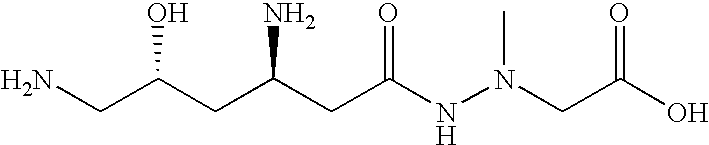
Patents
Literature
82 results about "Citrobacter freundii" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
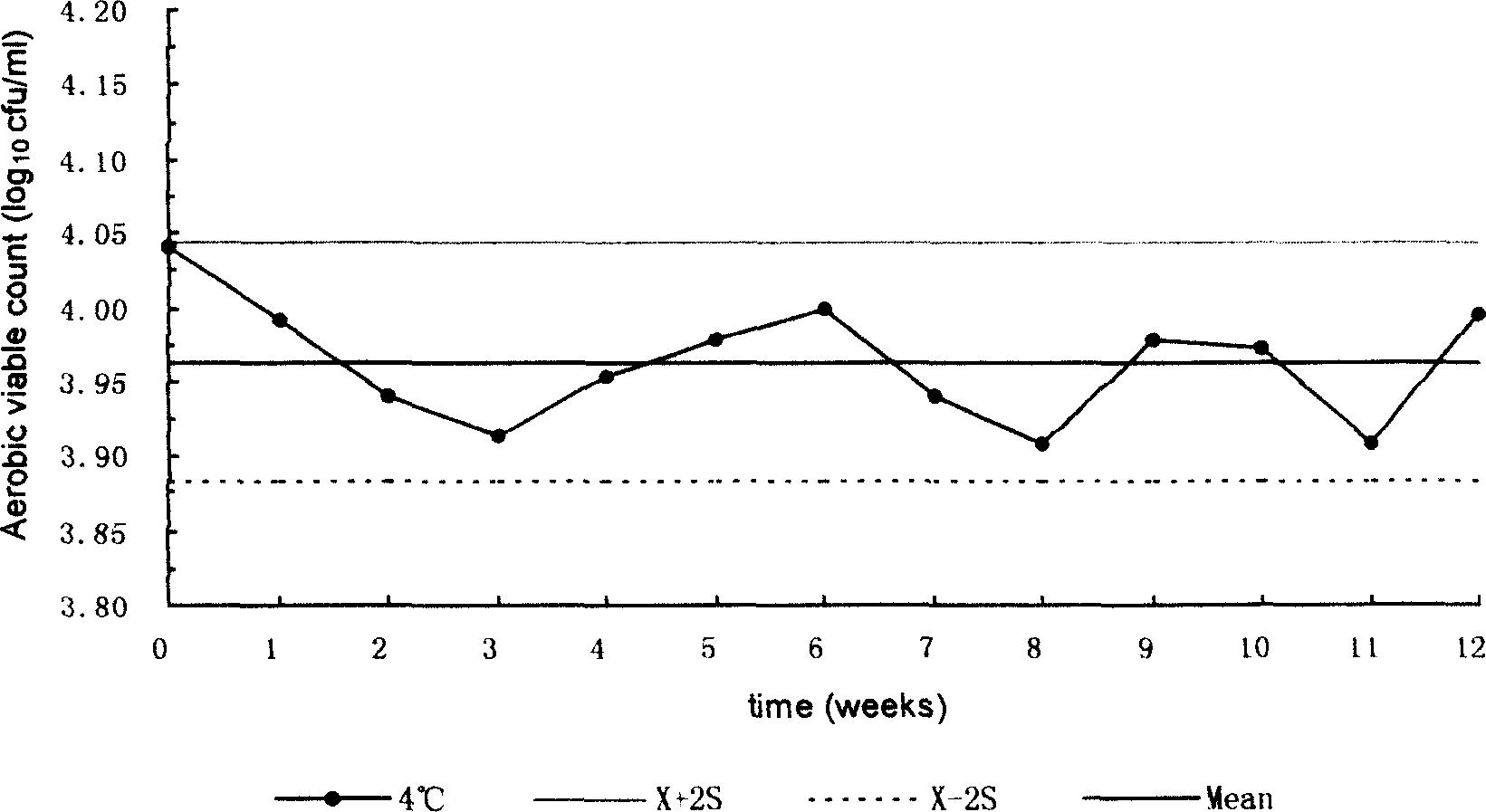
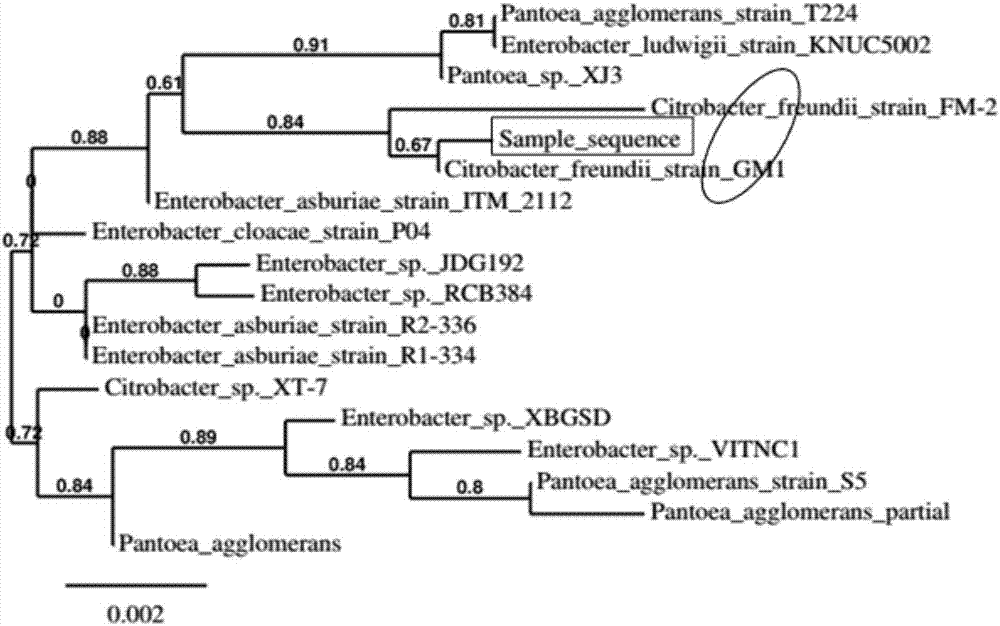
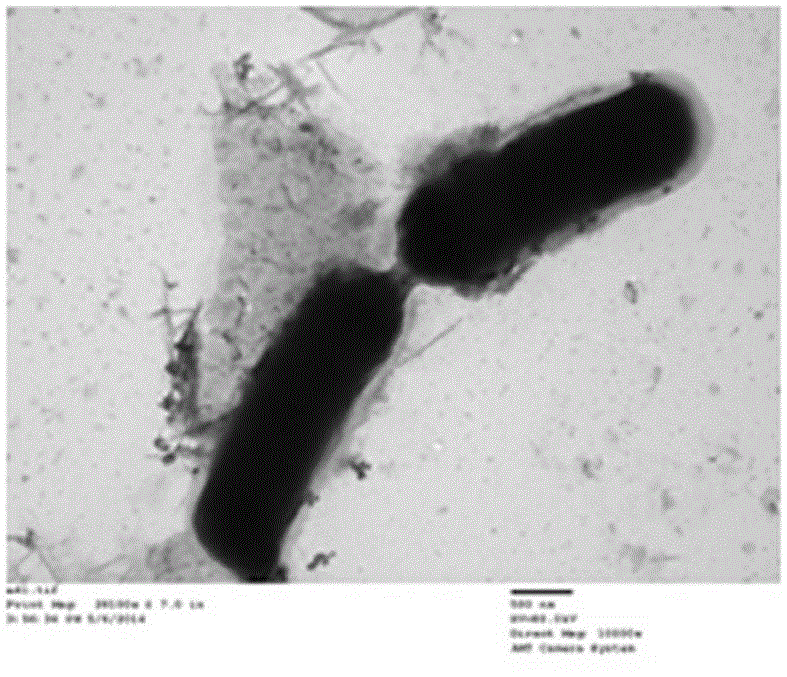
Citrobacter freundii is a species of facultative anaerobic gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The bacteria have a long rod shape with a typical length of 1–5 μm. Most C. freundii cells generally have several flagella used for locomotion, but some do not and are non-motile. C. freundii is a soil organism, but can also be found in water, sewage, food and in the intestinal tracts of animals and humans. The genus Citrobacter was discovered in 1932 by Werkman and Gillen. Cultures of C. freundii were isolated and identified in the same year from soil extracts.
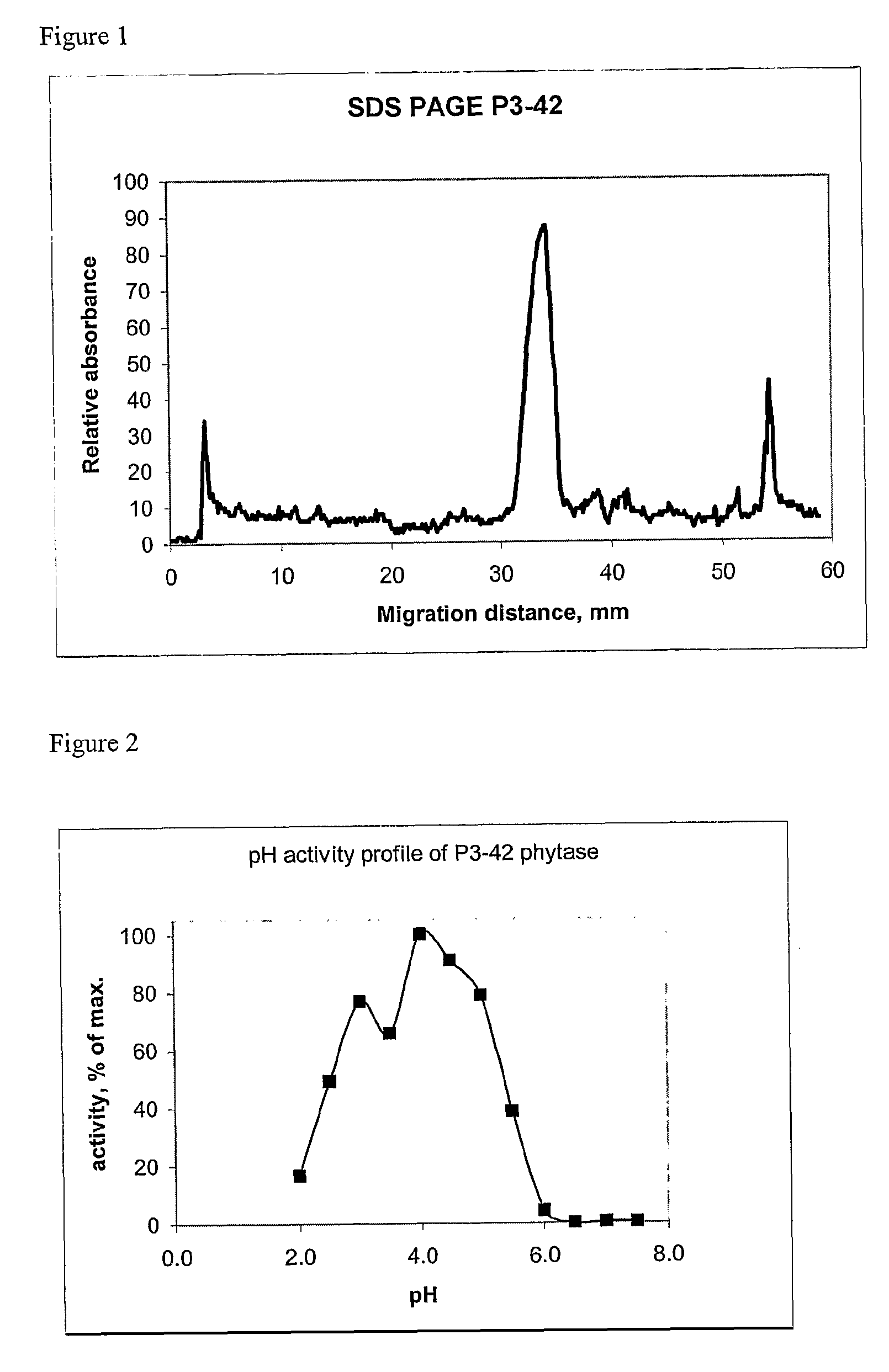
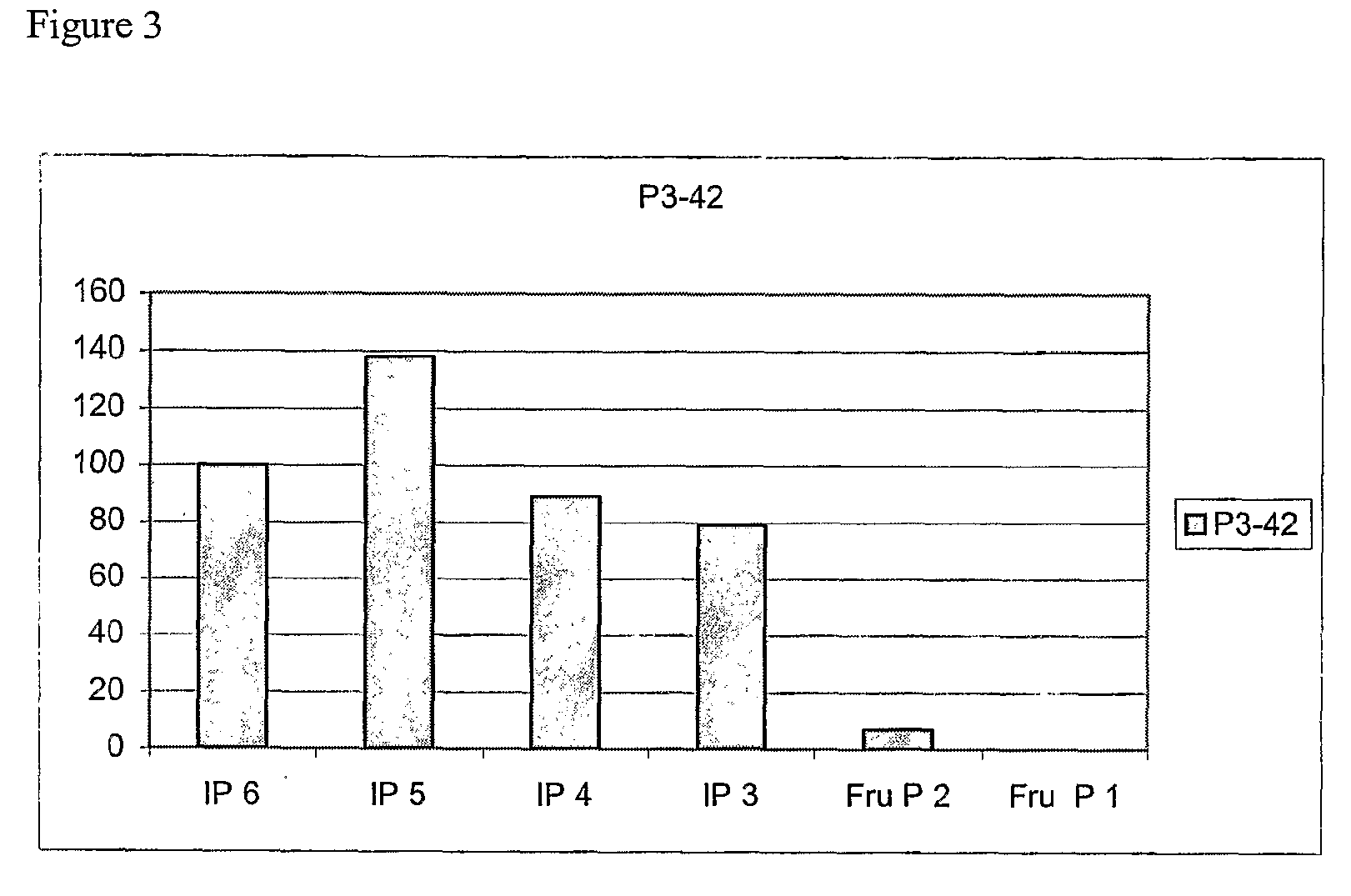
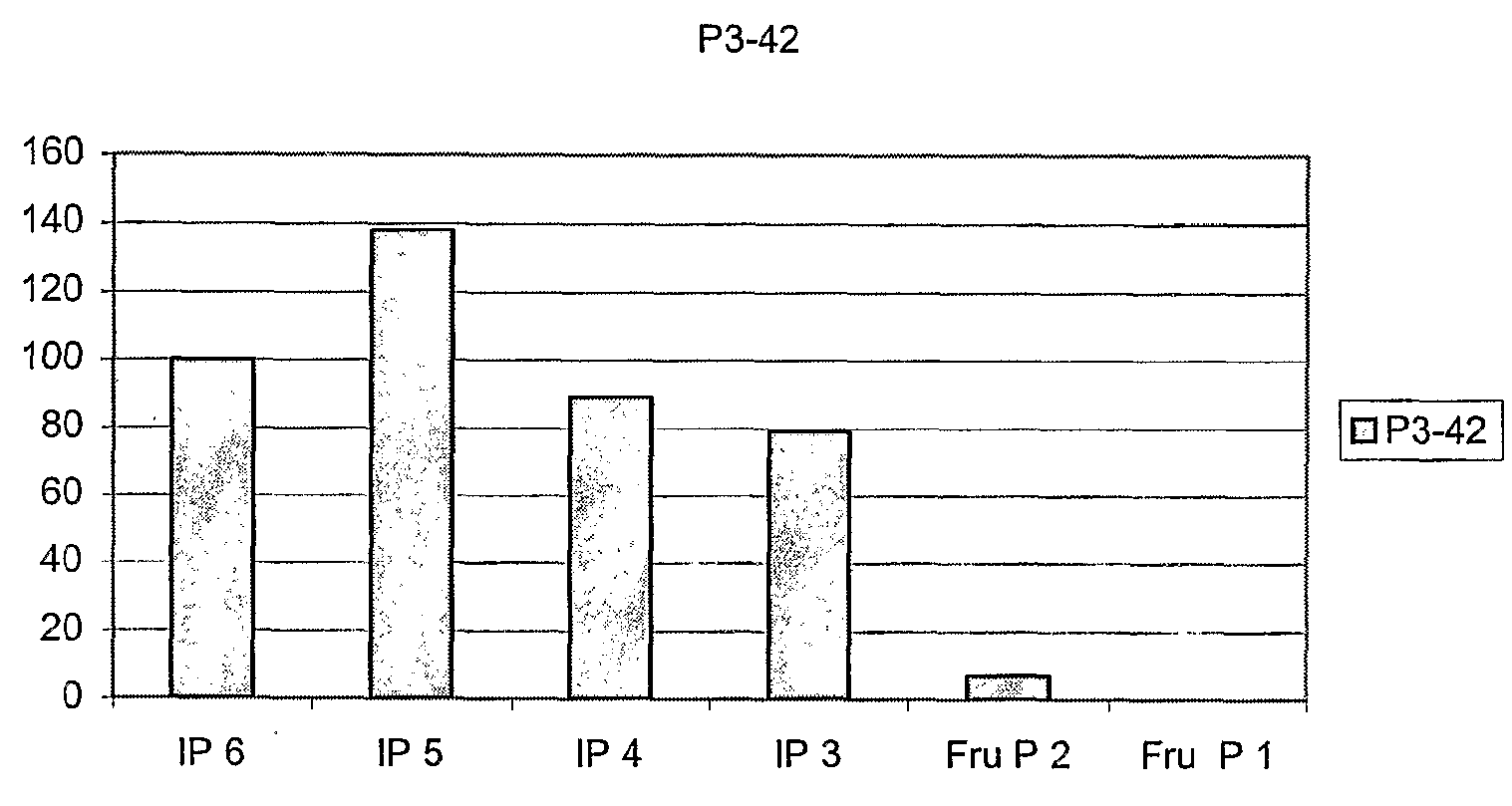
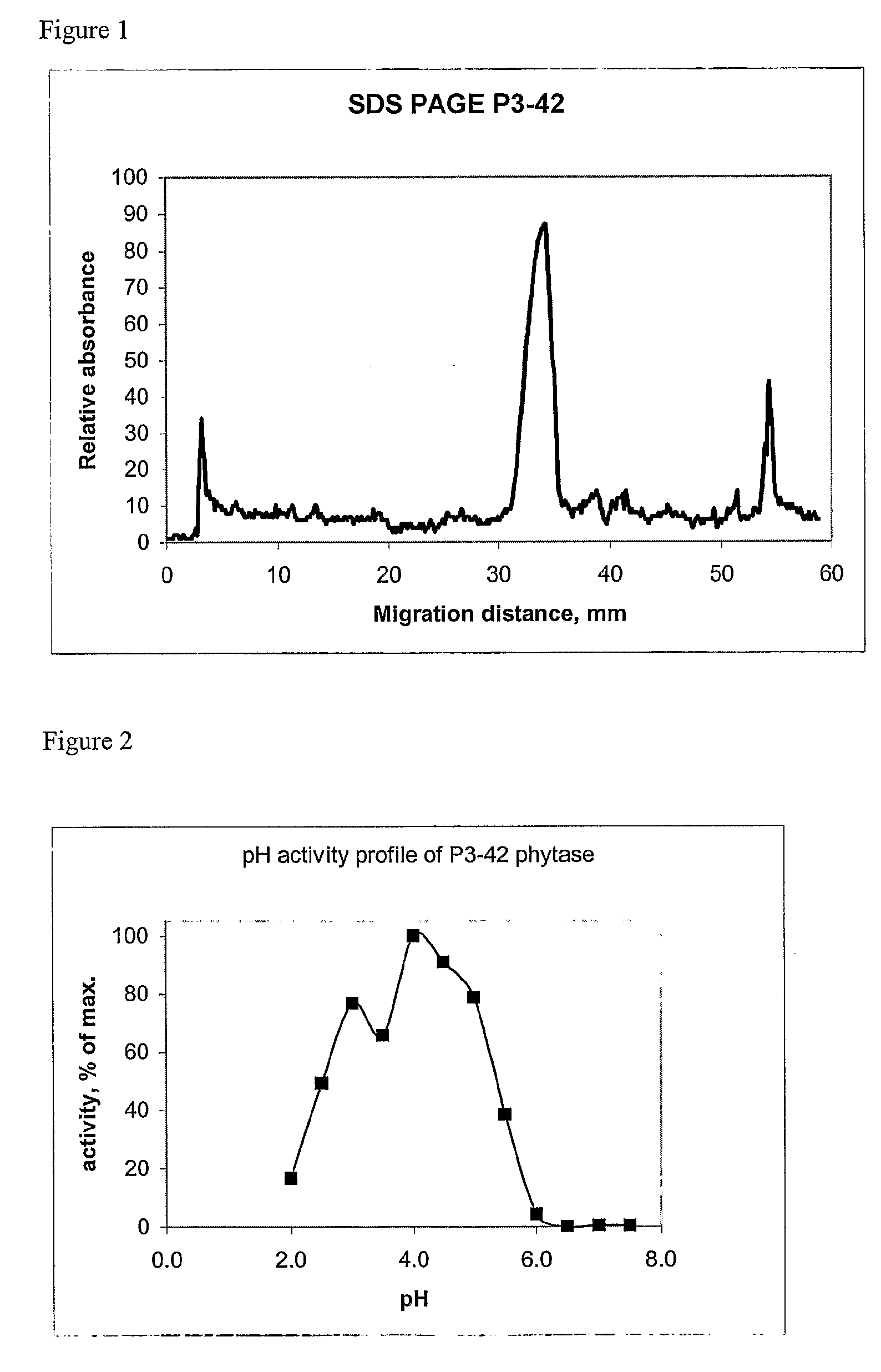
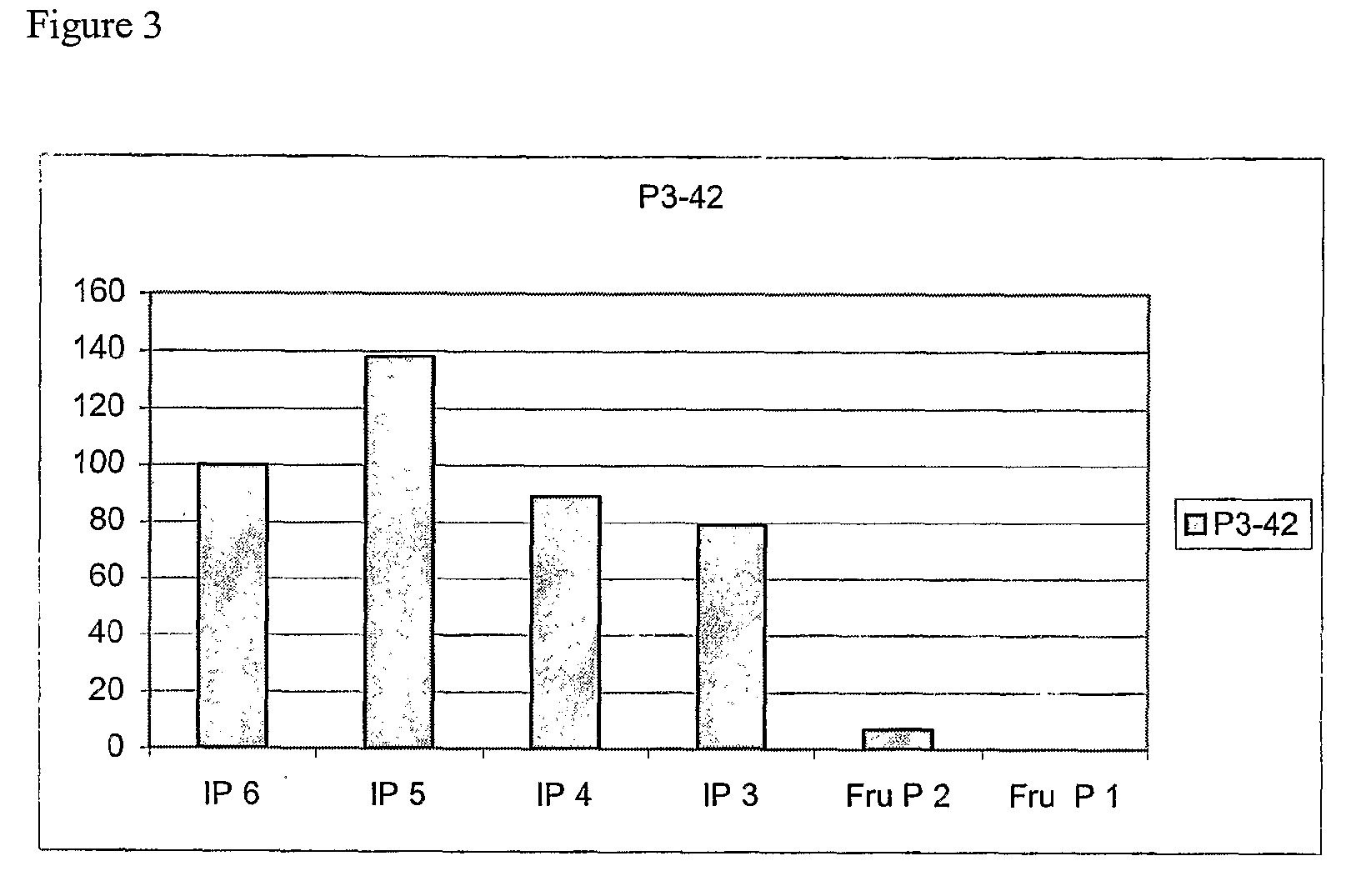
Mutant Citrobacter freundii phytase polypeptide
The present invention relates to enzymes and processes. In particular, there is described an isolated polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence corresponding to Citrobacter freundii phytase or a homologue, a modified form, a functional equivalent or an effective fragment thereof. There is also described a host cell transformed or transfected with a nucleic acid encoding a bacterial phytase enzyme or a modified form as well as the use of such a phytase or modified form in food or animal feed.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Bacterial colony number sample for verifying microbiological capacity of food and its prepn process
InactiveCN1706964AThe result will not affectAccelerate the pace of internationalization of certification and accreditationMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliColony number
The bacterial colony number sample for verifying food microbiological capacity relates to quality control technology in microbiological detection. The sample is matrix with added Bacillus cereus as leading bacteria and background bacteria. The matrix is practical food, and the background bacteria include one or several kinds of serratia marcescens, Citrobacter freundii, enteroaerogen and escherichia coli. The sample of the present invention has homogeneous colony number content, high finishing rate, and high stability, and may be used in test capacity verification of domestic and international labs. In the same time, the capacity verifying sample may be used in verification of detection method, calibration of test instrument, quality control and check of test result and other aspects.
Owner:卢行安 +2
Kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106591178AEfficient degradationFast degradation rateBacteriaSolid waste disposalStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus xylosus
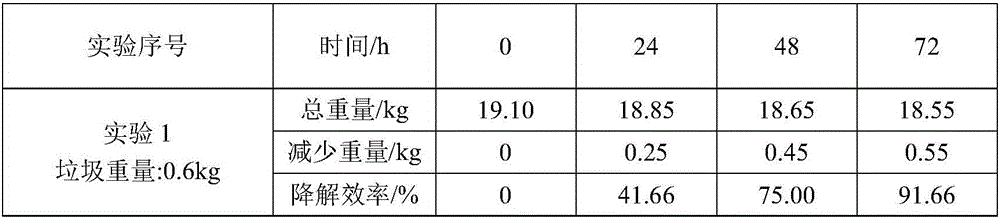
The invention relates to a kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and a preparation method and application thereof. The kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum is prepared by mixing a mixed inoculum of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, radiation-resistant methylobacterium, dispersed pantoea, pseudomonas oryzihabitans, citrobacter freundii and staphylococcus cohnii and a carrier, wherein the mass of the mixed inoculum accounts for 15-25% of the total mass of the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum; the mass ratio of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the radiation-resistant methylobacterium, the dispersed pantoea, the pseudomonas oryzihabitans, the citrobacter freundii and the staphylococcus cohnii is (1.5-3):(1-1.5):(1-1.5): (1-1.5):(1-1.5):(1-1.5); the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum is used for degrading kitchen garbage. Compared with the prior art, the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum has the advantages as follows: the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum can effectively degrade common vegetables, grains, fish, poultry meat and other kitchen garbage, has the degradation rate being above 80%, is high in degradation speed rate and small in odor, does not produce pollutants or poisonous substances, and is low in cost and stable in performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Gene chip and kit for detecting common pathogen in dairy products
ActiveCN101240335AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsKlebsiella oxytocaStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention provides a gene chip for detecting common pathogen in dairy, which comprises a solid-phase vector and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid-phase vector, wherein the oligonucleotide probe includes DNA fragment or its complementary DNA or RNA sequence selected from E. sakazakii, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Listeria monocytogenes, salmonella and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region of Bacillus cereus, as well as ipaH gene of Shigella or gyrB gene of citrobacter freundii. The invention further provides a reagent box which uses the gene chip to detect pathogen in dairy. The gene chip and the reagent box of the invention for detecting pathogen in dairy are easy to operate, highly precise and greatly repeatable.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD +1
Citrobacter freundii with phosphorus-dissolving potassium-dissolving capability and application thereof
The invention discloses citrobacter freundii with phosphorus-dissolving potassium-dissolving capability and application thereof. A bacterial strain ZSW-4 with relatively phosphorus dissolving capability is screened out from soybean rhizosphere, an ultraviolet-ray plasma composite mutation technology is utilized for performing multiple composite mutation on the bacterial strain, and a bacterial strain ZSW-4-2-5C with high dissolving efficiency on phosphorus and good stability is selected and bred, and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 8748. By using a liquid containing the bacterium or a solid inocula to inoculate corn, soybean, mustard and other crops, absorption of plants on phosphorus element in soil is promoted and crop output is improved.
Owner:西安金博瑞生态科技有限公司
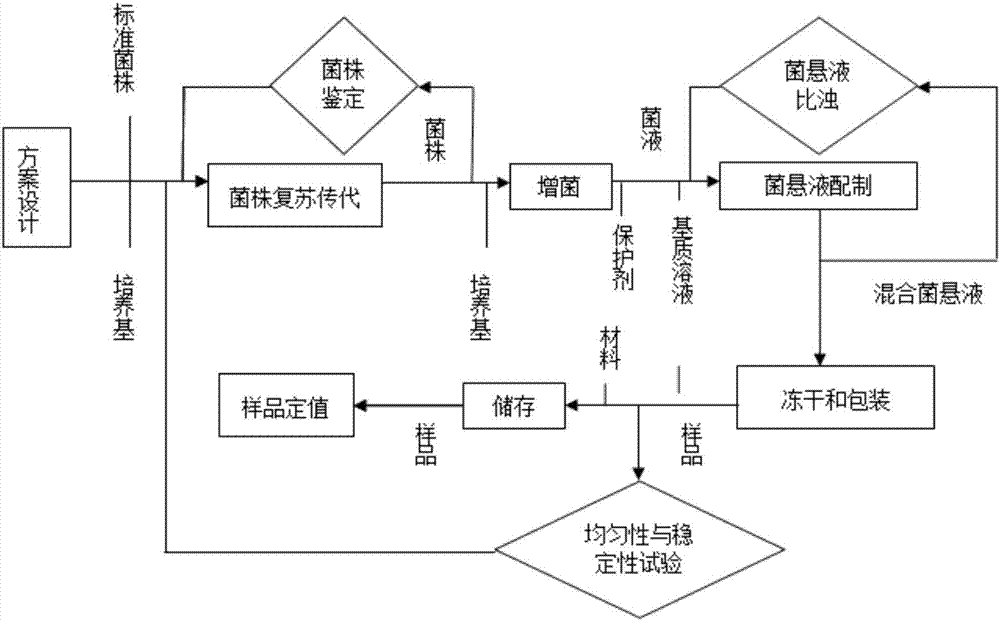
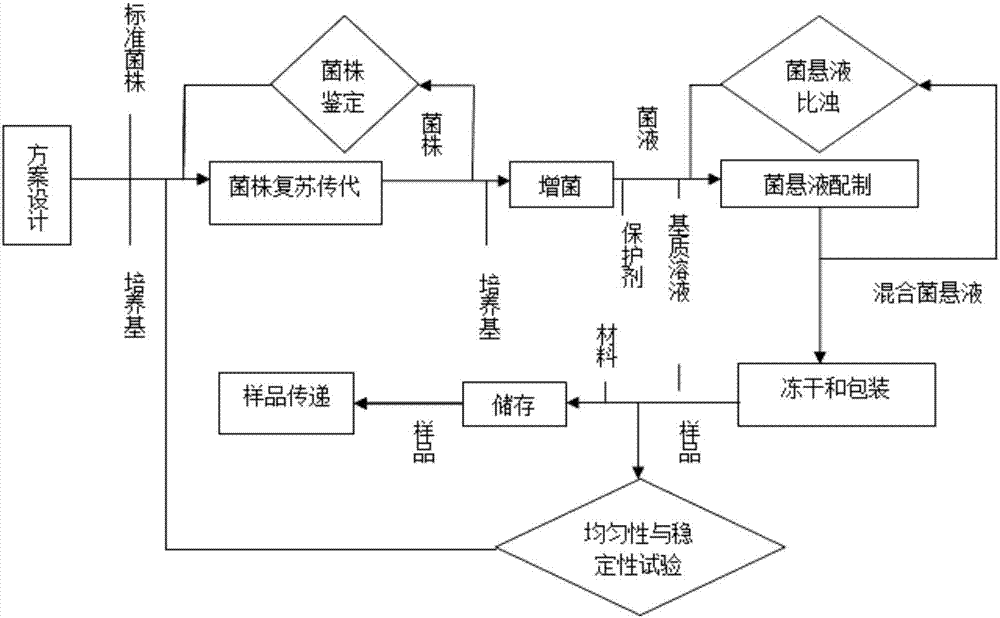
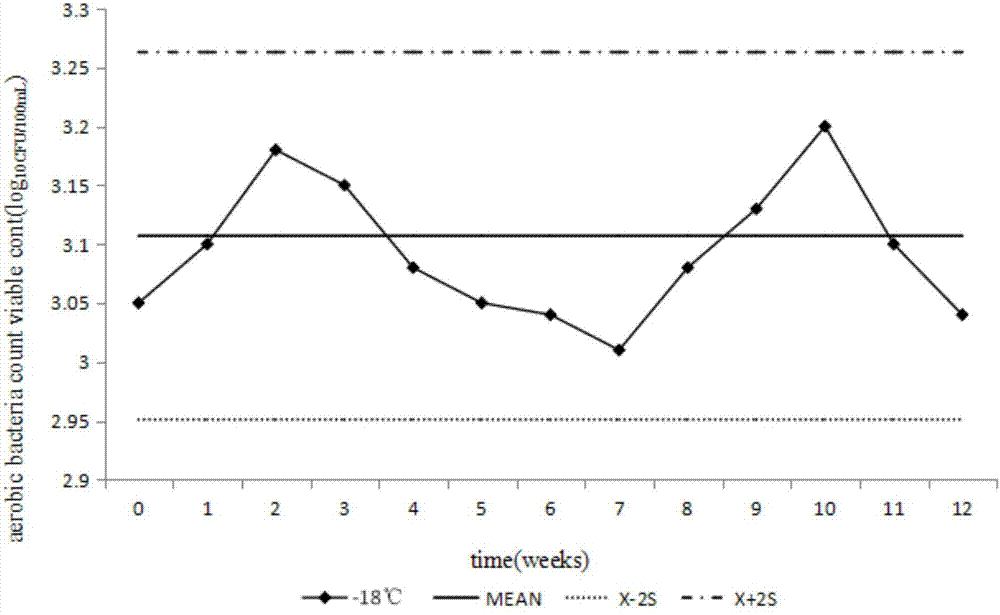
Microorganism ability verification salmonella sample preparation method
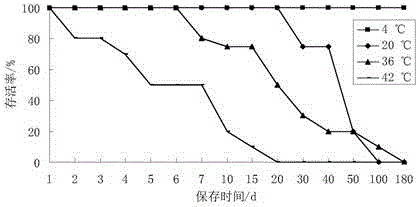
ActiveCN105176823AImprove stabilityImprove survival rateBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFreeze-drying
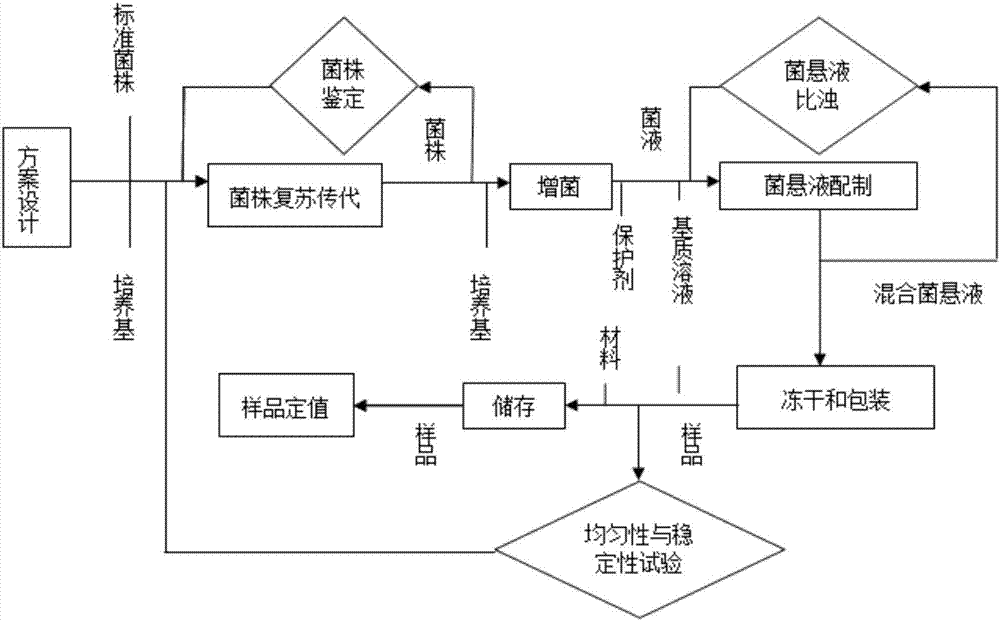
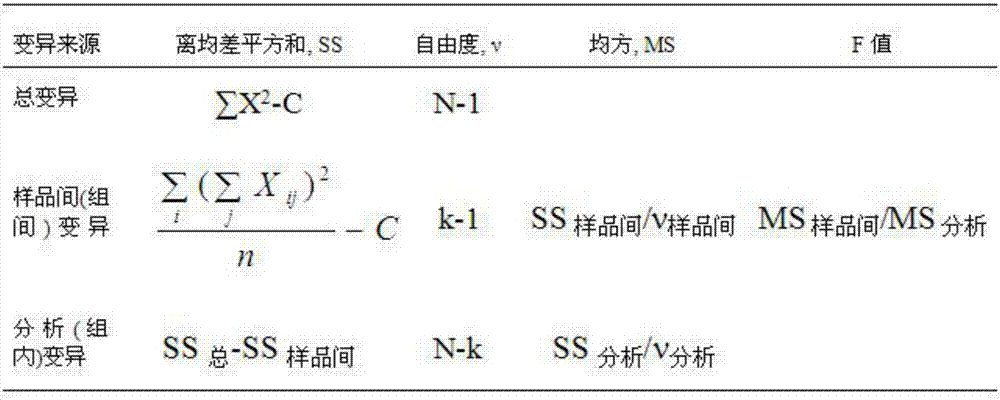
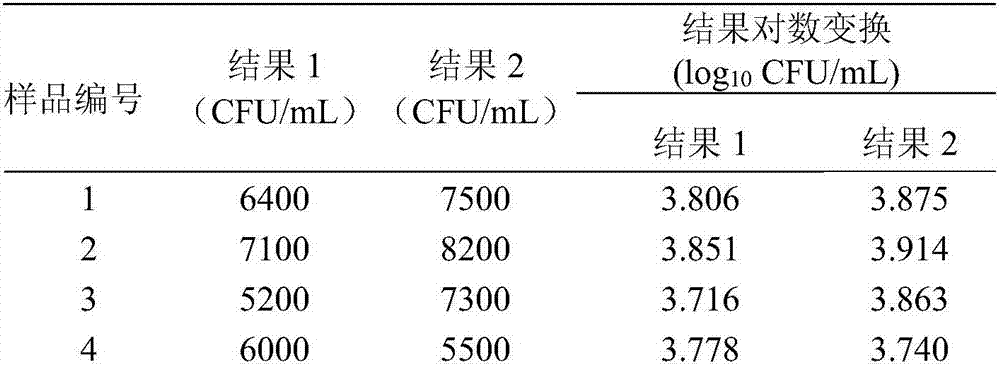
The present invention relates to the technical field of microorganism ability verification, and discloses a microorganism ability verification salmonella sample preparation method. According to the method, salmonella is adopted as target bacteria, and Serratia marcescens, Citrobacter freundii and Escherichia coli are adopted as interference bacteria; the method comprises: (A) strain resuscitation and amplification; (B) strain isolation; (C) bacterial suspension preparation; and (D) freeze-drying and packaging; and the prepared samples comprise a simple-level negative sample, a simple-level positive sample, an intermediate-level negative sample, an intermediate-level positive sample, a difficult-level negative sample and a difficult-level positive sample, wherein the sample having the same level are subjected to paired use. According to the present invention, the sample prepared through the method has the good stability, the strain survival rate is high, and the reasonable level standards with different difficulties are provided.
Owner:舟山出入境检验检疫局综合技术服务中心
Kitchen waste composite microbial degradation agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111961606AEfficient degradationImprove microbial activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyAmylase
The invention discloses a kitchen waste composite microbial degradation agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The degradation agent is prepared from Bacillus subtilis, Streptomyces thermodiastaticus, Bacillus stearothermophilus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Enteromorpha protease, Methylobacterium radiora, Pantoea dispersa, Pseudomonas oryzihabitans,Citrobacter freundii and Staphylococcus cohnii. The mixed strain accounts for 15-25% of the total mass of the degradation agent, the mass percentage of water in the degradation agent is 10-20%, the pH value of the degradation agent is 5.5-8.5, and each gram of the degradation agent contains 106-109 viable bacteria. The degradation agent has the beneficial effects that: kitchen waste containing various substances such as vegetables, grains and meat can be effectively degraded, the activity of microorganisms in the degrading agent is high, the degrading rate reaches 80% or above, the degradingrate is high, the use amount is small when the kitchen waste is treated, generated peculiar smells are small, the cost is low, use is convenient, toxic and harmful substances are not generated, and safety, reliability and environment friendliness are achieved.
Owner:人与自然环保生物科技(南京)有限公司
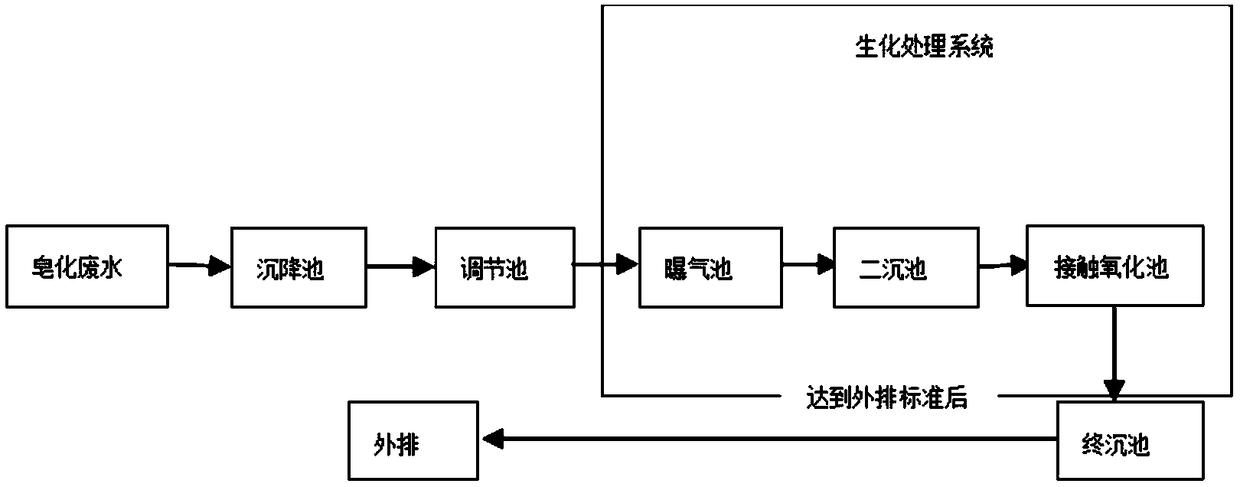
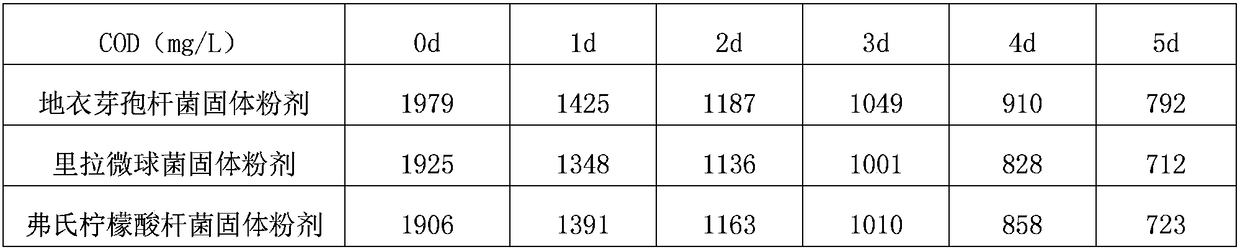
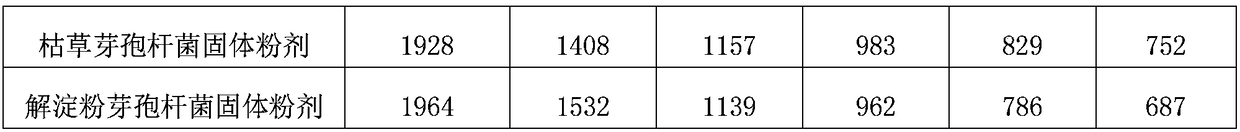
Method for treating COD(chemical oxygen demand) of high-salinity wastewater by utilizing compound microbial preparation and compound microbial preparation
InactiveCN108862633AToxic reductionHigh removal rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention relates to a method for treating the COD(chemical oxygen demand) of high-salinity wastewater by utilizing a compound microbial preparation and the compound microbial preparation. The compound microbial preparation is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 15-25% of bacillus licheniformis solid powder, 15-25% of micrococcus lylae solid powder, 15-25% of citrobacter freundii solid powder, 15-25% of bacillus subtilis solid powder and 15-25% of bacillus amyloliquefaciens solid powder. According to the method for treating the COD(chemical oxygen demand) of thehigh-salinity wastewater by utilizing the compound microbial preparation and the compound microbial preparation, the five microorganisms rapidly grow and propagate by utilizing organic matter which is easy to degrade in sewage, and the macromolecular organic matter in the wastewater are rapidly degraded after the microorganisms grow to a certain concentration; bacillus amyloliquefaciens decomposes the chlorine-contained organic matter, so that the toxic effect on microorganisms is reduced, and the COD(chemical oxygen demand) removal rate is increased; and all the components are coordinated with one another and work cooperatively, so that the COD(chemical oxygen demand) of effluent is obviously lowered.
Owner:BEFAR GROUP CO LTD
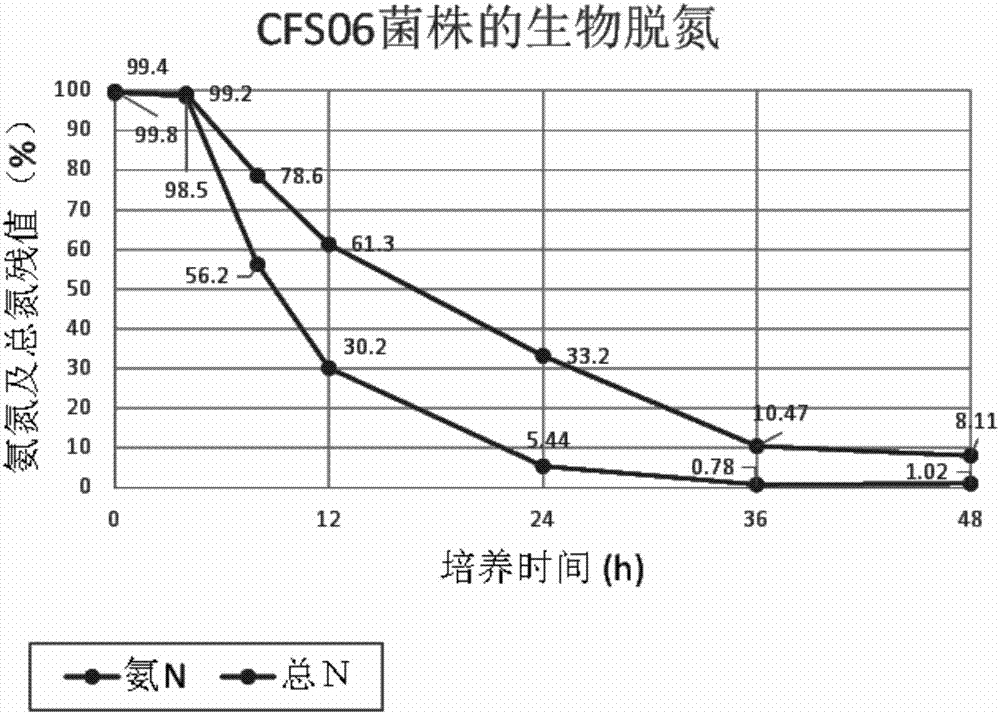
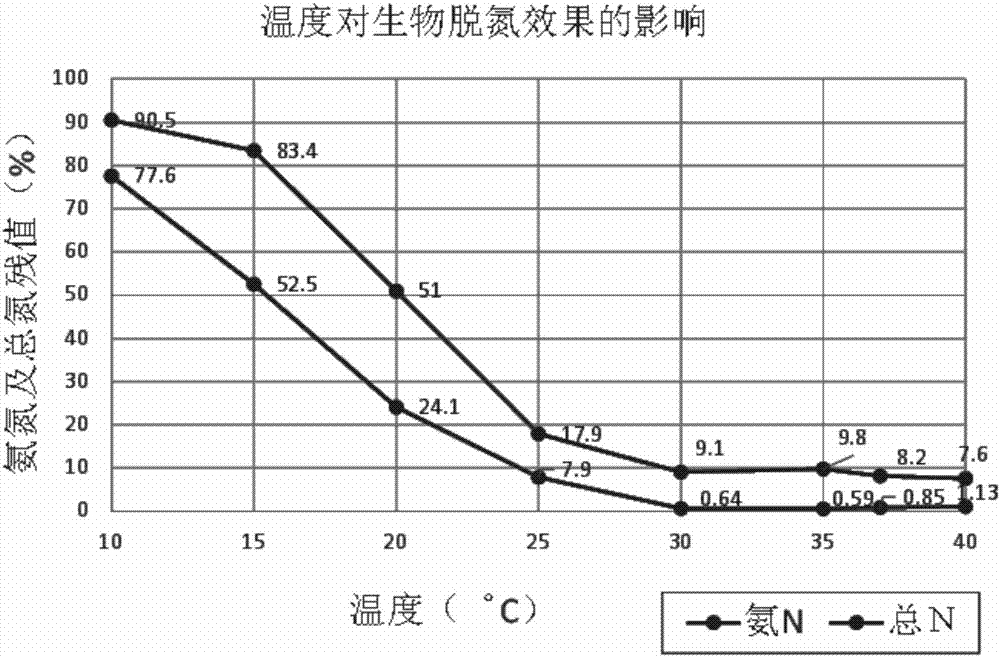
Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification Citrobacter species and application thereof
ActiveCN107460141AStrong growth adaptabilityLow nutritional requirementsBacteriaWater contaminantsMetaboliteAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification Citrobacter species applicable to the treatment of wastewaters from industrial and agricultural production or domestic wastewater. The species is already collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center under CGMCC No. 13434 and is applicable to biological denitrification of nitrogen-bearing water and biological degradation of various antibiotics in various water environments. Citrobacter freundii CFS06 herein is capable of biologically removing organic or inorganic nitrogen and is discovered to tolerate phenols in water and effectively degrade the same. The results of heterotrophic nitrification performance measurement show that the above Acinetobacter, Citrobacter freundii CFS06, has high removal rate for organic and inorganic ammonia nitrogen, with zero accumulation of intermediate metabolites, nitrates and nitrites; the species is capable of denitrifying nitrates under aerobic condition, has low requirement on C / N nutrition, has great breeding capacity in wastewater environments, and has a promising application prospect in terms of green treatment of river channel industrial contaminants owing to its tolerance and degradation for phenols.
Owner:FOSHAN YUHUANG ECOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT TECH
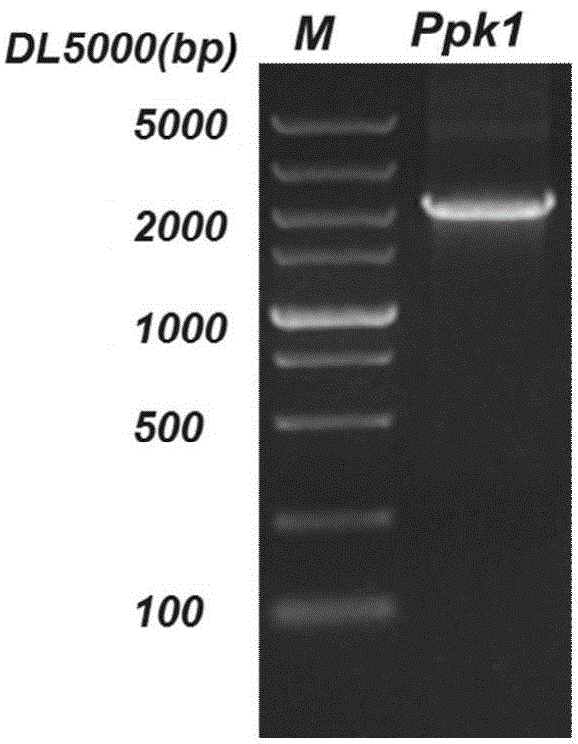
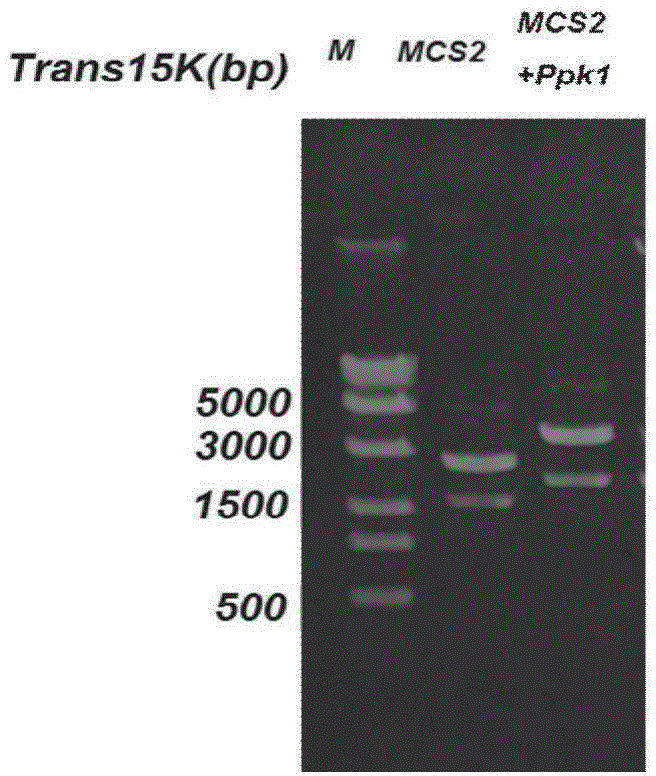
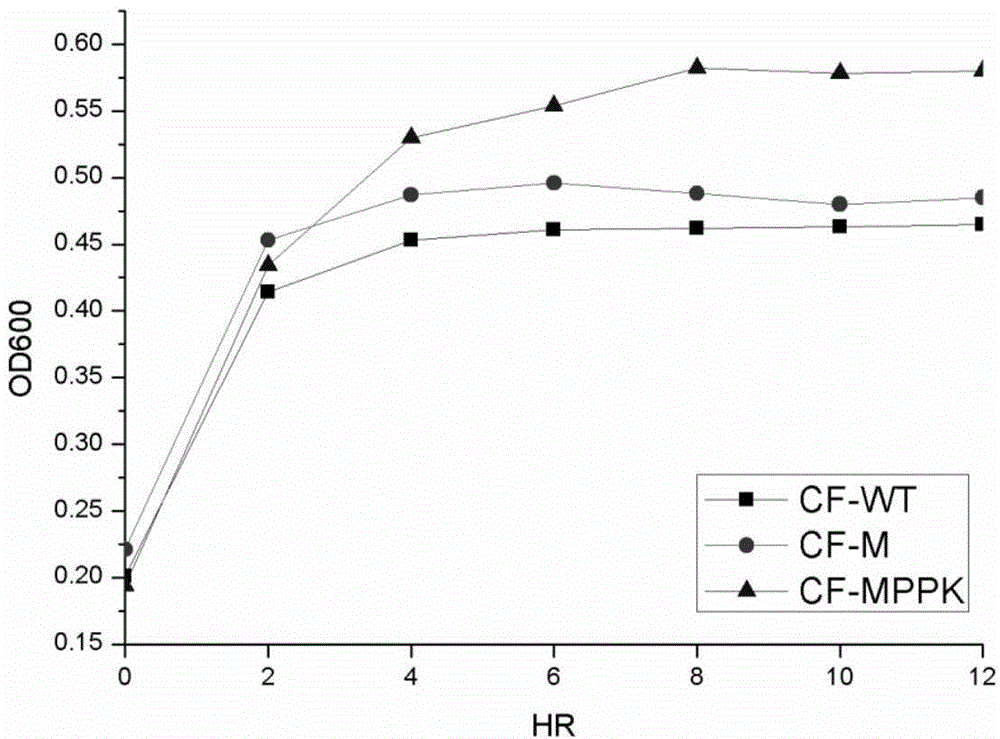
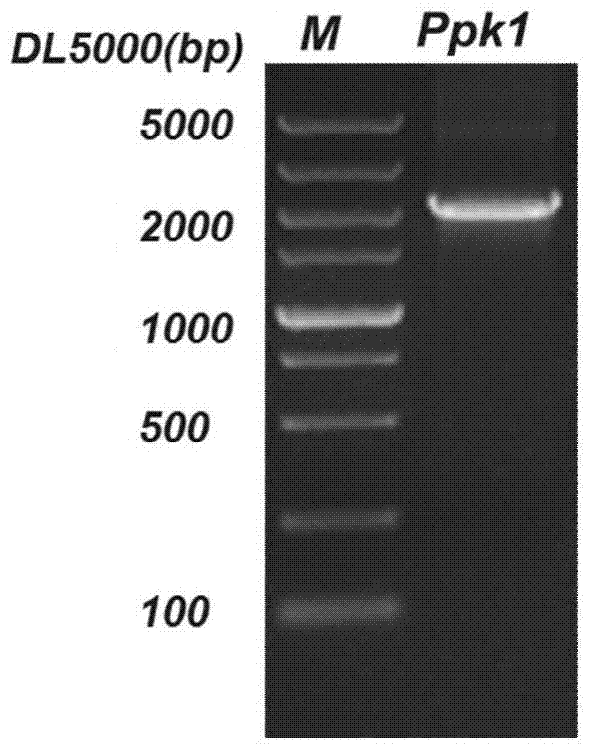
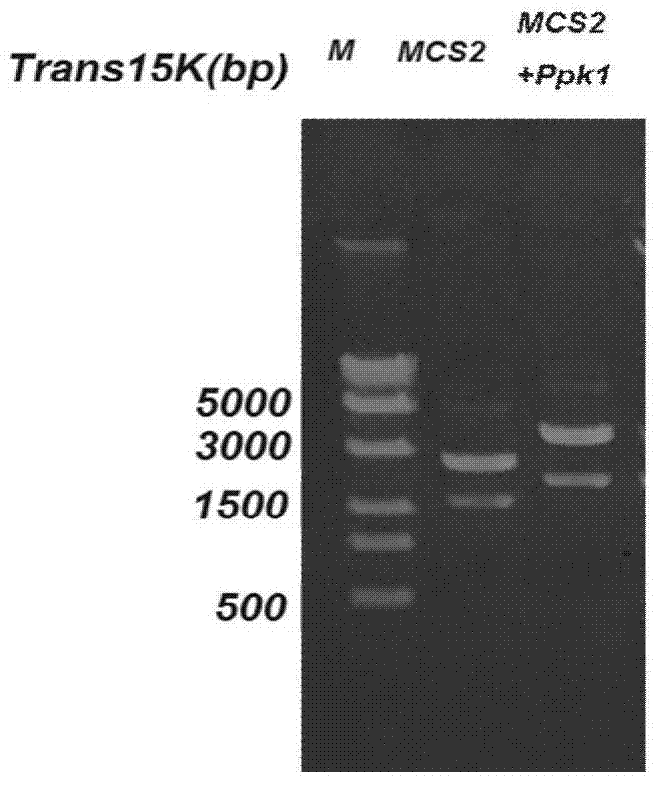
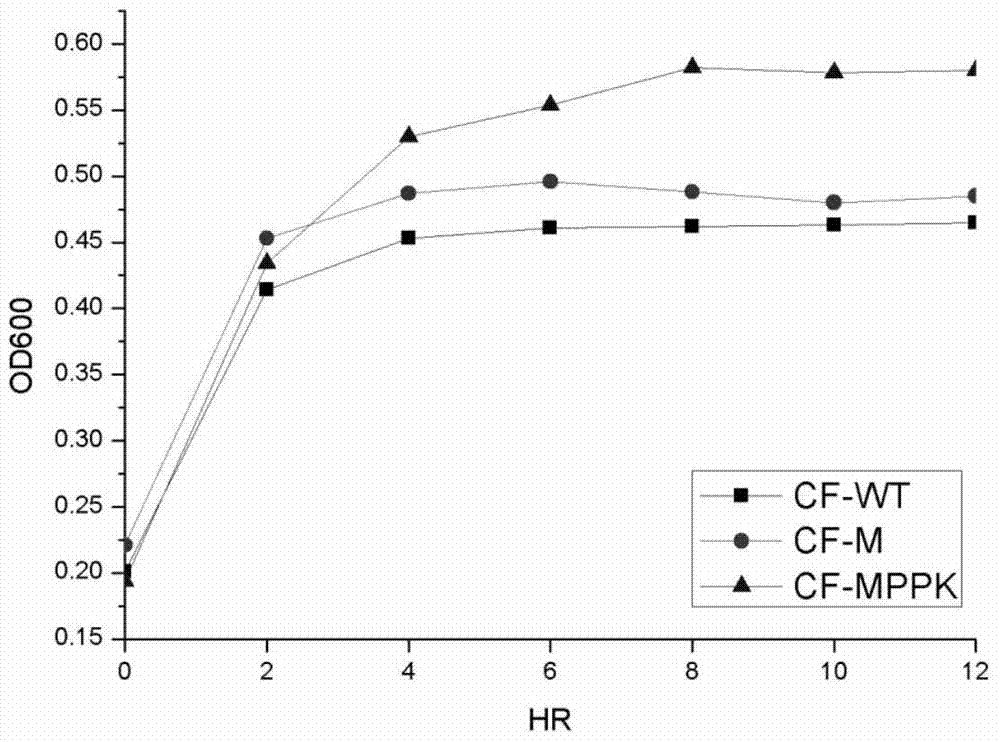
Citrobacter freundii with transformed phosphorus accumulating genes and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN104531599AEfficient removalConducive to survivalBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyBacteroides
The invention discloses a Citrobacter freundii with transformed phosphorus accumulating genes. Polyphosphate kinase Ppk1 genes derived from the Citrobacter freundii are led into the Citrobacter freundii. The DNA of the Citrobacter freundii only contains Ppk1 genes, and the control way of the Ppk1 genes and Ppx genes is dual-cis-trans cotranscription. The phosphorus accumulation ability of bacteria with the characteristics can be improved by means of the Ppk1 with host bacteria as a receptor to express the source. The invention further discloses a construction method of the Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes and the application of the Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes in waste water dephosphorization. The Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes has the advantage of being high in dephosphorization ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
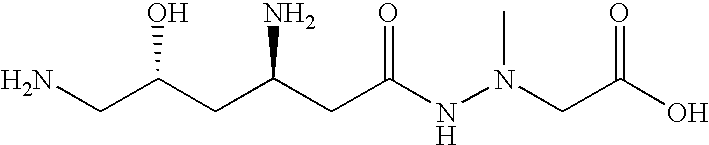
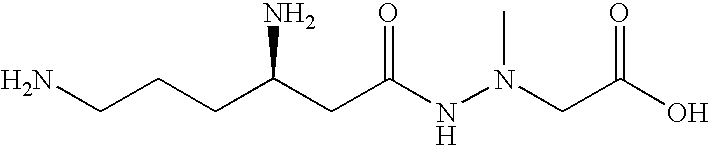
Administration of negamycin or deoxynegamycin for the treatment of bacterial infections
The invention provides a method for treating bacterial infections. In one aspect, the invention comprises orally administering a pharmaceutical composition to an animal, wherein the composition comprises a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient and an antibacterial effective amount of negamycin, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or isomer thereof. An aspect of the invention also relates to a method of treating a bacterial infection, wherein the method comprises intravenously administering a pharmaceutical composition to an animal, and wherein the composition comprises a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient and an antibacterial effective amount of deoxynegamycin, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or isomer thereof. An aspect of the invention also relates to a method of treating a bacterial infection, wherein the method comprises administering to an animal an antibacterial effective amount of negamycin or deoxynegamycin, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug or isomer thereof, and wherein the infecting bacteria are selected from a group of bacteria consisting of the following: Acinetobacter baumanii, Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter aerogenes, haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Staphylococcus aureus MRSA, Staphylococcus aureus GISA, Staphylococcus epidermis, Streptococcus pneumoniae PenR, Streptococcus pneumoniae PenS and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Owner:VERSICOR
Kit for identifying bacteria by use of molecular beacon-melting curve technology and application of kit
ActiveCN106834520AHigh homologyAvoid contamination riskMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesListeria monocytogenes
The invention discloses a molecular beacon and a kit for quickly identifying various clinically common bacteria and belongs to the technical field of microbiological detection. The sequences SEQ ID of the molecular beacon are as shown in v6p1, v6p2, v1p1 and v1r. Through comparison between various clinically common bacteria 16s ribosome RNA sequences in an NCBI gene sequence database and design of the molecular beacon at a tag sequence, clinically common 18 bacteria, including baumanii, A.hydrophila, burkholderia cepacia, citrobacter freundii, enterobacter cloacae, enterococcus faecium, enterococcus faecalis, enterobacter aerogenes, escherichia coli, klebsiella pneumoniae, listeria monocytogenes, proteus mirabilis, pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella, serratia marcescens and stenotrophomonas maltophilia, can be quickly identified. The invention further discloses the kit containing the molecular beacon and used for detecting various bacteria, and the kit can quickly and accurately identify various clinically common bacteria.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Bacterial strain capable of degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN106282057APromote growthWet surfaceBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMicrobiology
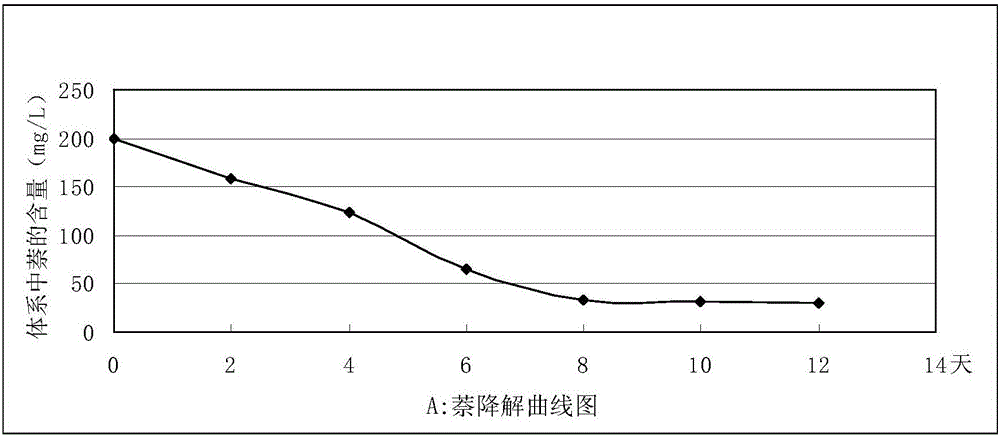
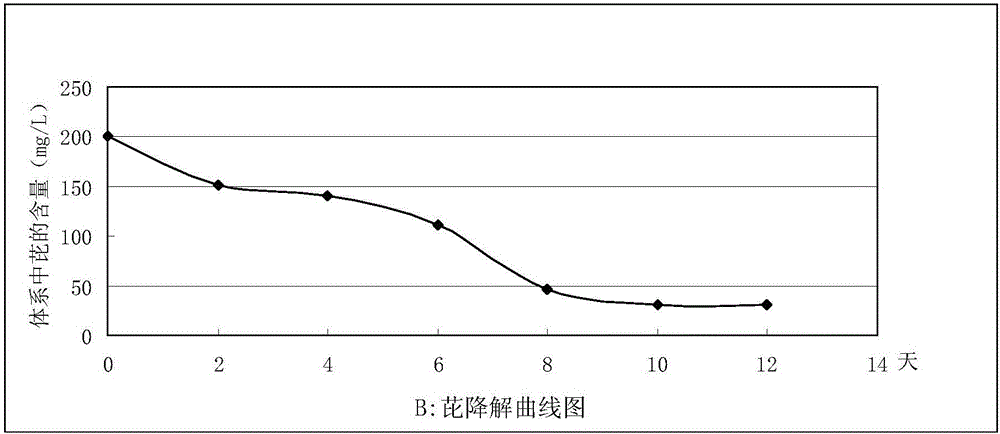
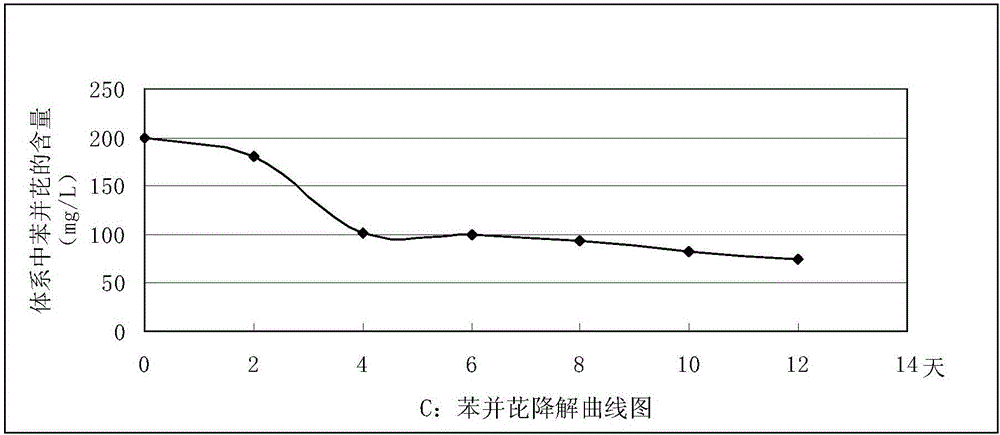
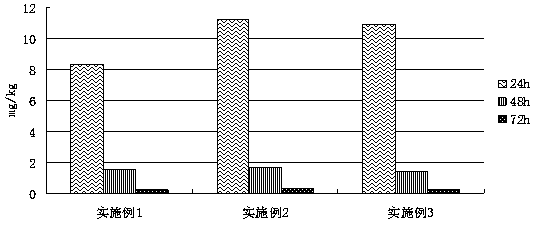
The invention relates to a bacterial strain capable of degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and application of the bacterial strain, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The novel bacterial strain aims at achieving the purpose of degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The bacterial strain is Citrobacter freundii L2-14, and the preservation number of the bacterial strain in China Center for Type Culture Collection is CCTCC NO:M2016371. The bacterial strain is used for remediating soil contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The bacterial strain capable of degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons has the capability of growing with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as a carbon source and an energy source, can rapidly degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminants and is wide in substrate degradation range and high in degradation rate.
Owner:TAIZHOU VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Compound biological preparation and application thereof in repairing polychlorinated biphenyls polluted soil
ActiveCN107586747ARepair pollutionEasy to prepareBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismBacillus pumilus
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and discloses a compound biological preparation. The compound biological preparation is prepared from rhodopseudomonas palustris, citrobacter freundii, shewanella, pseudomonas putida and bacillus pumilus. The compound biological preparation disclosed by the invention is prepared by matching five strains; all the strains promote each other, and a specific carrier is matched, so that the degradation capability on polychlorinated biphenyls is improved.
Owner:江苏诚冉环境修复工程有限公司
Standard sample of staphylococcus aureus in milk powder and preparation method of standard sample of staphylococcus aureus in milk powder
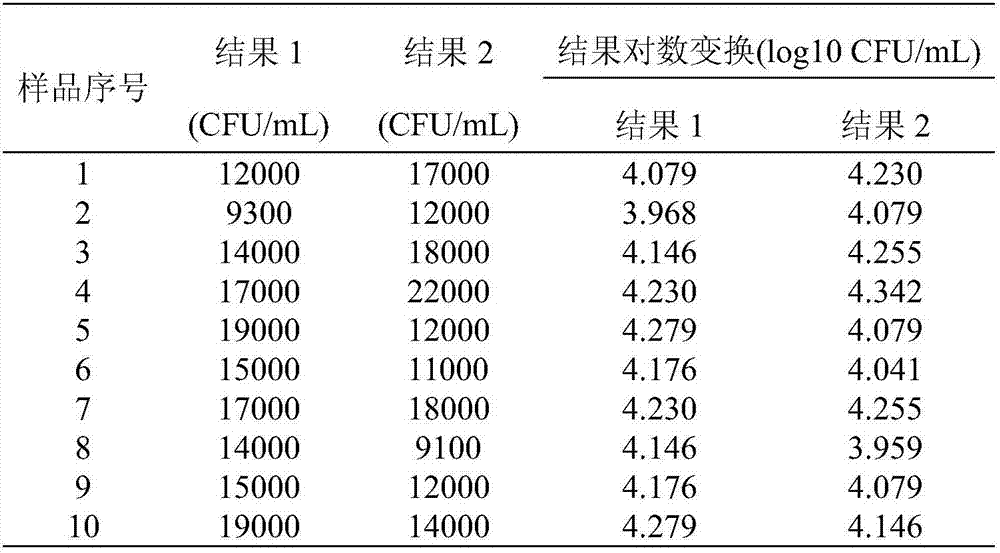
InactiveCN107236784ADoes not affect detectionGuaranteed stabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementCitrobacter freundiiStandard samples
The invention belongs to the field of quality control in microbial detection and particularly relates to a standard sample of staphylococcus aureus in milk powder and a preparationmethod of the standard sample of the staphylococcus aureus in the milk powder. The standard sample of the staphylococcus aureus in the milk powder comprises a target bacterium and background flora, wherein the target bacterium is the staphylococcus aureus; the background flora comprises Citrobacter freundii,E. coli, Klebsiella pneumonia and Bacillus cereus. The standard sample meets requirements for uniformity and stability, the stability of the standard sample can be guaranteed to the greatest extent, and a perfect preparation technology for the standard sample is formed by starting from meeting special transport conditions by means of research in special process, stability and uniformity and the like, is suitable for preparing the standard sample, meeting the requirements for uniformity and stability, of the staphylococcus aureus in the milk powder and is applicable to quality control, method validation and other purposes in a laboratory.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
A strain of Citrobacter freundii transgenic for phosphorus accumulation gene and its construction method and application
ActiveCN104531599BEfficient removalConducive to survivalBacteriaWater contaminantsBacteroidesGemella
The invention discloses a Citrobacter freundii with transformed phosphorus accumulating genes. Polyphosphate kinase Ppk1 genes derived from the Citrobacter freundii are led into the Citrobacter freundii. The DNA of the Citrobacter freundii only contains Ppk1 genes, and the control way of the Ppk1 genes and Ppx genes is dual-cis-trans cotranscription. The phosphorus accumulation ability of bacteria with the characteristics can be improved by means of the Ppk1 with host bacteria as a receptor to express the source. The invention further discloses a construction method of the Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes and the application of the Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes in waste water dephosphorization. The Citrobacter freundii with the transformed phosphorus accumulating genes has the advantage of being high in dephosphorization ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Coliform standard sample in food and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107227336ASimple processIncrease success rateBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEnterobacter cloacaeBacteria coliforms
The invention belongs to the field of quality control in an aspect of microbial detection, and particularly relates to a coliform standard sample in food and a preparation method thereof. The coliform standard sample in food comprises a target flora and a background flora, wherein the target flora consists of colon bacillus, klebsiella pneumoniae, enterobacter cloacae and citrobacter freundii; the background flora consists of rhodococcus equi, bacillus cereus and staphylococcus aureus. The uniformity and the stability conform to the capability verification requirements; the stability of a test sample can be ensured to the maximum degree; even when the content of colon bacillus changes in the transportation and storage process, the total quantity of the coliform cannot be influenced in a sense of statistics. The sample preparation method has the advantages that the process is simple; the success ratio is high.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
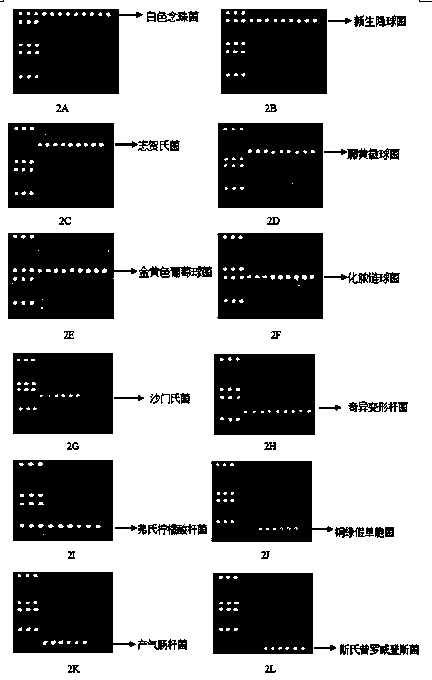
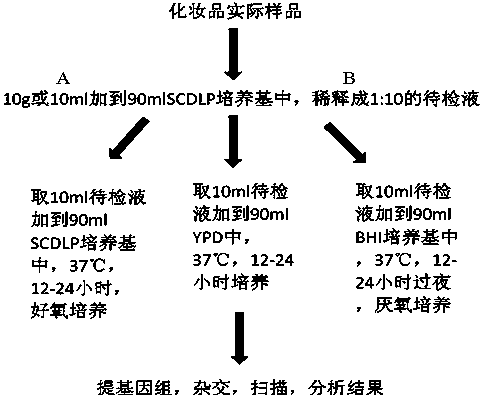
Gene chip and kit for detecting common pathogenic bacteria in cosmetics
ActiveCN103937897AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPseudomonas
The invention provides a gene chip for detecting common pathogenic bacteria in cosmetics. The gene chip comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe comprises DNA segments which are selected from 16S-23SrDNA intermediate zones of micrococcus luteus, staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus pyogenes, salmonella, proteus mirabilis, citrobacter freundii, pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacter aerogenes and providencia stuartii and 18S-28SrDNA intermediate zones of the ipaH gene of shigella, candida albicans and cryptococcus neoformans, or complementary DNA or RNA sequences of the DNA segments. The invention also provides a kit for detecting the common pathogenic bacteria in the cosmetics by use of the gene chip. The gene chip and the kit can be used for detecting the common pathogenic bacteria in the cosmetics, and are simple and convenient to operate, high in accuracy and excellent in repeatability.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Intestinal microorganism markers for multiple myeloma, application and detection preparation of intestinal microorganism markers
ActiveCN110669818AAccurately reflect clinical diagnosisAccurately reflect treatment effect assessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseKlebsiella variicola
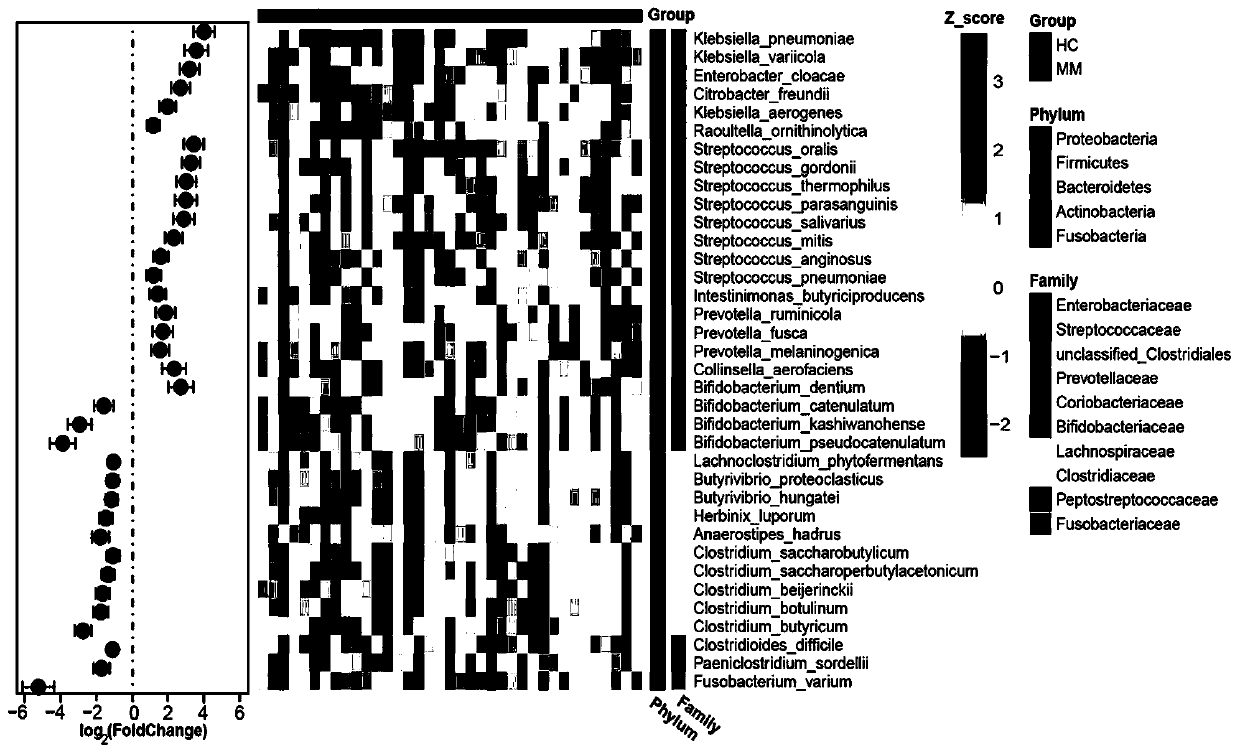
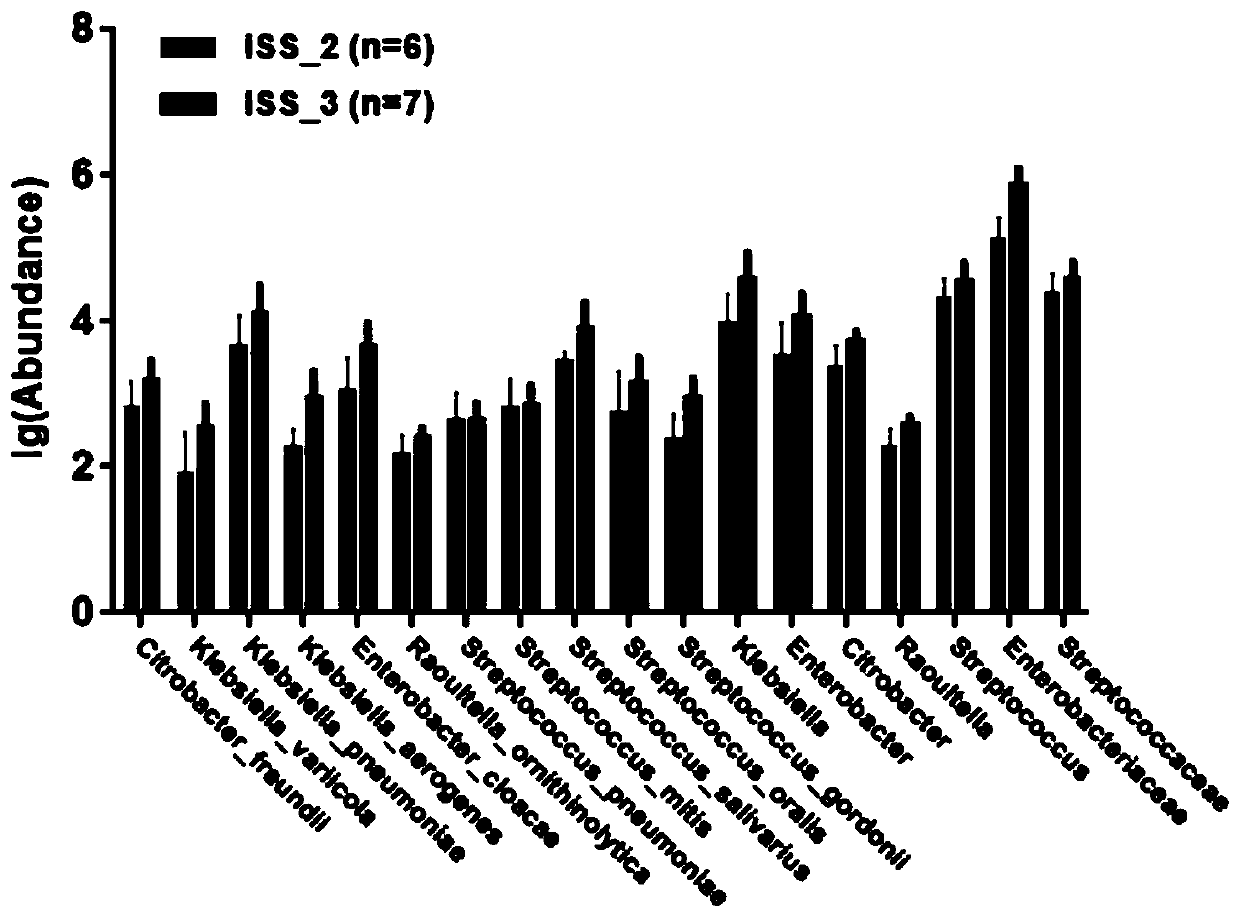
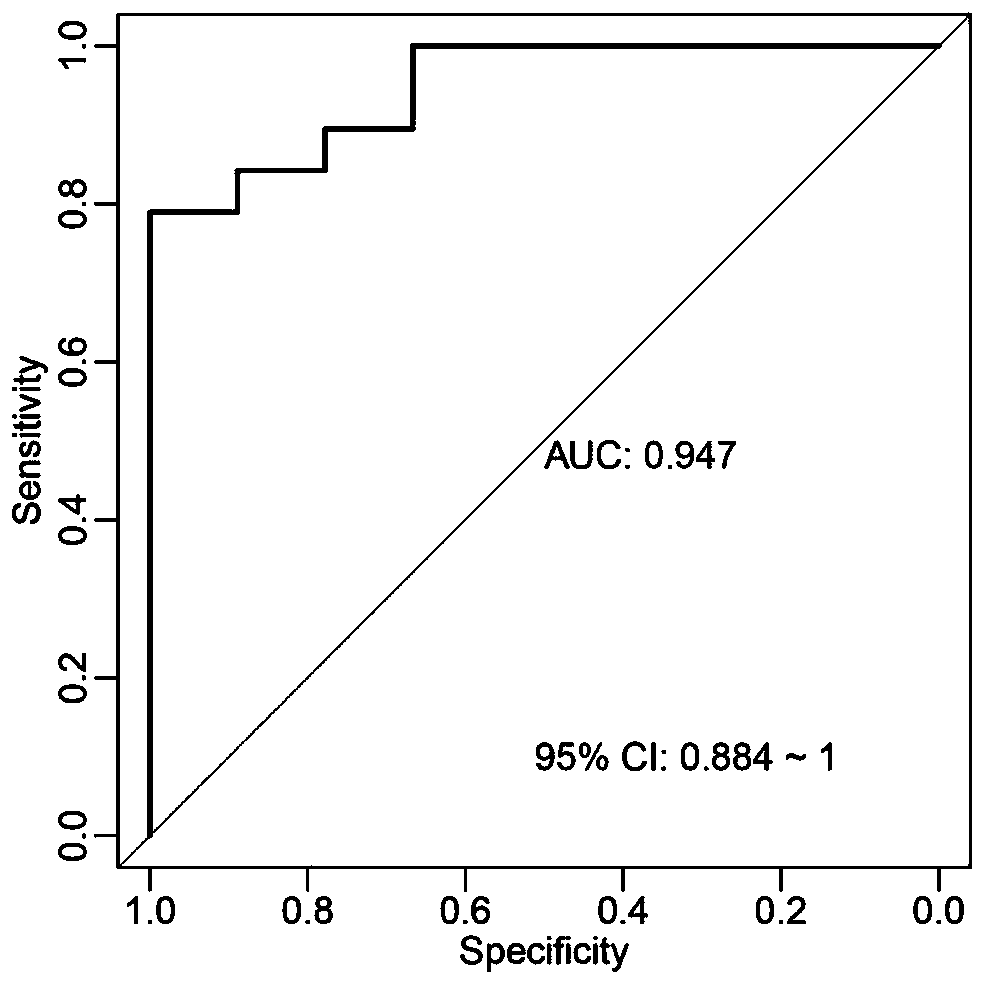
The invention discloses intestinal microorganism markers for detecting multiple myeloma diseases, and an application and detection preparation of the intestinal microorganism markers. The intestinal microorganism markers comprise citrobacter freundii, enterobacter cloacae, raoultella ornithinolytica, klebsiella aerogenes, klebsiella variicola, klebsiella pneumoniae, streptococcus salivarius, streptococcus oralis, streptococcus gordonii, streptococcus mitis, streptococcus pneumoniae, butyrate producing bacteria, clostridium butyricum and clostridium saccharobutylicum. The intestinal microbial markers can be used alone or in combination. The invention discloses a support vector machine (SVM) classification model constructed by taking the microbial markers as characteristics, and the SVM classification model is applied to clinical diagnosis of multiple myeloma diseases. The invention also discloses an application of the microorganism markers in preparation of a diagnostic preparation formultiple myeloma diseases.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
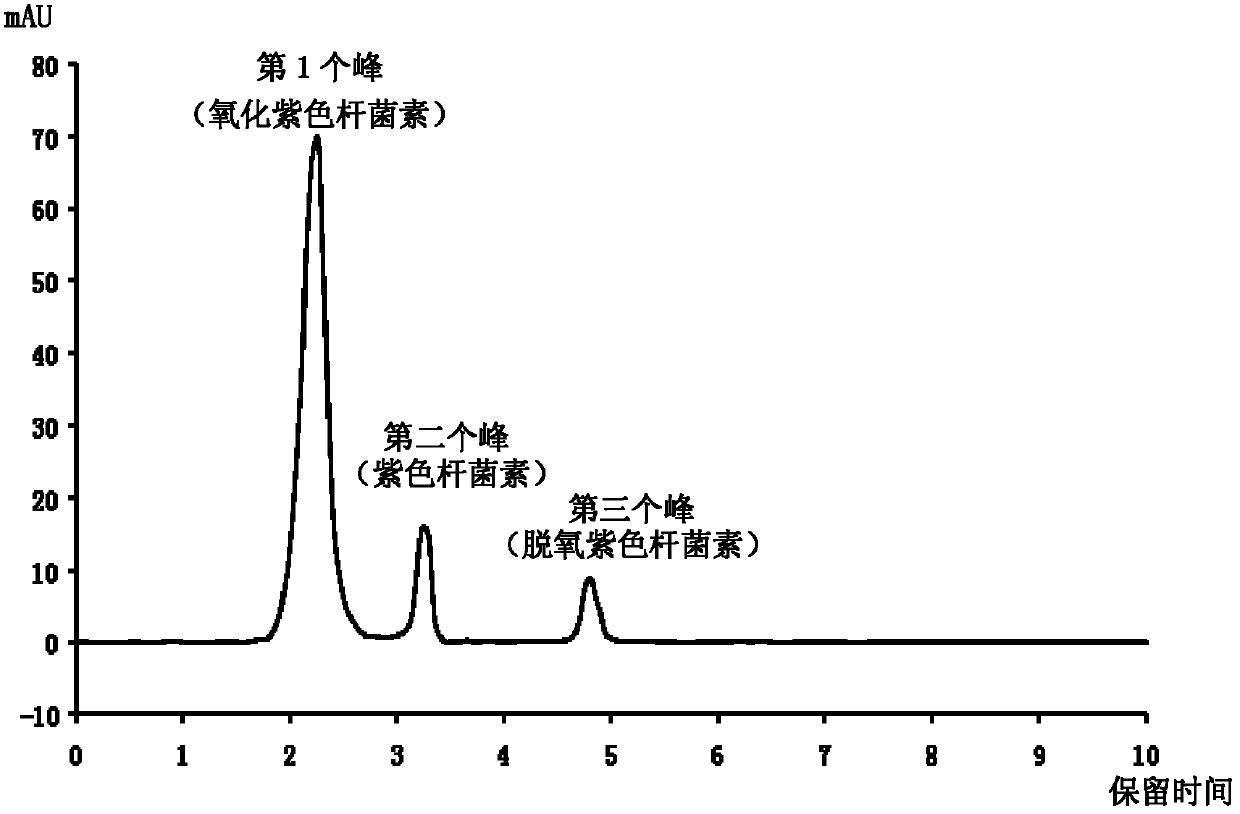
Microbial inhibitor
The invention discloses a microbial inhibitor. The microbial inhibitor provided in the invention is violacein substances (comprising violacein or violacein derivatives) which are extracted from Citrobacter freundii (pCOM10) strains, Citrobacter freundii (pCOMdeltaD) strains or Duganella B2 and have different chemical structures. Two of three extracts provided in the invention have strong inhibition on various plant causative fungi and gram positive bacteria. The extract from the Citrobacter freundii (pCOM10) strains can inhibit the various plant causative fungi, and the inhibition rate of the Citrobacter freundii (pCOM10) strains with the concentration of 4mg / mL on Phytophthora capsici can reach 100%. The microbial inhibitor establishes bases for developing agricultural antibiotics through utilizing violacein or the violacein derivatives.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Genes for detecting bacteria and detection method by using the same
The present invention relates to genes for detecting the genus <HIL><PDAT>Pectinatus frisingensis < / ITALIC><PDAT>or <HIL><PDAT>Pectinatus cerevisiiphilus < / ITALIC><PDAT>of the genus Pectinatus, which is known as beer-spoilage bacteria, and a method for detecting the bacteria by using the genes.< / PTEXT>The present invention provides gene sequences of spacer regions between 16S rRNA genes and 23S rRNA genes specific for the genus Pectinatus relating to beer-spoilage and a method for quickly and sensitively detecting the bacteria by using the sequences.< / PTEXT>
Owner:ASAHI BREWERIES LTD
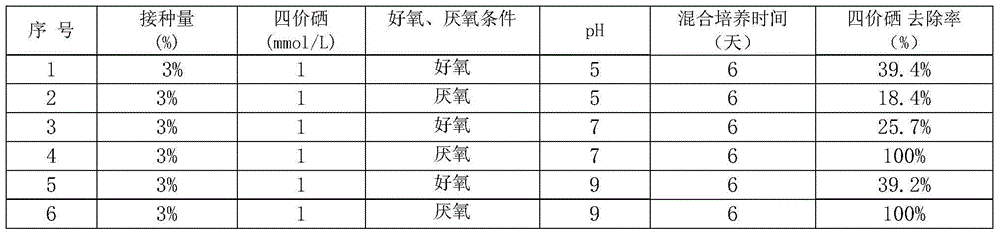
Method for purifying tetravalent selenium-containing sewage under anaerobic condition and aerobic condition by utilizing Citrobacter freundii
InactiveCN104386828ASimple processEasy to operateTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSodium acetateCitrobacter
The invention relates to a method for purifying tetravalent selenium-containing sewage under an anaerobic condition and an aerobic condition by utilizing citrobacter freundii. According to the method, the Citrobacter freundii Strain Y9, bought from America Type Culture Collection, is taken as a strain, the citrobacter freundii is inoculated in the tetravalent selenium-containing sewage under the anaerobic condition and the aerobic condition and takes sodium citrate, sodium acetate or sodium nitrate as an electron donor, tetravalent selenium in the wastewater is taken as an electron acceptor, and the tetravalent selenium is reduced into element selenium by the Citrobacter freundii Strain Y9 after a biochemical treatment, so that the aim of removing the tetravalent selenium from the sewage under the anaerobic condition and the aerobic condition is realized. The method is simple in process, convenient to operate, low in treatment cost, large in treatment range and free of secondary pollution.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
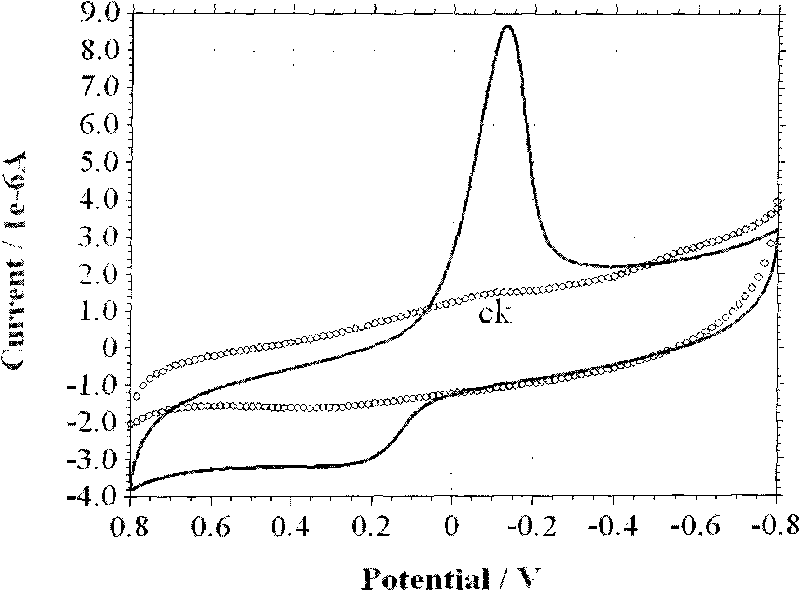
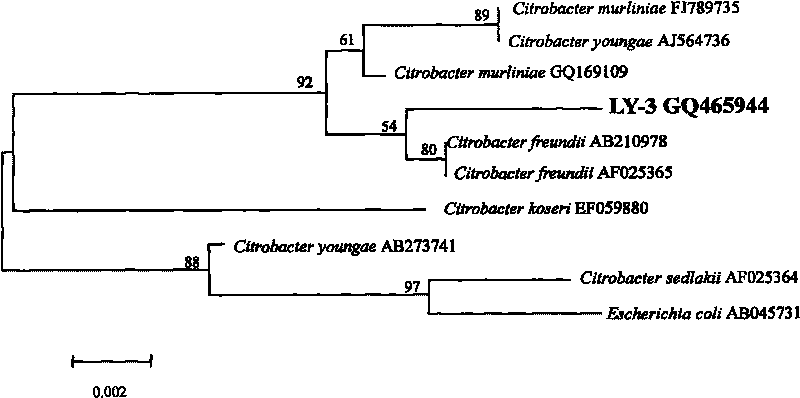
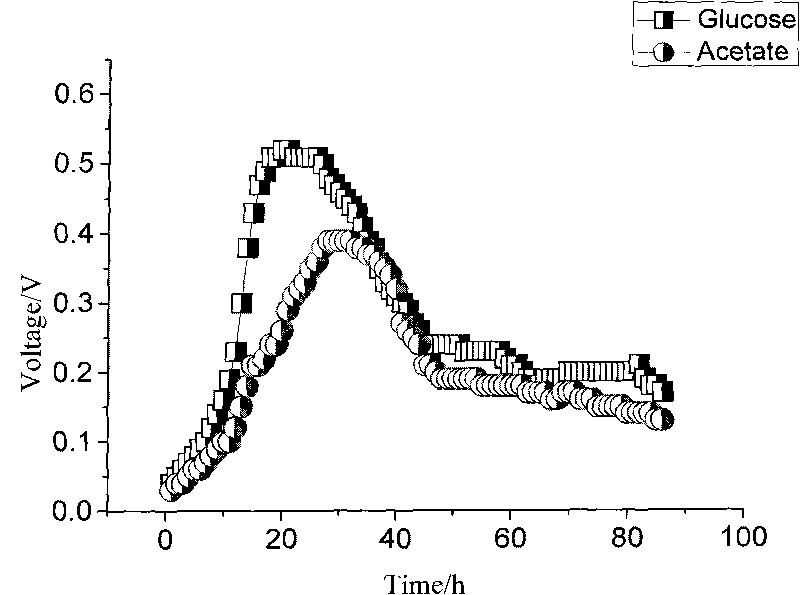
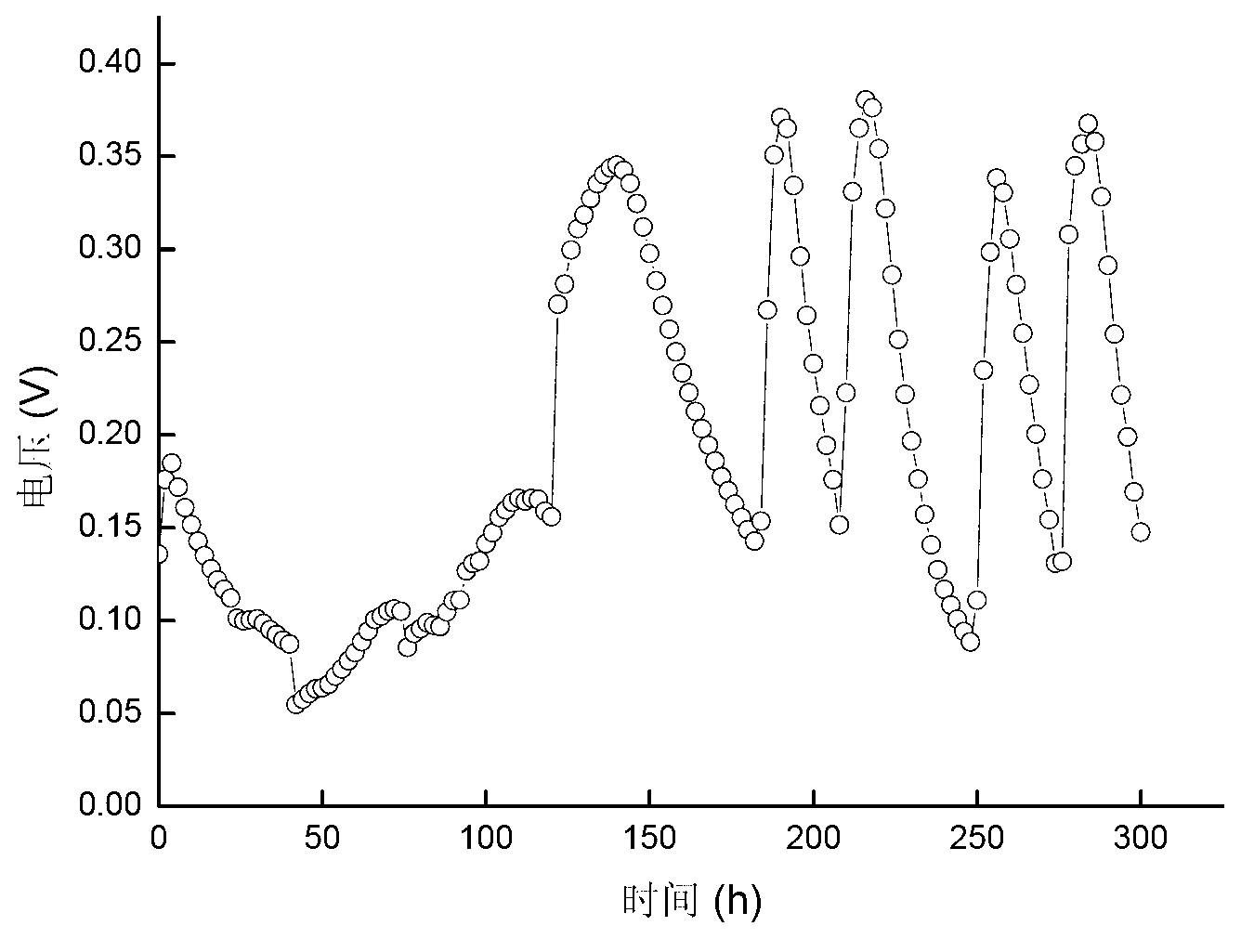
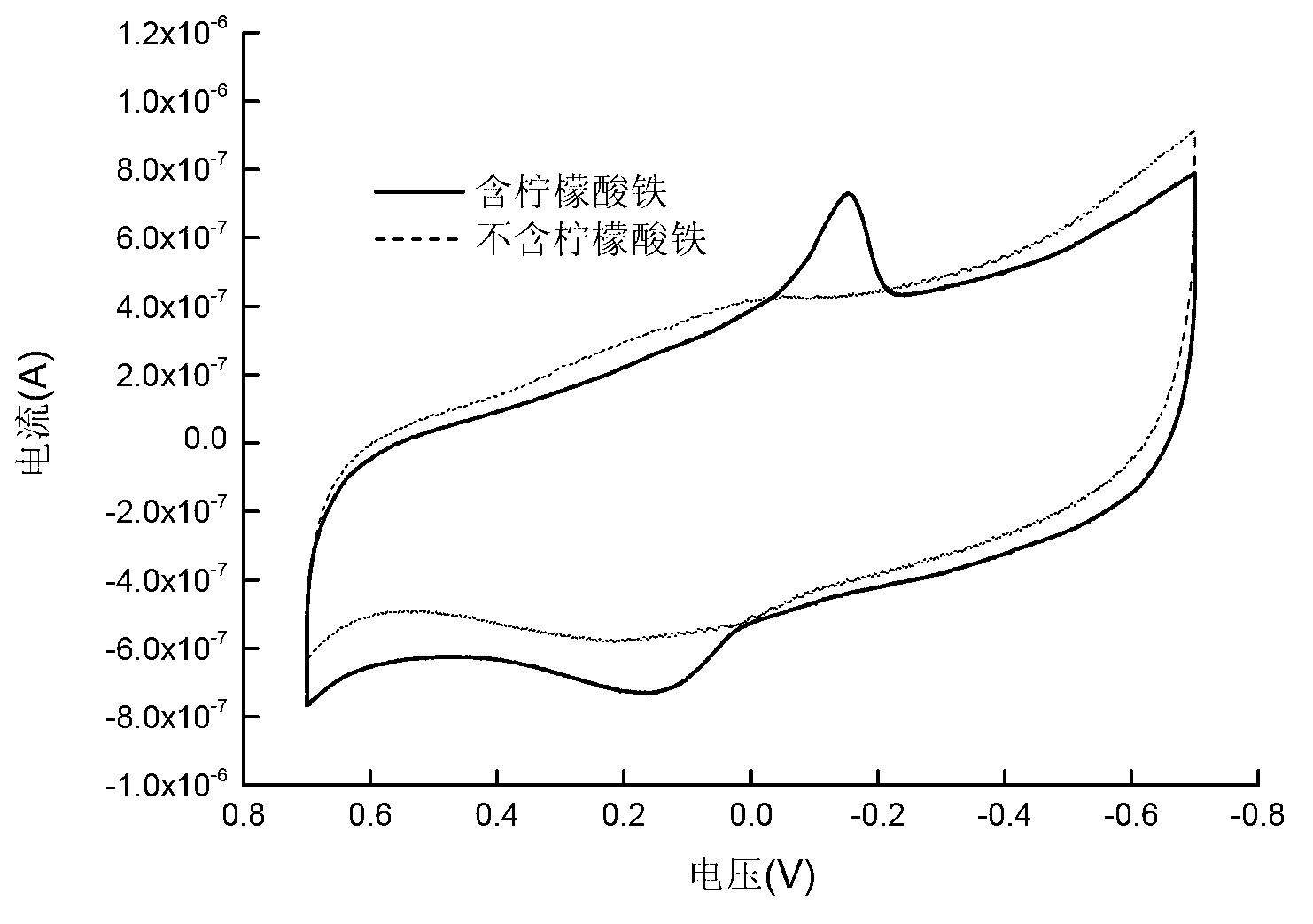
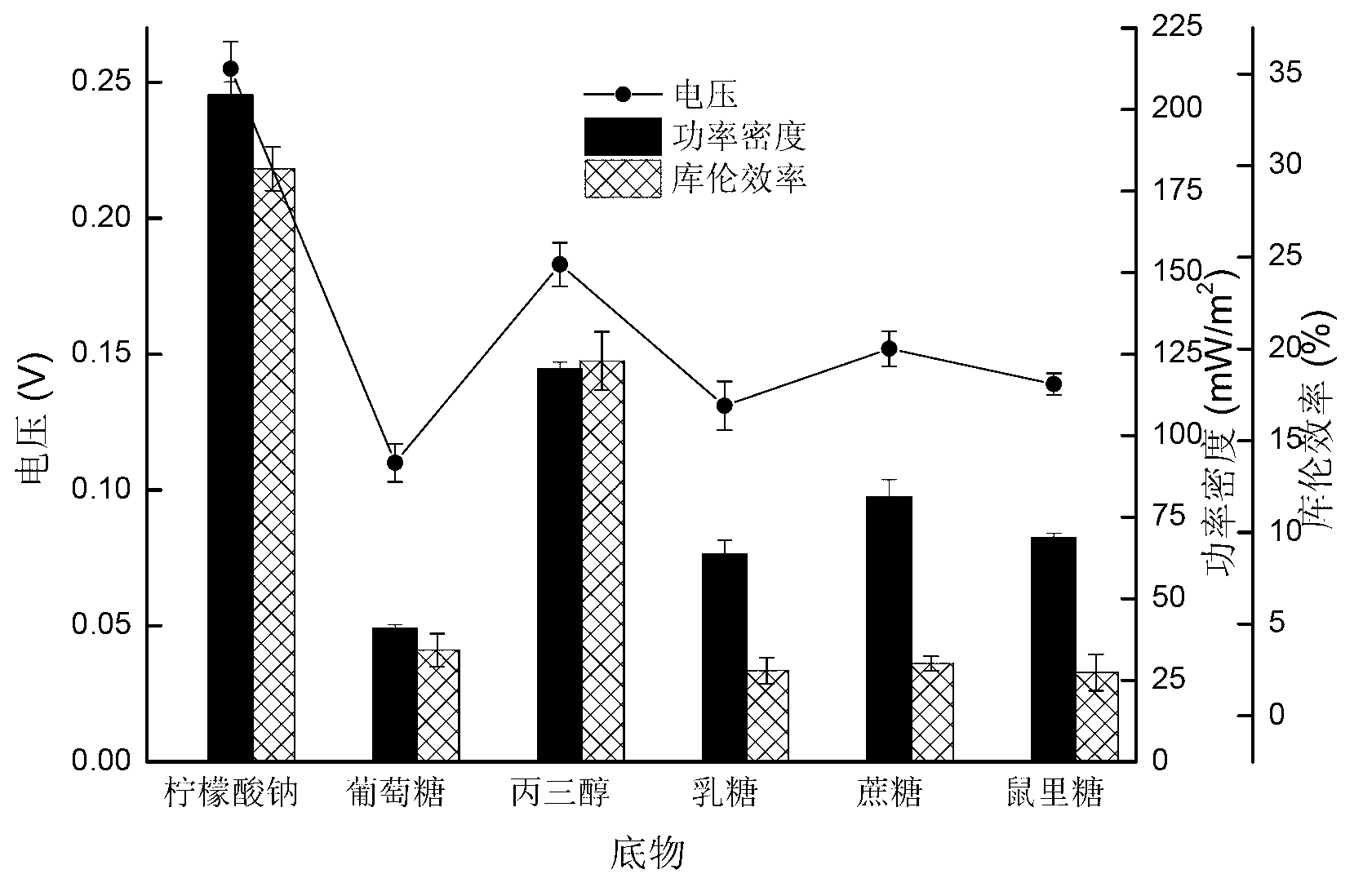
Application of citrobacter freundii in electricity generation by microorganism and electricity generation method
The invention discloses an application of citrobacter freundii in electricity generation by microorganism and an electricity generation method. The citrobacter freundii is taken as anode catalyst of the microbiological fuel cell to be applied to electricity generation by microorganism. The electricity generation method comprises preparing citrobacter freundii to be as inoculum for microbiological fuel cell; preparing catholyte and anolyte containing fuel; adding the inoculum for microbiological fuel cell into the anode chamber of the microbiological fuel cell, standing for culturing, and carrying out electricity generation detection. The invention opens up a new application field for citrobacter freundii and provides a new highly adaptable electrogenesis microorganism. The citrobacter freundii LY-3 is easy to culture, and the electrogenesis is high with various organism electrogenesis utilized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiplex PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer for simultaneously detecting salmonella, citrobacter, proteus and Edwardsiellas and design method thereof
InactiveCN103146827AQuick checkSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesCitrobacterEdwardsiella tarda
The invention provides a multiplex PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer for simultaneously detecting salmonella, citrobacter, proteus and Edwardsiellas and a design method thereof, and relates to the detection of salmonellae and the like. A PCR amplified fragment corresponding to a salmonella primer is 526bp, a PCR amplified fragment corresponding to a citrobacter freundii primer is 161bp, a PCR amplified fragment corresponding to a proteus mirabilis primer is 396bp and a PCR amplified fragment corresponding to an edwardsiella tarda primer is 330bp. The design method comprises the following steps of: 1, designing a multiplex PCR primer combination; 2, screening primers in the primer combination and reserving the primers which can not be used for synthesizing primer dimers; 3, judging competitive advantageous and disadvantageous states of the reserved primers and comparing GC% of the primers which are reserved in the step 2, and can not be used for synthesizing the primer dimers with a base number; selecting and judging the primers with the high GC content as the primers with the advantageous competitive states and performing step 5, and otherwise, performing step 4; step 4, screening the primers with the disadvantageous competitive states again; and 5, amplifying the primers with the advantageous competitive states.
Owner:厦门市农产品质量安全检验测试中心 +1
Citrobacter freundii and application thereof to production of bioelectricity
ActiveCN103215205ALower requirementImprove electrochemical activityBacteriaFinal product manufactureMicroorganismMicrobial fuel cell
The invention discloses a citrobacter freundii and an application thereof to the production of bioelectricity. The (citrobacter freundii) Z7 is collected in the China center for type culture collection short for CCTCC on November 6th 2012, wherein the collection number of the (citrobacter freundii) Z7 is CCTCC NO: M2012447. The citrobacter freundii can transfer electrons to an extracellular electron acceptor under an anaerobic condition, can be inoculated in a microbial fuel cell and can generate electric energy while degrading organisms. Compared with other strains, the (citrobacter freundii) Z7 not only has strong electrochemical activity, but also can generate electricity by taking various types of organisms as a unique carbon source. Based on the characteristics, the citrobacter freundii can be well applied to environment pollution restoration and biological energy recovery.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Enzymes
The present invention relates to enzymes and processes. In particular, there is described an isolated polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence corresponding to Citrobacter freundii phytase or a homologue, a modified form, a functional equivalent or an effective fragment thereof. There is also described a host cell transformed or transfected with a nucleic acid encoding a bacterial phytase enzyme or a modified form as well as the use of such a phytase or modified form in food or animal feed.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
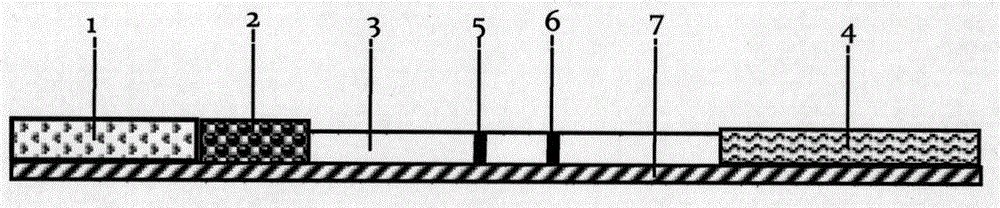
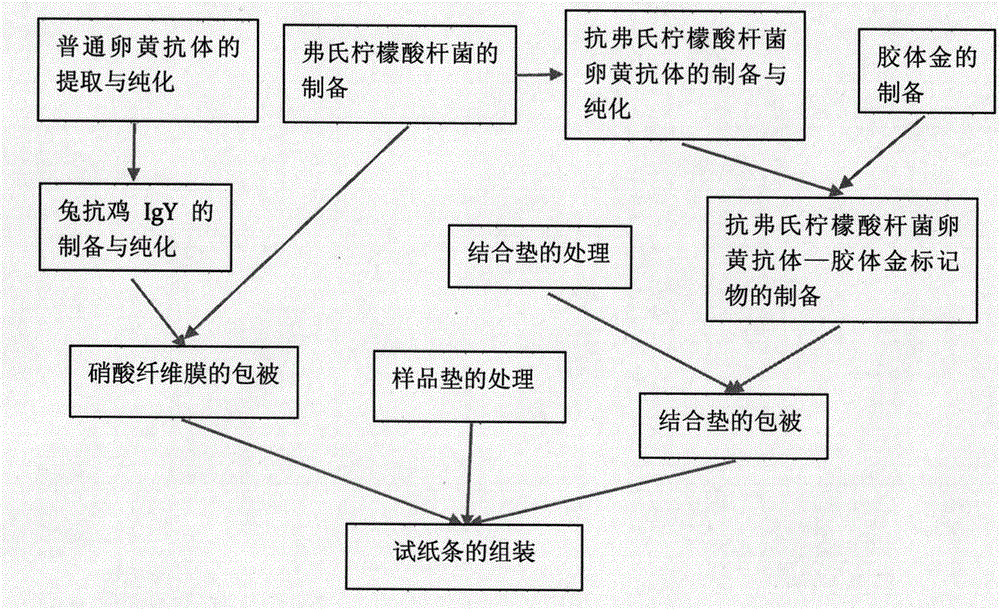
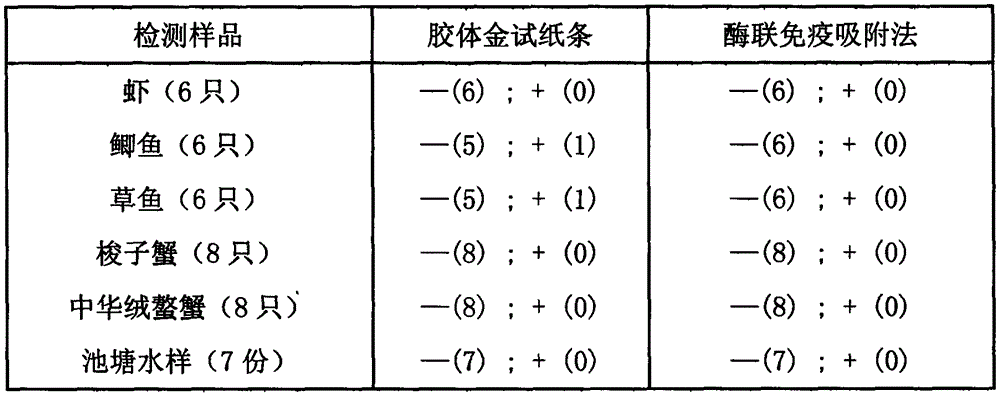
Test strip for detecting citrobacter freundii and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a test strip for detecting citrobacter freundii and a preparation method thereof. The test strip comprises a sample pad, a combining pad, a nitrocellulose membrane, a water-absorbing pad and a PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) bottom board. The test strip is characterized in that the sample pad, the combining pad, the nitrocellulose membrane and the water-absorbing pad are adhered in order and sequence on the PVC bottom board; the combining pad is coated with an anti-citrobacter-freundii egg-yolk antibody-colloidal gold marker; and the nitrocellulose membrane is coated with a detection line formed by citrobacter-freundii ultrasonic breaking liquid and a quality control line formed by rabbit-anti-chicken egg-yolk antibodies. The test strip disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, simplicity in operation, fast detection and high accuracy.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Electricity-producing bacterium capable of degrading cellulose and application of electricity producing bacterium in fuel cells
The invention discloses an electricity-producing bacterium capable of degrading cellulose and an application of the electricity-producing bacterium in fuel cells. The strain of the electricity-producing bacteria is collected as citrobacter freundii HBUZL-1 in CGMCC with the collection number of CGMCC No.10335 on January 9, 2015; the 16SrDNA gene sequence of the strain is SEQ ID NO: 1. The electricity-producing bacteria are easy to culture; a plurality of organic matters can be taken as a substrate, and more importantly, the rich cellulose can be taken as the substrate for generating electricity; if being applied to the microbial fuel cells, the electricity-producing bacteria are high in adaptability and high in electricity-producing voltage, and have relatively high economic value and wide application prospect.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Sample for verifying total number counting capability of aerobic bacteria in drug and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107142301ASimple processIncrease success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementQuality controlStaphylococcus aureus
The invention belongs to the field of quality control on the aspect of microbial detection and particularly relates to a sample for verifying the total number counting capability of aerobic bacteria in a drug and a preparation method thereof. The sample for verifying the total number counting capability of aerobic bacteria in the drug includes target florae easily contaminated in drugs or production process, wherein the target florae include staphylococcus aureus, bacillus cereus, escherichia coli, klebsiella pneumoniae and citrobacter freundii. The homogeneity and stability meet the capability verifying requirements, the stability of the sample can be ensured to the most degree, and even if the convent of the escherichia coli in transportation and storage changes, and the total counting amount of the aerobic bacteria is also not affected on the aspect of statistical significance. The preparation method of the sample is simple in process and high in success rate.
Owner:中检科(北京)测试认证有限公司
Method for mineralizing mercury in soil using dissimilatory reduzate of aerobic bacteria
InactiveCN104889154APollution controlSimple processContaminated soil reclamationTrappingRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for mineralizing mercury in soil using dissimilatory reduzate of aerobic bacteria. The method includes selecting the aerobic bacteria, Citrobacter freundii, which is capable of performing dissimilatory reduction on sodium selenite and is purchased from American Type Culture Collection, under the accession number of ATCC 8090; transferring and culturing the bacteria in a culture medium with the sodium selenite to obtain the dissimilatory reduzate of the aerobic bacteria, and subjecting the mixed bacterial solution containing the dissimilatory reduzate of the aerobic bacteria to crushing in an ultrasonic cell crusher; adding the dissimilatory reduzate of the aerobic bacteria into the soil polluted by the mercury, performing culturing at room temperature for a few days and terminating the experiment. The dissimilatory reduzate of the aerobic bacteria, which uses the sodium selenite as an electron acceptor, is a good mercury trapping agent and is capable of converting the mercury in the soil to residual mercury, so as to mineralize the mercury in the soil and remediate mercury pollution of the soil. The method is applicable to surface mercury polluted soil. The method has the advantages of process simplicity, ease of operation, low cost of processing, wide processing range and no secondary pollution.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com