Method for quality-divided crystallization and salt extraction from coal chemical industry high-salinity wastewater
A technology for high-salt wastewater and coal chemical industry, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal sulfite/sulfite, inorganic chemistry, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, improving efficiency, and reducing heat loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
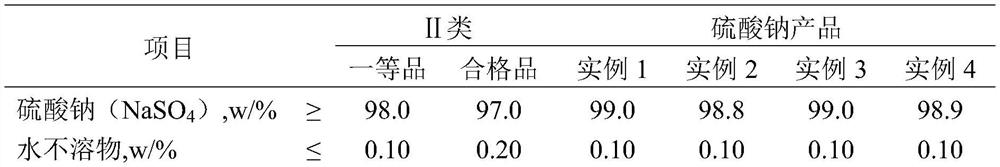
[0025] Embodiment 1: A method for extracting salt from high-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry by fractional crystallization: In this example, high-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry has been processed by a pretreatment unit and an advanced oxidation unit. High-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry passes through multi-stage nanofiltration (influent pressure 1.6MPa, divalent salt concentrated water side flow 550L / h, monovalent salt production water side pressure 0.16MPa, flow 200L / h), The salt is separated and concentrated. After the nanofiltration membrane separation, the TDS of the concentrated water side of the nanofiltration is 47.56g / L, and the TDS of the produced water side of the nanofiltration is 10.03g / L. Nanofiltration concentrated water is concentrated by MVR evaporation (evaporation temperature 95°C, cooling water flow 390L / h, rotating speed 100rpm, vacuum degree is adjusted according to the liquid level of the evaporation device) to a supers...
Embodiment 2
[0026]Example 2: A method for extracting salt from high-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry by fractional crystallization: In this example, high-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry has been processed by a pretreatment unit and an advanced oxidation unit. High-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry passes through multi-stage nanofiltration (influent pressure 1.55MPa, divalent salt concentrated water side flow 545L / h, monovalent salt production water side pressure 0.15MPa, flow 190L / h), The salt is separated and concentrated. After the nanofiltration membrane separation, the TDS of the concentrated water side of the nanofiltration is 46.82g / L, and the TDS of the produced water side of the nanofiltration is 9.65g / L. Nanofiltration concentrated water is evaporated and concentrated by MVR (evaporation temperature 100 ℃, cooling water flow 400L / h, rotating speed 95rpm, vacuum degree is adjusted according to the liquid level of the evaporation device) to a supersa...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: A method of extracting salt from high-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry by fractional crystallization: In this example, high-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry has been processed by a pretreatment unit and an advanced oxidation unit. High-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry passes through multi-stage nanofiltration (influent pressure 1.7MPa, divalent salt concentrated water side flow 540L / h, monovalent salt production water side pressure 0.17MPa, flow 210L / h), The salt is separated and concentrated. After the nanofiltration membrane separation, the TDS of the concentrated water side of the nanofiltration is 48.21g / L, and the TDS of the produced water side of the nanofiltration is 10.56g / L. Nanofiltration concentrated water is evaporated and concentrated by MVR (evaporation temperature 100°C, cooling water flow 395L / h, rotational speed 105rpm, vacuum degree is adjusted according to the liquid level of the evaporation device) to a supe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com