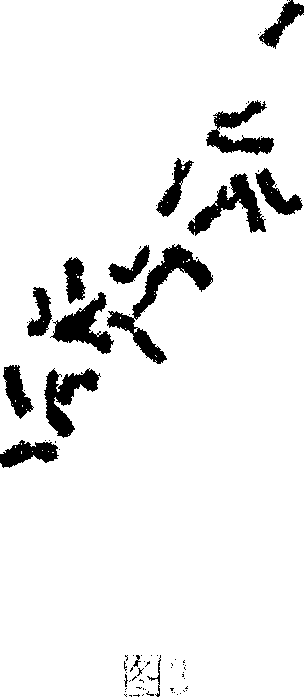Method for transferring Tibetan medicinal effective component into receptor cell using somatic cell cross breeding technology
A technology of medicinal ingredients and hybridization technology, applied in the field of plant cell engineering, can solve problems such as affecting curative effect, lack of wild resources, and unfavorable foreign trade export
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0075] Example 1: Using asymmetric somatic cell hybridization to transfer the effective components of Swertia chinensis in Western Sichuan to Bupleurum chinensis
[0076] 1 Materials and methods
[0077] 1.1 The source of parental protoplasts Suspension cell lines were established from Bupleurum angustifolia callus. The suspension cell line subcultured for 3 days was used to separate and prepare protoplasts as recipients.
[0078] The protoplasts were isolated from the callus of Swertia chinensis in western Sichuan, and the method was the same as that of wheat. The protoplasts were subjected to 380μW / cm 2 After irradiating 1min and 2min of ultraviolet rays, they were used as fusion donors.
[0079] 2 Fusion and cultivation of protoplasts
[0080] The donor and acceptor were divided into 1×10 6 The density per ml was mixed at a ratio of 1:1, and fused by PEG method.
[0081] 3 Identification of hybrid properties of regenerated callus and regenerated plants
[0082] Inclu...
example 2
[0086] Example 2: Utilizing asymmetric somatic hybridization to transfer the active ingredients of Gentiana chinensis to Bupleurum chinensis
[0087] Method and steps are the same as in Example 1.
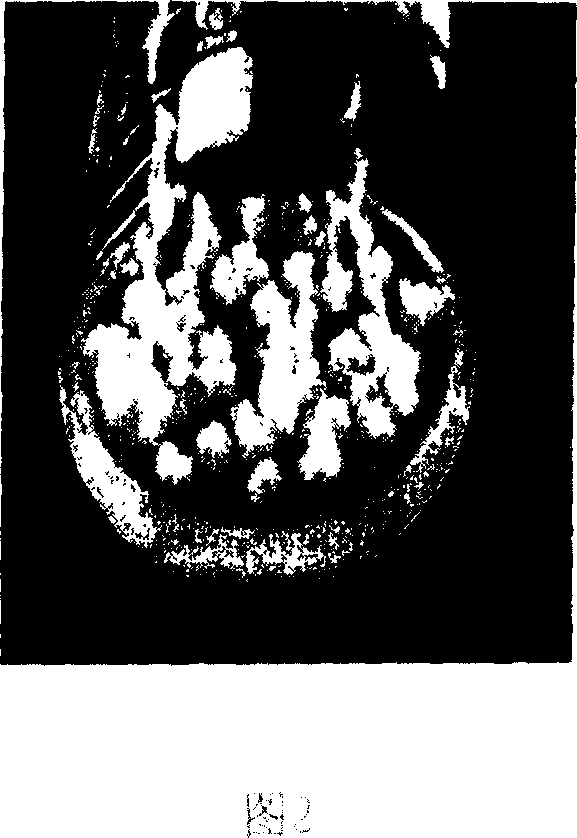
[0088] Results: The strength of Gentiana tuberosa protoplasts was 380μw / cm 2 After ultraviolet irradiation for 0 min, 1 min, and 2 min, respectively, they fused with Bupleurum protoplasts under the induction of PEG. The hybrid morphology (Fig. 6), chromosome, isozyme (Fig. 7) and RAPD (Fig. 8) analysis of 20 single-cell clones regenerated by fusion showed that 18 of them were somatic hybrid cell lines. Chromosomal observation showed (Fig. 2) that the number of chromosomes in the regenerated plants of the 11 clones was distributed in the range of 11-13, and the isoenzyme and RAPD analysis showed that they all had parental characteristic bands, confirming that they were interfamily somatic hybrids. The results of the determination of the content of the active ingredient (gentiopicr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com