Method for assisting whole-cell transformation to synthesize L-asparagine
A whole-cell transformation, asparagine technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as unstable properties, increased difficulty in product separation and purification, and inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: Construction of Escherichia coli Rosetta(DE3) / pET21a-DfiPPK2s genetic engineering bacteria
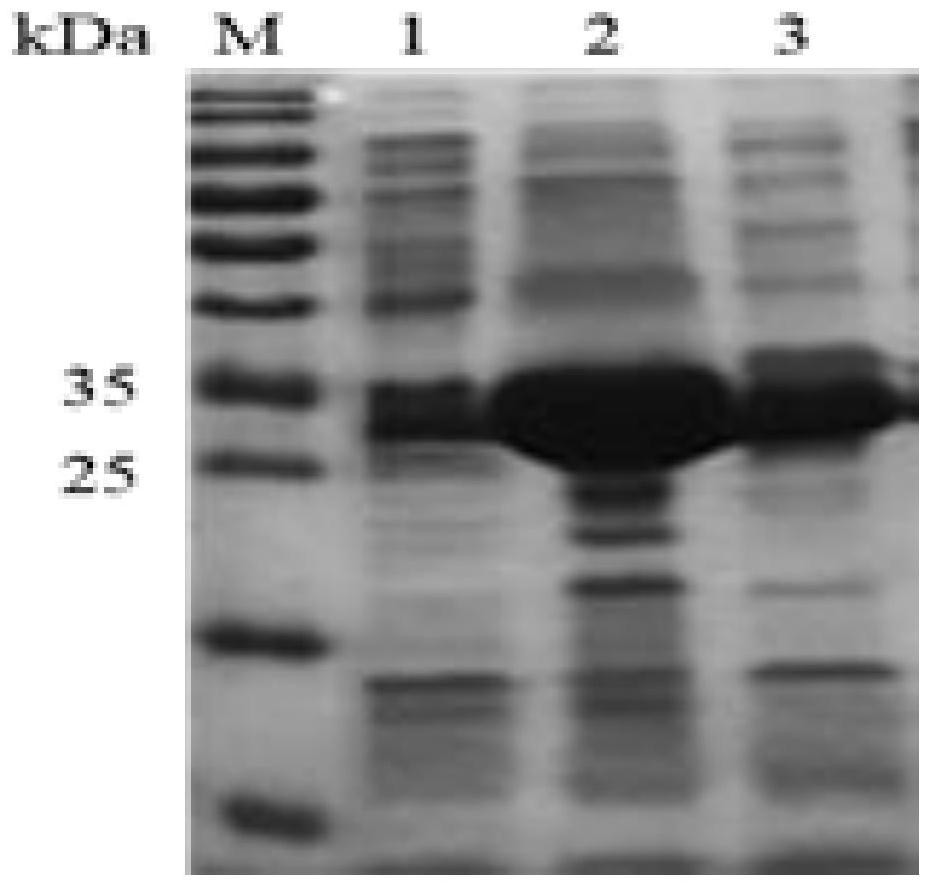
[0025] The Deinococcus ficus genome was extracted using a kit, and using it as a template, primer PPK2s-F (SEQ ID NO.2) (ACAGCAAATGGGTCGGGATCCATGAAAACCGACCGGTACCG, carrying a BamHI restriction site) and primer PPK2s-R (SEQ ID NO.3) (TGGTGGTGCTCGAGTGCGGCCGCGATGCGGACTTCCTTGGGG, carrying NotⅠ restriction site) PCR amplified DfiPPK2s gene. Ligate the amplified gene to the pET21a vector, transform the constructed recombinant plasmid into E.coli BL21(DE3), E.coli Rosetta(DE3) and E.coli RosettatamiB(DE3), pick the transformants, and identify Positive bacteria, obtain recombinant bacteria that can express DfiPPK2s, and compare the effects of different hosts on gene expression, the results are as follows figure 2 As shown, using E.coli Rosetta (DE3) as a host can promote the expression of DfiPPK2s gene.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: Fermentation of Escherichia coli Rosetta(DE3) / pET21a-Dfi-PPK2s
[0027] Escherichia coli Rosetta(DE3) / pET21a-Dfi-PPK2s was inoculated into LB medium (LB / Amp-Chl) medium supplemented with ampicillin and chloramphenicol at 37°C, cultured at 200rmp overnight, and 2% was inoculated into TB / Amp Grow to OD 600 0.6, add 0.1mM IPTG 16 ℃, 200rmp culture for 24 hours.
Embodiment 3
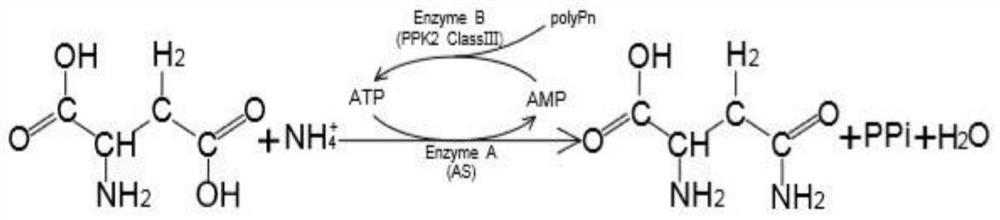
[0028] Example 3: Conditions for whole cell catalysis of L-aspartic acid to produce L-aspartic acid
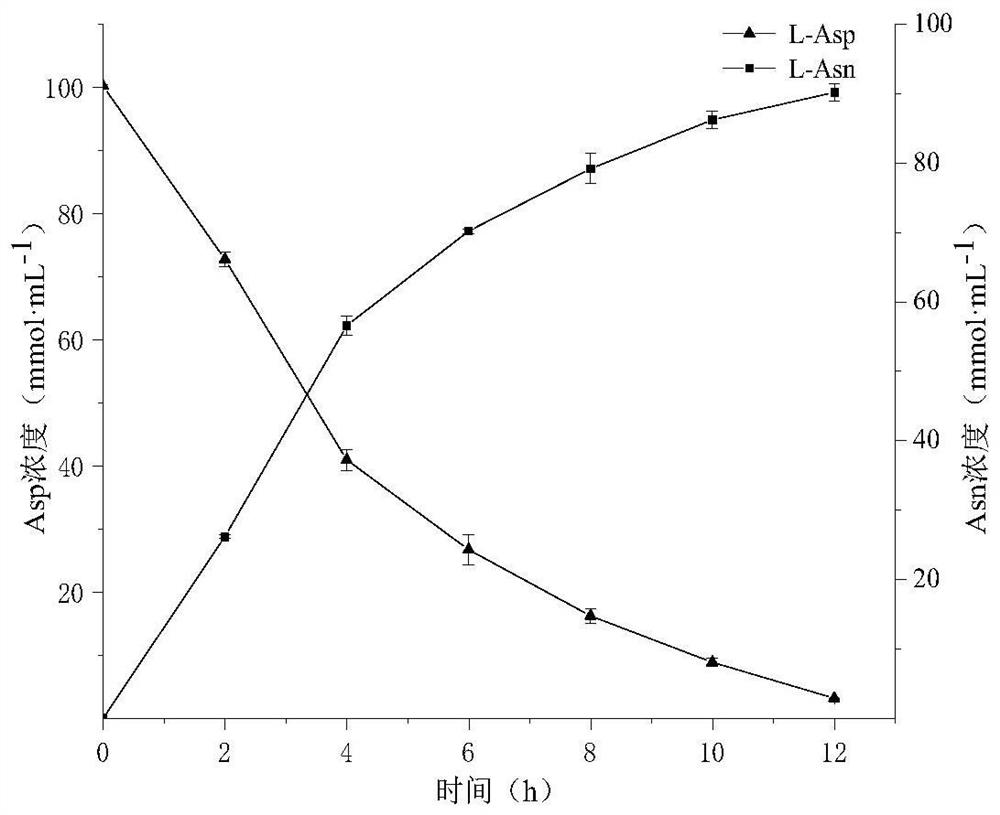
[0029] Add 0.1mol·L to the 5mL reaction system -1 Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 0.1mol L -1 L-Asp, 0.4mol·L -1 NH 4 Cl, 6mmol L -1 ATP, 200mmol·L -1 MgCl 2 , 60mmol·L -1 Sodium hexametaphosphate, 1% Triton X-100, OD 600 Recombinant strain B. subtilis WB600 / pMA5-LsaAS-A and OD expressing asparagine synthetase for 10 600 For the recombinant bacteria expressing class III polyphosphate kinase obtained by fermenting Example 2 of 10, the reaction starts from the addition of ATP, the reaction temperature is 40°C, and the rotation speed is 180rpm. -1 Sodium hexametaphosphate, after 12 hours of reaction, boiled water bath for 5 minutes to terminate the reaction.
[0030] Among them, the recombinant bacteria B.subtilis WB600 / pMA5-LsaAS-A expressing asparagine synthase was previously constructed and preserved in the laboratory, and was published in "Gene Mining and Enzymatic Properties of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com