Interface joint material based on industrial solid waste and preparation method thereof
An industrial solid waste and interface technology, applied in the field of building interface joint materials, can solve the problems of low strength, not easy to bond, and become brittle, and achieve the effects of good adhesion, improved utilization, and high strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
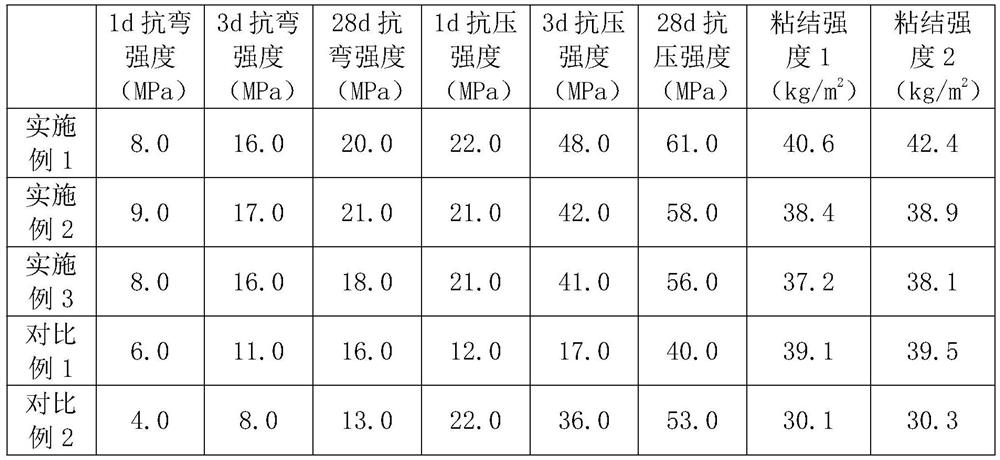
[0042] Accurately weigh the raw materials by weight: 100 parts of slag Portland cement, 100 parts of metakaolin, 100 parts of industrial solid waste, 30 parts of sodium silicate, 10 parts of sodium hydroxide, 25 parts of magnesium acrylate, 5 parts of calcium acrylate, three parts 3 parts of polytrivinyl cyanate, 3 parts of sodium sulfite, 3 parts of sodium persulfate, 5 parts of polycarboxylate water reducing agent, and 70 parts of water.
[0043] Preparation:
[0044] Step 1, mix the above-mentioned slag Portland cement, metakaolin, industrial solid waste, polycarboxylate water reducer, magnesium acrylate, calcium acrylate, trivinyl cyanurate and sodium sulfite to obtain a mixture A ;
[0045] Step 2, mixing the above-mentioned weight parts of sodium silicate, sodium hydroxide and 35 parts of water to obtain a mixture B, immediately adding the mixture B to the mixture A to obtain the mixture C;
[0046] Step 3, mixing the above-mentioned sodium persulfate in parts by weigh...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Accurately weigh the raw materials by weight: 80 parts of slag Portland cement, 130 parts of metakaolin, 130 parts of industrial solid waste, 35 parts of sodium silicate, 12 parts of sodium hydroxide, 30 parts of magnesium acrylate, 6 parts of calcium acrylate, three parts 2 parts of polytrivinyl cyanate, 2 parts of sodium sulfite, 2 parts of sodium persulfate, 6 parts of polycarboxylate water reducing agent, and 80 parts of water.
[0049] Preparation:
[0050] Step 1, mix the above-mentioned slag Portland cement, metakaolin, industrial solid waste, polycarboxylate water reducer, magnesium acrylate, calcium acrylate, trivinyl cyanurate and sodium sulfite to obtain a mixture A ;
[0051] Step 2, mixing the above-mentioned weight parts of sodium silicate, sodium hydroxide and 40 parts of water to obtain a mixture B, immediately adding the mixture B to the mixture A to obtain the mixture C;
[0052] Step 3, mixing the above-mentioned sodium persulfate in parts by weight...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Accurately weigh the raw materials by weight: 130 parts of slag Portland cement, 80 parts of metakaolin, 80 parts of industrial solid waste, 25 parts of sodium silicate, 8 parts of potassium hydroxide, 25 parts of magnesium acrylate, 5 parts of calcium acrylate, three parts 1 part of hydroxypropane trivinyl ether, 1 part of potassium sulfite, 1 part of potassium persulfate, 3 parts of sulfamate water reducing agent, and 60 parts of water.
[0055] Preparation:
[0056] Step 1, the above-mentioned weight parts of slag Portland cement, metakaolin, industrial solid waste, sulfamate water reducing agent, magnesium acrylate, calcium acrylate, trihydroxypropane trivinyl ether and potassium sulfite are mixed uniformly to obtain Mixed material A;
[0057] Step 2, mixing the above-mentioned weight parts of sodium silicate, potassium hydroxide and 30 parts of water to obtain a mixture B, immediately adding the mixture B to the mixture A to obtain the mixture C;
[0058] Step 3,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com