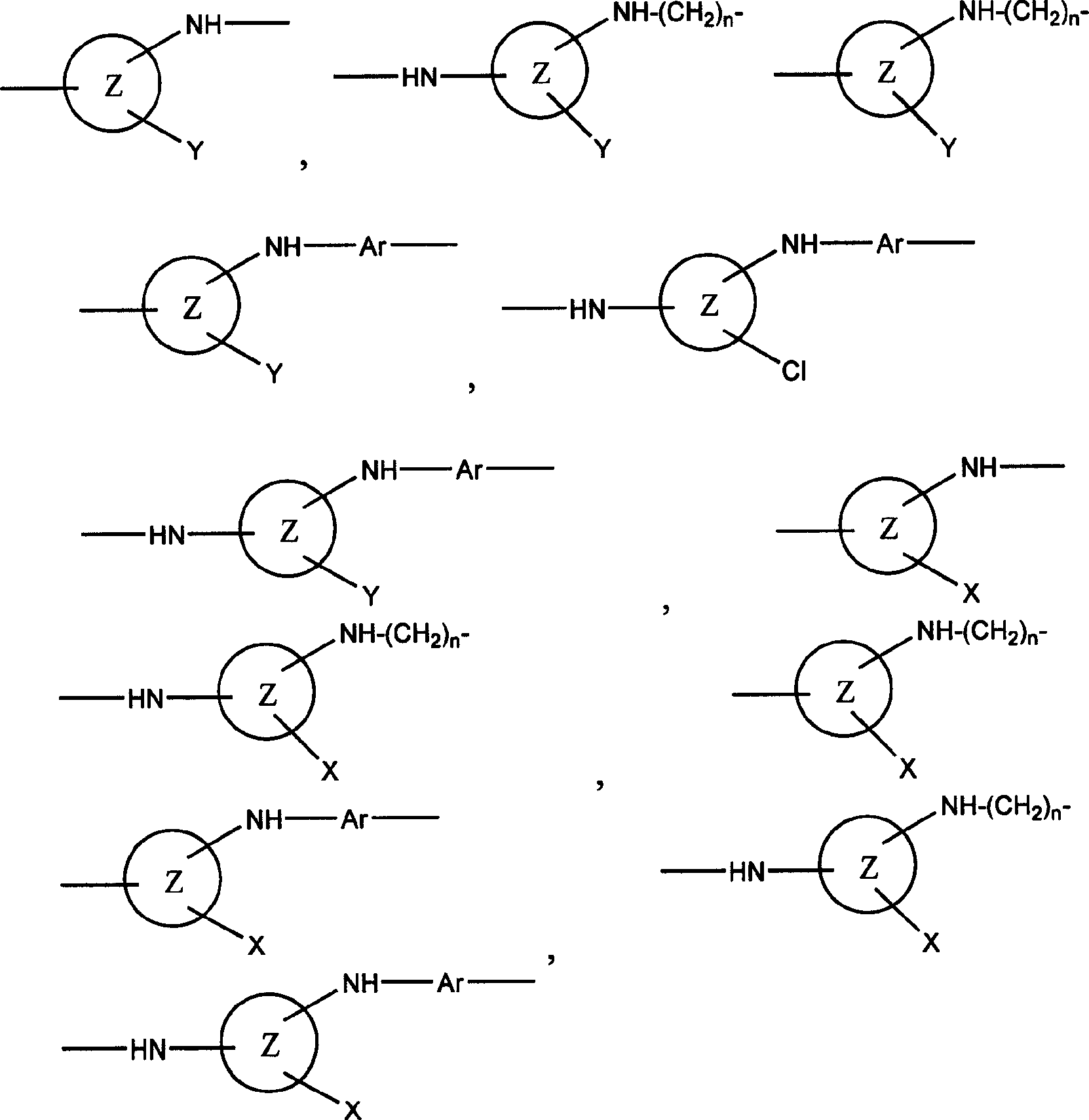
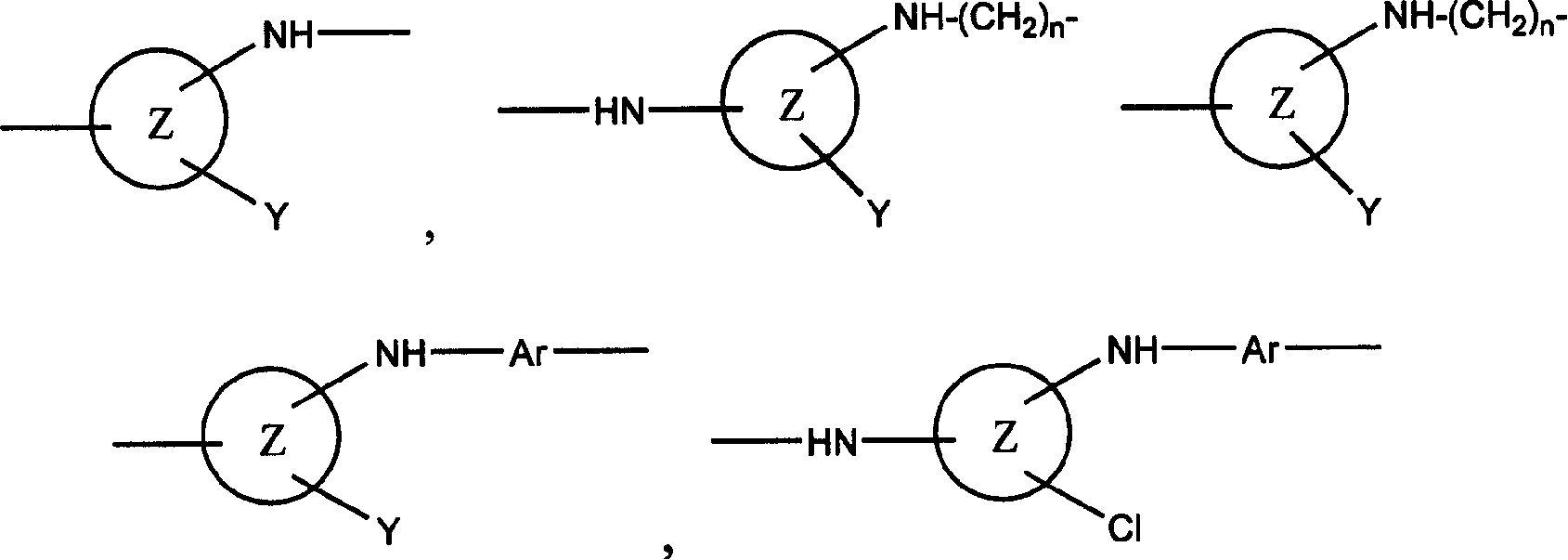
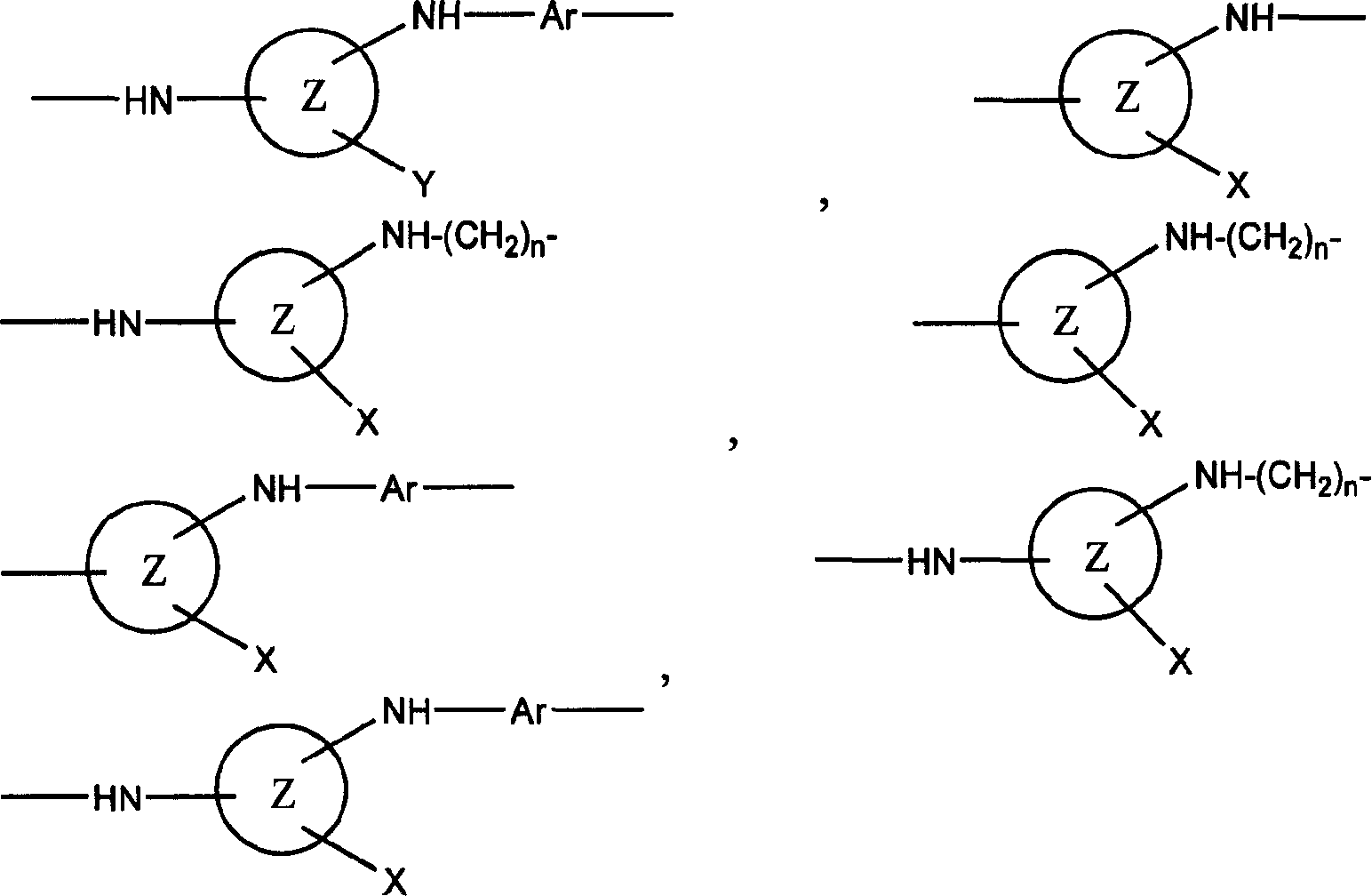
Reactive dye compounds
A technology of reactive dyes and dye compositions, applied in the field of reactive dye compounds, to achieve the effects of increased affinity, greater coloring strength, and increased efficacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0061] The invention also relates to a process for the preparation of the dyes of the invention. In general, the dyes of the present invention are prepared by a process comprising the steps of reacting a first material (preferably 1 mole) with a second material (preferably 1 mole), the first material containing at least one chromophore , at least one through SO 2 C 2 h 4 The sulfur atom of the group is directly connected to the chromophore group or is connected to the chromophore group through a linking group (such as Remazol dye). 2 C 2 h 4 group, the second starting material is a compound containing a suitable Y group, for example a hydrated form of a carbohydrate such as sucrose or glucose, or a hydrated form of formic acid. As mentioned above, the carbohydrate substance in hydrated form is preferably obtained by acid hydrolysis. Of course, there are other methods of obtaining hydrated forms, such as those of naturally occurring aldehydes or ketones such as 4-piperido...
Embodiment 17
[0115] All of the dye compounds prepared according to Examples 1-16 were used to dye cotton using the dyeing procedure detailed below. After performing the cotton dyeing step, it is also possible to perform a soaping process of the cotton fibers.
[0116] cotton dyeing steps
[0117] An aqueous dye solution containing the dye compound of any one of Examples 1-16 was prepared. The dye solution contains 1% dye based on fiber mass, 80g / L Na 2 SO 4 and 5% sodium acetate based on fiber mass. The cotton fabric was soaked in water, and then dyed for 15 minutes at 25° C. in the above-mentioned dyeing bath with a pH value of 7. Then, in a dyeing bath with a pH value of 11.5, 30 g / L trisodium phosphate was added to fix the dyed cotton fabric, and the dyeing was continued at 25° C. for 45 minutes. Rinse the stained fabric with water.
[0118] In the above dyeing process, the dye bath of each dye compound was almost completely evacuated (i.e. there was only slight color in the dye...
Embodiment 20
[0129] All of the dye compounds prepared in Examples 1-16 can be used to dye nylon or wool using the dyeing methods detailed below. After the nylon / wool dyeing step is complete, a wash test procedure can be performed on the dyed fabric to test the wash fastness of the dye compound.
[0130] Wool / Nylon Dyeing Steps
[0131] The wool / nylon fabric was soaked in a solution of 2% w / w Alcopol-O (40% w / w sodium d-isooctylthio-succinate from Allied Colloids). Then, under the conditions of 100 DEG C and pH value of 3.5, the fabric was dyed for 1 hour in a dyebath containing the following composition: 1.2% of the dyes prepared in Examples 1-7 based on fiber mass, 5% based on fiber mass based sodium acetate, 1% Albegal B (available from Ciba). The dyed wool / nylon fabric is then rinsed with water.
[0132] In the above procedure, each of the compounds prepared in Examples 1-16 provided strong staining.
[0133] Test procedure for Co2 (ISO) wash fastness of wool / nylon fabrics
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com