In-situ produced titanium carbide dispersion strengthening copper based composite material and method for preparing the same
A technology of dispersion-strengthening copper and in-situ generation, which is applied in the field of ceramic particle reinforced metal matrix composite materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of small increase in copper strength and weak interface bonding strength, and achieve high hardness, improve interface bonding, simple craftsmanship
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
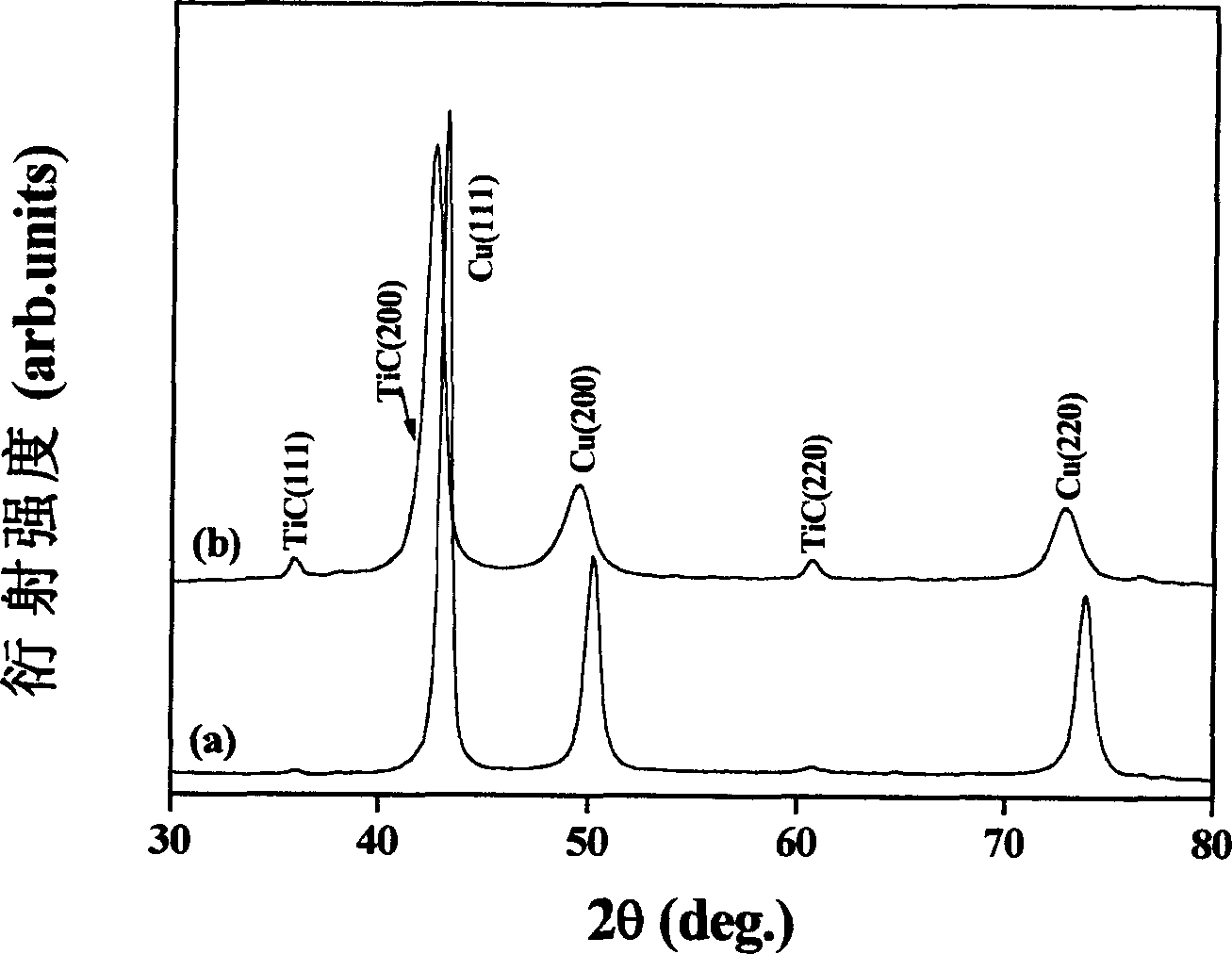
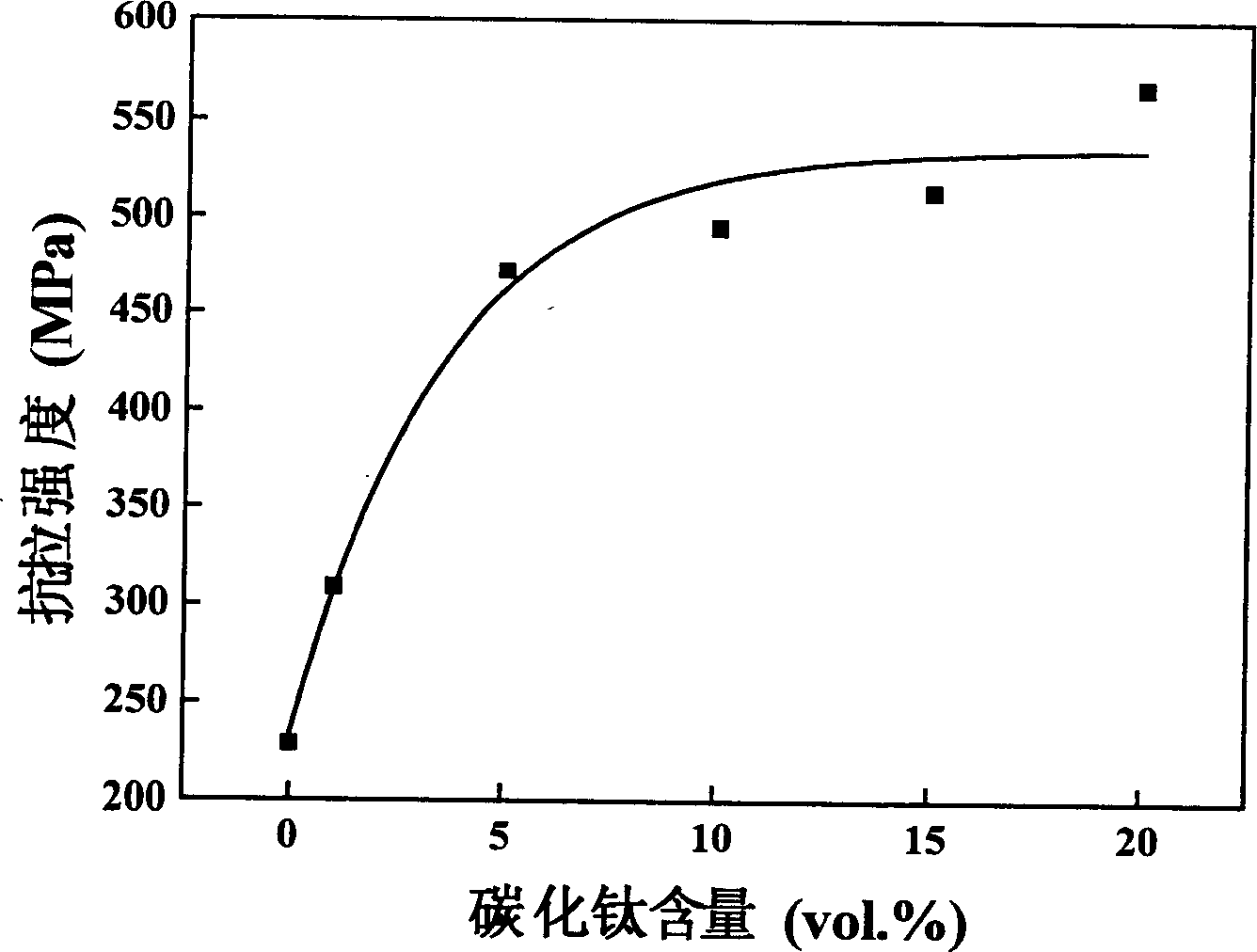
[0017] Titanium carbide dispersion-strengthened copper-based composites with a series of components were synthesized by decomposing tin-titanium carbide in situ to generate titanium carbide particles dispersed in the copper matrix. Using tin titanium carbide powder as raw material, the tin titanium carbide powder is purified by hot hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 90°C to remove the elemental tin, and then ball milled for 20 hours by planetary ball milling at a speed of 300 rpm to obtain an average particle size of 0.5 Micron ultrafine powder.
[0018] 1.62 grams of tin-titanium carbide powder with an average particle size of 0.5 microns and 138.38 grams of copper powder with an average particle size of 30 microns were ball milled for 5 hours in a ball mill using a planetary ball milling method, and then loaded into a graphite mold It is formed by medium cold pressing, and the applied pressure is 10MPa, and it is put into a hot pressing furnace for hot pressing and sinter...
Embodiment 2
[0020] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0021] Using tin titanium carbide powder as raw material, the tin titanium carbide powder is purified by hot hydrochloric acid at a temperature of 100°C to remove elemental tin, and then ball milled by planetary ball milling method for 12 hours, the ball mill speed is 400 rpm, and the average particle size is 1 Micron ultrafine powder.
[0022] 15.96 grams of tin titanium carbide powder purified by hot hydrochloric acid with an average particle size of 1 micron and 124.04 grams of copper powder with an average particle size of 20 microns were ball milled in a ball mill jar for 10 hours by planetary ball milling, and then loaded into a graphite mold It is formed by medium cold pressing, and the applied pressure is 15MPa, and it is put into a hot pressing furnace for hot pressing and sintering. The heating rate is 8°C / min, heated to 800°C and kept for 3 hours, while the pressure is gradually increased to 30MPa. The resulting composite...
Embodiment 3
[0024] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0025] Using tin titanium carbide powder as raw material, the tin titanium carbide powder is purified by hot hydrochloric acid at 80°C to remove elemental tin, and then ball milled by planetary ball milling method for 10 hours, the ball mill speed is 250 rpm, and the average particle size is 2 Micron ultrafine powder.
[0026] 31.44 grams of tin titanium carbide powder purified by hot hydrochloric acid with an average particle size of 2 microns and 108.56 grams of copper powder with an average particle size of 40 microns were ball-milled for 15 hours in a ball mill using a drum milling method, and then loaded into a graphite mold It is formed by intermediate cold pressing, and the applied pressure is 5MPa, and it is put into a hot pressing furnace for hot pressing and sintering. The heating rate is 5°C / min, heated to 900°C and kept for 1 hour, while the pressure is gradually increased to 50MPa. The resulting composite was then annea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com