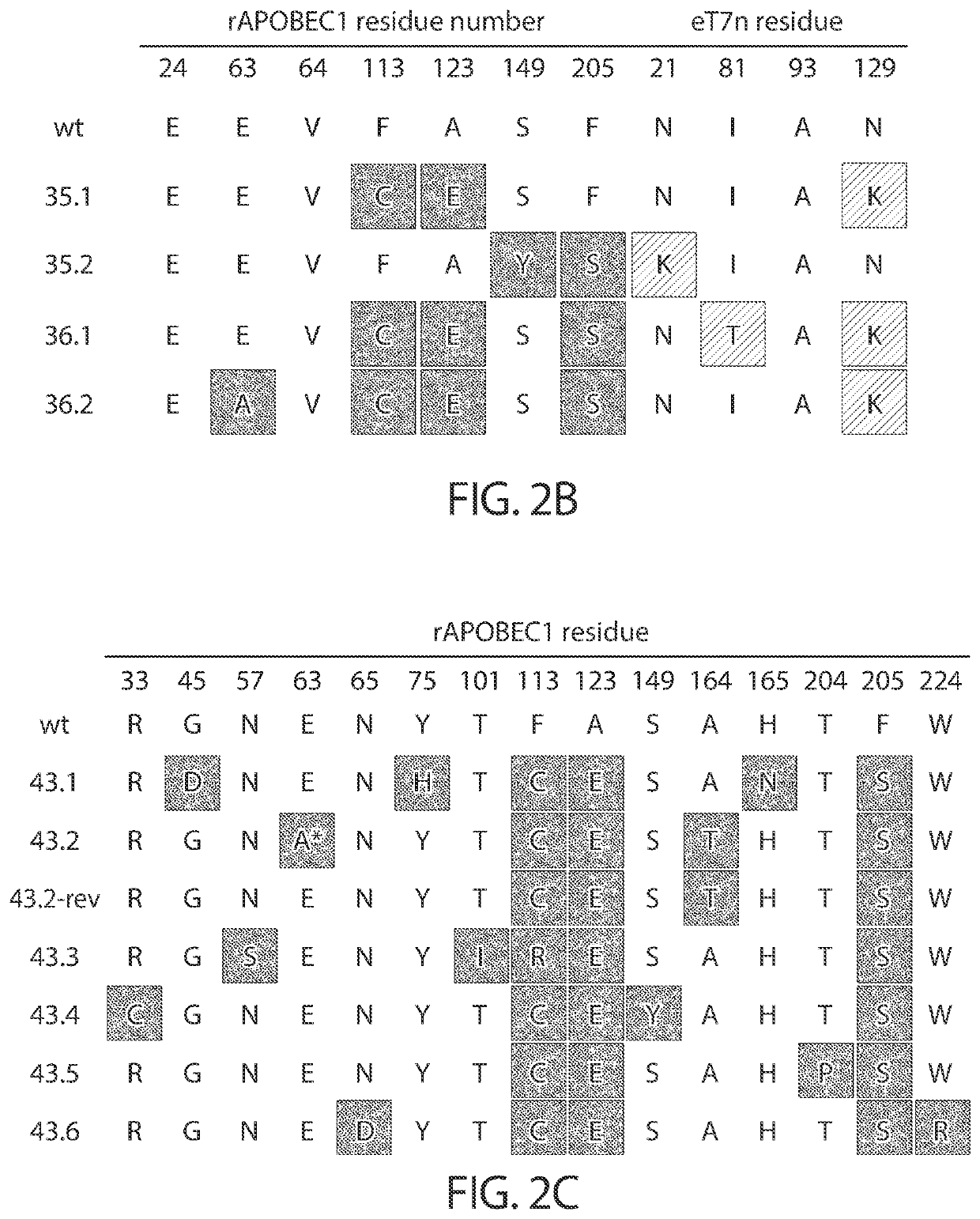
Patents
Literature
61 results about "Cytidine deaminase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
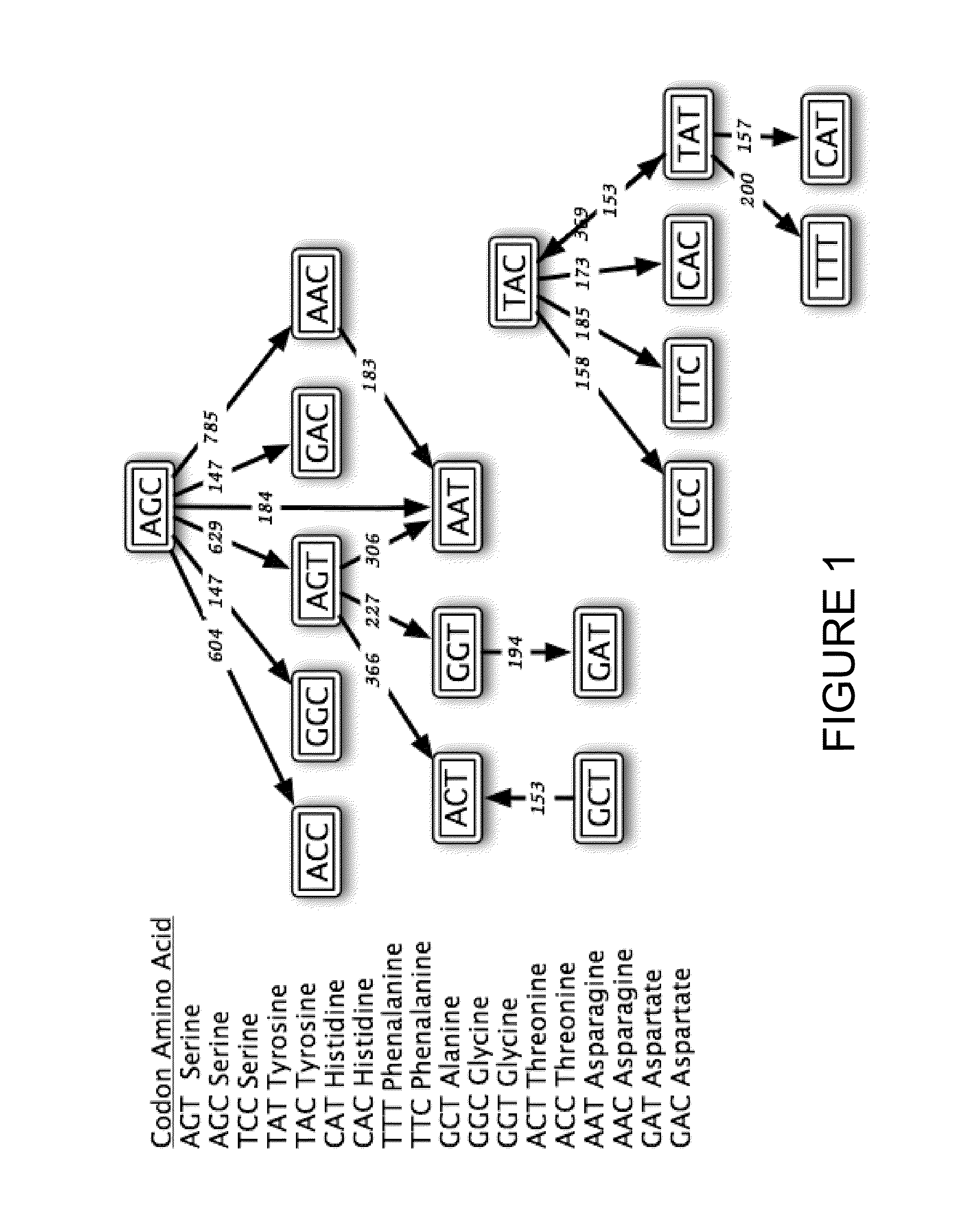
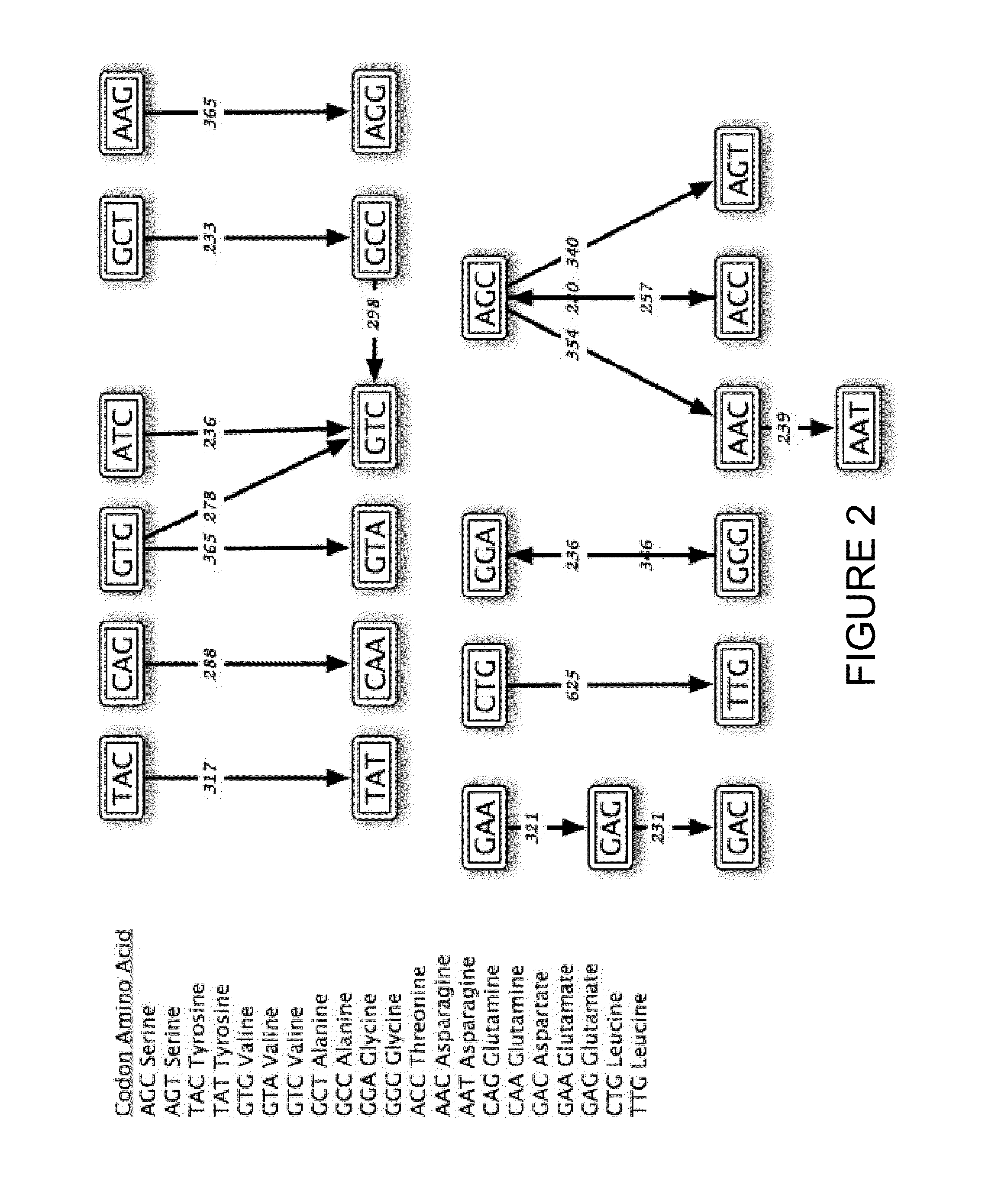
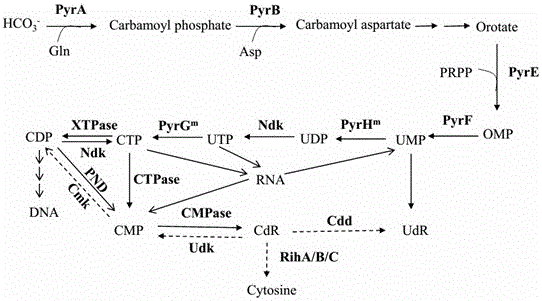
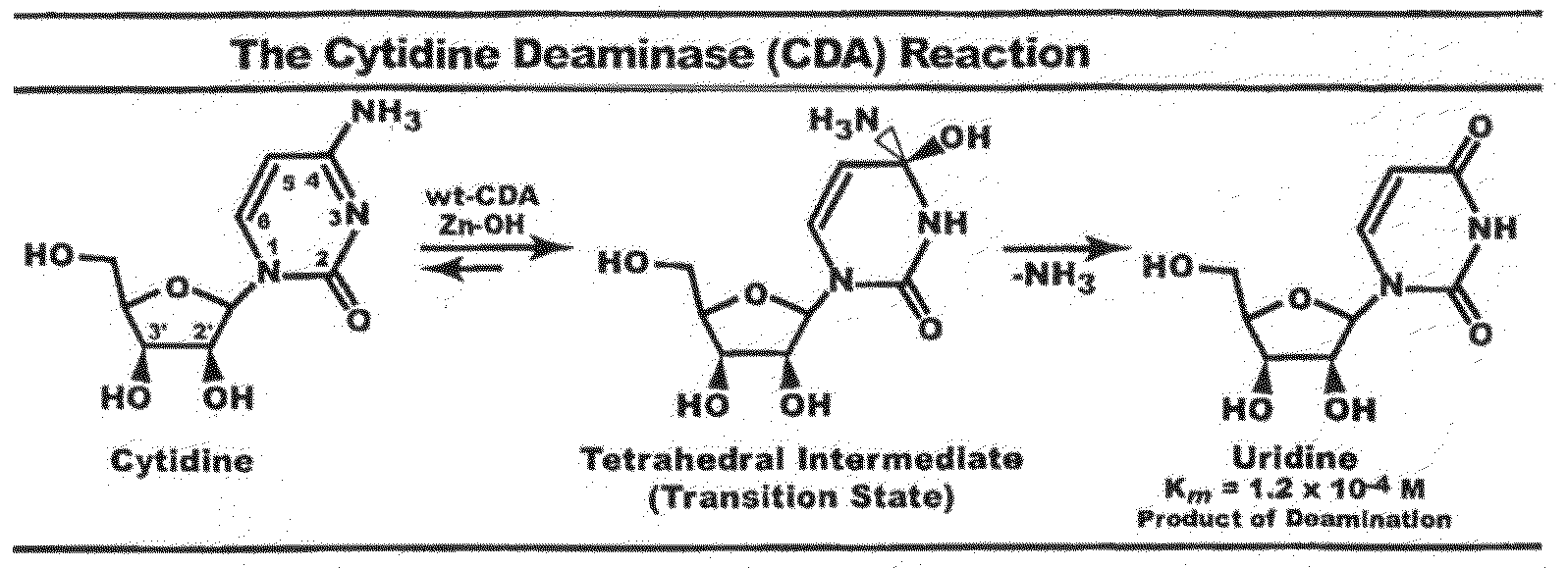
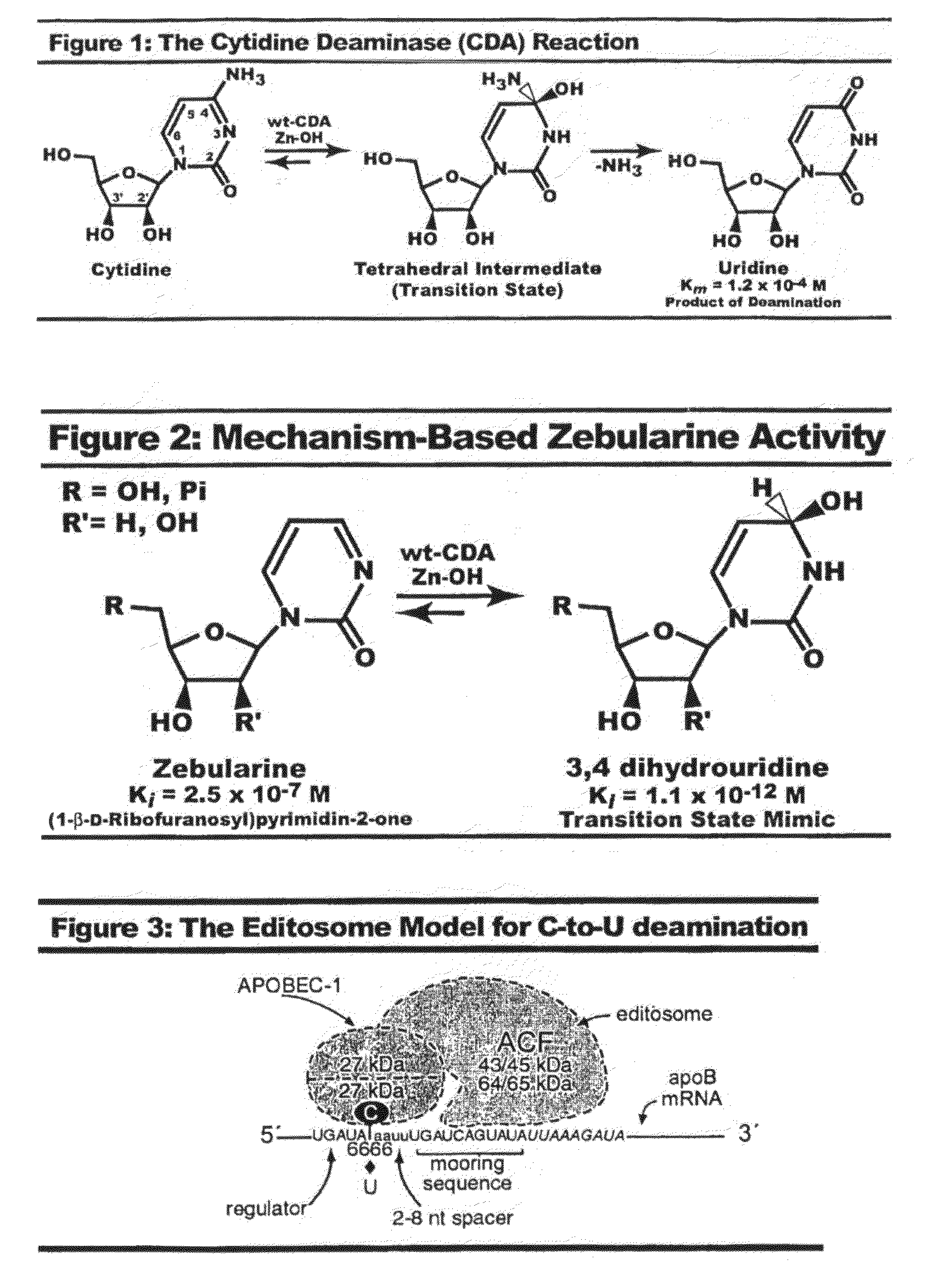
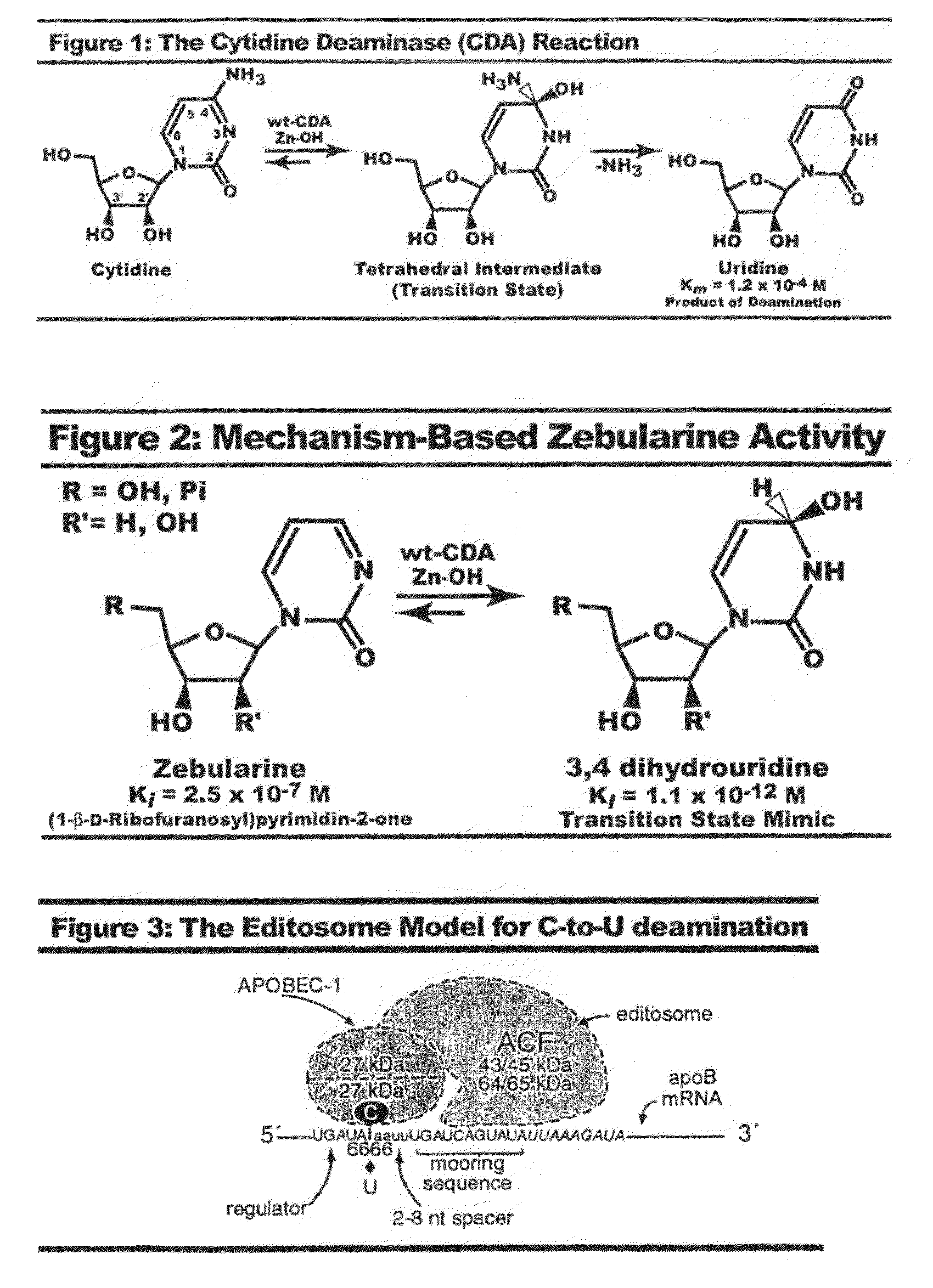
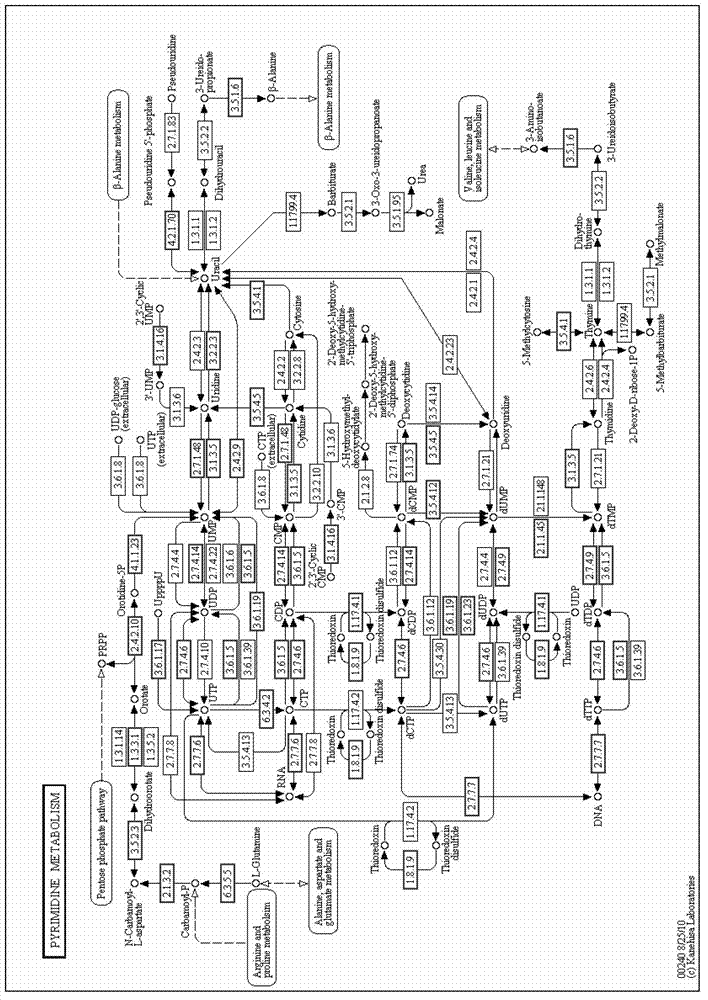
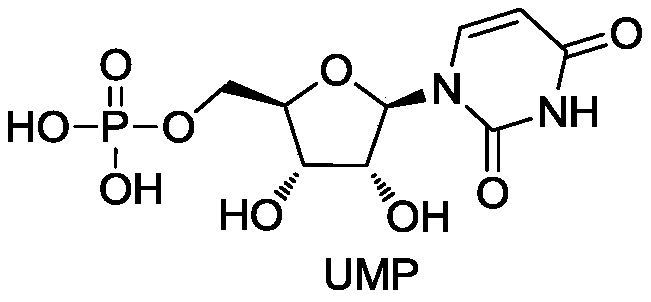
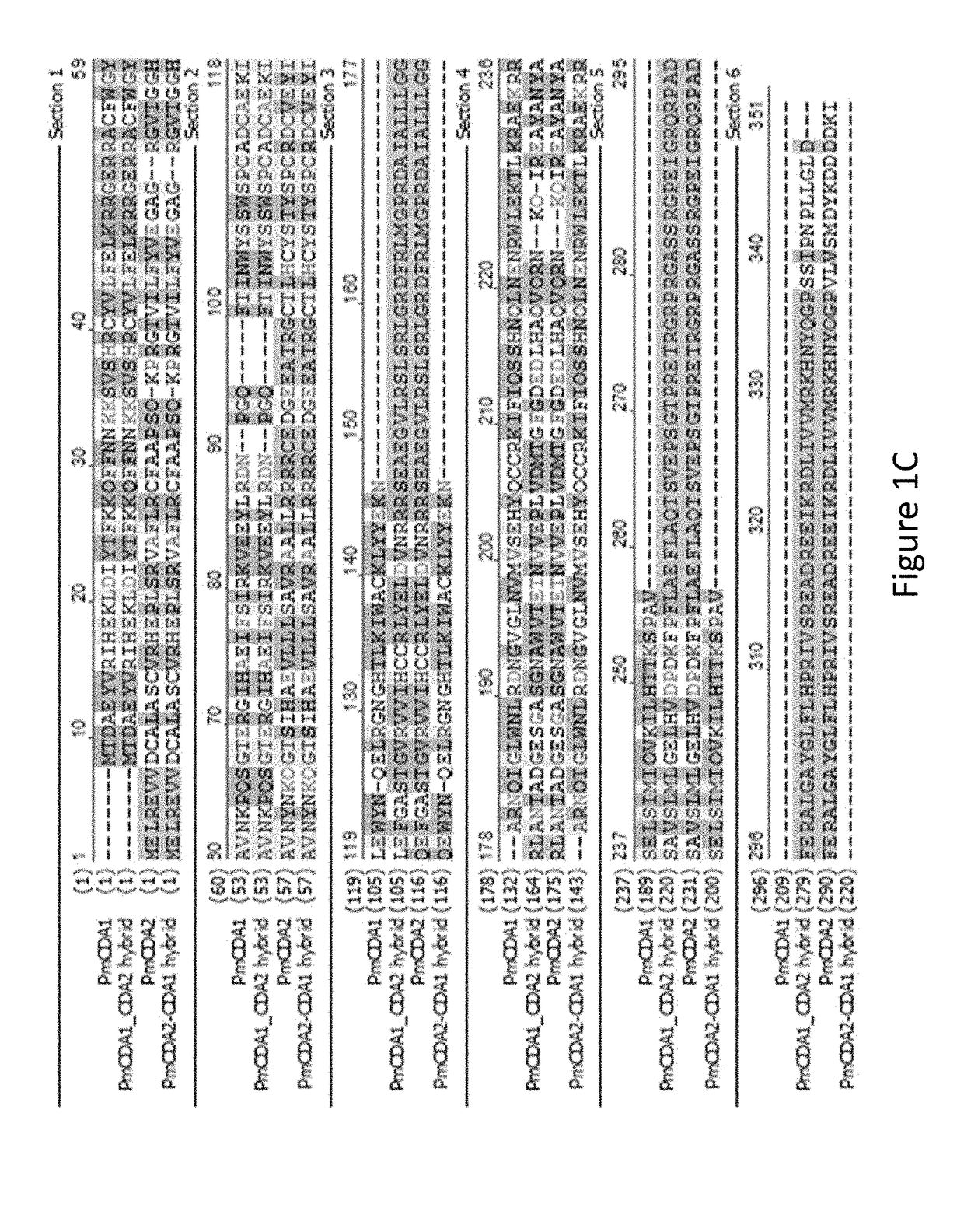
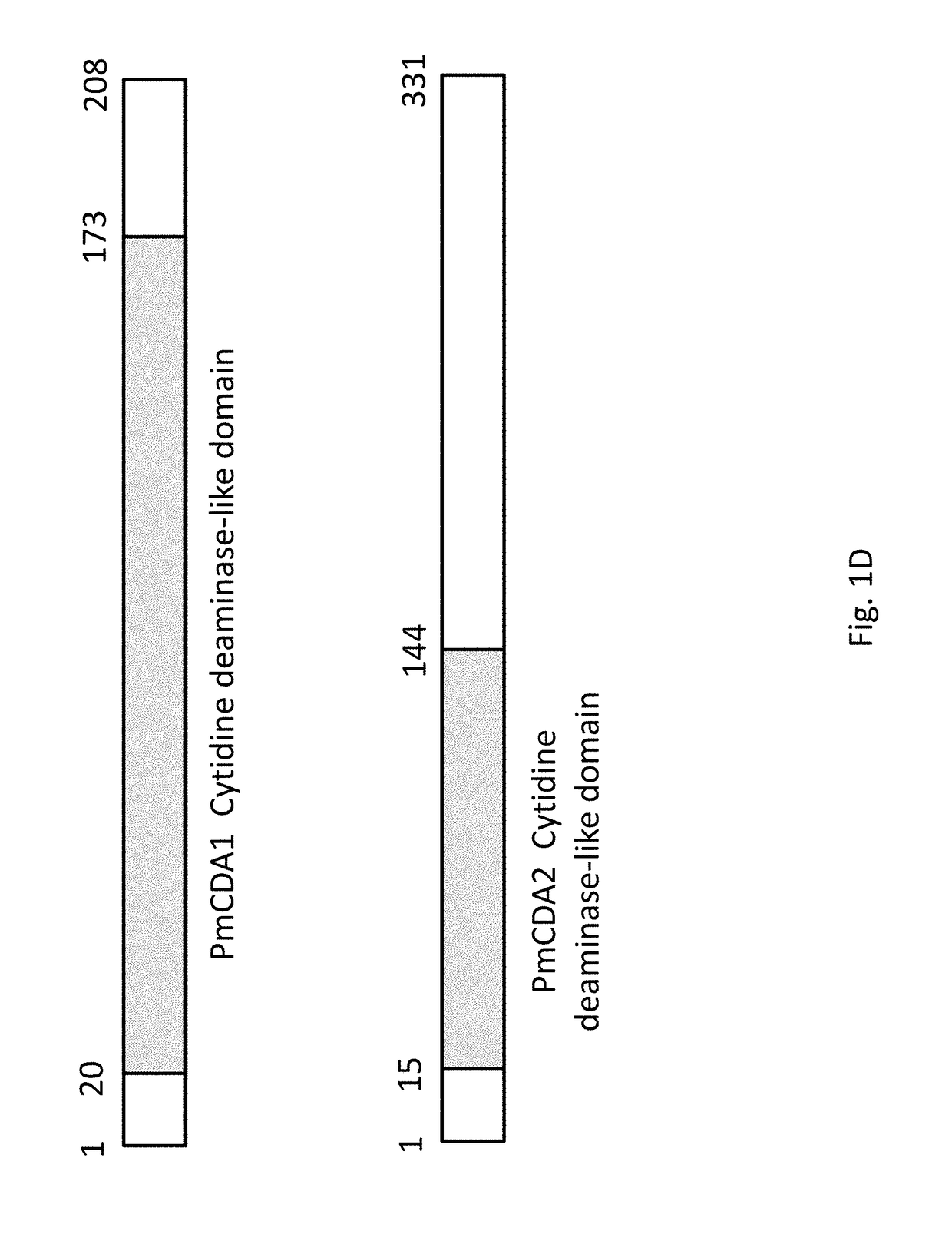
Cytidine deaminase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDA gene. This gene encodes an enzyme involved in pyrimidine salvaging. The encoded protein forms a homotetramer that catalyzes the irreversible hydrolytic deamination of cytidine and deoxycytidine to uridine and deoxyuridine, respectively. It is one of several deaminases responsible for maintaining the cellular pyrimidine pool. Mutations in this gene are associated with decreased sensitivity to the cytosine nucleoside analogue cytosine arabinoside used in the treatment of certain childhood leukemias.
Genetically altered antibody-producing cell lines with improved antibody characteristics
InactiveUS20050048621A1Increase variabilityBetter pharmacokinetic profileAnimal cellsSugar derivativesBiological bodyGenetic diversity
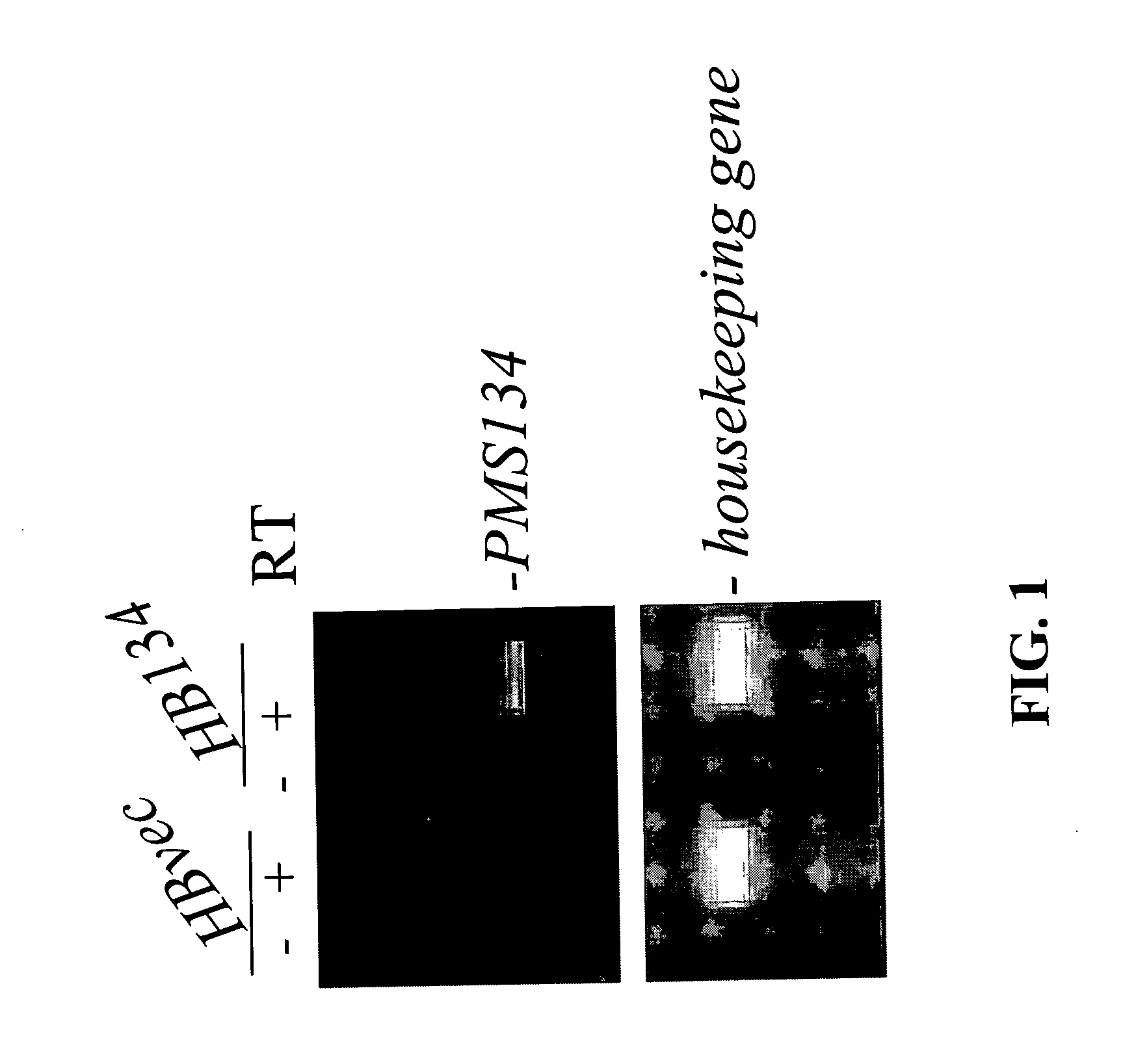
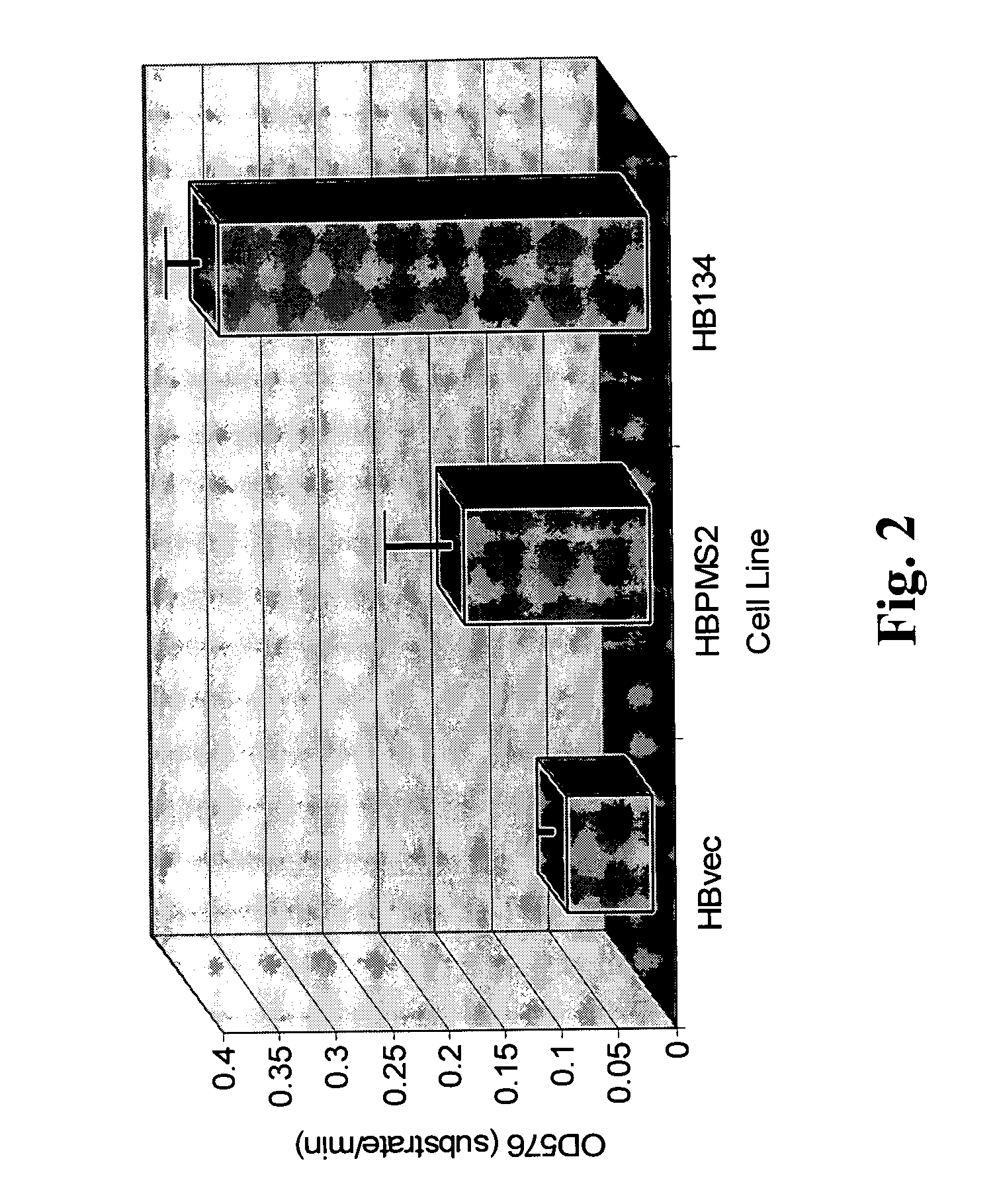
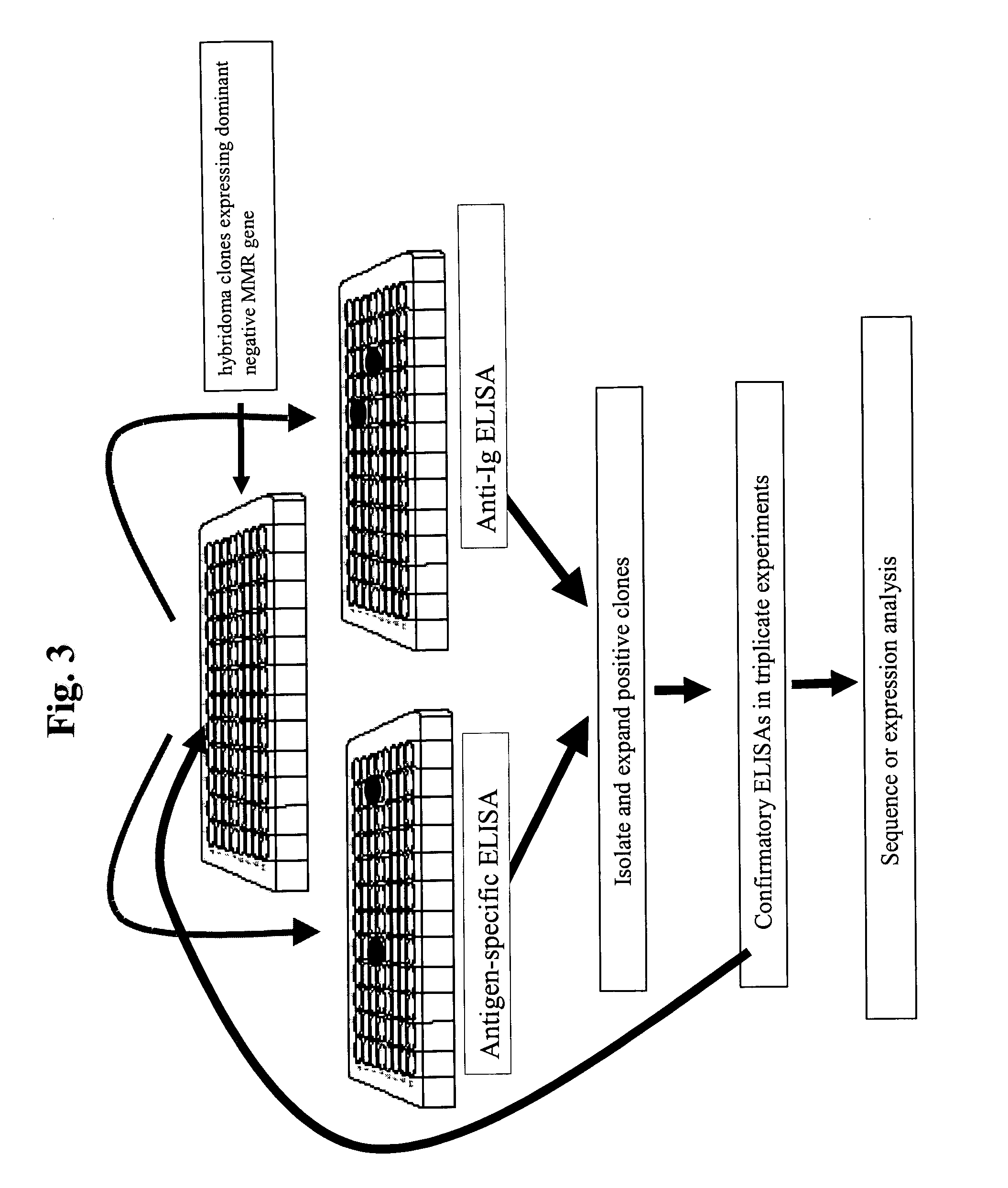
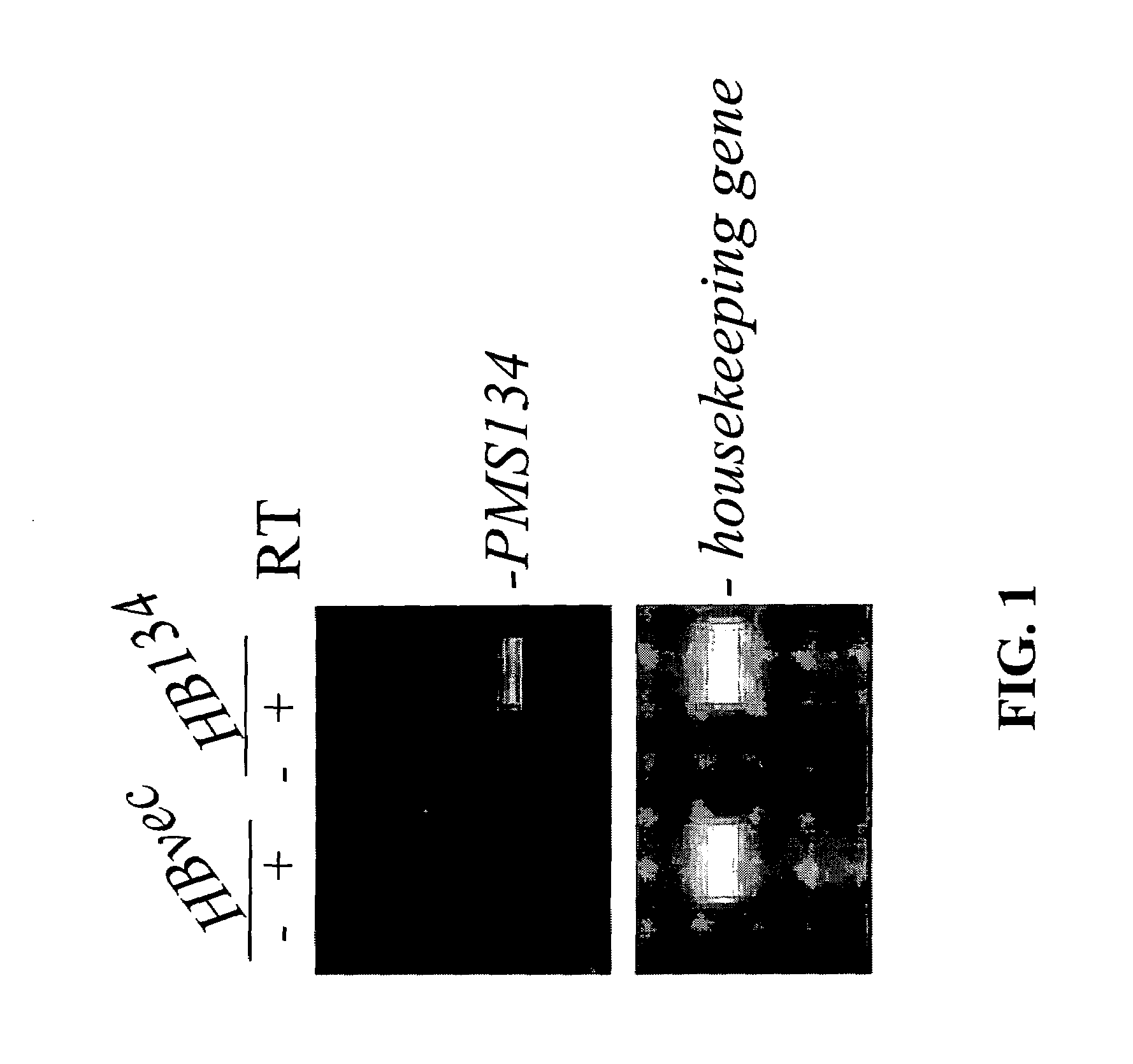
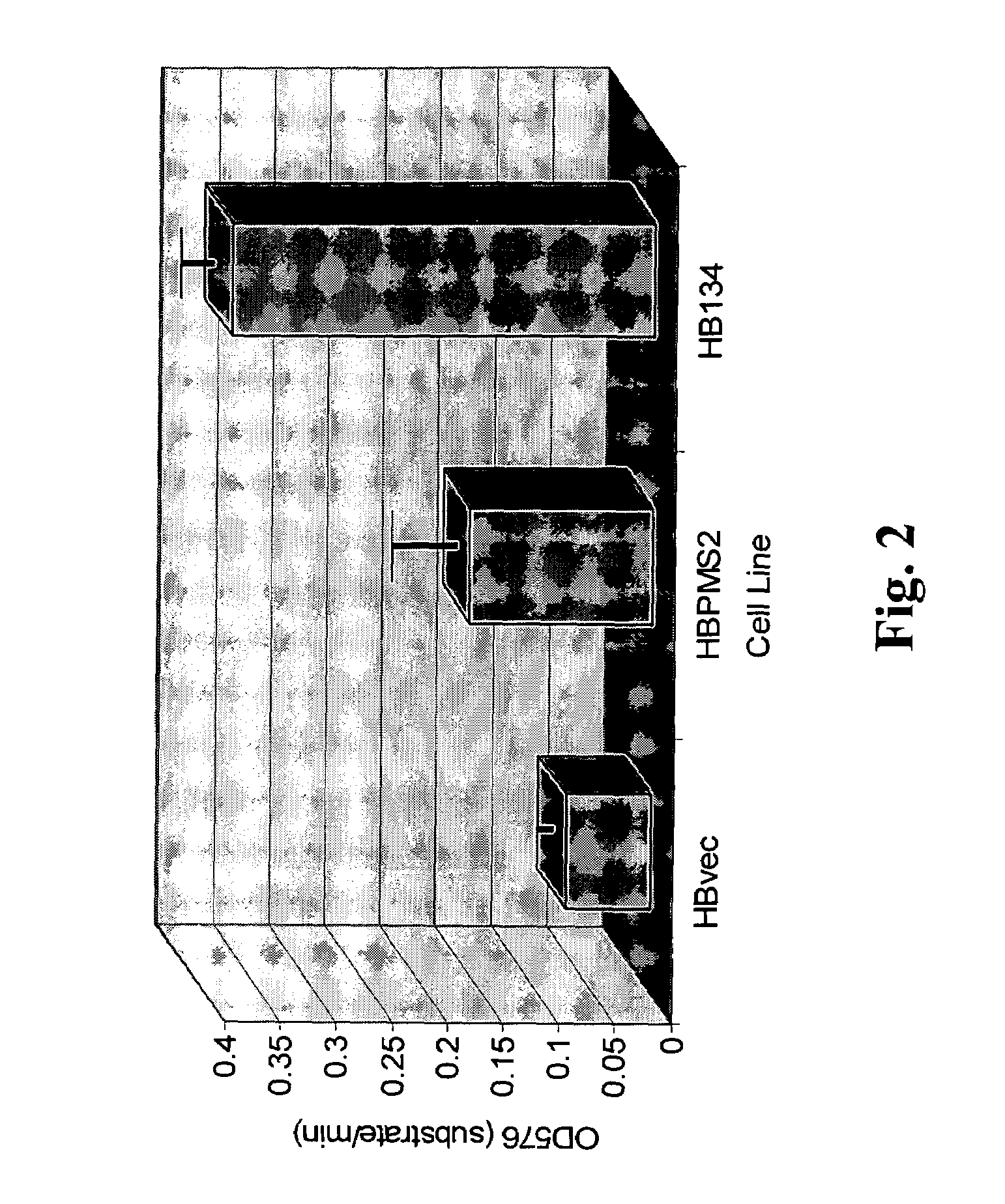
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. Cells may be selected for expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), stimulated to produce AID, or manipulated to express AID for further enhancement of hypermutability. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production.
Owner:EISAI INC
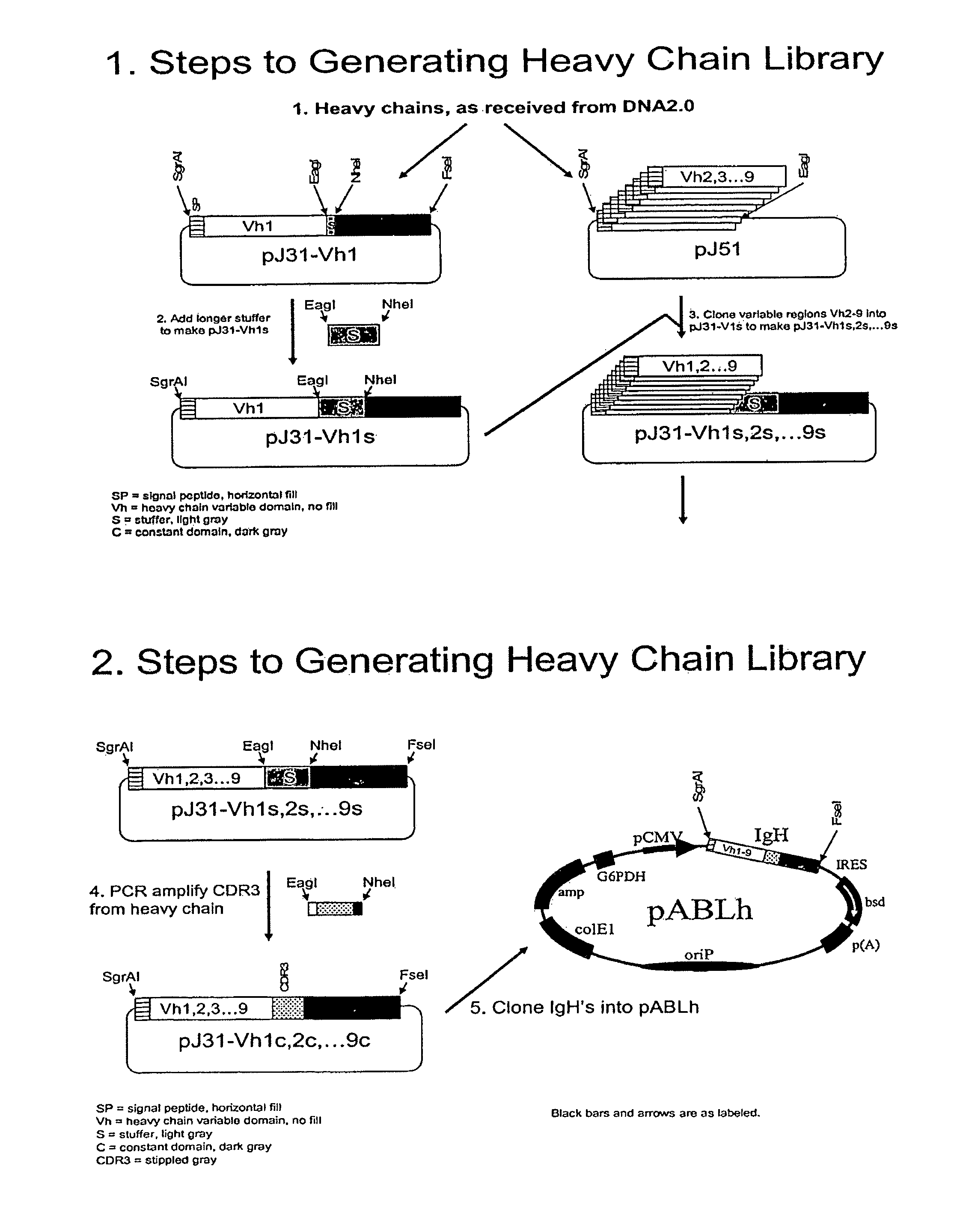
Methods of generating libraries and uses thereof
ActiveUS8685897B2High affinityHigh reactivityImmunoglobulins against growth factorsFermentationHeavy chainActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminase
This invention relates to methods for the generation of humanized antibodies, particularly a humanized antibody heavy chain protein and a humanized antibody light chain protein. The method comprises using cells that express or can be induced to express Activation Induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID).
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
Recombinant microorganism for producing cytidine and method for producing cytidine
ActiveCN106754602ARealize large-scale industrial productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaTransferasesRibonucleosideGenetic engineering
The invention provides a recombinant microorganism for producing cytidine and a method for producing the cytidine from the recombinant microorganism. A degradation and use gene of the cytidine is knocked off, and the gene encodes cytidine ammonialyase, ribonucleotide hydrolase, cytidine / uridine kinase and nucleoside transporter. Meanwhile key enzymes in biological synthesis process of the cytidine are over-expressed, including degrading cytidine triphosphoric acid to cytidine triphosphoric acid pyrophosphorylase of the cytidine monohosphoric acid, and catalyzing the cytidine monohosphoric acid to cytidine monohosphoric acid phosphorylase of the cytidine. In addition, pyrimidine nucleoside process is subjected to genetic engineering reform, and feedback inhibition of the synthesis process is relieved. By using a biological fermentation method, the cytidine yield greater than 20g / L can be achieved for a recombinant strain in a fermentation tank of 5L, industrial on-scale production can be achieved, and meanwhile the recombinant microorganism is low in cytidine production cost, small in pollution, green and environmental-friendly and relatively high in popularization and application value.
Owner:BIOSYNTHETICA INC
Somatic hypermutation systems
InactiveUS20120028301A1Avoid problemsDecrease and increase in rateImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRecombinant DNA-technologyActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminaseIn vivo
The present application relates to somatic hypermutation (SHM) systems and synthetic genes. Synthetic genes can be designed using computer-based approaches to increase or decrease susceptibility of a polynucleotide to somatic hypermutation. Genes of interest are inserted into the vectors and subjected to activation-induced cytidine deaminase to induce somatic hypermutation. Proteins or portions thereof encoded by the modified genes can be introduced into a SHM system for somatic hypermutation and proteins or portions thereof exhibiting a desired phenotype or function can be isolated for in vitro or in vivo diagnostic or therapeutic uses.
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
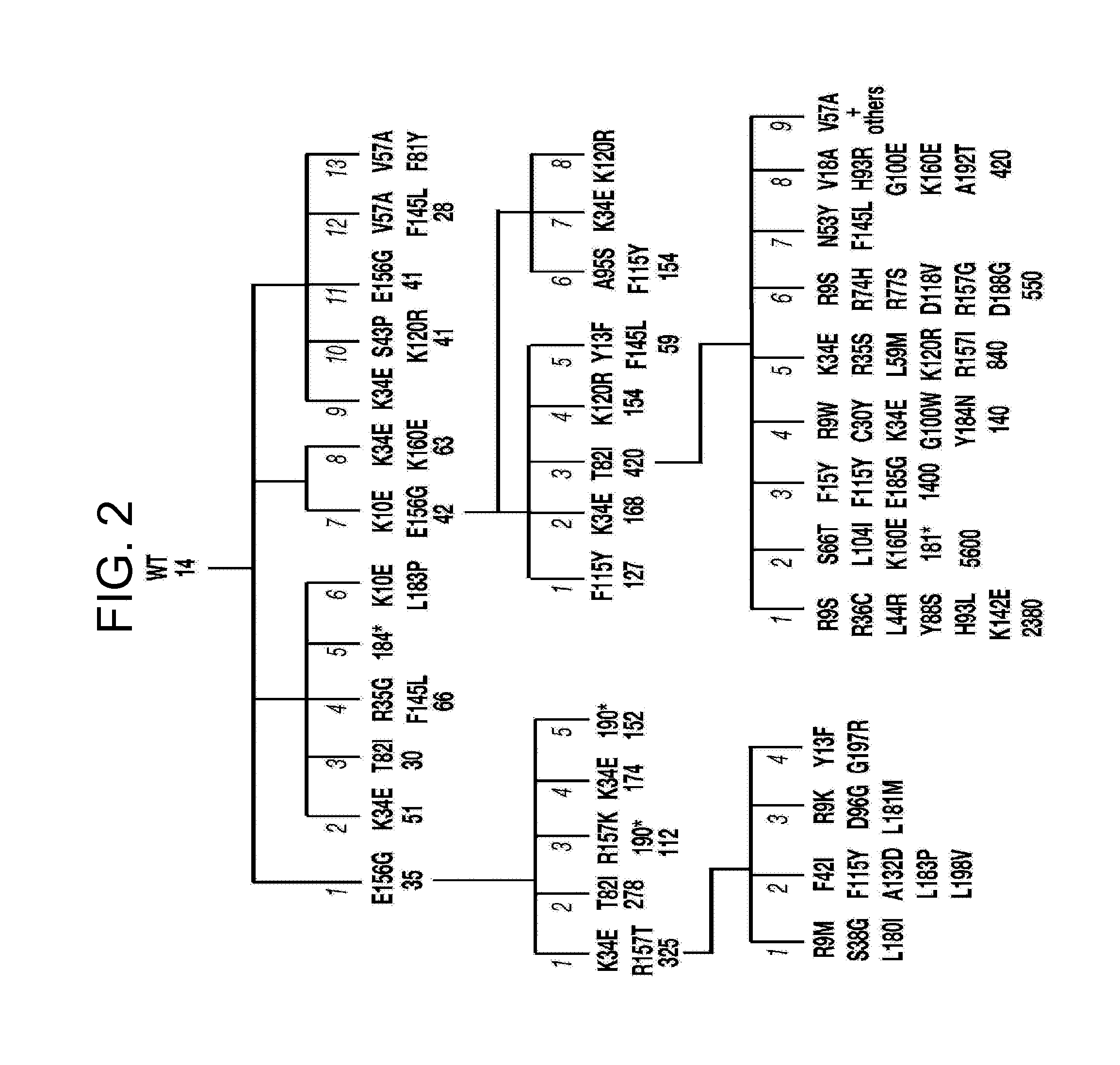
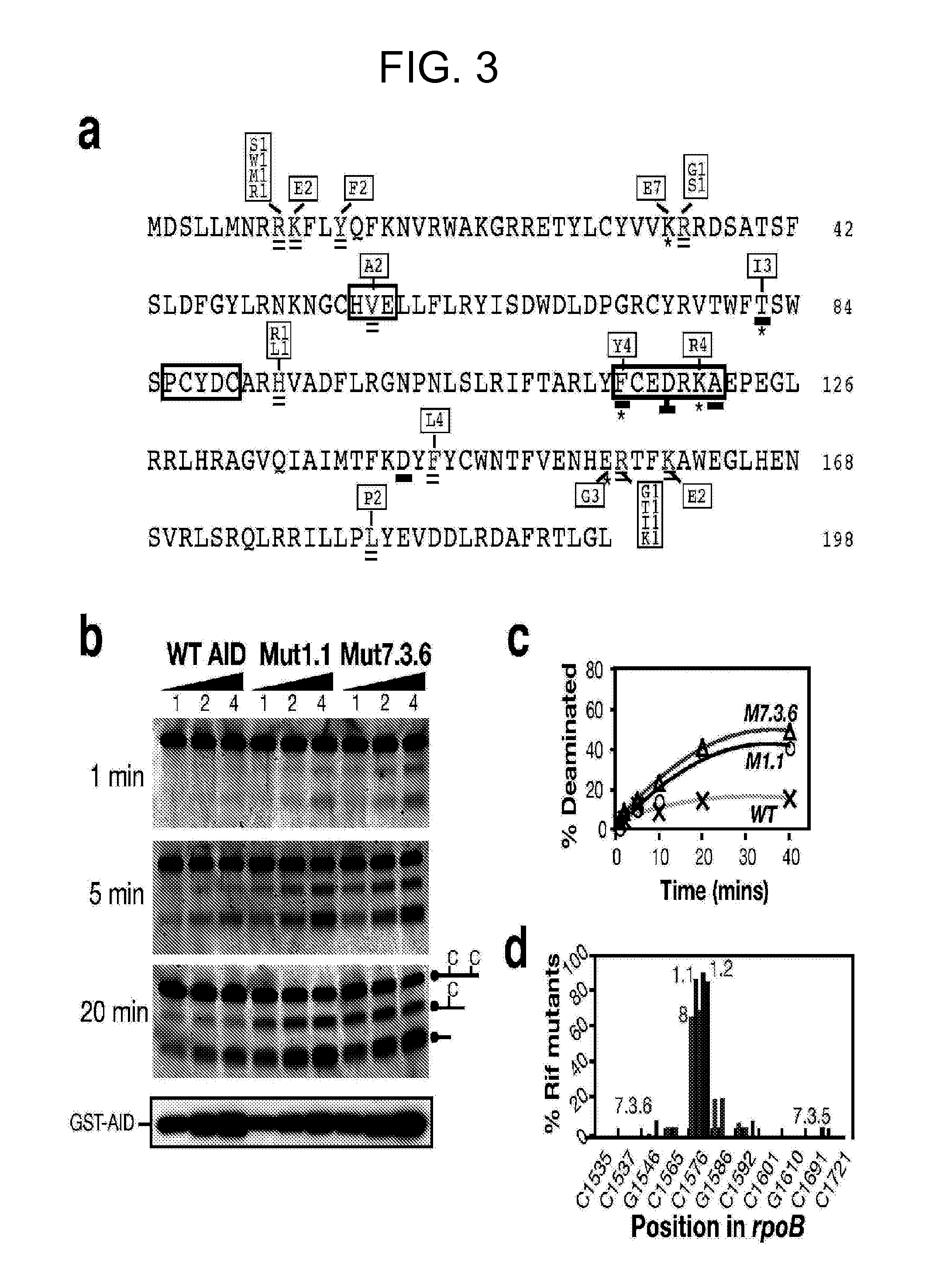
Mutants of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and methods of use
The invention provides functional mutants of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) protein that have increased activity as compared to a wild-type AID protein. The invention also provides nucleic acids encoding the functional AID mutants, and vectors and cells comprising the nucleic acids. The invention further provides methods of using the functional mutant AID proteins.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
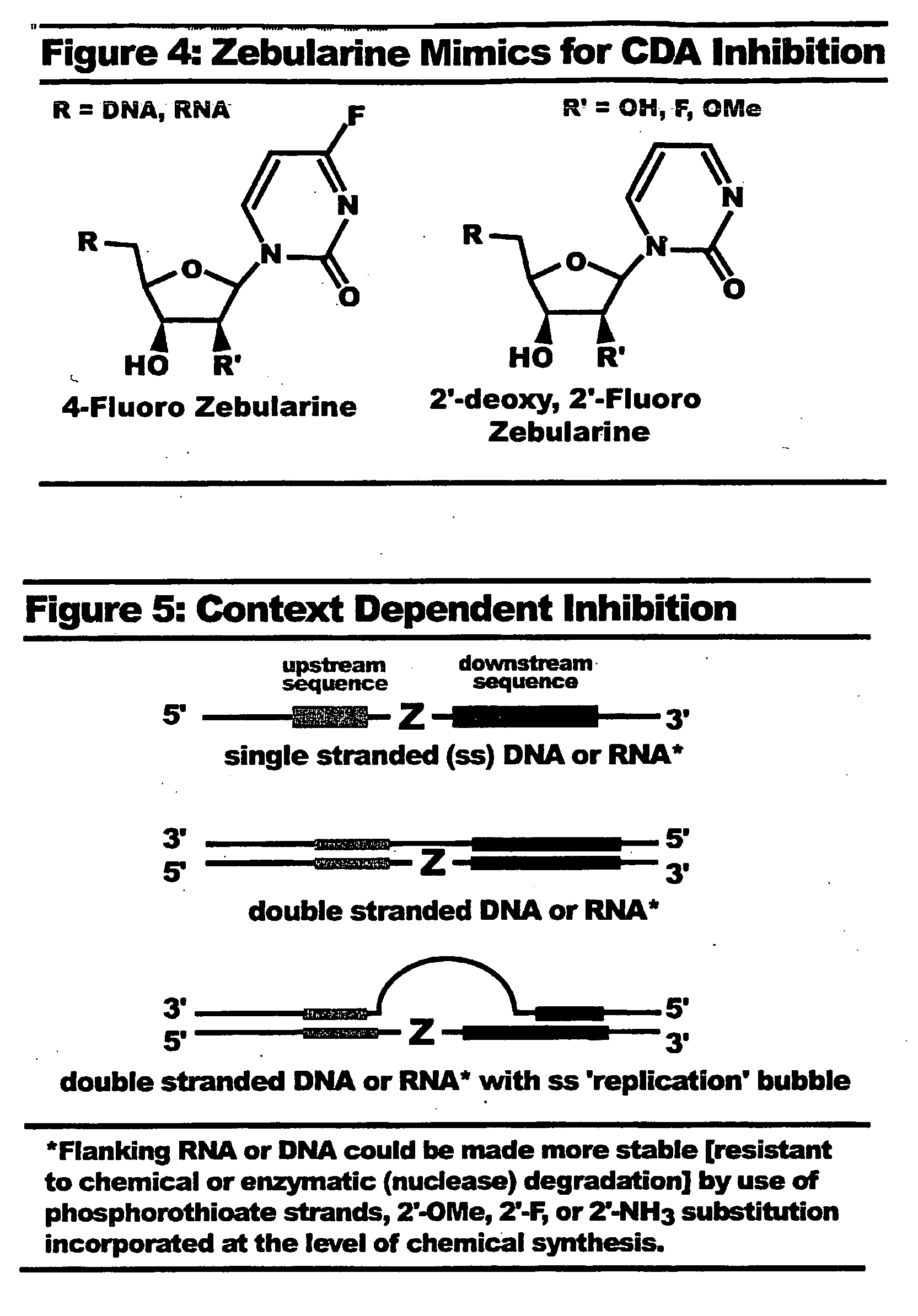
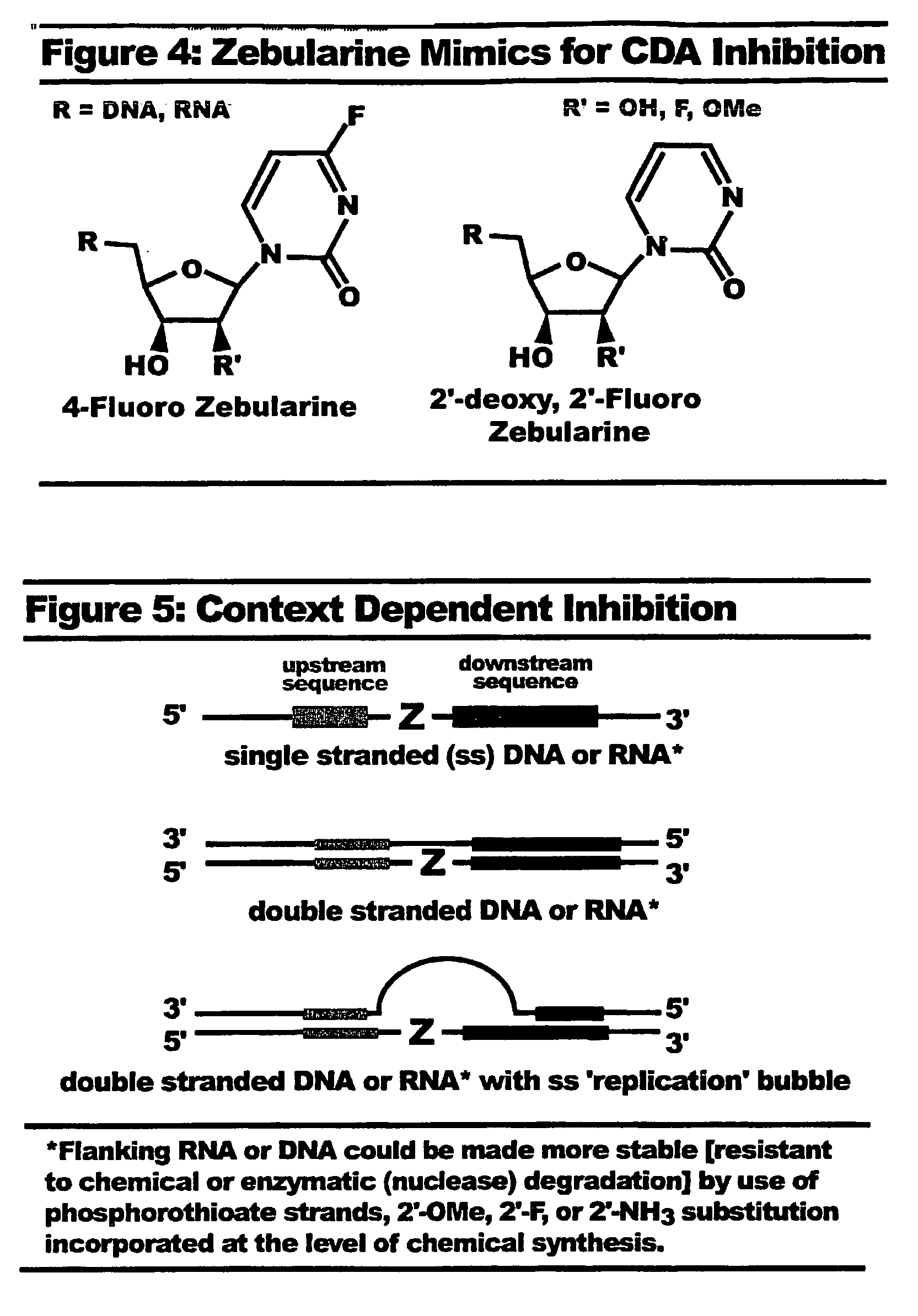
Context dependent inhibitors of cytidine deaminases and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090099105A1Effective inhibitorHigh affinityBiocideSugar derivativesBiologyCytidine deaminase
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
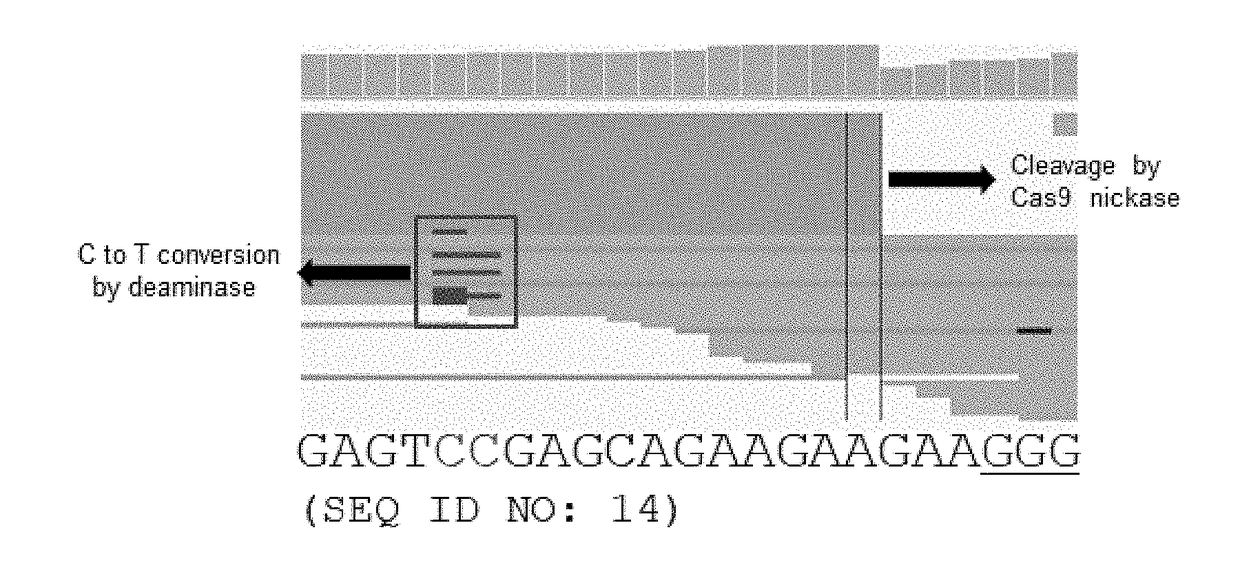
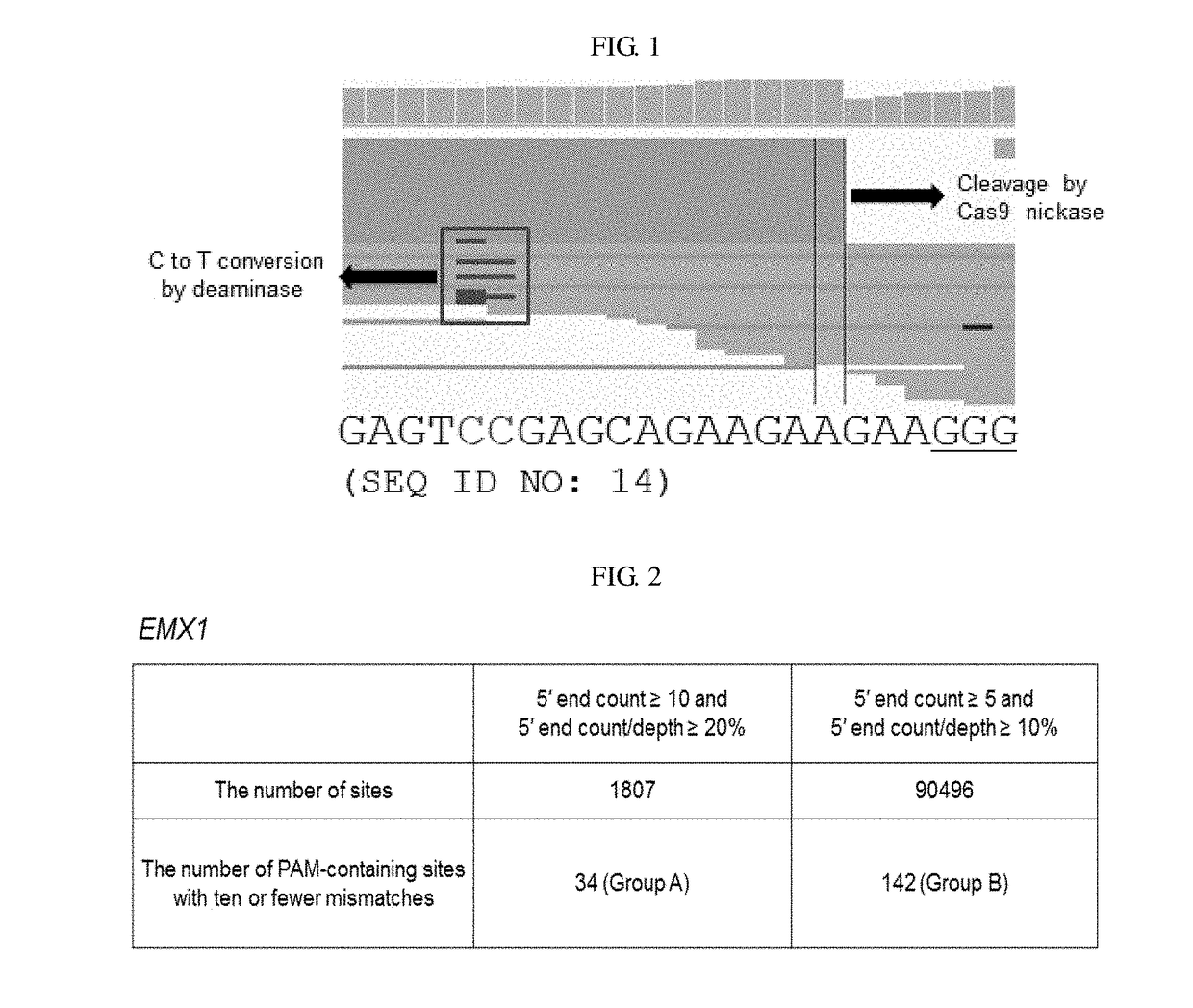
Method of identifying genome-wide off-target sites of base editors by detecting single strand breaks in genomic DNA
InactiveUS20180258418A1Accurately and effectively identify base editing sites, target specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAGenomic DNASingle strand
Provided are a composition for inducing DNA single strand breaks in DNA, the composition comprising a cytidine deaminase, an inactivated target-specific endonuclease, and a guide RNA, a method for inducing a single-strand break in DNA, using the same, a method for analyzing a nucleic acid sequence of a base-editing-introduced DNA, and a method for identifying (or measuring or detecting) a base-editing site, base-editing efficiency at an on-target site, an off-target site, and / or target specificity.
Owner:INST FOR BASIC SCI
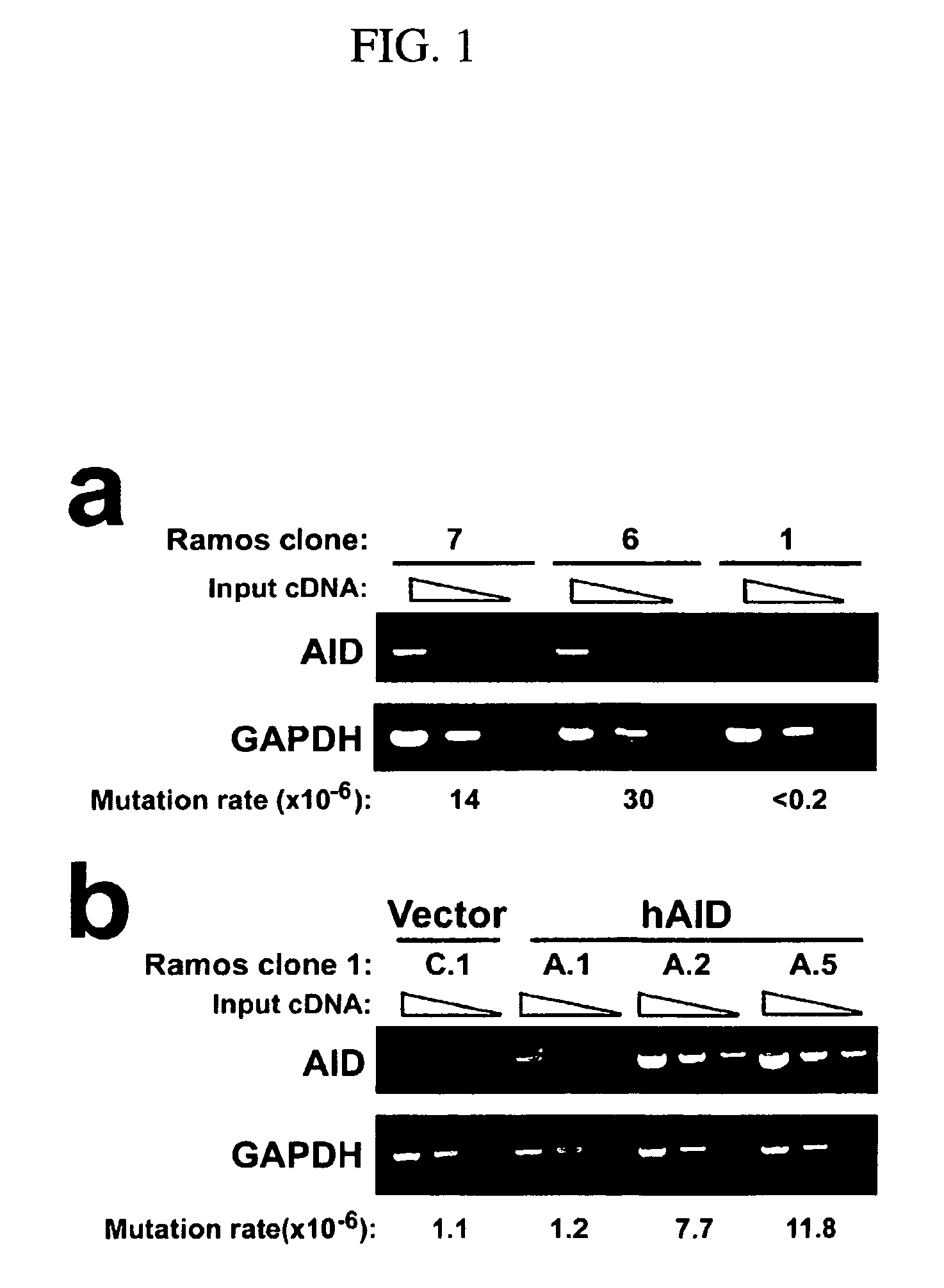
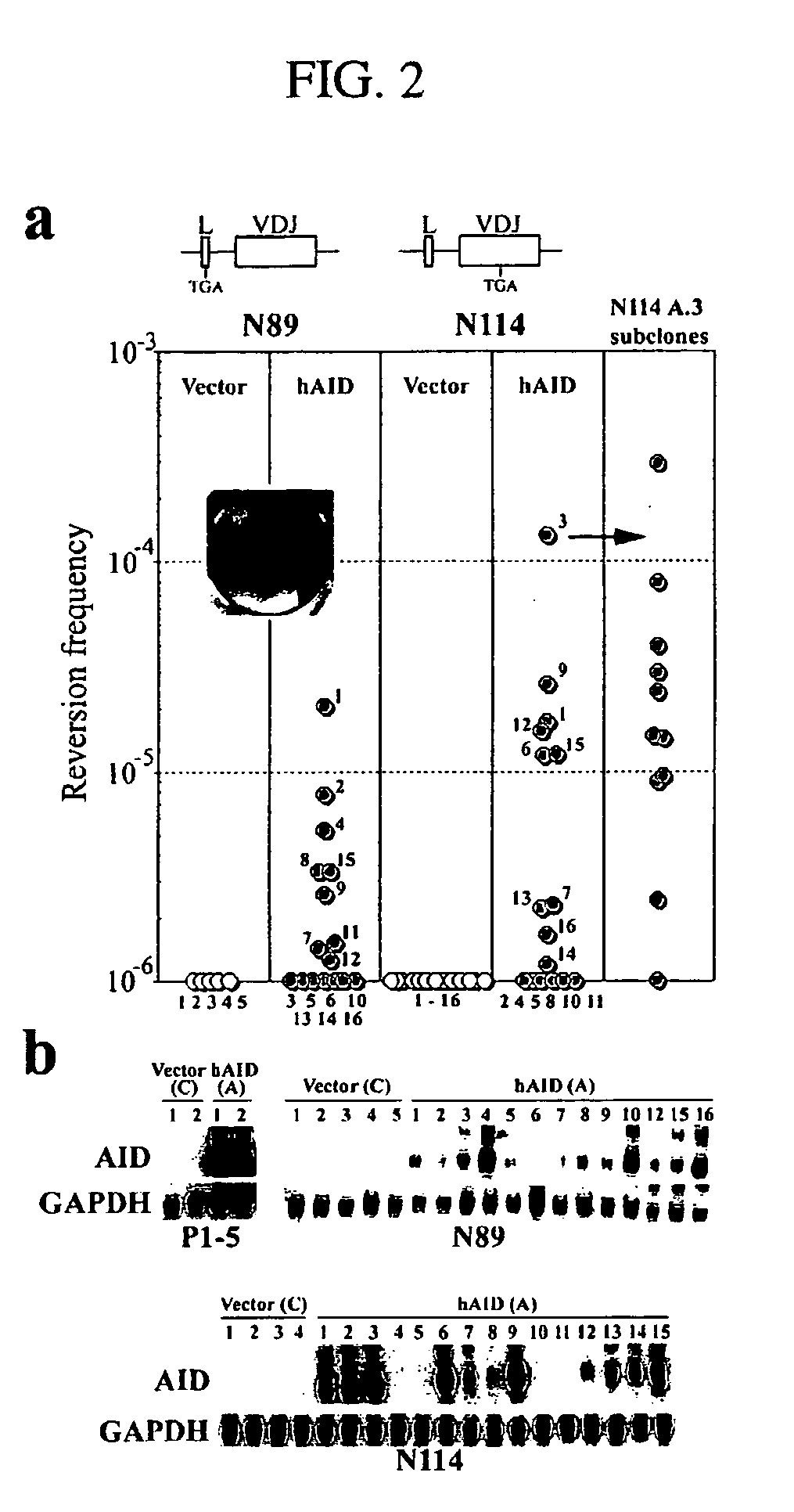
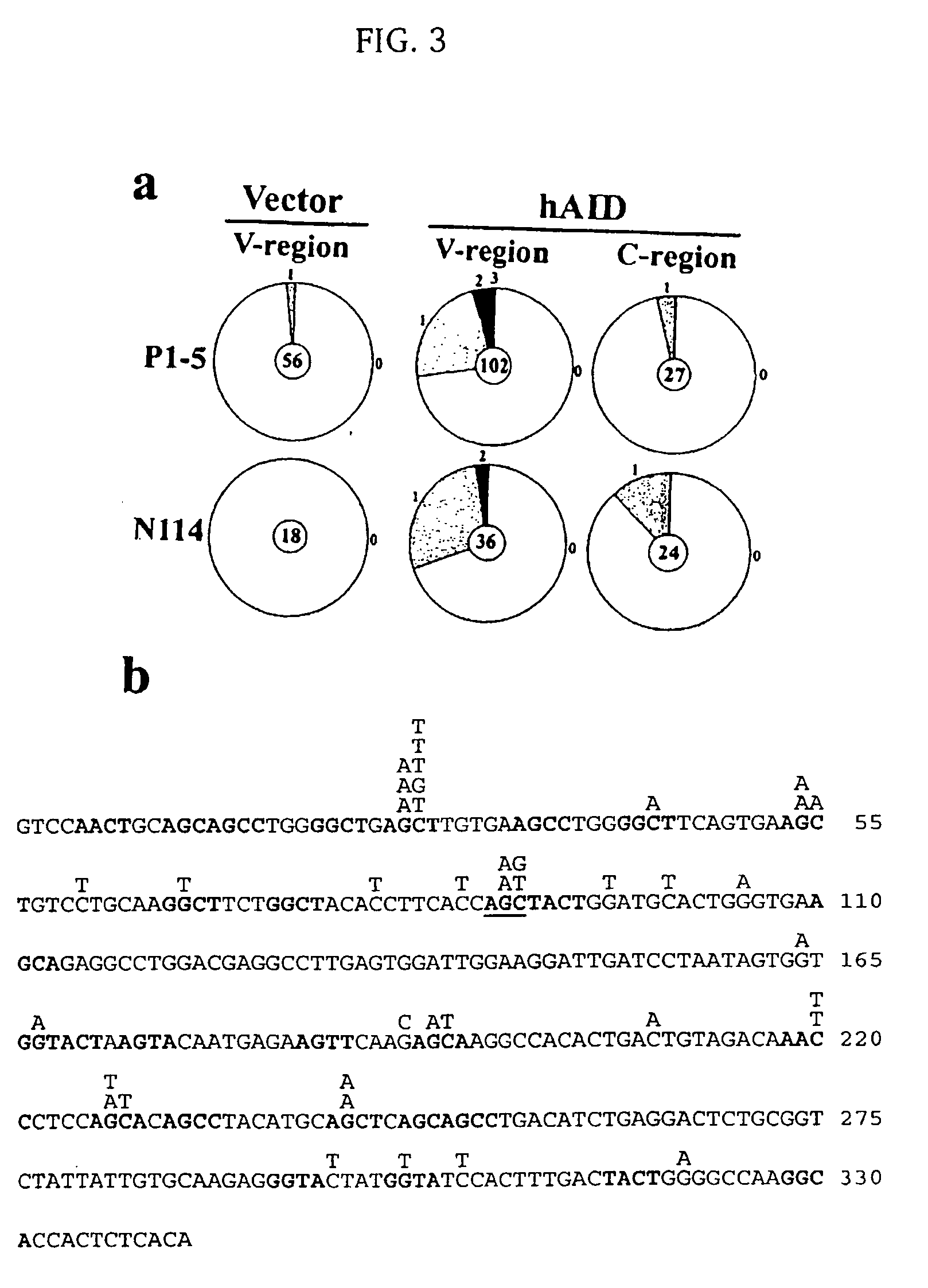
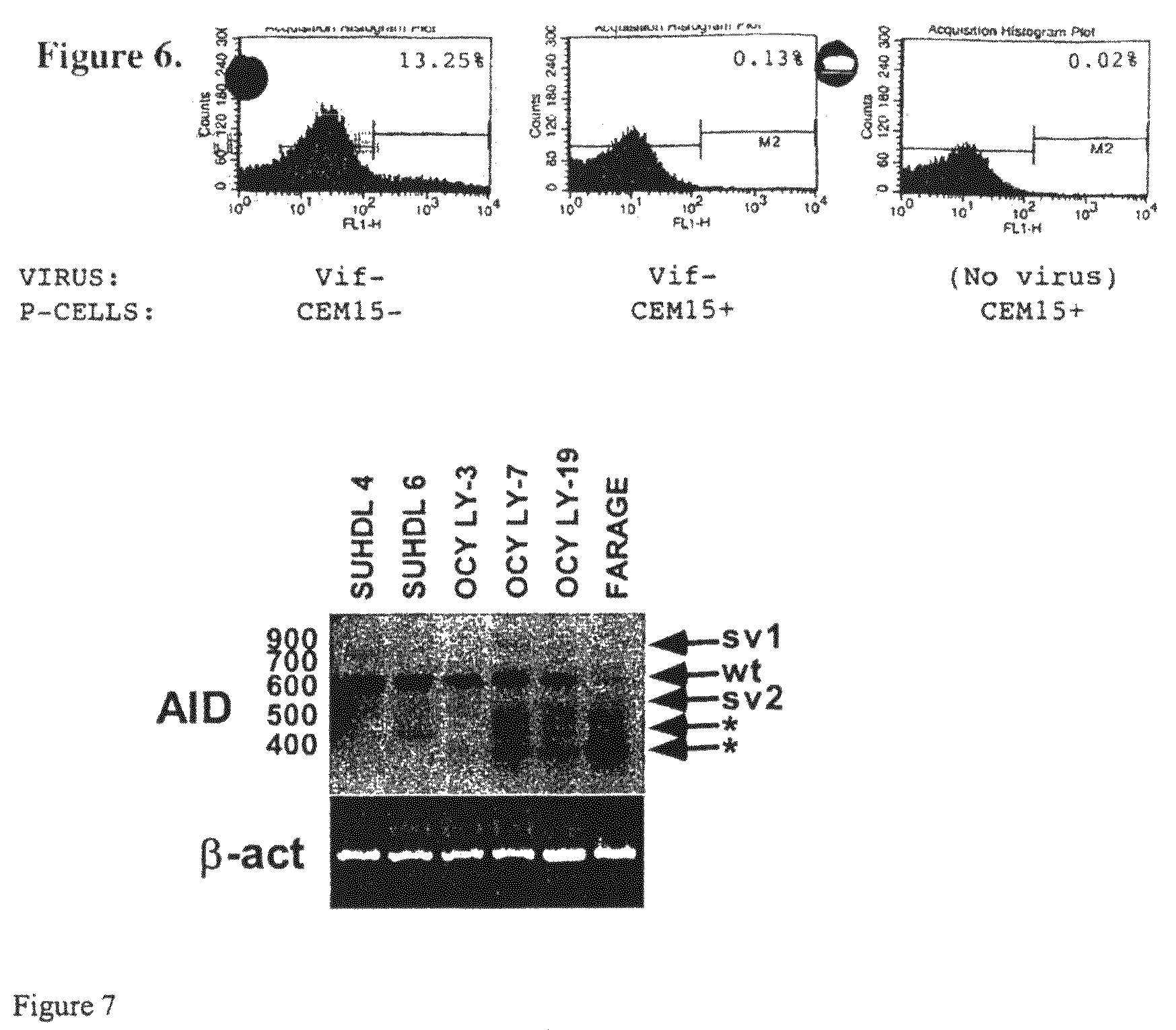
Mutations caused by activation-induced cytidine deaminase
InactiveUS20050095712A1Microbiological testing/measurementFused cellsActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminaseFhit gene
Methods for causing mutations in genes expressed in eukaryotic cells are provided. The methods involve expressing an activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) in the cells. The mutated genes can be any gene that is operably linked to a promoter, where the gene is within about 2 kilobases of the promoter. Examples include antibody genes. Also provided are cells expressing AID. The cells can be from any eukaryote, and include hybridoma cells and myeloma fusion partners.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
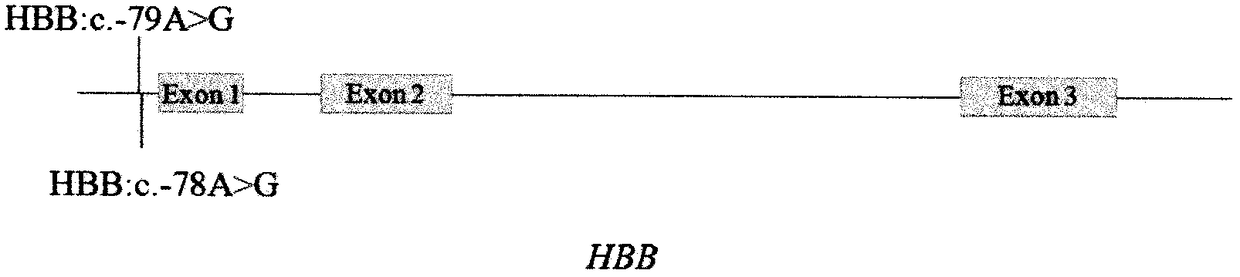
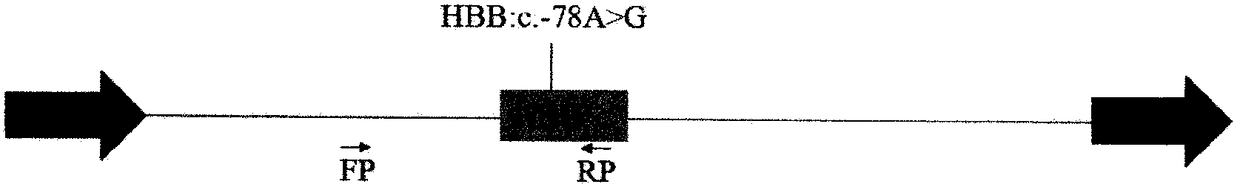
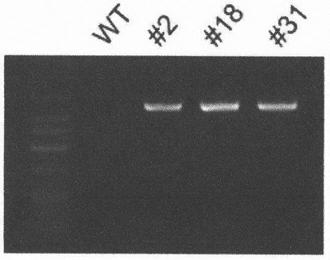
Basic group editing system and method for specifically repairing HBB gene mutation, kit and application of system and method and kit in human genital system
The invention provides a basic group editing method for specifically repairing HBB gene mutation in a human genital system. The method comprises the steps of delivering a basic group editing system used for specifically repairing HBB gene mutation so that the basic group editing system is close to relevant sequences of HBB mutant genes, and obtaining repaired HBB genes, wherein the basic group editing system comprises a basic group editing enzyme and gRNA, the basic group editing enzyme is fusion protein, and the fusion protein includes effect protein structural domains, cytidine deaminase structural domains and uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitor structural domains of a CRISPR / Cas system. The gene editing system is guided into a human germ cell, a human fertilized ovum or a human embryo, A>Gpathogenic mutation can be precisely repaired, and thus beta-mediterranean anemia is cured. The basic group editing method has a wide application prospect in the field of genetic therapy.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A method for base editing in plants
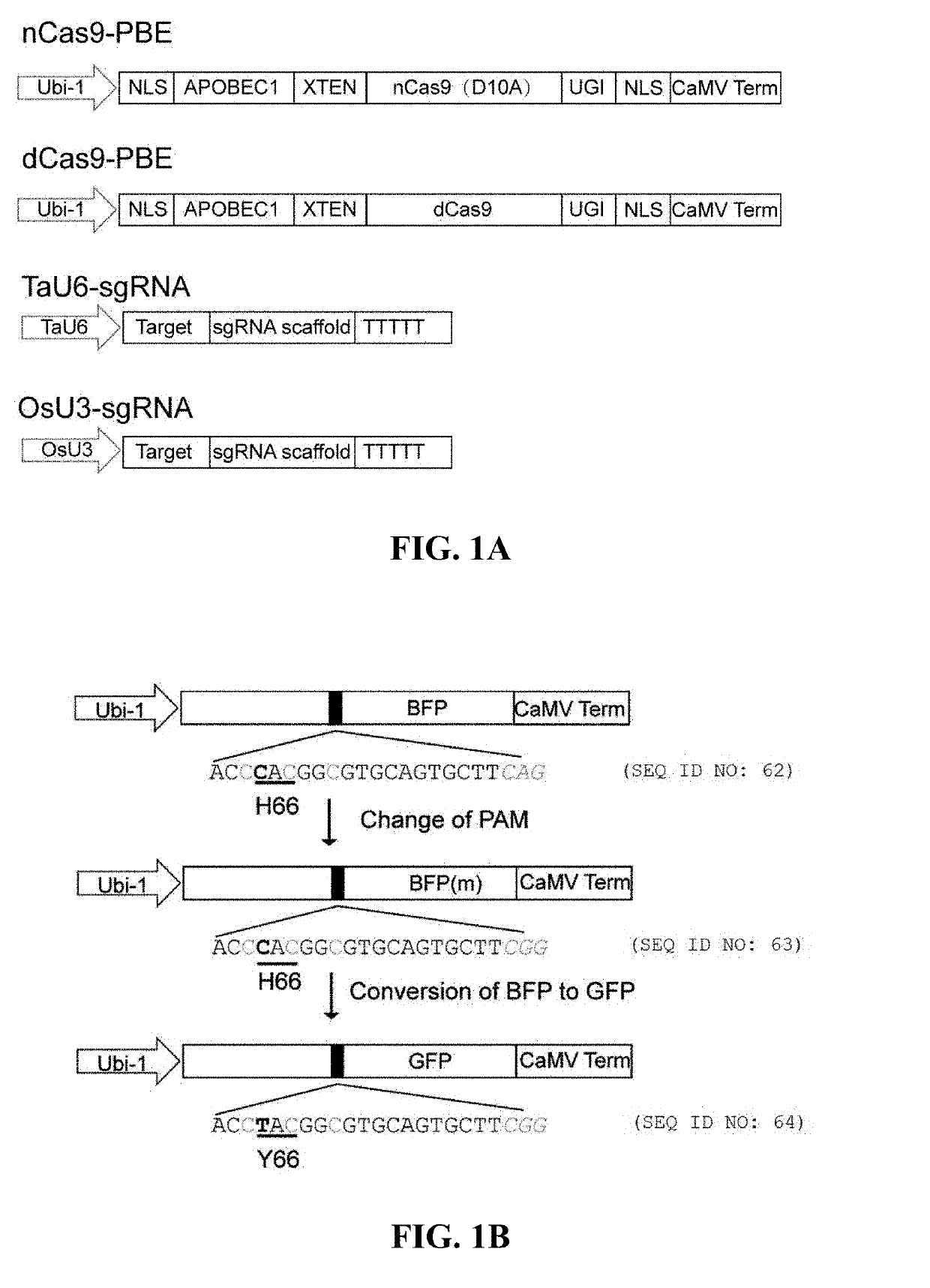
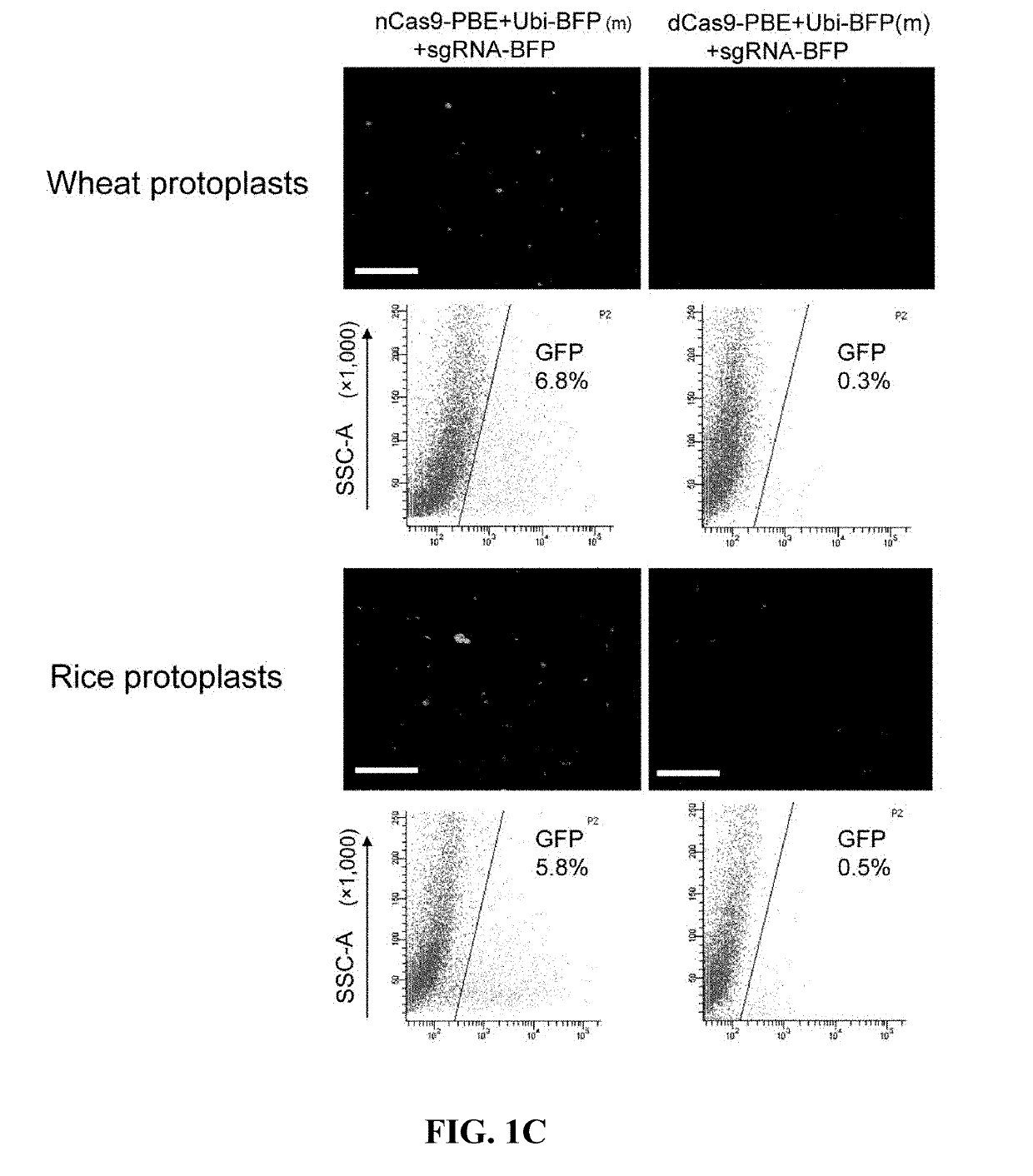
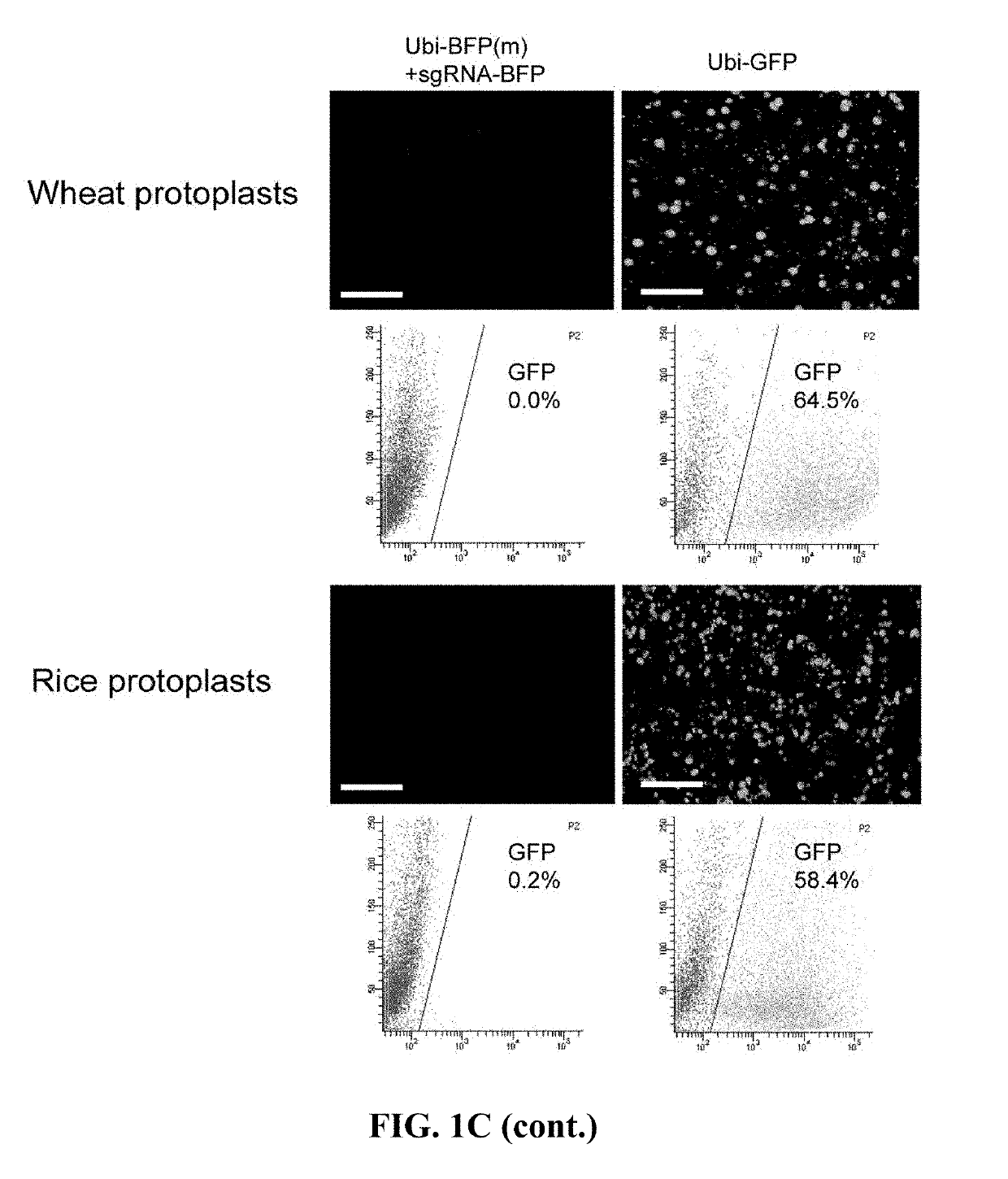
ActiveUS20190292553A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesPlant genetic engineeringCytidine deaminase
The present invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. Specifically, the invention relates to a method for base editing in plants. More particularly, the invention relates to a method for performing efficient base editing to a target sequence in the genome of a plant (such as a crop plant) by a Cas9-cytidine deaminase fusion protein, as well as plants produced through said method and progenies thereof.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genetically altered antibody-producing cell lines with improved antibody characteristics
InactiveUS7604994B2Altering the hypermutability of an antibody-producing cellGenetic stabilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGenetic diversityActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminase
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. Cells may be selected for expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), stimulated to produce AID, or manipulated to express AID for further enhancement of hypermutability. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production.
Owner:EISAI INC
Method for knocking out cytidine deaminase (cdd) gene in escherichia coli by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 technology and application
InactiveCN111321101ASimple way to knock out E. coli genesSimple methodBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCytidine Deaminase Gene
The invention discloses a method for knocking out a cytidine deaminase (cdd) gene in escherichia coli by utilizing a CRISPR-Cas9 technology and application. The method comprises the following steps: 1, making escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) competence containing a Cas9 plasmid; 2, designing and synthesizing a mutant sgRNA; 3, constructing Donor DNA; 4, transforming the sgRNA plasmid and the Donor DNAinto the escherichia coli competence carrying the Cas9 plasmid by employing an electro transformation method, and knocking out the cdd gene; and 5, introducing a target plasmid pET28a-UCK into a knock-out strain to produce cytidylic acid. The method has the advantages that operation is simple, the knockout success rate of the cdd gene is high, and the conversion rate of the knock-out strain on a substrate is improved, and is suitable for industrial production of the cytidine acid and the like. Compared with producing the cytidylic acid without strain knockout, producing the cytidylic acid withstrain knockout improves the conversion rate of the substrate cytidine and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by 15%, and the conversion rate reaches 99%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Evolution of cytidine deaminases
PendingUS20210261938A1Reduce effortShorten the timeHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsWild typeCytidine deaminase
Some aspects of this disclosure relate to strategies, systems, methods, compositions, and kits that are useful for production (e.g., evolution) of cytidine deaminase protein variants that are characterized by increased soluble expression and / or stability relative to the wild-type cytidine deaminase protein from which they are evolved. In some embodiments, evolved cytidine deaminase variants described by the disclosure are useful for incorporation into targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, for example in fusion proteins with a Cas9 domain or variant thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella uridine-cytidine kinase, coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103031285AIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyBiosynthetic genes
The invention relates to an enzyme from Bailing production bacterium Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella for synthesizing metabolic pyrimidine nucleotide from pyrimidine nucleoside, a gene for coding the enzyme and application thereof. The enzyme is uridine-cytidine kinase which has more than 90% of homology with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1; and the coding gene has more than 90% of homology with nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention researches the metabolic pathway of pyrimidine nucleoside synthesized pyrimidine nucleotide in details in principle. The cloned DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) comprising the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transformed into engineering bacterium by transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer. By adjusting the expression of the pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesized gene, the host pyrimidine nucleotide is endowed with high expressivity, thereby providing an effective way for enhancing the yield of the pyrimidine nucleotide and having great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for regulating RNA splicing by inducing splice site base mutation or polypyrimidine region base substitution
PendingCN109295053APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsCytosine deaminaseIntein
A method of regulating RNA splicing by inducing splice site base mutation or polypyrimidine region base substitution is disclosed, the method comprises expressing targeted cytidine deaminase in cellsto induce AG to AA mutation of 3' splicing site of intron of interested of gene of interested in the cells, or GT to AT mutation of 5' splicing site of the intron of interested of the gene of interested in the cells, or respective mutation of multiple C in a polypyrimidine region of the intron of interested of the gene of interested to T. The method can specifically block the exon recognition process, regulates the alternative splicing process of endogenous mRNA, induces exon skipping, activates alternative splicing sites, induces mutual exclusive exon conversion, induces intron retention andenhances exon retention.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation and application of induced mutant protein based on activated induced cytidine deaminase
ActiveCN111518794ASmall molecular weightHigh mutation efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainBase JMutated protein
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Cordyceps cytidine deaminase, coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103031295AIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaHydrolasesExpressivityNucleotide
The invention relates to an enzyme from Bailing production bacterium Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella for synthesizing metabolic (desoxy) uridine from (desoxy) cytidine, a gene for coding the enzyme and application thereof. The enzyme is cytidine deaminase which has more than 90% of homology with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1; and the coding gene has more than 90% of homology with nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention researches the metabolic pathway of (desoxy) cytidine synthesized (desoxy) uridine in details in principle. The cloned DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) comprising the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transformed into engineering bacterium by transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer. By adjusting the expression of the (desoxy) uridine biosynthesized gene, the host (desoxy) uridine is endowed with high expressivity, thereby providing an effective way for enhancing the yield of the (desoxy) uridine and having great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
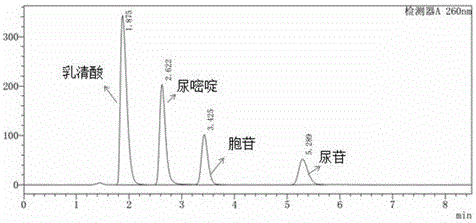
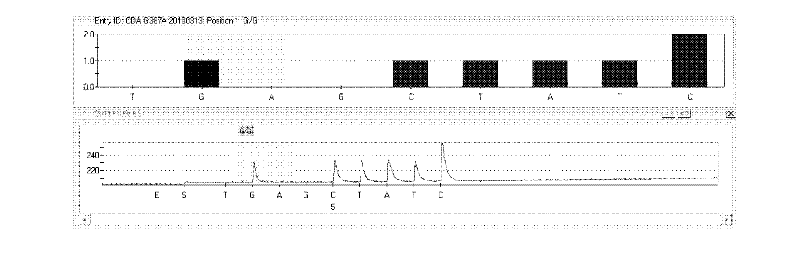
Kit and method for detecting CDA (cytidine deaminase) genetic polymorphism by use of pyrosequencing technique
InactiveCN102643907AQuick analysisAccurate analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGemcitabine
The invention discloses a kit and method for detecting CDA (cytidine deaminase) genetic polymorphism by use of the pyrosequencing technique. The kit checks the CDA genetic polymorphism which specifically refers to the rs60369023 (G>A) single nucleotide polymorphism. The kit comprises the primer shown by SEQ ID NO.2-4. The kit and method disclosed by the invention can realize accurate, quick and high-flux detection on the CDA genetic polymorphism so as to realize safe, reasonable and effective personalized administration of substrate gemcitabine.
Owner:湖南宏灏基因生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing uridylic acid by enzyme method
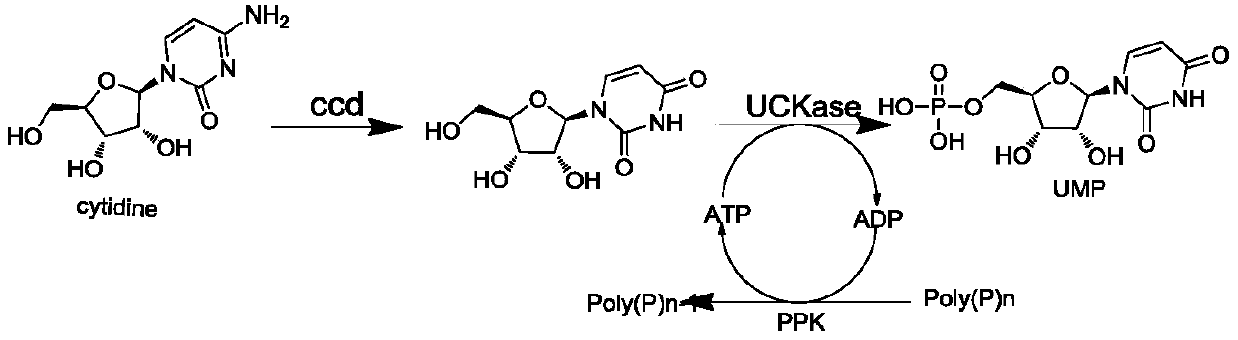
InactiveCN110885812APromote safe productionSafe preparationHydrolasesTransferasesKinaseCytidine deaminase
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy and biochemical engineering, discloses an enzyme composition for uridylic acid production and a method for preparing uridylicacid by an enzyme method. The enzyme composition is prepared by cytidine deaminase, polyphosphate kinase and uridine-cytidine kinase. The three enzymes are reasonably combined to efficiently catalyzeand prepare uridylic acid. The enzyme composition disclosed by the invention can be recycled and is low in cost; and energy-saving and environment-friendly effects are realized. According to the invention, the cytidine is used as a substrate and the enzyme composition for uridylic acid production is added, so that the uridylic acid is prepared with low cost and high safety and reliability; the cost of the existing route is reduced; and the large-scale production is realized. The application of uridylic acid in fields of biocatalysis and medicines is guaranteed.
Owner:杭州唯泰生物药业有限公司 +1
Mutants of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and methods of use
The invention provides functional mutants of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) protein that have increased activity as compared to a wild-type AID protein. The invention also provides nucleic acids encoding the functional AID mutants, and vectors and cells comprising the nucleic acids. The invention further provides methods of using the functional mutant AID proteins.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Cordyceps cytidine deaminase, coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103031295BIncrease productionEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaHydrolasesNucleotideDeoxyuridine
The invention relates to an enzyme from Bailing production bacterium Cordyceps Chinese Hirsutella for synthesizing metabolic (desoxy) uridine from (desoxy) cytidine, a gene for coding the enzyme and application thereof. The enzyme is cytidine deaminase which has more than 90% of homology with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1; and the coding gene has more than 90% of homology with nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention researches the metabolic pathway of (desoxy) cytidine synthesized (desoxy) uridine in details in principle. The cloned DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) comprising the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transformed into engineering bacterium by transduction, conversion and conjugal transfer. By adjusting the expression of the (desoxy) uridine biosynthesized gene, the host (desoxy) uridine is endowed with high expressivity, thereby providing an effective way for enhancing the yield of the (desoxy) uridine and having great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
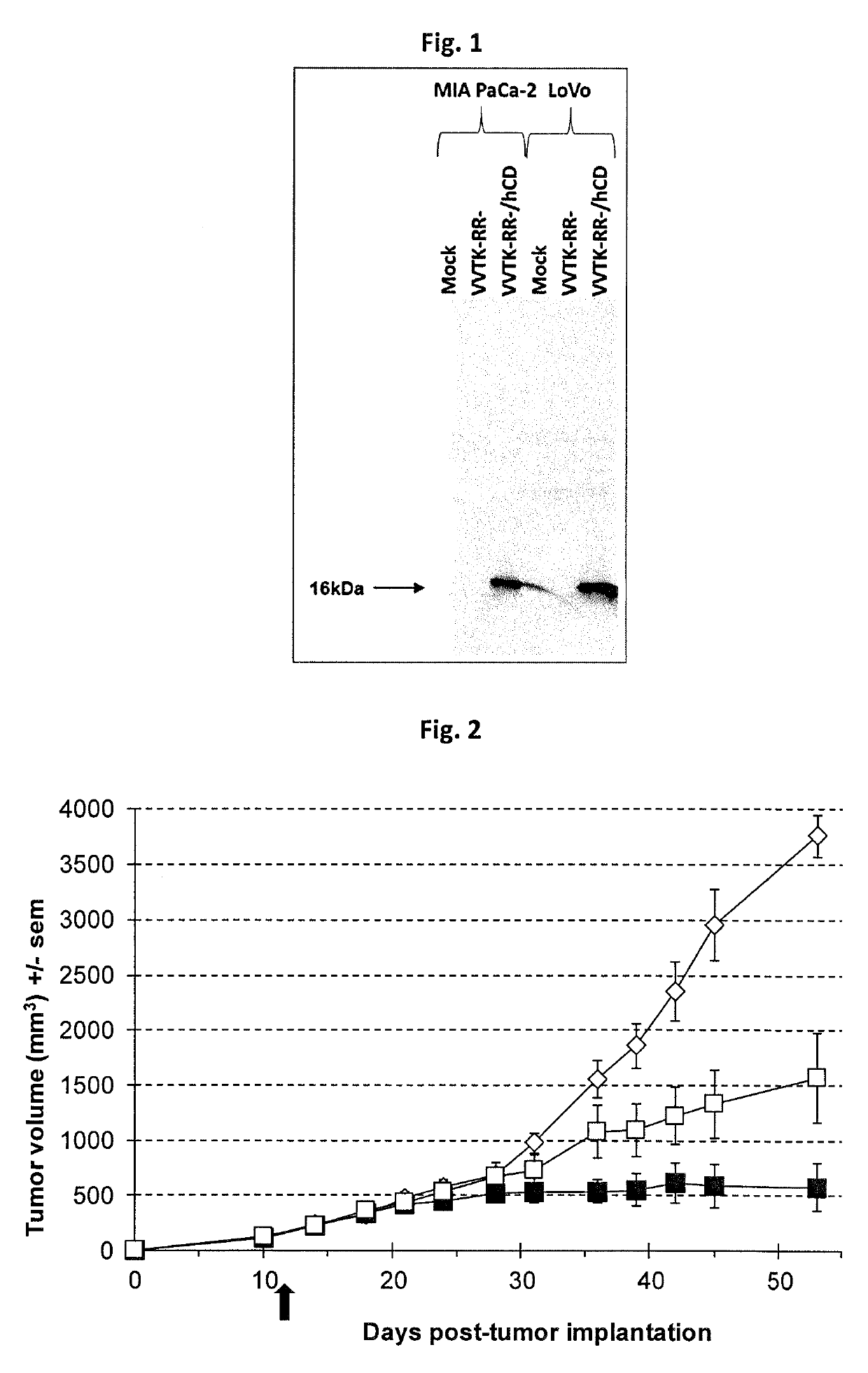
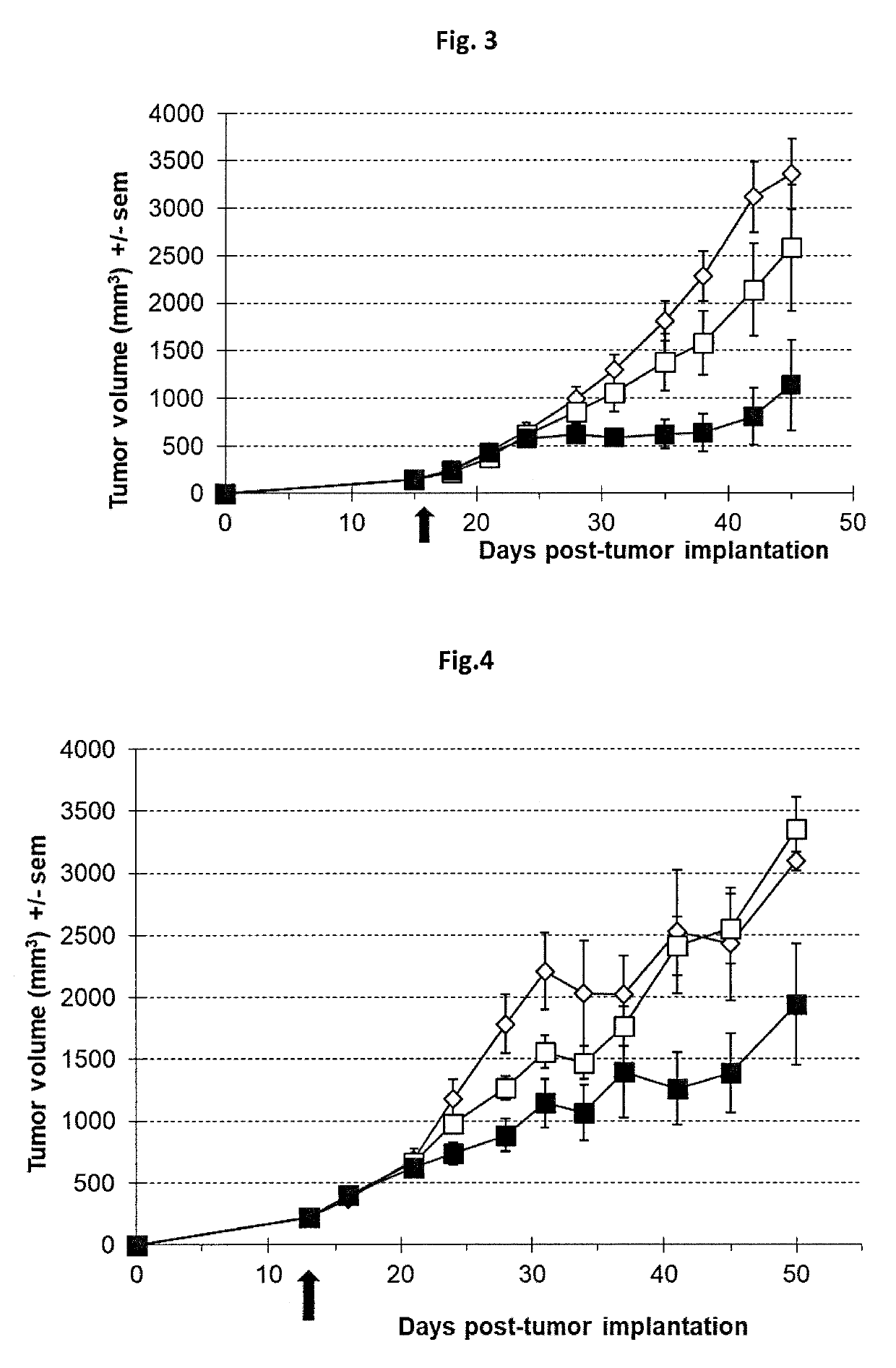
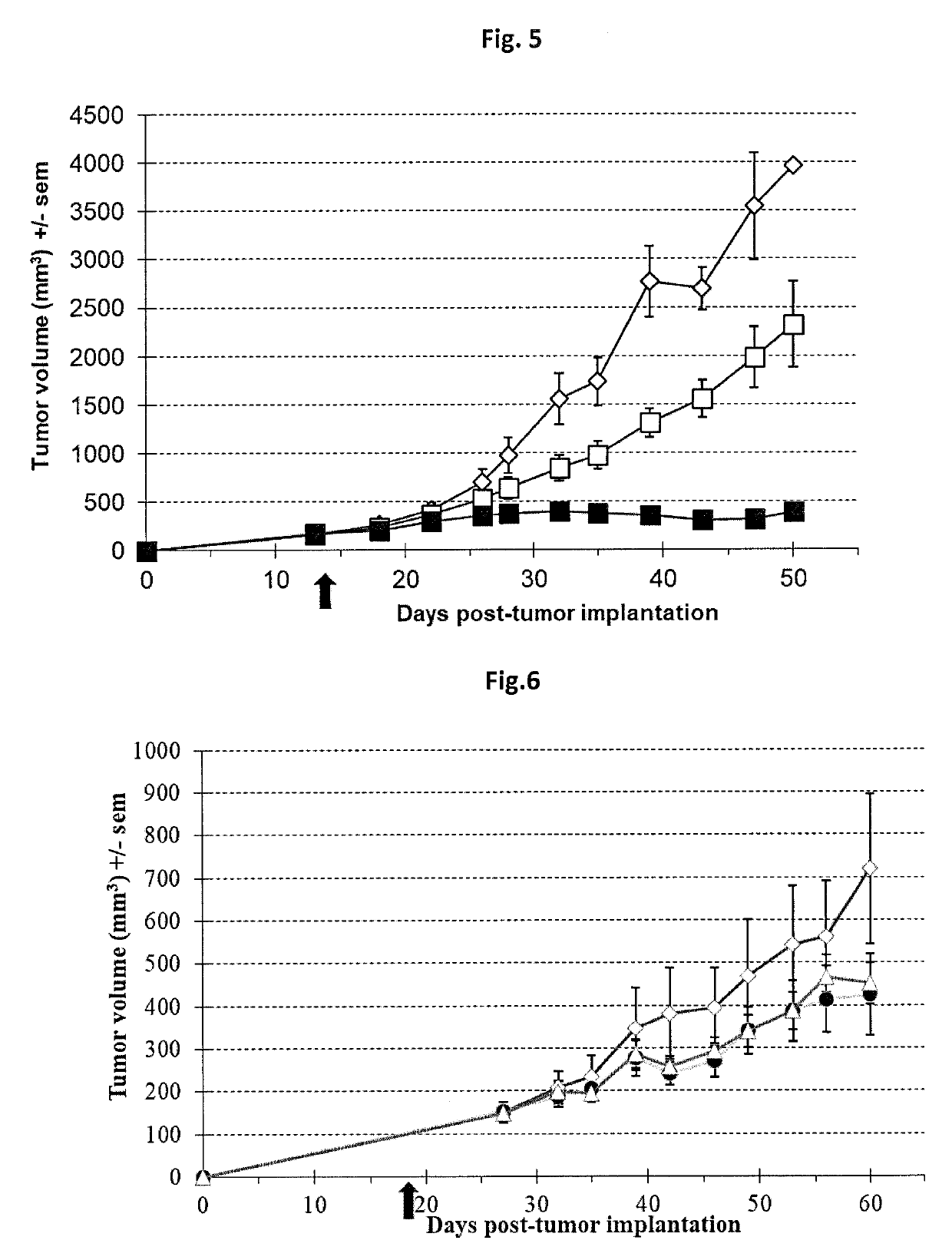
Oncolytic viruses and therapeutic molecules
The present invention relates to an oncolytic virus encoding a cytidine deaminase (CDAse) polypeptide, a composition comprising it, as well as their use for prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, and more particularly for the treatment of cancer. The present invention also provides a method for treating a disease or a pathologic condition comprising the administration of such an oncolytic virus orcomposition thereof and a process for preparing such an oncolytic virus.
Owner:TRANSGENE SA
5'-position dibenzyl phosphoric acid ester of 5-azacytidine or 2'-deoxy body thereof
InactiveCN108290920AInhibit synthesisShow cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphoric Acid EstersMetabolic enzymes
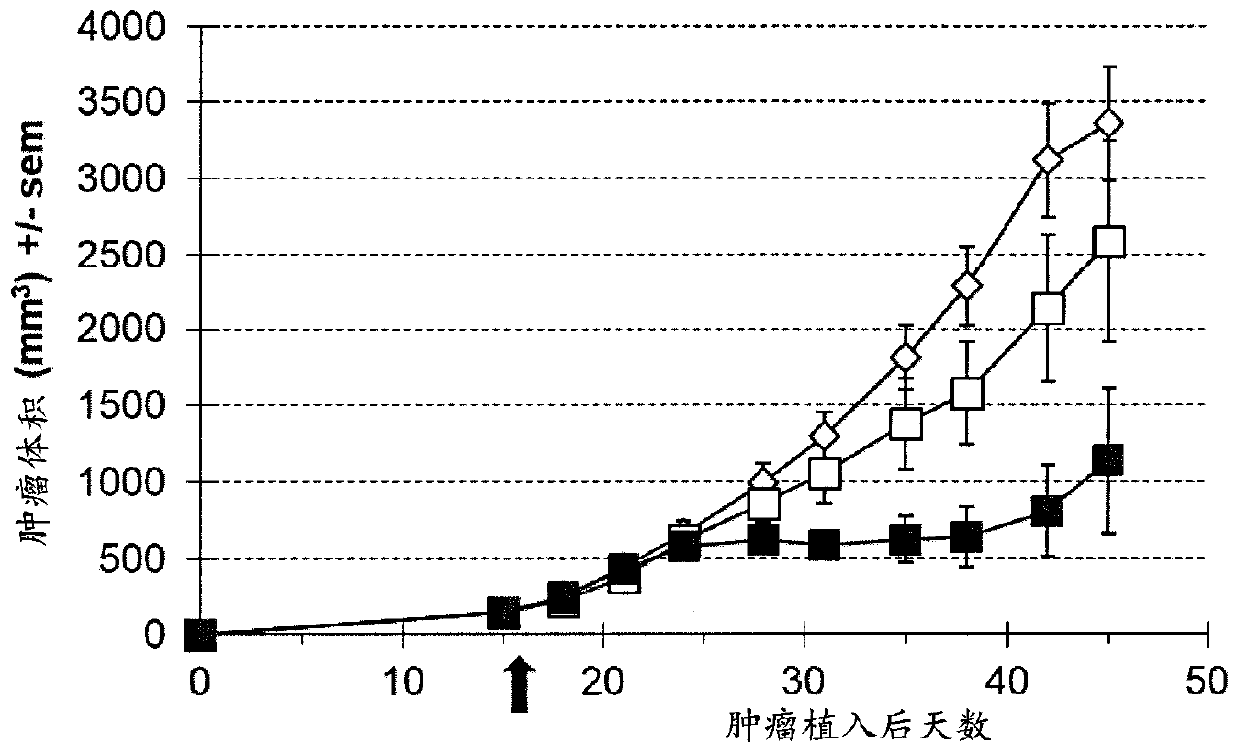
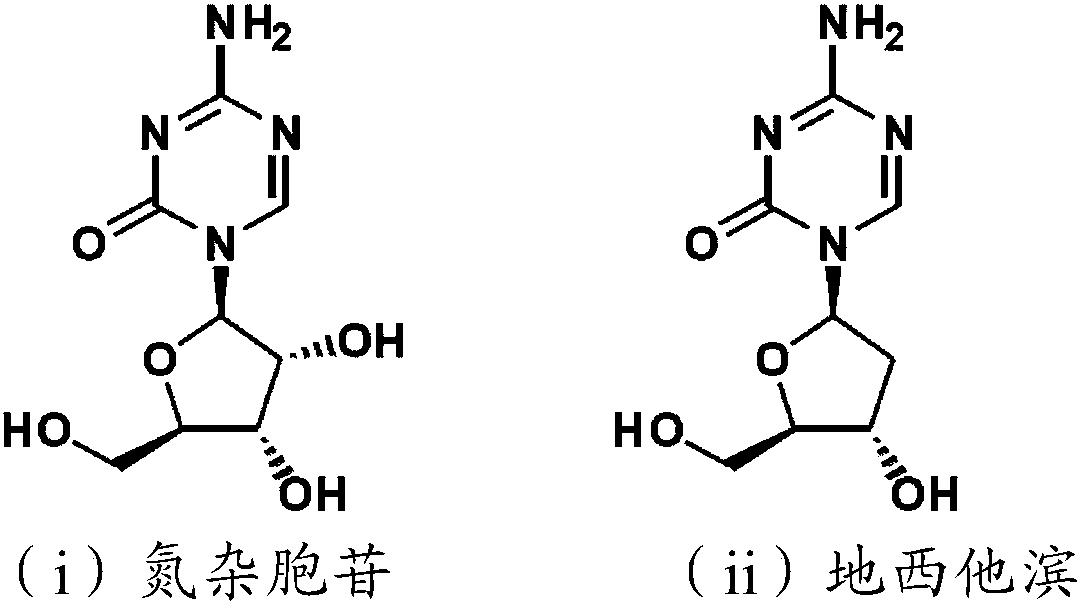
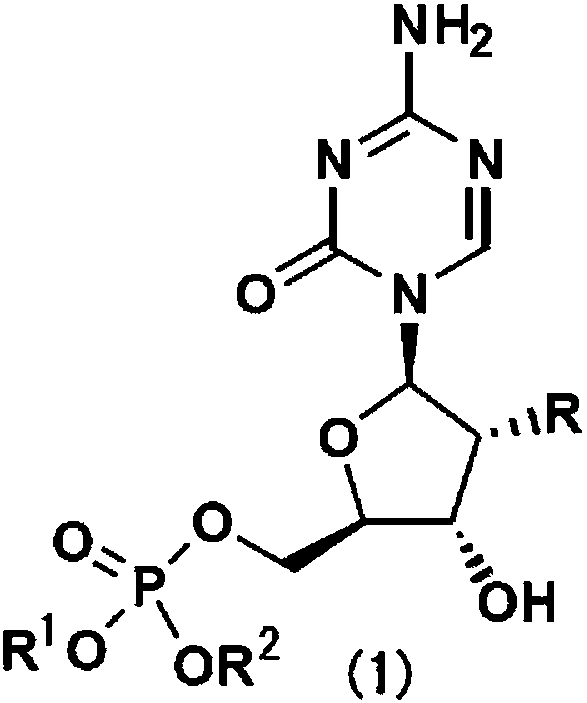
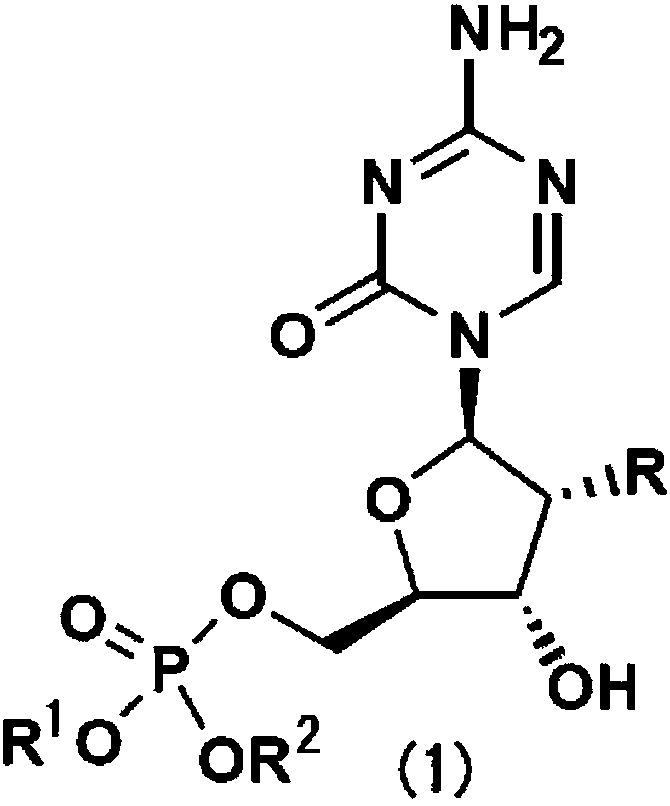
The abovementioned problem is solved by a novel compound represented by formula (1): (in the formula, R is a hydroxyl group or a hydrogen atom, and R1 and R2 are benzyl groups that may have a substituent group).To provide a drug that substitutes for injections (5-azacytidine or 2'-deoxy-5-azacytidine) that are clinically used as bone marrow tumor therapeutic drugs, said drug having high stabilitywith respect to metabolic enzyme cytidine deaminase, being absorbed in the body even by means of oral administration, and having an effect of being integrated into an RNA and DNA biosynthesis pathwayand inhibiting protein synthesis.
Owner:OHARA PHARMA
Mutations caused by activation-induced cytidine deaminase
InactiveUS20110143440A1Animal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminase
Owner:MARTIN ALBERTO +1
Composition and method for diversifying polypeptide libraries
Provided, among other things, is a yeast cell comprising: (A) a recombinant DNA that constitutively or inducibly expresses a cytidine deaminase comprising sequence with about 90% sequence identity or more with a cytidine deaminase domain of (i) SEQ ID NO. 2 or SEQ ID NO. 4, or (ii) a chimera between the two starting with SEQ ID NO. 3 or SEQ ID NO. 4 sequence and having one transition to end in SEQ ID NO. 1 or SEQ ID NO. 2 sequence, or (iii) a chimera between the two starting with SEQ ID NO. 1 or SEQ ID NO. 2 sequence and having one transition to end in SEQ ID NO. 3 or SEQ ID NO. 4 sequence; and (B) a second recombinant DNA that constitutively or inducibly expresses a binding scaffold protein for presentation on the outer surface of the yeast, wherein the cytidine deaminase as expressed by the first recombinant DNA is effective to contribute to a mutagenic process for inducing mutations in the binding scaffold protein of the yeast cell.
Owner:ABZYME THERAPEUTICS LLC
High-throughput screening method of microorganism strain producing cytidine at high yield
ActiveCN105505844AMeet the testing requirementsHigh detection throughputBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a high-throughput screening method of a microorganism strain producing cytidine at high yield. The method includes the steps of (a) inoculating single colony to a deep pore plate I filled with a liquid seed culture medium, and performing shaking table culture; (b) correspondingly inoculating the seed liquid in the deep pore plate I to a deep pore plate II filled with a fermenting culture medium, and performing shaking table culture; (c) performing centrifugation to the deep pore plate to obtain a supernate to detect the content of the cytidine; (d) adding the supernate of a fermentation liquid, a buffer liquid and a proper amount of cytidine deaminase in pores of an ELISA plate, and performing a reaction in a bath at 30-40 DEG C for 10-40 min; (e) instantly adding a reaction solution A and a reaction solution B after the reaction is finished, and performing a reaction in a bath at 30-40 DEG C for 20-50 min; and (f) measuring the absorbance of the reaction solution through an ELISA instrument, and calculating the yield of the cytidine according to a standard curve and dilution ratio of the supernate of the fermentation liquid. The method achieves high-throughput culturing, high-throughput preparation of fermentation liquid, and high-throughput measurement of the cytidine.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing b cell which produces human-type antibody
InactiveUS20130244907A1Avoid difficult choicesImprove developmentAnimal cellsStable introduction of DNACre recombinaseCytosine deaminase
Provided is a method for preparing B cells which produce a human-type antibody, comprising substituting an antibody gene of B cells with a human antibody gene, wherein the B cells are non-human vertebrate B cells capable of inducing or halting AID (activation induced cytidine deaminase) expression with the induction of the expression of an exogenous Cre recombinase gene through extracellular stimulation followed by the inversion of the direction of the exogenous AID gene by expressed Cre recombinase.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA
Oncolytic viruses and therapeutic molecules
PendingUS20190330655A1Effective anti-tumor effectContributes to their lysisHydrolasesDigestive systemDiseaseBioinformatics
The present invention relates to an oncolytic virus encoding a cytidine deaminase (CDAse) polypeptide, a composition comprising it, as well as their use for prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, and more particularly for the treatment of cancer. The present invention also provides a method for treating a disease or a pathologic condition comprising the administration of such an oncolytic virus or composition thereof and a process for preparing such an oncolytic virus.
Owner:TRANSGENE SA
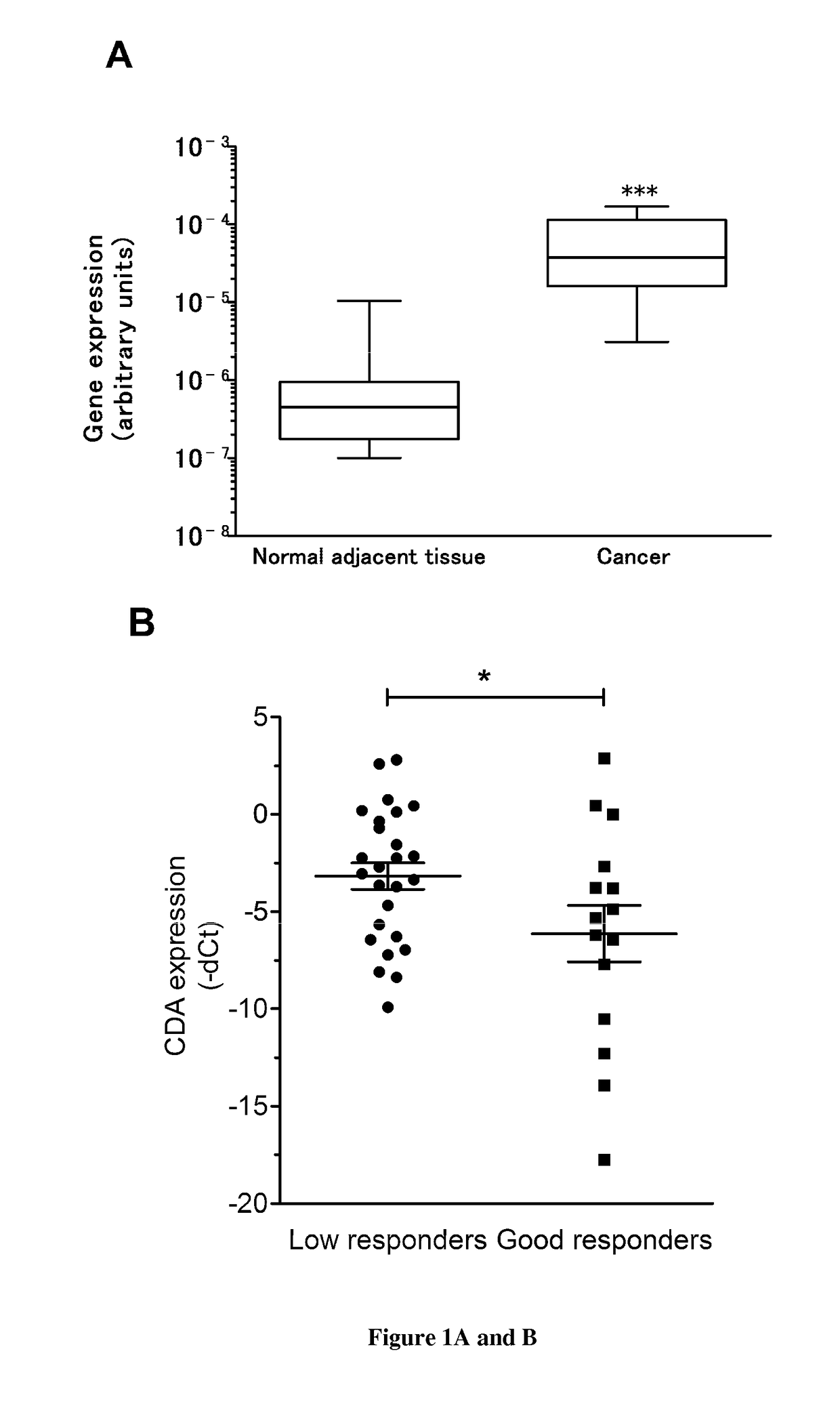
Cytidine deaminase inhibitors for the treatment of pancreatic cancer
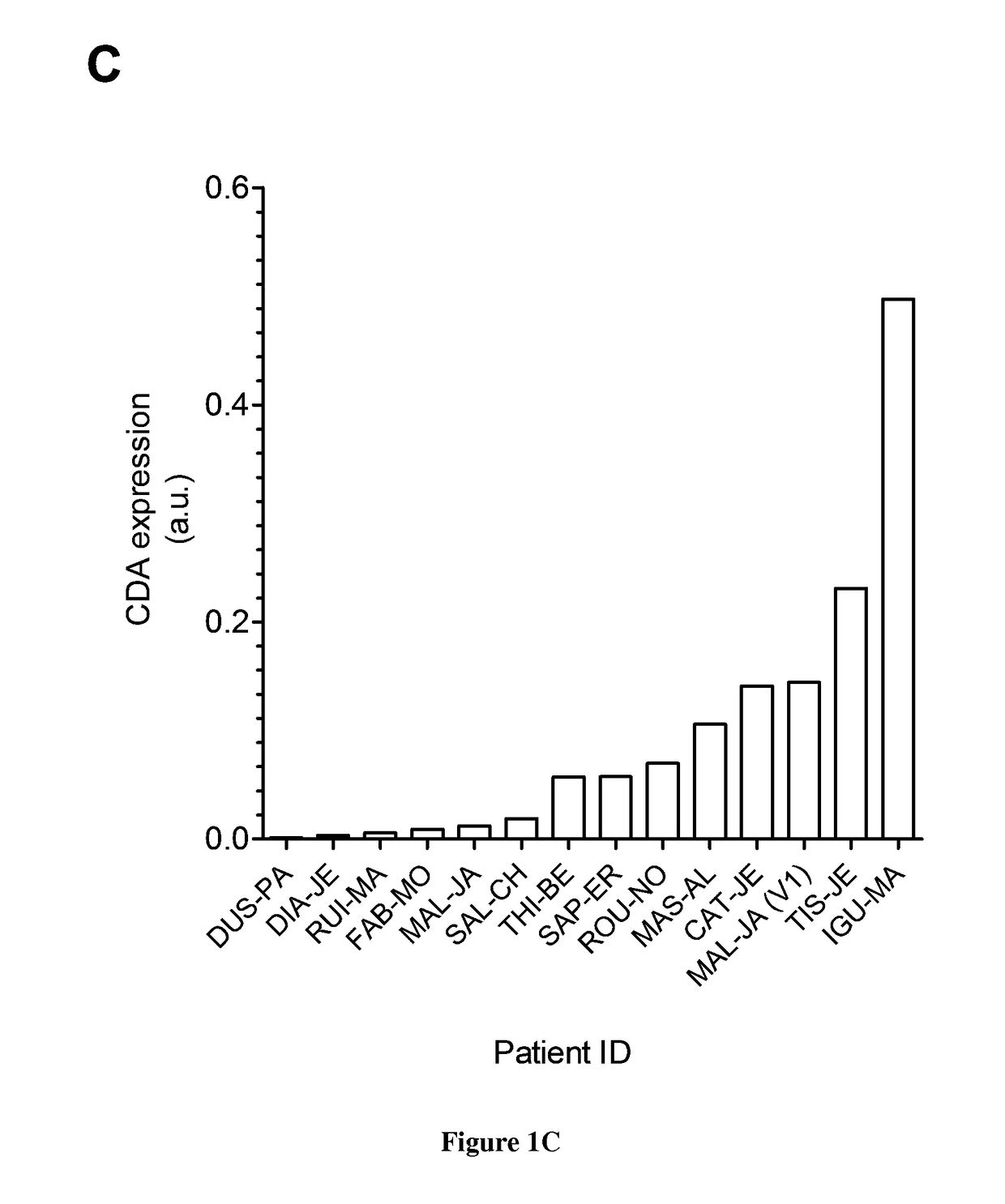
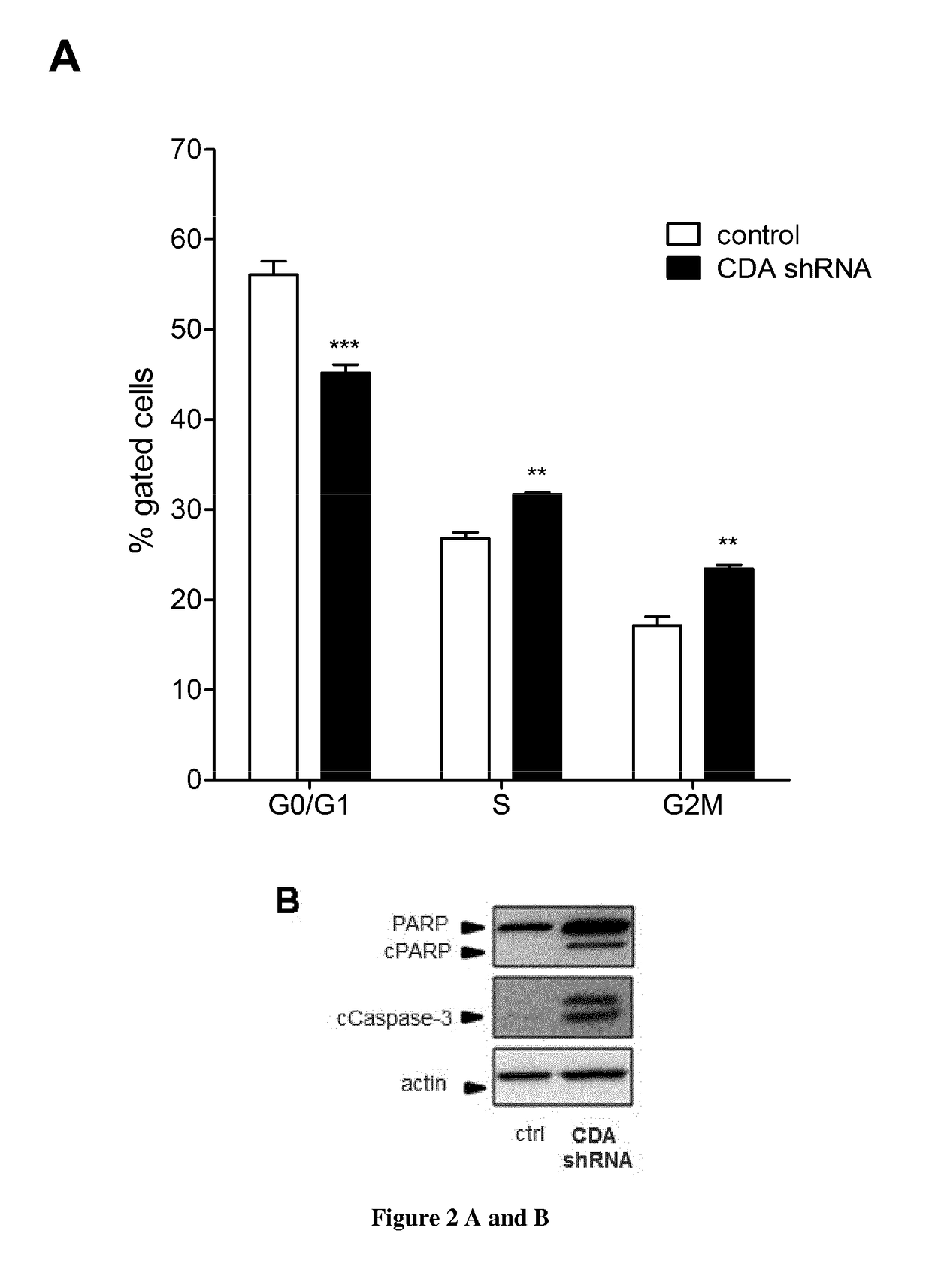
InactiveUS20190076464A1High affinityStrong specificityCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsAdenosine Deaminase InhibitorCancer cell
The present invention relates to methods and pharmaceutical compositions for use in the treatment of pancreatic cancer in a subject in need thereof. The inventors showed that targeting cytidine deaminase sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy (gemcitabine dFdC) both in vitro and in vivo in experimental models of PDA, with very high efficacy. To their surprise, CDA targeting in the absence of chemotherapy strongly alters cell proliferation and tumor progression. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for treating pancreatic cancer in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a cytidine deaminase inhibitor in combination with an anti-pancreatic cancer treatment selected from the group consisting of CHK1 inhibitor, WEE1 inhibitor, ART inhibitor, DHODH inhibitor or gene therapy.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com