Intestinal microorganism markers for multiple myeloma, application and detection preparation of intestinal microorganism markers
A technology for multiple myeloma and intestinal microbiology, applied in the direction of microbiological determination/testing, microbiology, and microbiological-based methods, which can solve problems such as accumulation and kidney damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Stool sample collection and DNA extraction
[0028] In the example, we complied with relevant ethical requirements and obtained fresh stool samples from 19 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) and collected stool samples from 18 healthy controls (HC). The sex ratio, age and BMI index of the samples of the two groups (MM, HC) were matched and had no significant difference (Table 1).
[0029] After obtaining two groups of fresh feces samples to be tested, immediately use a sterile cotton swab to dip the feces in the middle part, put them into sterile cryopreservation tubes, and immediately freeze them in liquid nitrogen and store them at -80°C for a long time. If it is necessary to extract fecal bacterial DNA immediately, put the fresh sample into a sterile EP tube for later use.
[0030] Microbial DNA in stool samples was extracted using Mogen’s Fecal Microbial DNA Extraction Kit (HiPure Stool DNA Kits, MogenD3141-02) according to the instructi...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Sample metagenomic sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
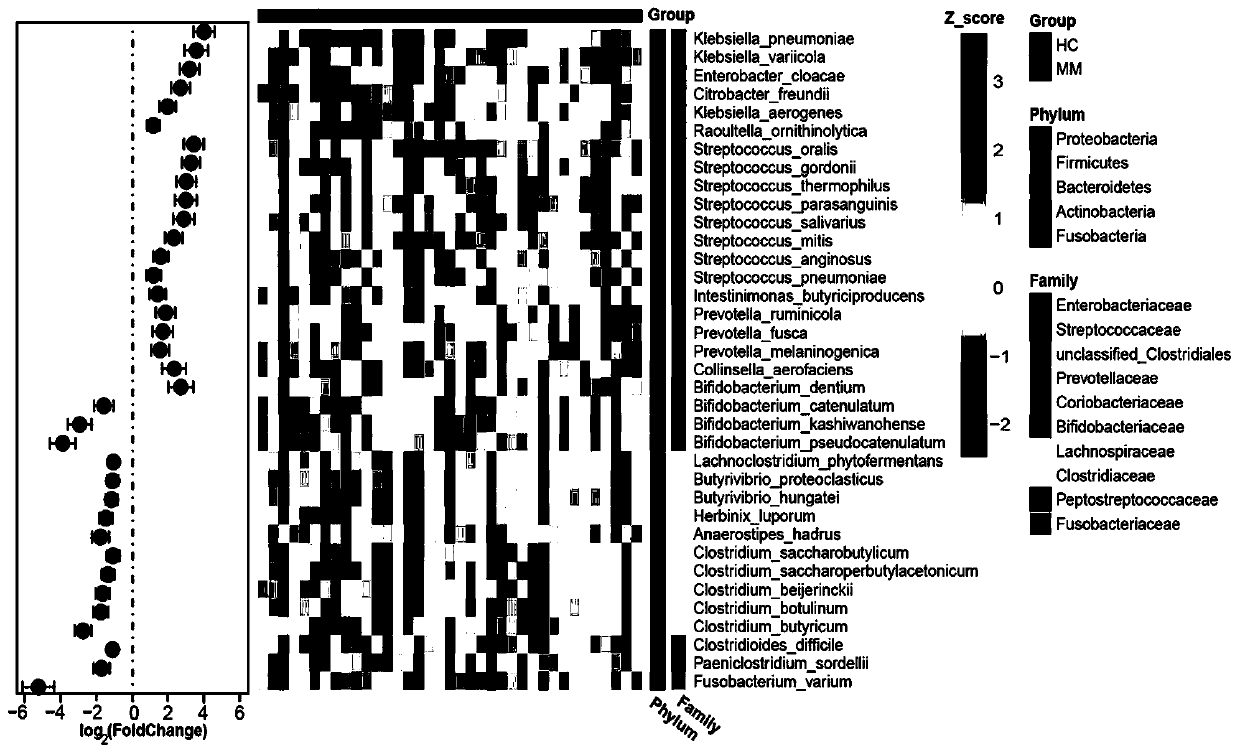
[0036] Using the Illumina HiSeq 2500 sequencing platform, the metagenomic double-end sequencing of the extracted DNA samples was completed. Low-quality sequences were removed from the original sequences using the software Trimmomatic, and human sequences were removed from the original sequences using Bowtie2 reference to the hg38 genome to retain high-quality microbial sequence reads. Then, use Kraken software and Kraken standard database to annotate species taxonomy, and obtain the abundance matrix of each taxonomic level (phylum, class, order, family, genus, species) in each sample (using Kraken software to compare The number of reads for a species was considered absolute abundance; data normalized to the absolute abundance of each sample was considered relative abundance). Finally, the R packages vegan and DESeq2 were used to analyze and compare the species diversity of the two groups of samples,...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection of relative abundance of differential microorganisms in stool samples
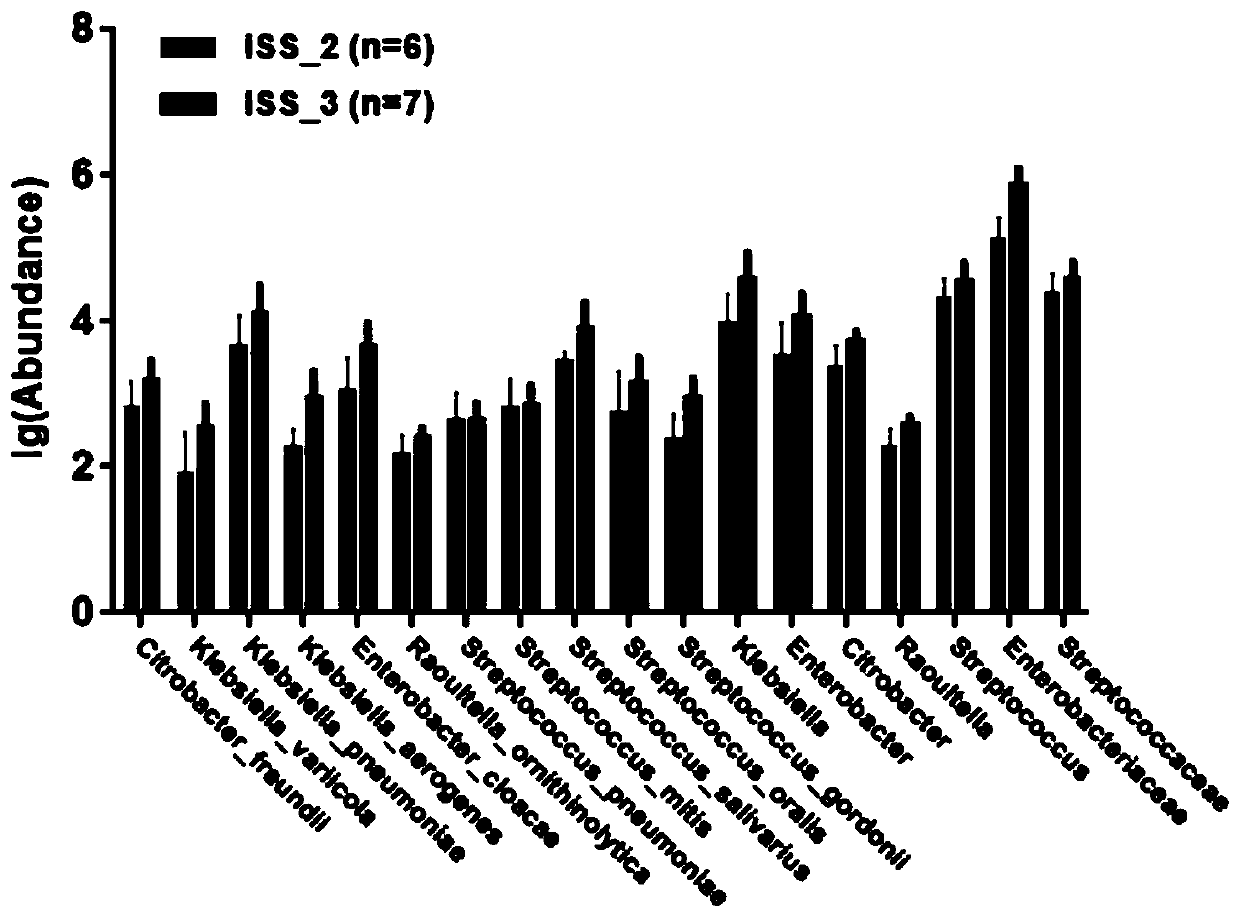
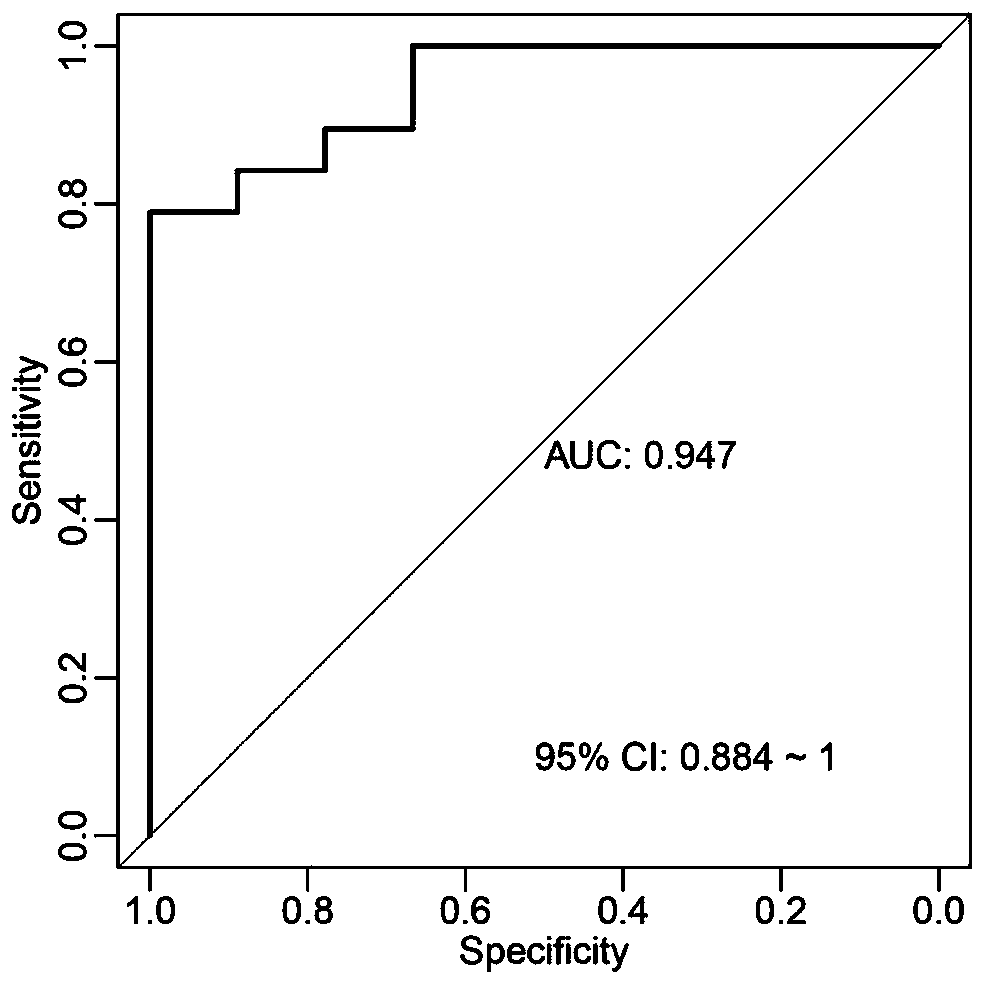
[0039] In order to eliminate the bias introduced by metagenomic sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, we further verified the 36 significantly different bacterial species identified in Example 2 by fluorescent quantitative PCR (qPCR) in the enlarged sample. First, find the 16S rDNA gene sequence of the differential strain in the NCBI database, design primers for it and biosynthesize it for use. The designed primers can use the TestPrime tool (https: / / www.arb-silva.de) to view the bacterial coverage of the primers. The lower the coverage, the higher the specificity of the primers. Since we only found the 16S rDNA sequences of 34 of them, only 34 of them were verified in this example (Table 2). In addition, in this example, in addition to designing primers for 16S rDNA of different bacterial species, a pair of universal primers is also needed, which...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com