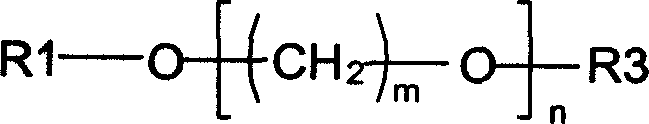Electrolyte media for the deposition of tin alloys and methods for depositing tin alloys
A tin alloy and alloy technology, applied in the field of tin alloy deposition, can solve the problems of difficulty in maintaining tin concentration, impossible to directly dissolve tin anode, unstable stannous ions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Make a bath medium of the following formula:
[0049] Sodium Gluconate 150g / l
[0050] Boric acid 100g / l
[0051] Anhydrous stannous sulfate 30g / l
[0052] Cobalt sulfate hexahydrate 100g / l
[0053] Lugalvan BNO24* 1g / l
[0054] Empicol ESB3 Anionic Surfactant** 1g / l
[0055] The bath was heated to 50°C and a Hull cell test was performed at 1 amp for 10 minutes using agitation by means of a mechanical stirrer. The resulting deposit is smooth and uniform. at corresponding to 4A / dm 2 At the on-board position of the primary current density of , a tin-cobalt alloy with a composition of about 16% cobalt with a balance of tin is obtained. This example demonstrates the significant reduction in cobalt content (compared to intermetallic composition) that can be achieved using the electrolyte medium of the present invention. However, still further reductions in the cobalt content are desired.
[0056] *Lugalvan BNO24 is an ethoxylated β-naphthol belonging to the class of...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Make a bath medium of the following formula:
[0060] Sodium Gluconate 150g / l
[0061] Boric acid 100g / l
[0062] Anhydrous stannous sulfate 30g / l
[0063] Nickel sulfate hexahydrate 75g / l
[0064] Cobalt sulfate hexahydrate 7g / l
[0065] Lugalvan BNO24 1g / l
[0066] Empicol ESB3 1g / l
[0067] The Hull cell test was carried out as in Example 1 at a temperature of 20°C. The resulting deposit is smooth and uniform. at corresponding to 4A / dm 2 A tin-nickel-cobalt alloy having a composition of about 8-10% nickel and 1-2% cobalt with a balance of tin is obtained at the on-board position of the primary current density. This example demonstrates that a ternary tin-cobalt-nickel alloy can be produced using this electrolyte medium, resulting in an alloy with effective amounts of nickel and cobalt.
Embodiment 3
[0069] The Hull cell test was carried out in a bath of composition according to Example 1, but substituting nickel sulfate hexahydrate for cobalt sulfate hexahydrate, and using the same conditions as in Example 1. A tin-nickel alloy having a composition of about 14% nickel with a balance of tin is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com