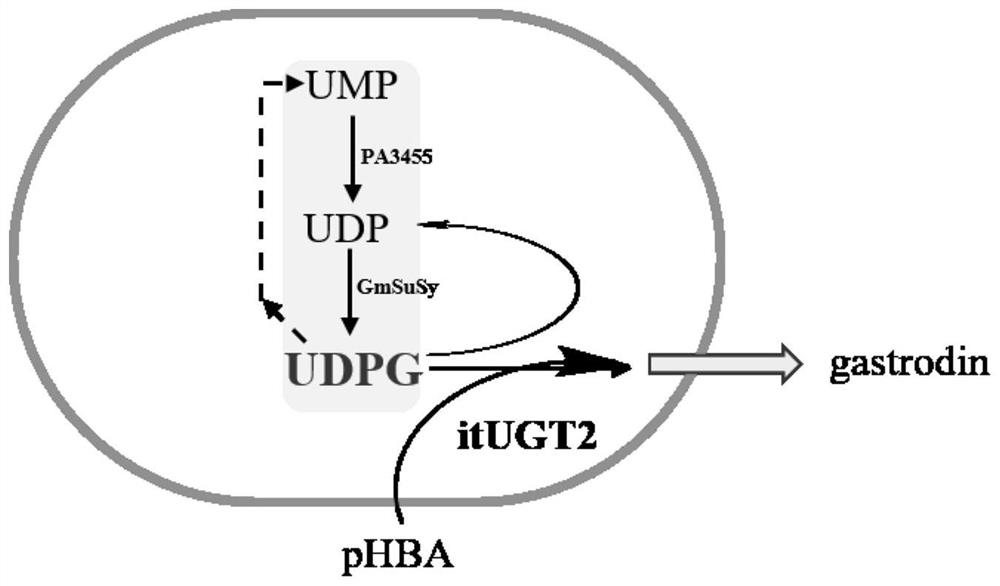
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a recombinant genetically engineered bacterium for producing gastrodin, a construction method and application. According to the recombinant genetically engineered bacterium, glycosyl transferase is introduced into a host, glycosyl transferase is expressed through a host strain to catalyze a substrate to synthesize gastrodin, sucrose synthase and polyphosphate kinase are introduced into the host, synthesis and cyclic regeneration of UDPG are achieved, the amount of glycosyl donor of a glycosylation reaction is increased, a whole-cell catalytic conversion method is constructed, on the basis that no extra UPDG is added, the conversion rate of gastrodin reaches up to 95% or above, the gastrodin yield is increased, and the gastrodin production cost is reduced.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
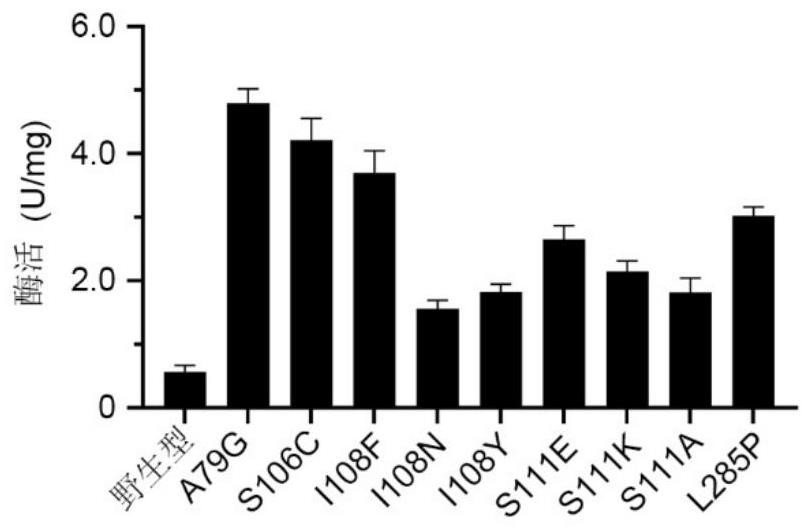
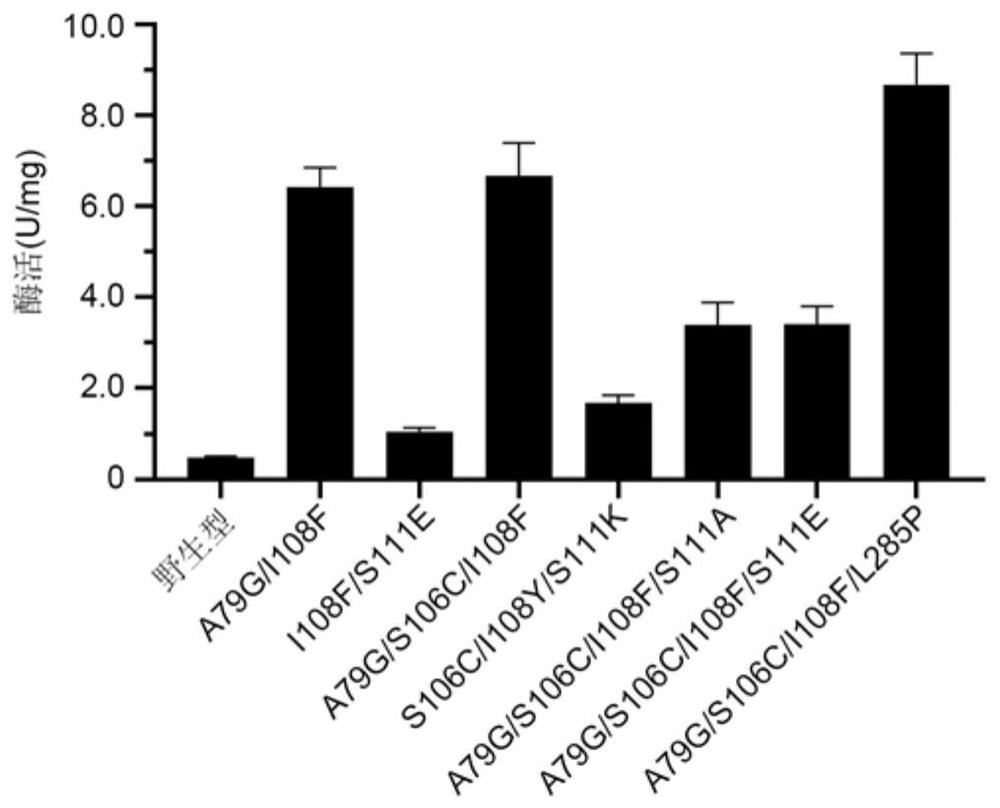
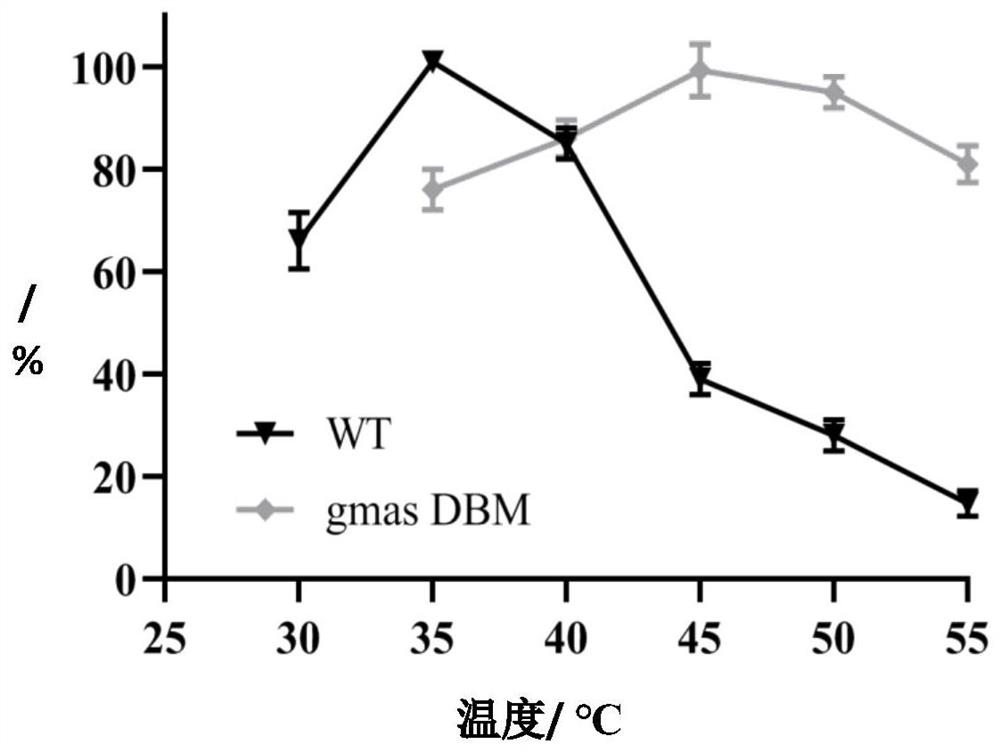
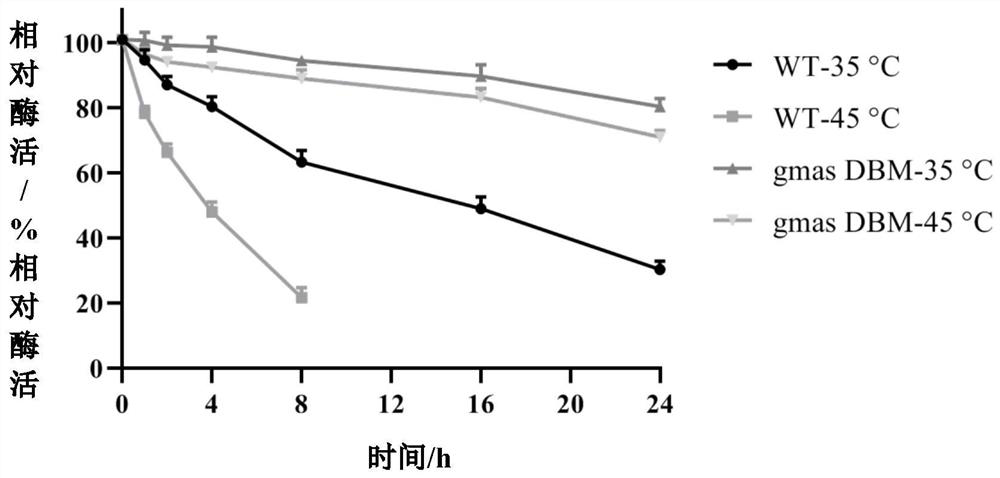
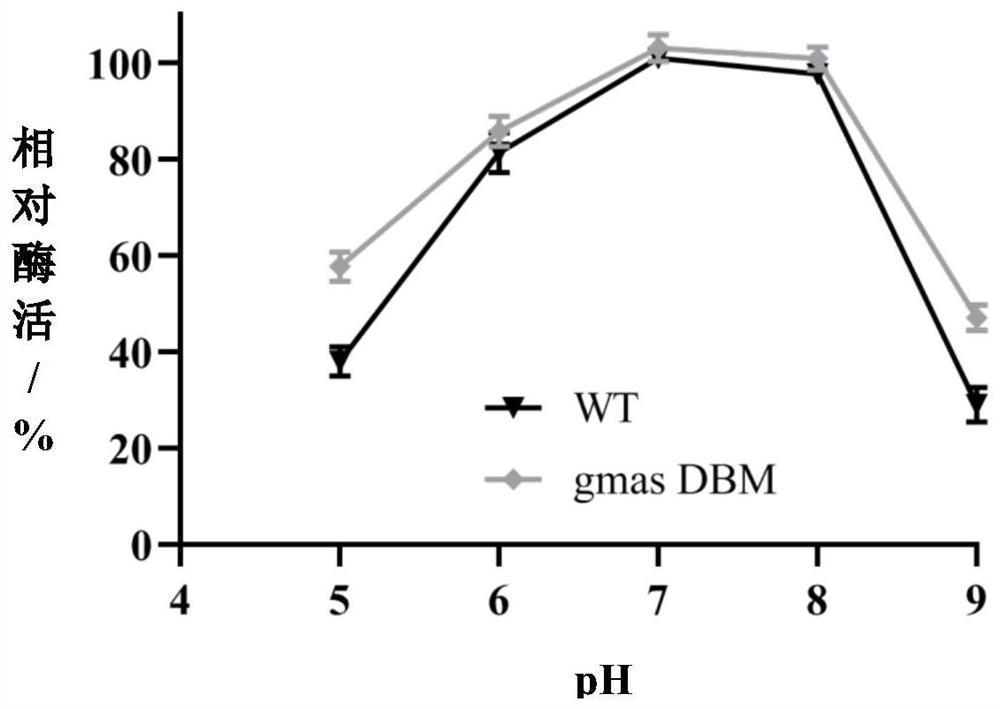
Polyphosphokinase mutant, engineering bacterium and application thereof
PendingCN114606213AReduce usageDoes not affect final yieldBacteriaTransferasesSpecific enzymeSingle mutation
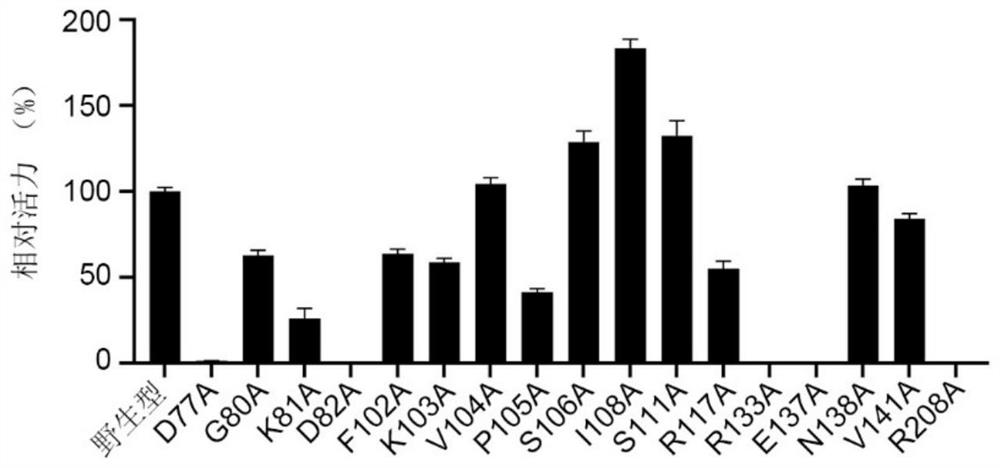
The invention discloses a polyphosphate kinase mutant, an engineering bacterium and application of the polyphosphate kinase mutant and the engineering bacterium. The polyphosphate kinase mutant is obtained by performing single mutation or multiple mutation on the 79th site, the 106th site, the 108th site, the 111th site or the 285th site of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention provides a plurality of polyphosphokinase mutants derived from Cytophaga hutchinsonii, the specific enzyme activity of the mutants is increased by 2.7-17.9 times compared with that of female parent polyphosphokinase, an ATP regeneration system formed by the mutants can reduce the consumption of ATP in ATP-dependent biocatalytic synthesis reaction by 70% or more, and the mutant has a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
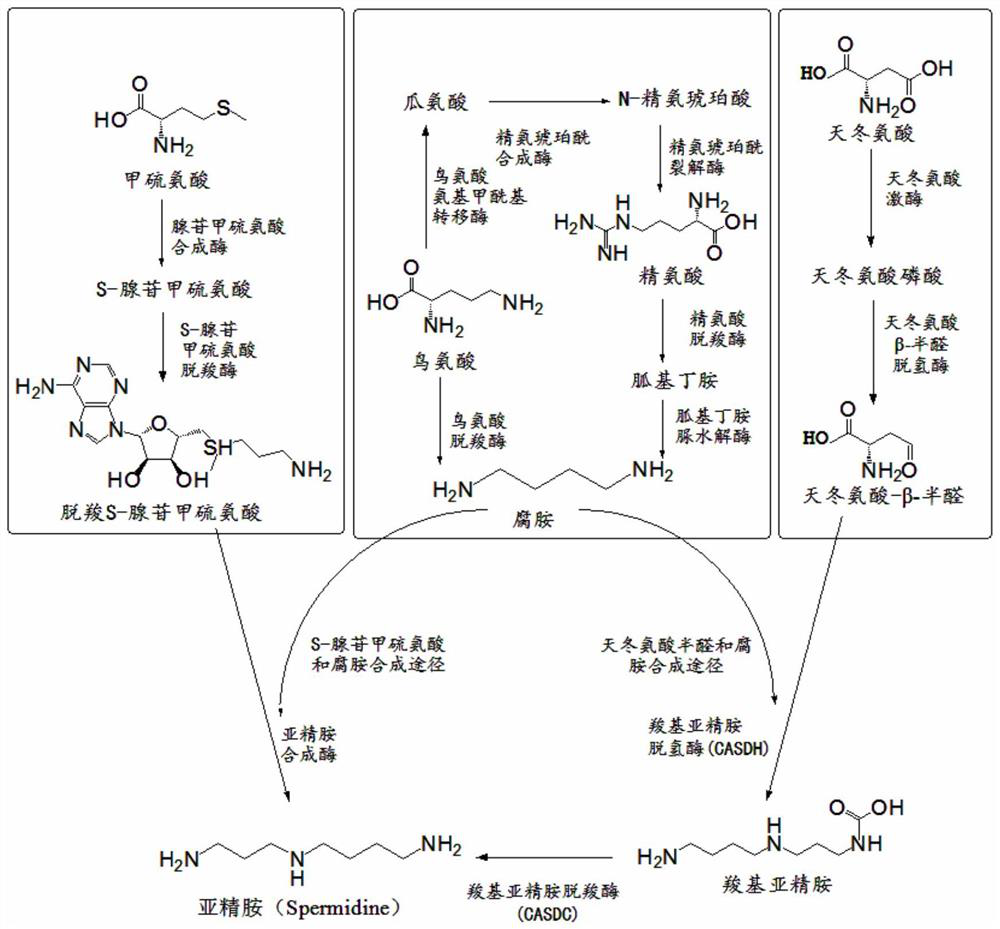
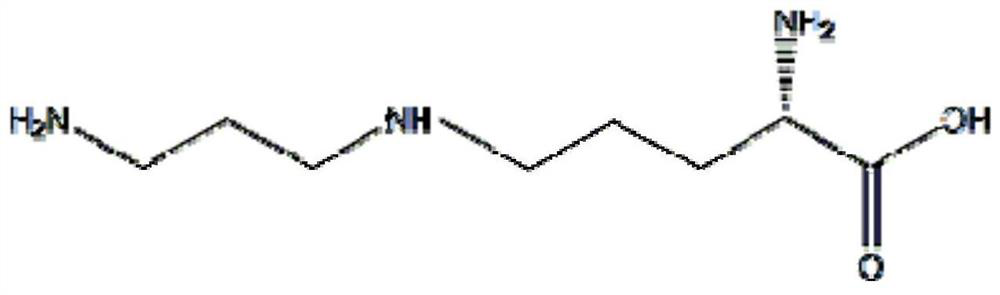
Method for producing spermidine by using cheap substrates and engineering bacterium
ActiveCN112442518ASimple methodRaw materials are easy to getBacteriaTransferasesCarboxyl radicalArginine
The invention discloses a method for producing spermidine by using cheap substrates and engineering bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method is characterized in thatrecombinant cells or a combination of recombinant cells expressing gamma-glutamyl kinase, glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, aspartokinase, aspartate-beta-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, amine dehydrogenase, L-2,4-diaminobutanoate decarboxylase, carboxyspermidine dehydrogenase, carboxyspermidine decarboxylase, glucose dehydrogenase, and polyphosphate kinase 2-I are constructed; and aspartic acidand arginine are catalyzed to synthesize the spermidine by utilizing the recombinant cells or the combination of the recombinant cells. According to the method, selected oxidoreductase can efficientlyuse NAD (NADH) as coenzyme, and the product feedback inhibition is avoided in a reaction process; and the method has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Method for assisting whole-cell transformation to synthesize L-asparagine
ActiveCN111850065AEfficient biotransformationLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationPtru catalystSodium phosphates
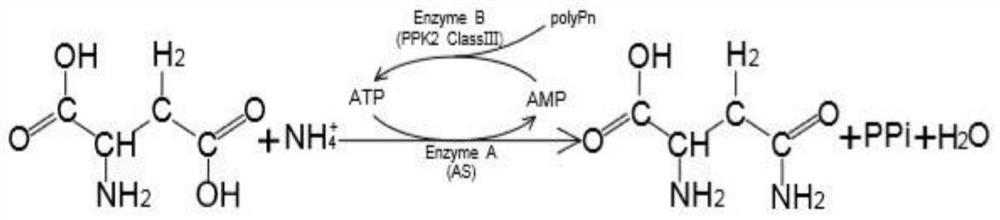
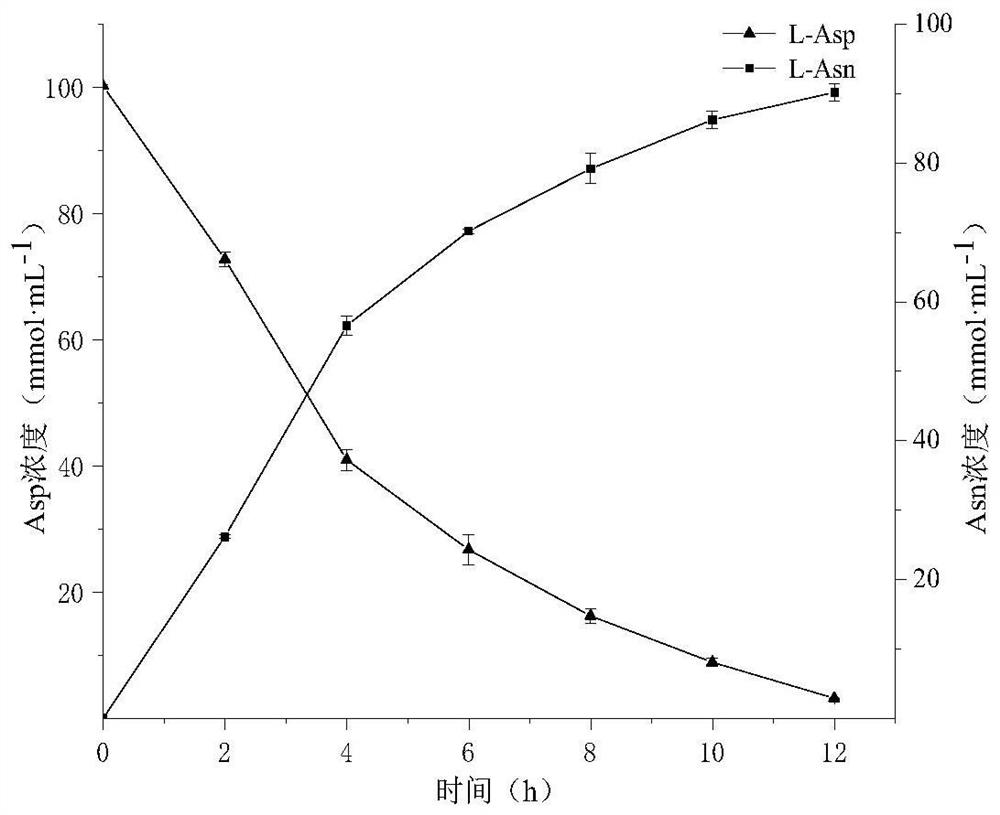
The invention discloses a method for assisting whole-cell transformation to synthesize L-asparagine, which constructs a system for regenerating ATP by single-enzyme transformation of AMP by utilizingIII-class polyphosphate kinase 2, and applies the system to biosynthesis of L-asparagine. The method comprises the following steps: expressing III-type PPK2 from Deinococcus ficus in Escherichia coliRosetta (DE3), wherein the enzyme activity of the III-type PPK2 is 13.19 U.mL <-1 >, and the enzyme activity of the III-type PPK2 from Deinococcus ficus is 13.19 U.mL<-1>. E. Coli Rosetta (DE3) / pET21a-DfiPPK2-III and B. Subtilius WB600 / pMA5-LsaAS-A whole cells are used as catalysts to catalyze L-Asp to synthesize L-Asn, and the reaction conditions are optimized. Results show that the yield of L-Asn reaches 90.15%, which is 80% higher than that of sodium hexametaphosphate directly added with 180mmol. L<-1>, by supplementing sodium hexametaphosphate with the final concentration of 60mmol. L <-1>twice to wet cells of the two recombinant bacteria under optimal reaction conditions.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enzymatic synthesis method of nicotinamide mononucleotide
ActiveCN112961890AGood removal effectAvoid expensiveFermentationBulk chemical productionEnzymatic synthesisNicotinamide mononucleotide
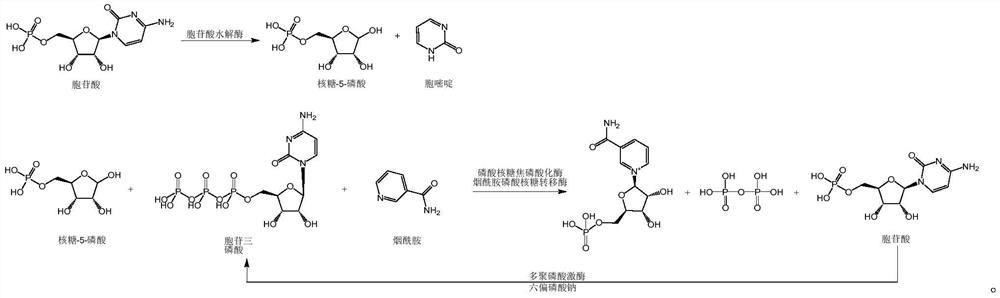
The invention discloses an enzymatic synthesis method of nicotinamide mononucleotide. The enzymatic synthesis method comprises the following steps: S1, taking ribose-5-phosphate, cytidine monophosphate, polyphosphate and nicotinamide as raw materials, and generating nicotinamide mononucleotide under the catalytic action of ribose phosphate pyrophosphorylase, polyphosphate kinase and nicotinamide ribose phosphate transferase. The applicant uses polyphosphate kinase to catalyze cytidine monophosphate to cyclically obtain cytidine triphosphate by using a phosphate group provided by the polyphosphate, and the cytidine triphosphate is used as a pyrophosphoric acid donor of the ribose phosphate pyrophosphorylase to promote the enzymatic reaction of the ribose-5 phosphate and the nicotinamide, thereby avoiding the use of expensive ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Besides, the cytidine monophosphate and the cytidine triphosphate in the enzymatic reaction process provided by the invention are almost insoluble in water under an acidic condition, so that impurities in the product can be quickly, simply and conveniently removed by directly adjusting the pH value after the reaction is finished, the purification process is simplified, and the separation and purification difficulty is reduced.
Owner:深圳希吉亚生物技术有限公司
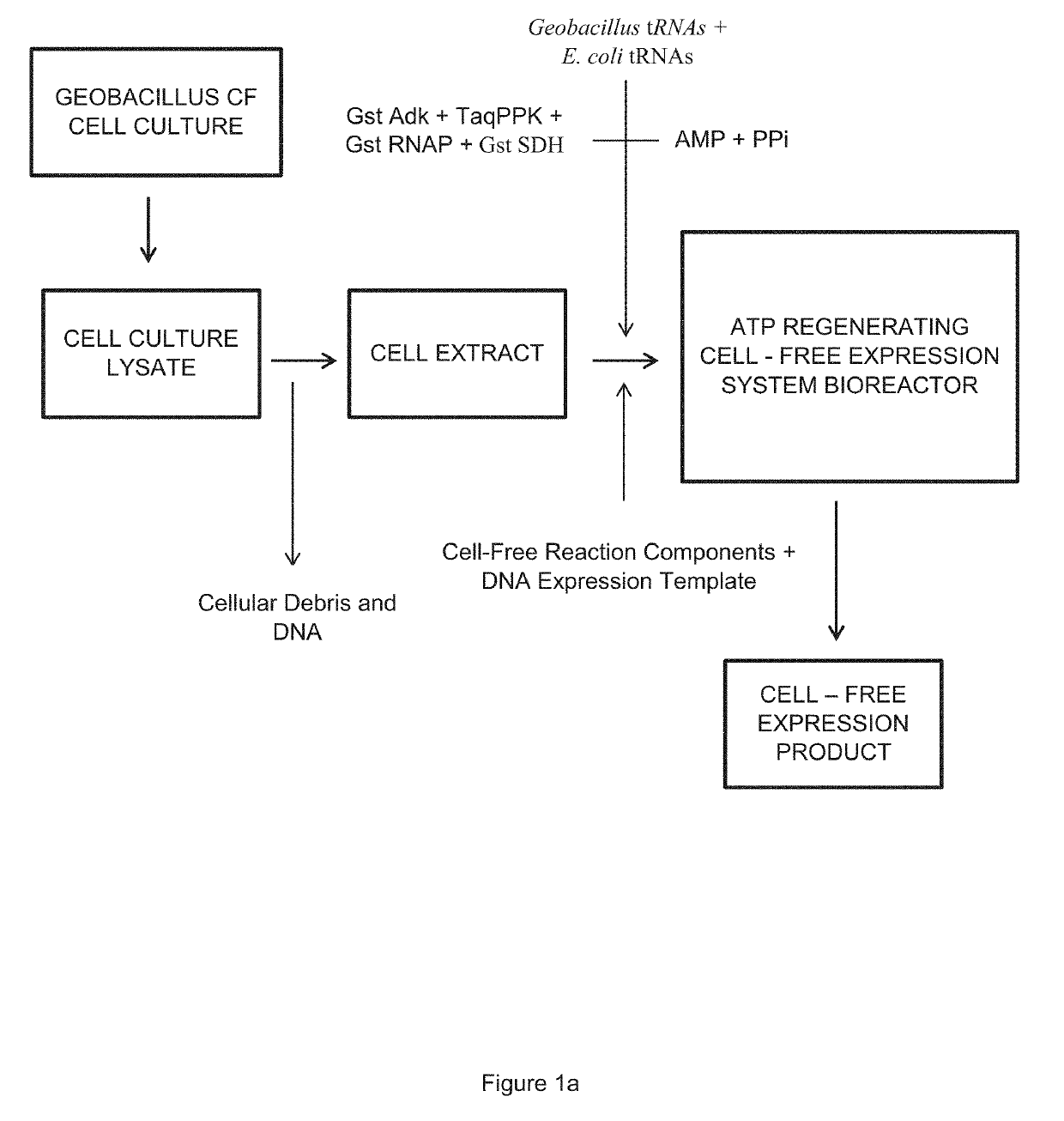
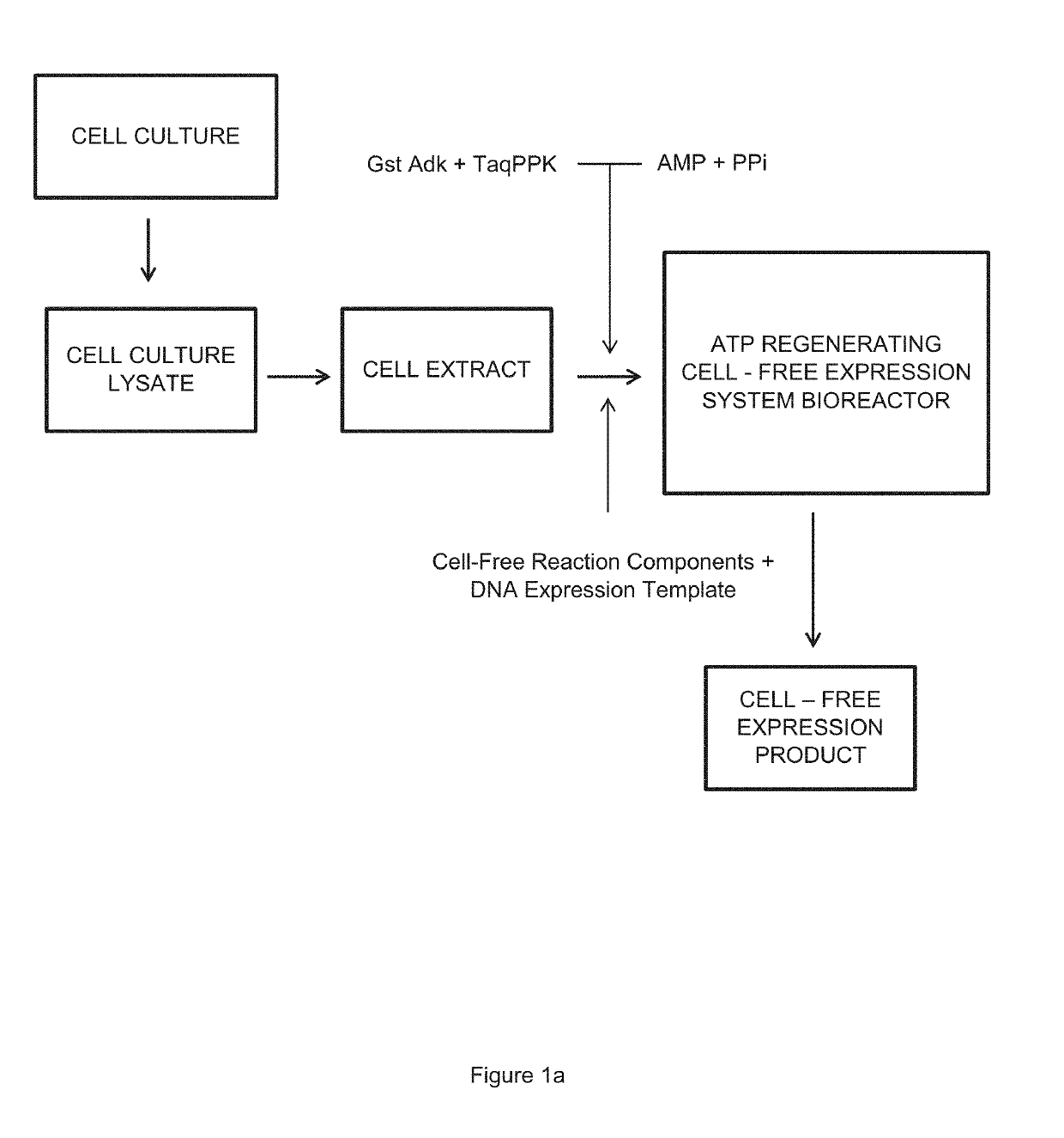
Cell-Free Expression System Having Novel Inorganic Polyphosphate-Based Energy Regeneration
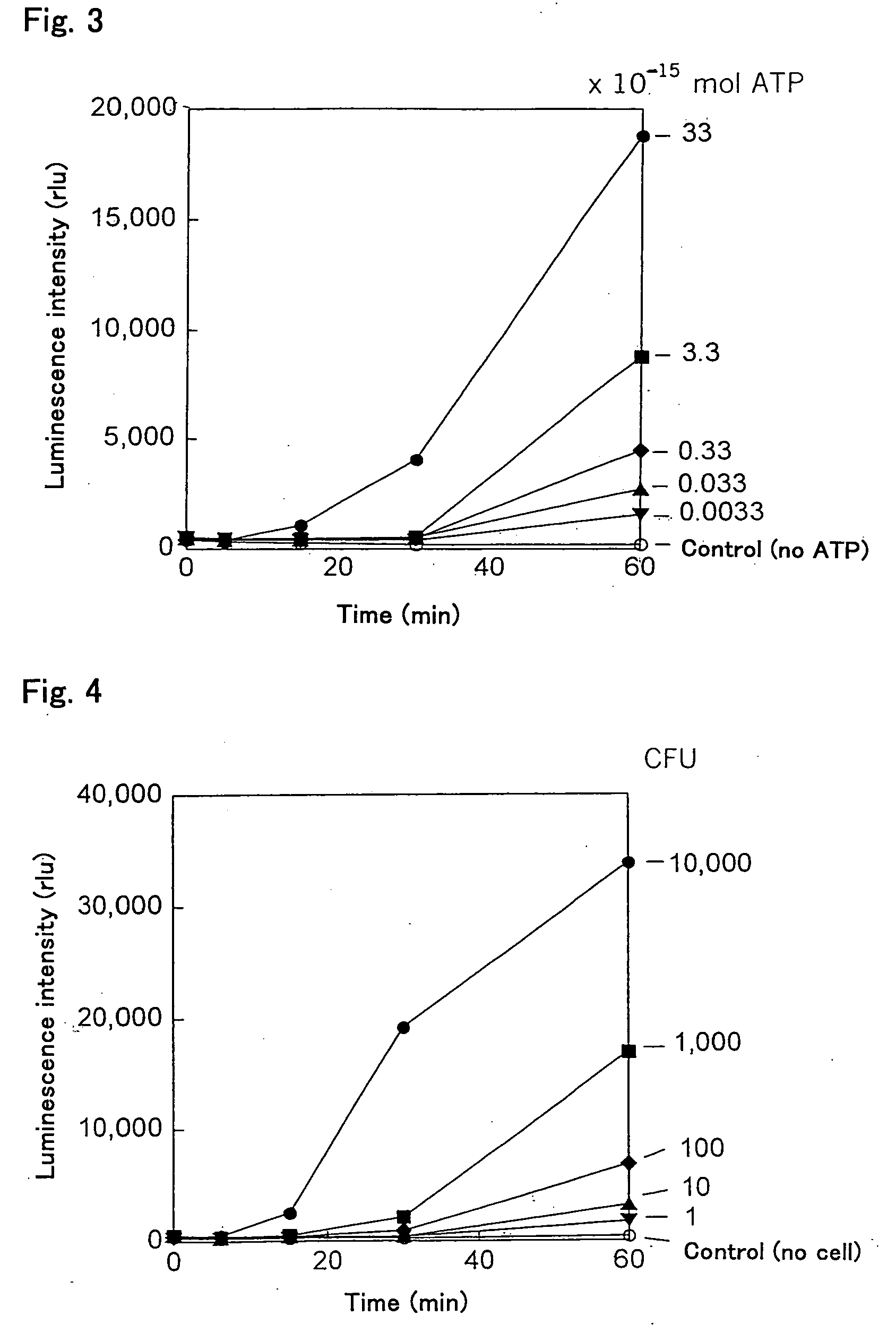
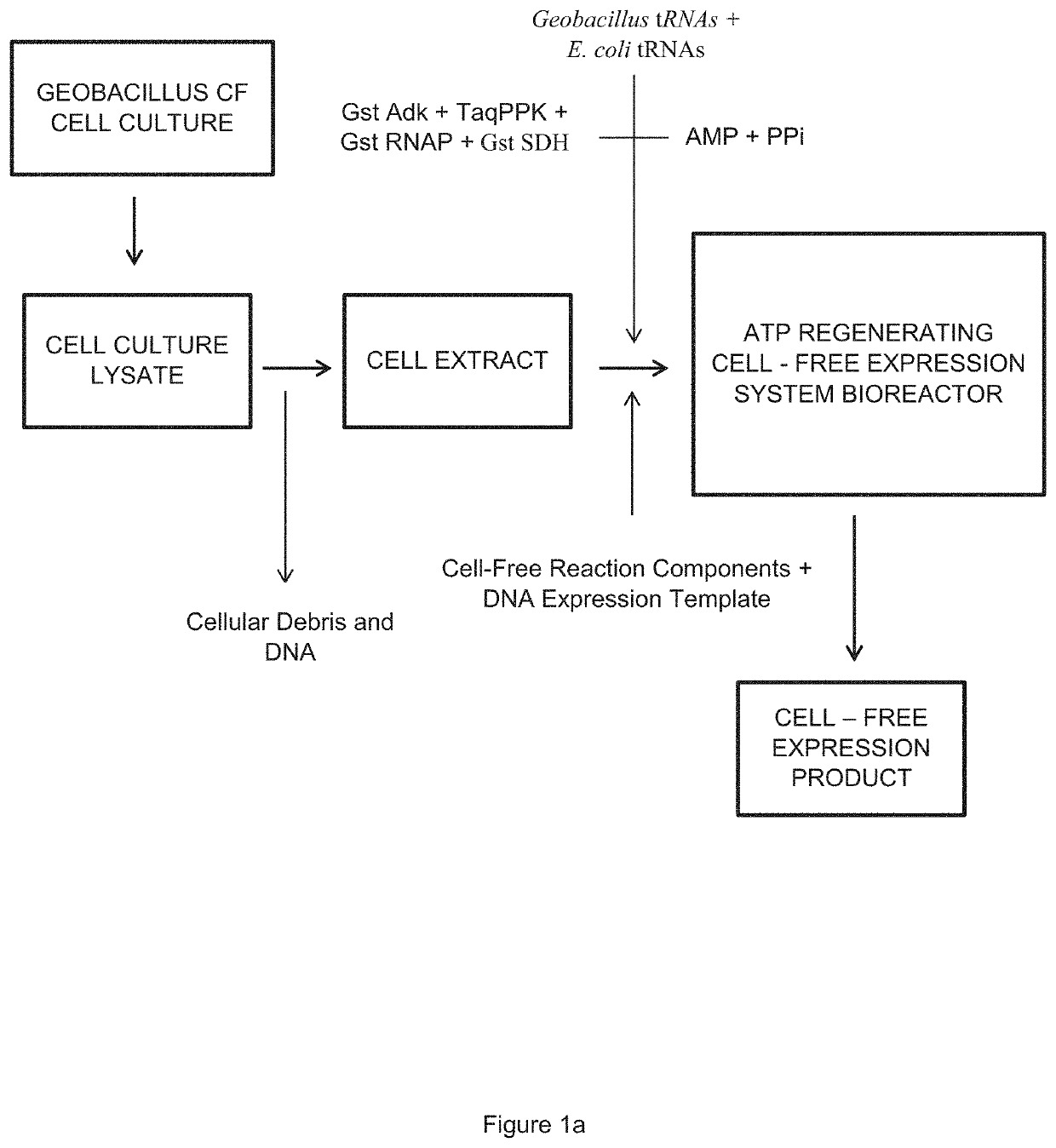
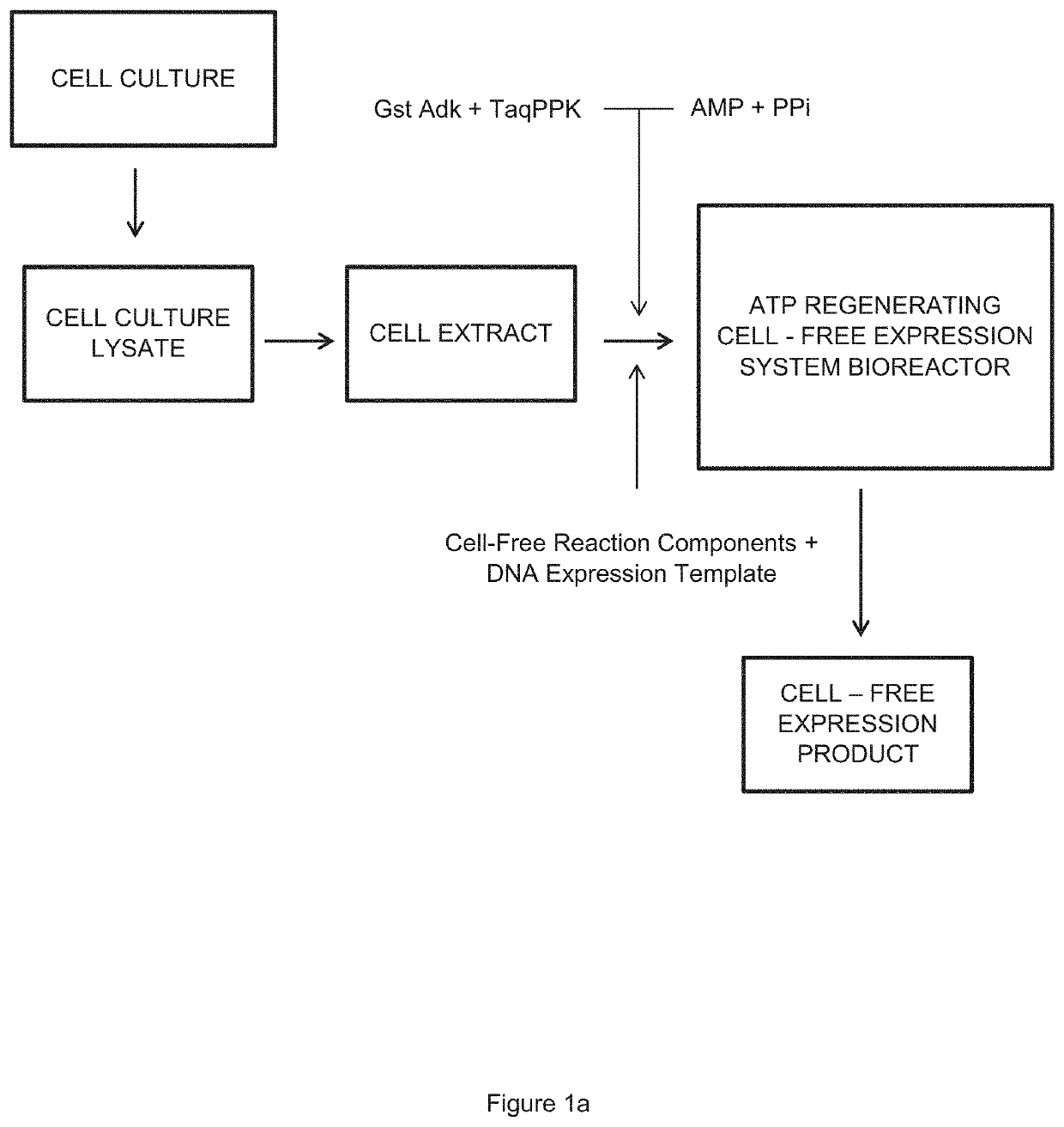
ActiveUS20190309311A1Long reaction timeImprove reaction efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesCell freeEnzyme system
The invention relates to an in vitro cell-free expression system incorporating a novel inorganic polyphosphate-based energy regeneration system. In certain embodiments, the invention includes a cell-free expression system where the cellular energy source, ATP, is regenerated from inorganic polyphosphate using a dual enzyme system. In this embodiment, this dual enzyme system may include thermostable Adenosyl Kinase, and / or Polyphosphate Kinase enzymes.
Owner:NATURES TOOLBOX INC
Inositol polyphosphate kinase genes and uses thereof
InactiveUS7608755B2Improve nutritional qualityReduce environmental impactBryophytesSugar derivativesNucleotidePhytic acid
This invention relates to newly identified polynucleotides and polypeptides in the phytic acid biosynthetic pathway, variants and derivatives of same; methods for making the polynucleotides, polypeptides, variants, derivatives and antagonists. In particular the invention relates to polynucleotides and polypeptides of the inositol polyphosphate kinase gene family. In particular this invention relates to using the newly identified polynucleotides and polypeptides to modulate phytic acid biosynthesis in such a way as to decrease phytate and / or increase non-phytate phosphorous in plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
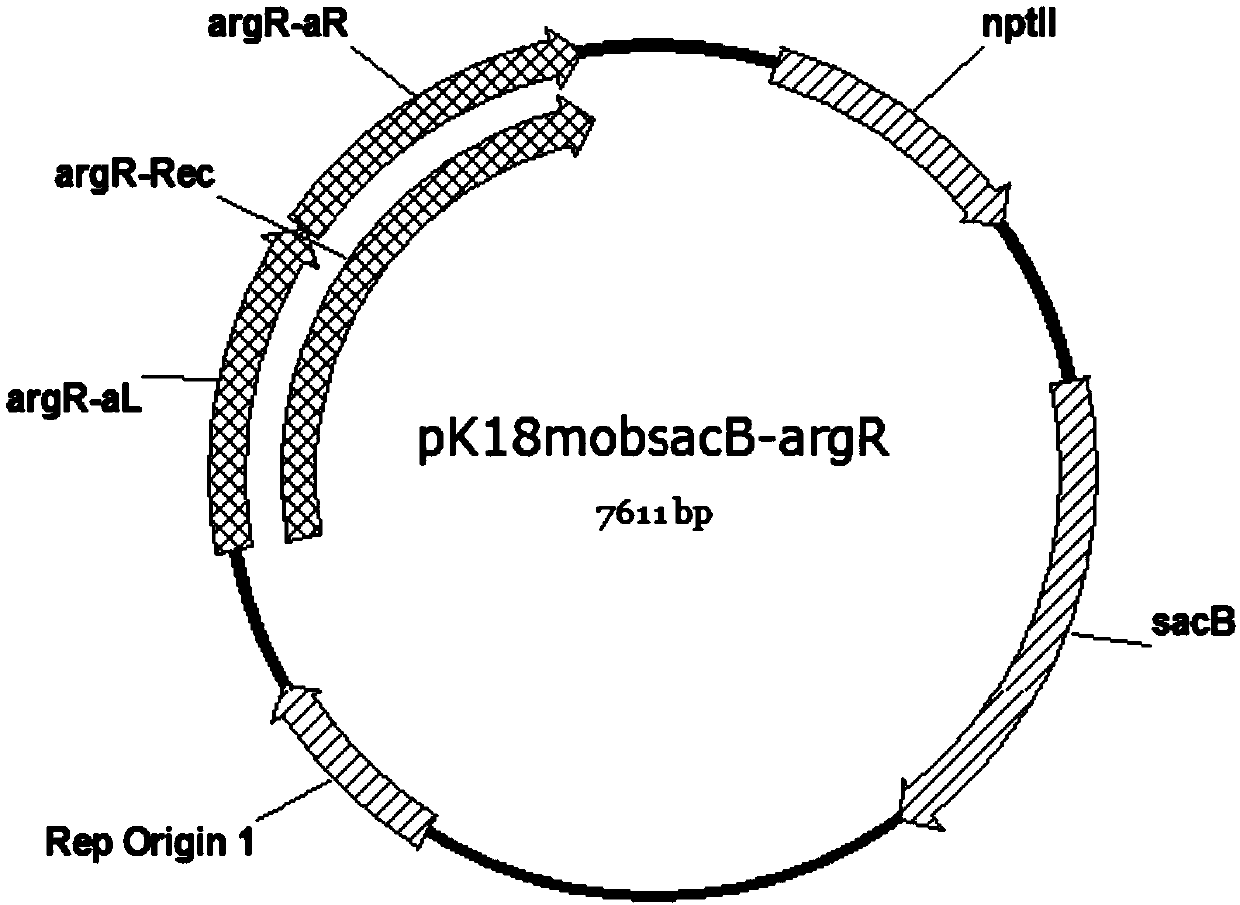
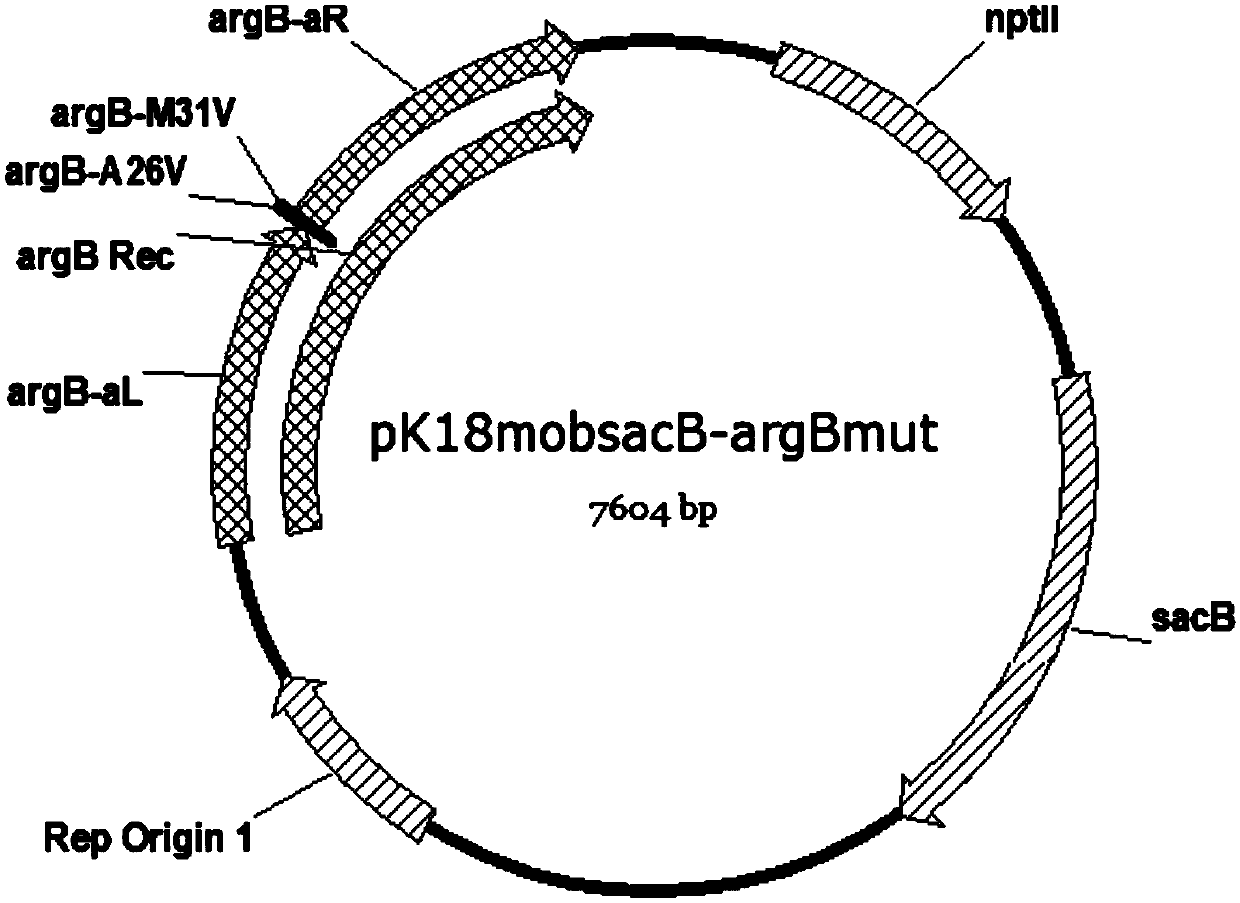
Method for improving production capacity of L-arginine strain
The invention discloses a method for improving production capacity of an L-arginine strain through genetic engineering, which comprises the following steps: knocking out an argR gene in a corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032 genome to obtain a gene knockout strain ATCC13032 (delta argR); carrying out A26V and M31V mutation on the argB gene in the genome of the gene knockout strain to obtain a genemutation strain ATCC13032 (delta argR, argBmut (A26V M31V)); and mutating a base sequence of an upstream regulation region of an initiation codon of a polyphosphate kinase gene (NCgl2620) in a genomeof a gene mutation strain to obtain a gene engineering strain ATCC13032 (delta argR, argBmut (A26V M31V) and NCgl2620mut6). According to the method, the L-arginine production capacity of the strain can be improved by at least 15 times.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
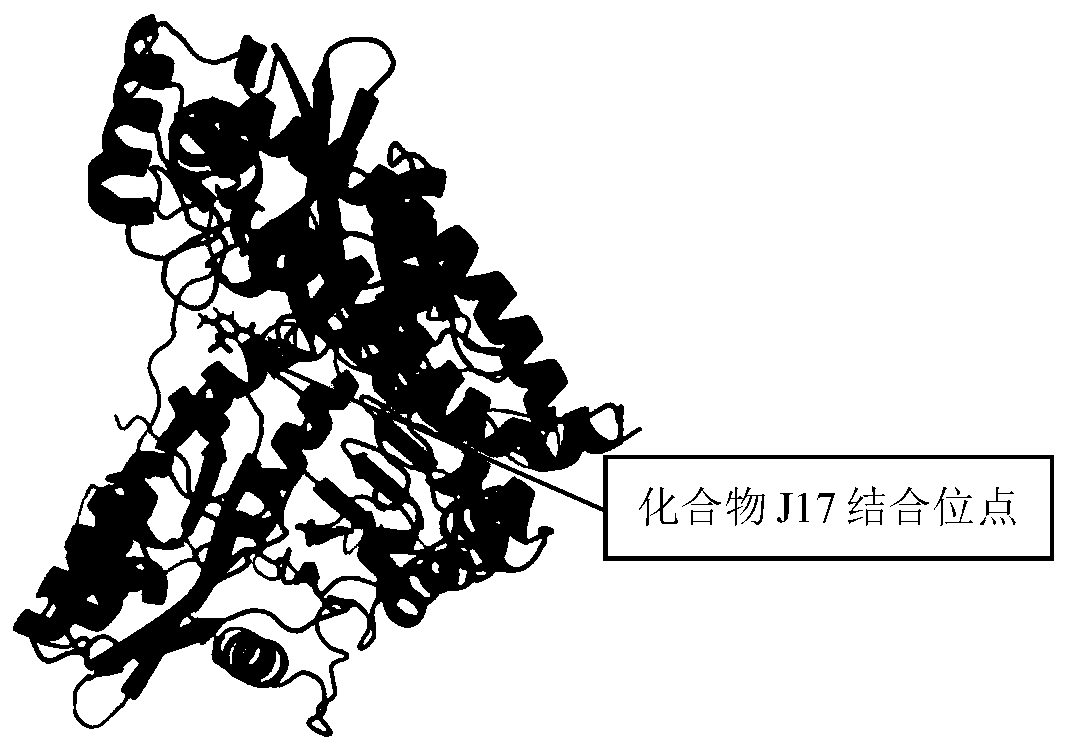
Polyphosphate kinase targeting inhibitor J17
PendingCN110215444AInhibition of invasion functionInhibitor J17 suppresses invasion functionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsUrothelial CellPathogenicity
The invention relates to a polyphosphate kinase targeting inhibitor. The polyphosphate kinase targeting inhibitor is a compound J17, the molecular formula is C15H11OF3Cl, and the structural formula isshown in the formula (I). The polyphosphate kinase targeting inhibitor can inhibit the resistance of pathogenicity escherichia coli of the urinary tract to oxidation pressure, the formation of a biological membrane of the pathogenicity escherichia coli of the urinary tract and the invasion function of the pathogenicity escherichia coli of the urinary tract to epithelial cells of the urinary tract. The polyphosphate kinase targeting inhibitor is expected to be prepared into drugs which are applied to treatment of infection of the urinary tract.
Owner:THE FIFTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV +1
Method of Amplifying Atp and Use Thereof
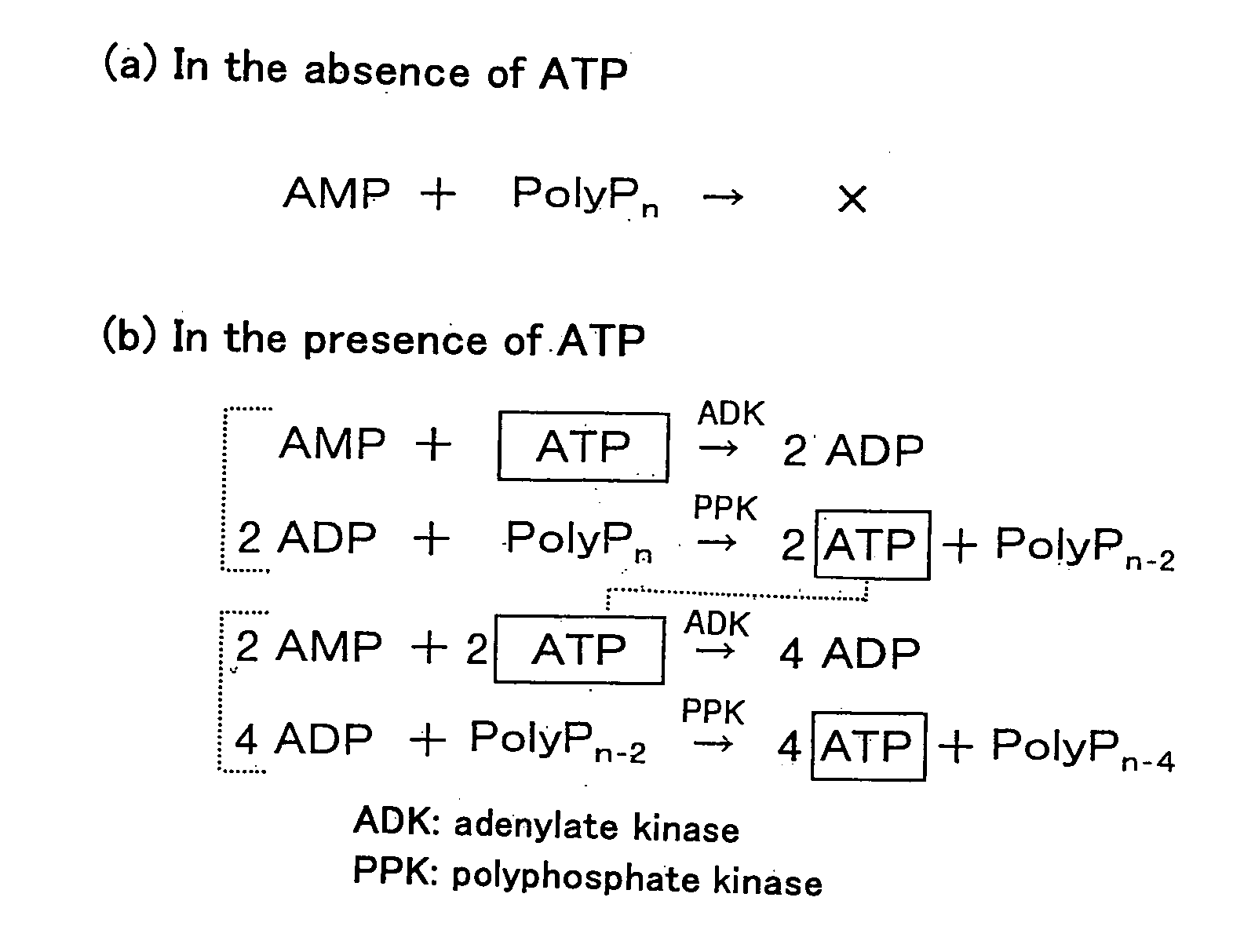
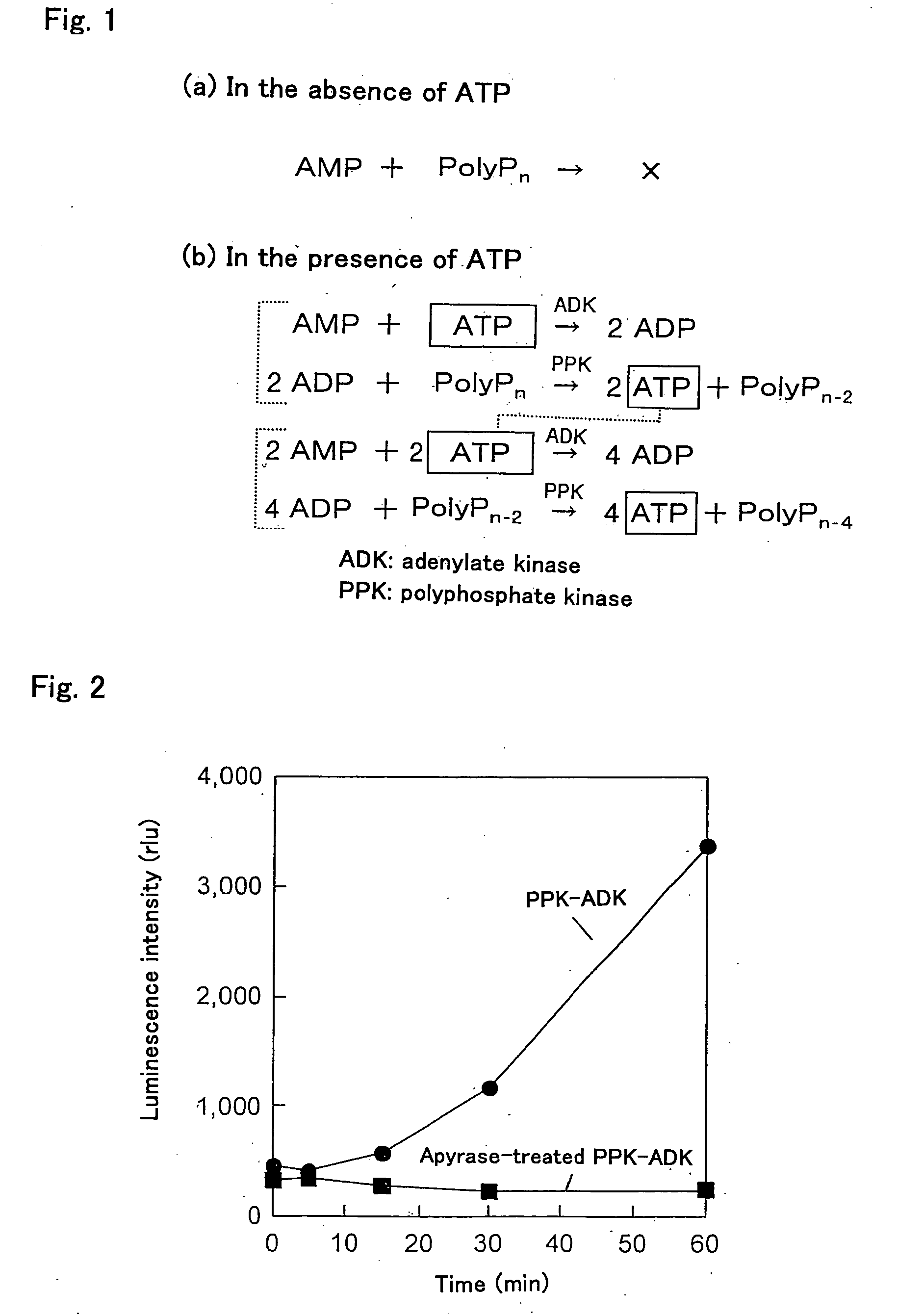
InactiveUS20080213754A1Quick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesMicroorganismAdenylate kinase
The ATP amplification method of the present invention is a method for amplifying and detecting a very trace amount of exogenous ATP by allowing a fusion protein (PPK-ADK) of a polyphosphate kinase and an adenylate kinase, the fusion protein not containing ADP, to act on a mixture of ATP, AMP, and a polyphosphate compound. The present invention also provides an ultrasensitive ATP amplification method by which ATP at a single cell level can be amplified and detected, and an ultrasensitive microbial assay based on this ATP amplification method.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Cell-Free Expression System Having Novel Inorganic Polyphosphate-Based Energy Regeneration
PendingUS20210024912A1Long reaction timeImprove reaction efficiencyTransferasesOxidoreductasesCell freeEnzyme system
The invention relates to an in vitro cell-free expression system incorporating a novel inorganic polyphosphate-based energy regeneration system. In certain embodiments, the invention includes a cell-free expression system where the cellular energy source, ATP, is regenerated from inorganic polyphosphate using a dual enzyme system. In this embodiment, this dual enzyme system may include thermostable Adenosyl Kinase, and / or Polyphosphate Kinase enzymes.
Owner:NATURES TOOLBOX INC
Mutant with thermal stability of gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase and encoding gene, amino acid sequence and application of gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase mutant
The invention discloses a mutant with thermal stability of gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase, an encoding gene and amino acid and application of the mutant to production of theanine. Specifically, the mutant of the gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase is obtained through a genetic engineering method. The mutant is long in half-life period; while the thermal stability of the mutant of the gamma-glutamine methylamine synthetase is improved, the optimum temperature of the enzyme is increased by 10-15 DEG C, the mutant can play a very good catalytic effect without being in a buffer salt solution, and meanwhile, the theanine is efficiently synthesized by utilizing the mutant through a method of coupling polyphosphate kinase; and according to the method, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) regeneration can be implemented while the theanine is synthesize by catalysis, and an effective way is provided for enzymatic industrial production of the theanine.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com