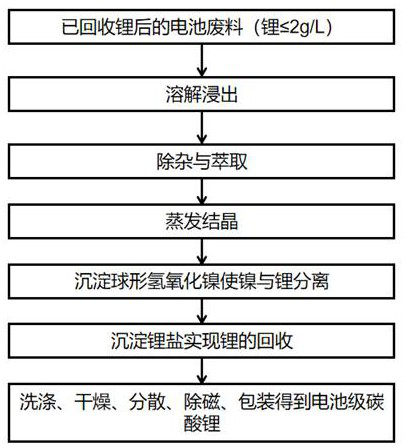
Method for recovering lithium from low-lithium-content battery waste
A technology for recovering lithium and batteries, which is applied in the field of lithium recovery, can solve the problems of low lithium recovery rate, high recovery cost, and high processing cost, so as to reduce production cost and operation requirements, avoid the use of extraction agents, and avoid alkali metal pollution Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
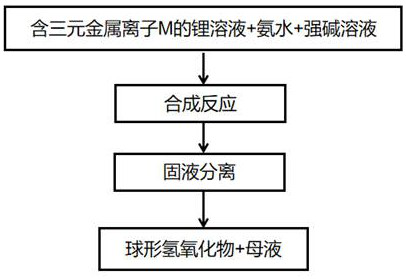
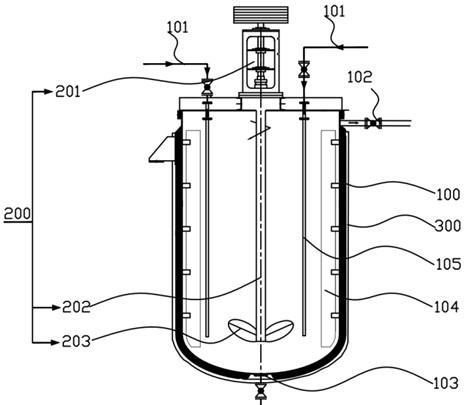
[0093] Lithium sulfate solution containing ternary metal ion M (nickel), nickel concentration of 120g / L, lithium concentration of 18.0g / L, lithium sulfate solution containing ternary metal ion M (nickel) together with sodium hydroxide solution and ammonia water Enter the synthesis reaction kettle, control the stirring speed to be 160 rpm, the pH value to be 12.0, and the synthesis temperature to be 60 ° C. After the reaction kettle is full, it overflows normally, and the overflowed slurry is separated from solid and liquid by a centrifuge, and the ternary metal ion M is realized. (Ni) effective separation of M and lithium in lithium sulfate solution, and detection of residual lithium in the obtained spherical nickel hydroxide and residual M content in lithium sulfate solution.
Embodiment approach 2
[0095] Lithium sulfate solution containing ternary metal ion M (nickel), nickel concentration of 120g / L, lithium concentration of 25.0g / L, lithium sulfate solution containing ternary metal ion M (nickel) together with sodium hydroxide solution and ammonia water Enter the synthesis reaction kettle, control the stirring speed to be 160 rpm, the pH value to be 12.0, and the synthesis temperature to be 60 ° C. After the reaction kettle is full, it overflows normally, and the overflowed slurry is separated from solid and liquid by a centrifuge, and the ternary metal ion M is realized. (Ni) effective separation of M and lithium in lithium sulfate solution, and detection of residual lithium in the obtained spherical nickel hydroxide and residual M content in lithium sulfate solution.
Embodiment approach 3
[0097] Lithium sulfate solution containing ternary metal ion M (cobalt), cobalt concentration of 110g / L, lithium concentration of 30.0g / L, lithium sulfate solution containing ternary metal ion M (cobalt), potassium hydroxide solution, ammonia water together Enter the synthesis reaction kettle, control the stirring speed to be 160 rpm, the pH value to be 12.0, and the synthesis temperature to be 60 ° C. After the reaction kettle is full, it overflows normally, and the overflowed slurry is separated from solid and liquid by a centrifuge, and the ternary metal ion M is realized. The effective separation of M and lithium in the lithium sulfate solution of (cobalt), and the detection of the residual lithium in the obtained spherical cobalt hydroxide and the residual M content in the lithium sulfate solution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com