Method for detecting defect of single crystal structure of gallium arsenide in large size
A single crystal structure and defect detection technology, which is applied in the direction of optical testing flaws/defects, preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problems of reducing measurement points, affecting measurement accuracy, and detection accuracy can not meet the requirements, etc., reaching the range of crystal orientation Expansion, short heating time, accurate detection effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1, the detection steps of the dislocation defect of 150mm gallium arsenide are as follows:
[0034] (1) Grinding, grinding the cut 150mm gallium arsenide single wafer with emery to make the surface smooth, smooth and scratch-free, and cleaning;
[0035] (2) Polishing: chemical polishing is adopted, and the formula of the polishing liquid is sulfuric acid: hydrogen peroxide: water = 3: 1: 1. When polishing a crystal orientation single crystal, it is necessary to stir the prepared polishing liquid and place it at room temperature, and then put Immerse the single crystal in the polishing solution until the single crystal is polished, and the temperature of the polishing solution does not need to reach room temperature when polishing other single crystals;
[0036](3) Dislocation corrosion, put potassium hydroxide in a silver crucible and heat it, and when the potassium hydroxide is melted and heated to a clear state, put it into the wafer sample for corrosion...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Detection of Dislocation Density on Gallium Arsenide Single Wafer with a Size of 180 mm
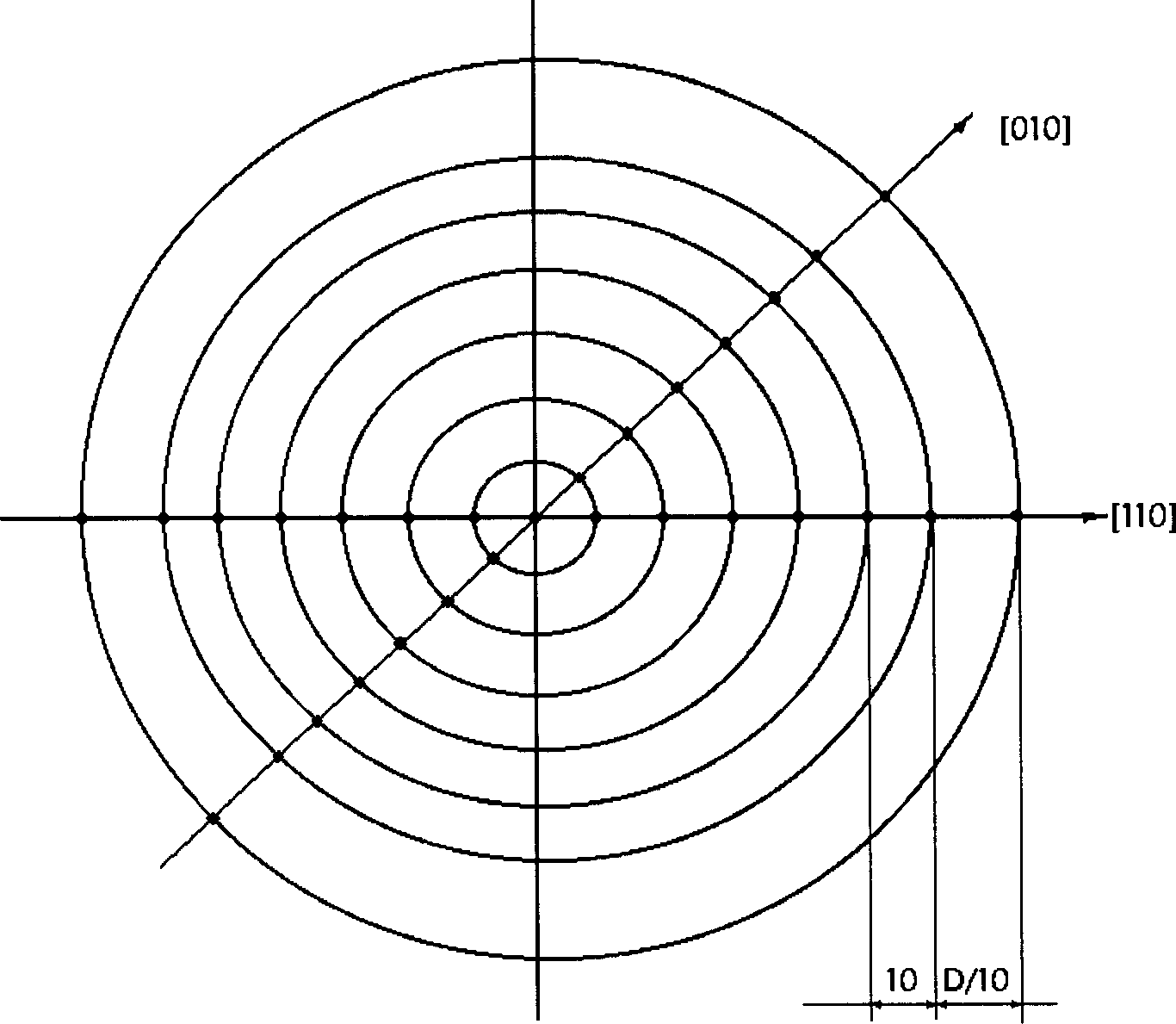
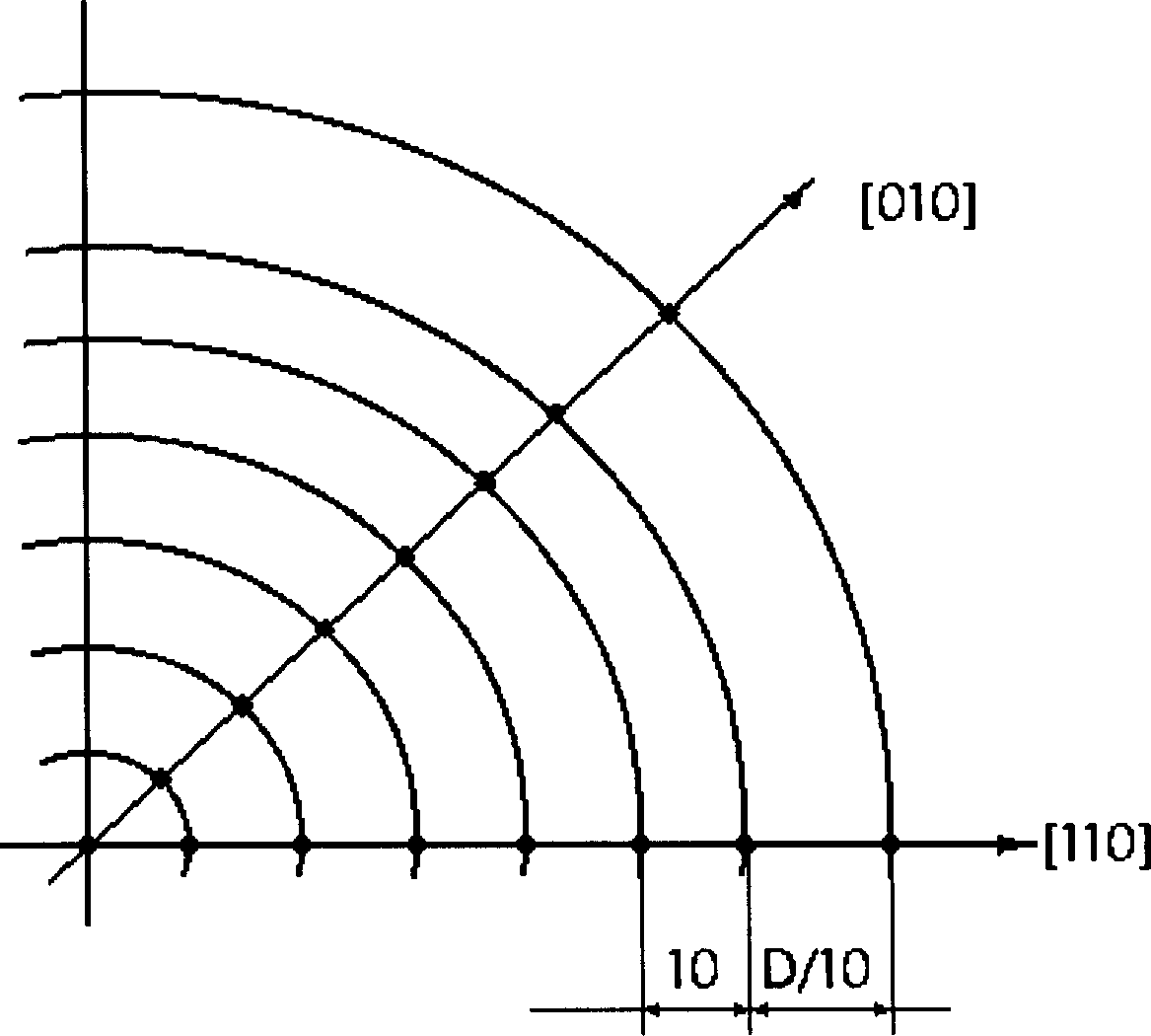
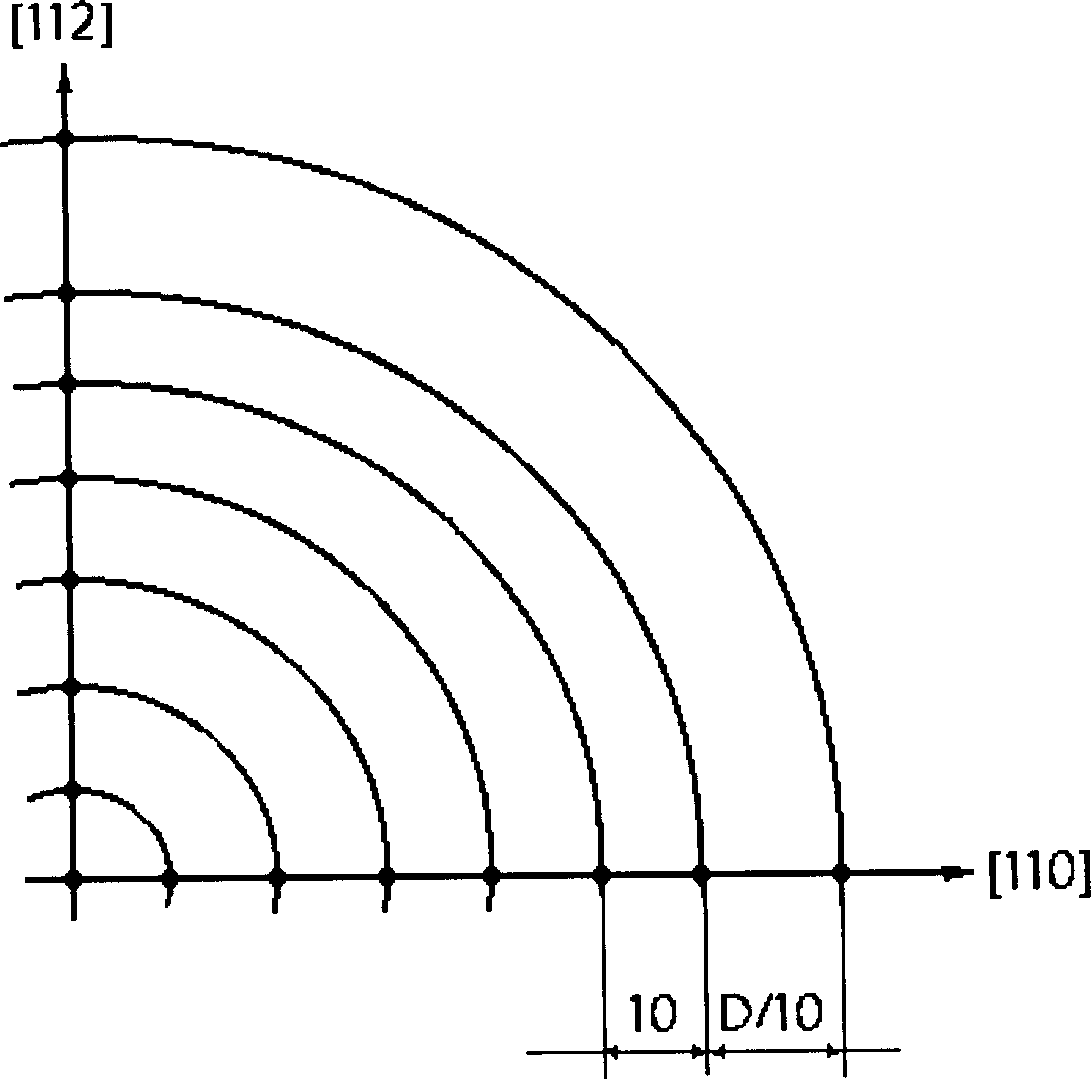
[0049] The whole implementation steps are the same as the 150mm diameter gallium arsenide single wafer, except that the selection of the detection field position is different, that is, the mask preparation is different. The first measurement point is selected at D / 10mm from the edge of the wafer, which is 18mm. Every 12mm interval of measurement points is a measurement field of view, and the selection direction is the same, so that the number of measurement points is the same as that of a 150mm diameter single crystal, but the selected positions are different. Other grinding-polishing-corrosion-observation-calculation are the same.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com