Method of extracting diosgenin in Japanese dioscorea by enzymolysis-supercritical carbon dioxide fluid
A diosgenin and supercritical technology is applied in the field of extraction of effective components of natural plants, which can solve the problems of low extraction rate, serious pollution, large consumption of organic solvents and the like, and achieve the effect of simplifying the operation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Example 1: Using cellulase to hydrolyze the supercritical CO of Pangshanlong decoction pieces 2 Fluid extraction diosgenin
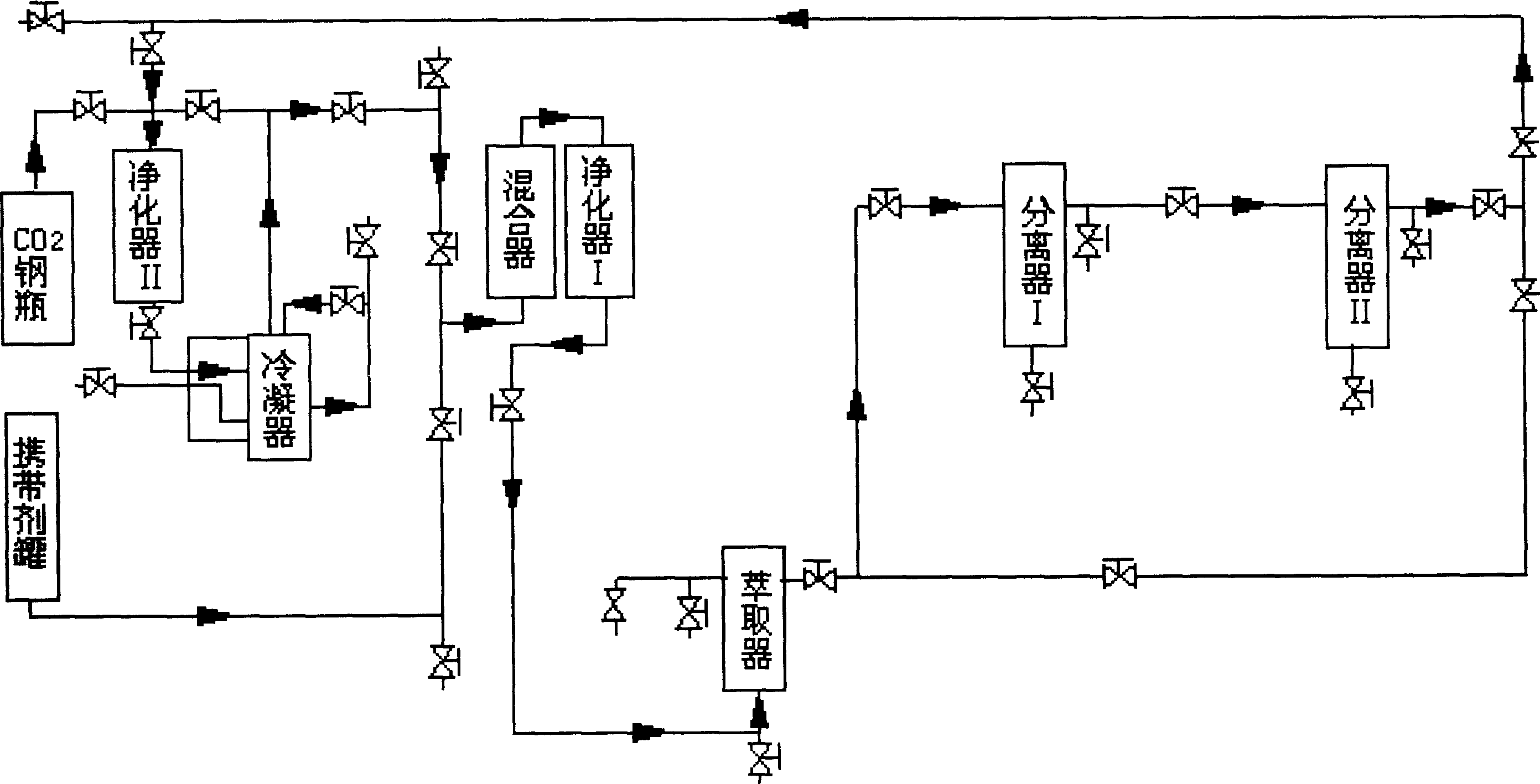
[0018] Add 100U cellulase to each gram of P. pangasius decoction pieces, and enzymatically hydrolyze them in a constant temperature water bath at 40°C for 24 hours; hydrolyze the digested panzantines in a 2.0 mol / L sulfuric acid solution for 4.0 h, and then use anhydrous sodium carbonate And drying for standby; crush the dried powder to 40 mesh and add it to the supercritical fluid extraction tank. The process flow is as follows figure 1 Open CO as shown 2 In the steel cylinder, the gas enters the condenser for liquefaction after passing through the purifier I, and then pressurized by the plunger pump and then enters the purifier II for further liquefaction, and enters the bottom of the extractor through the pipeline. Set the pressure of the separator I to 6MPa and the temperature to 60℃ ; The pressure of the secondary separator II is 6MPa, the temper...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2: Using α-amylase to hydrolyze the supercritical CO of Panshan long slices 2 Fluid extraction diosgenin
[0021] Add 100U α-amylase to each gram of raw material of Chinese herbal medicine, and enzymatically hydrolyze it in a constant temperature water bath at 40°C for 24 hours;
[0022] The following process is the same as that of Example 1, and the extraction rate is 2.66%, which is 0.43% higher than that of the dicetaceae slices without enzymatic hydrolysis treatment (the original extraction rate is 2.23%).
Embodiment 3
[0023] Example 3: Supercritical CO with absolute ethanol as carrier agent 2 Fluid extraction diosgenin
[0024] Anhydrous ethanol was used as the carrier, and the others were the same as in Example 1.
[0025] Supercritical CO of the present invention 2 The fluid extraction equipment is selected from Jiangsu Nantong Huaan Supercritical Extraction Co., Ltd., cellulase is produced by He Shibi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and α-amylase is produced by Beijing Shuangxuan Microbial Culture Medium Products Factory.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com