Method for cultivating phaffiafhodozyma using astaxanthin synthesis accelerant
A technology of Phaffia rhodozyma and astaxanthin, which is applied in the directions of fermentation and fungi, can solve the problems of high production cost and low yield of astaxanthin, and achieve the advantages of low raw material cost, high promotion and utilization value, and increased yield. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
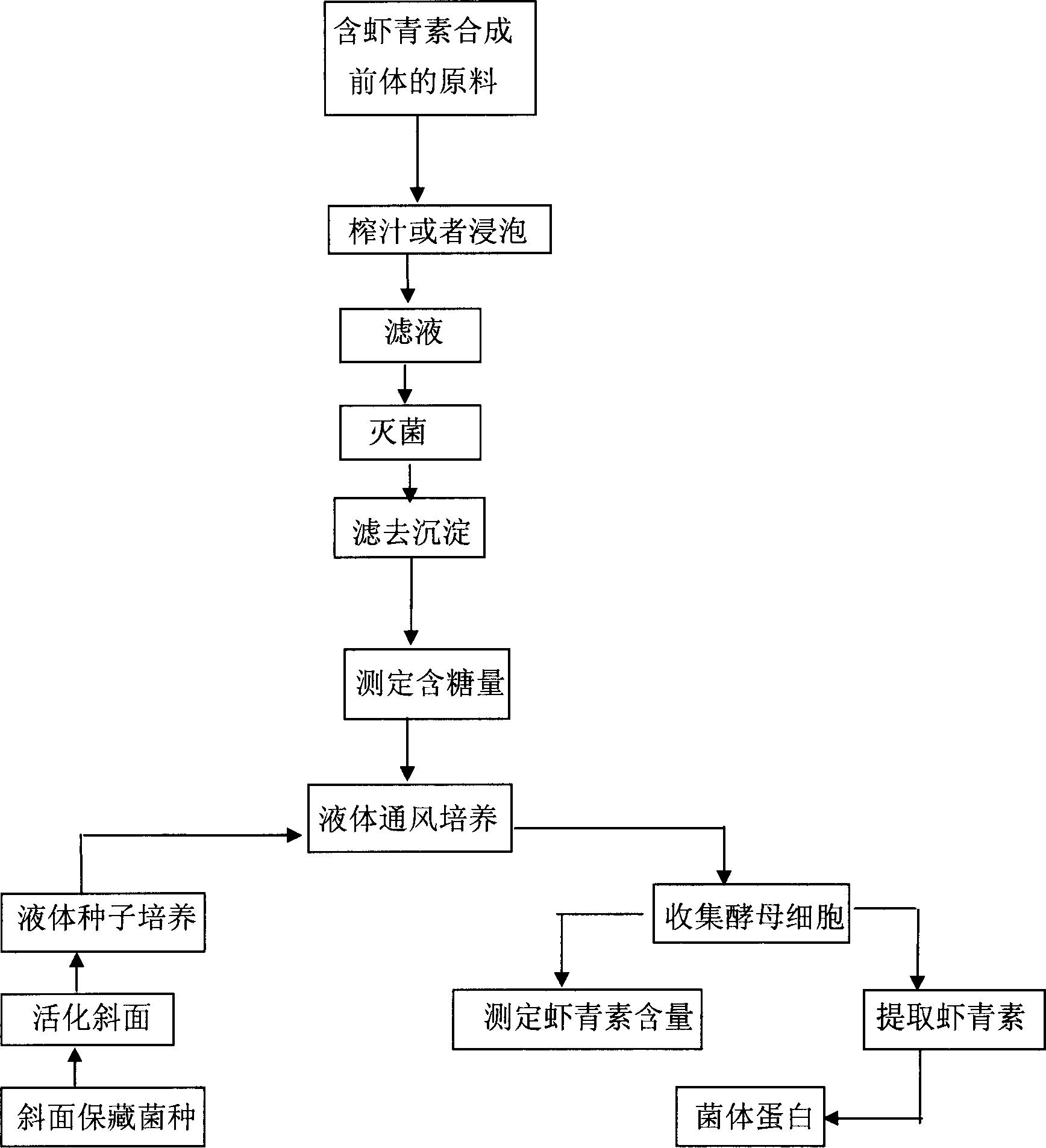
[0017] A, the selection of raw materials: select the bright orange that contains the synthetic precursor of Phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin to peel and weigh;
[0018] B. Juicing: Juicing fresh oranges to obtain a solid-liquid mixture;
[0019] C. Preparation of accelerator additive liquid: filter the solid-liquid mixture squeezed out of the juice, sterilize the filtrate at 115°C for 20 minutes, then aseptically filter to remove the precipitate, measure the reducing sugar content, and store it at 4°C for later use;
[0020] D. Liquid seed culture: activate the slant-preserved strains on 10Bx wort slant medium at 22°C, and culture them in YM medium at 22°C with liquid ventilation;
[0021] E. Fermentation of Phaffia rhodozyme: Add the liquid seeds cultivated in step d with 8% of the total volume of the YM medium, and cultivate Phaffia rhodozyme at 22° C. with liquid ventilation for 24 hours;
[0022] F. Liquid aeration culture: Add the accelerator additive solution prepared in s...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Get banana and implement by A, B, C, D steps in embodiment 1;
[0027] E, Phaffia rhodozyme fermentation: After adding the liquid seeds cultivated in step d with 12% of the total volume of the YM medium, directly add the accelerator additive solution prepared in step C;
[0028] F. Liquid ventilation culture: Add the accelerator additive solution prepared in step C to 4% of the total volume of the fermented liquid in the cultured Phaffia rhodozyme, continue to ferment for 96 hours, and collect yeast cells.
[0029] G. Extract astaxanthin: measure astaxanthin content in yeast cells, then extract astaxanthin according to conventional methods, and then extract bacterial protein.
[0030] The obtained cell yield, astaxanthin yield and cell astaxanthin content can be increased by 54.4%, 65.5% and 7.2% respectively compared with the control.
Embodiment 3
[0032] A. Selection of raw materials: select fresh spinach containing the synthetic precursor of Phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin, remove the roots and yellow leaves, wash and dry, then weigh;
[0033] B. Juicing: Take 700 grams of spinach and add 300 milliliters of water to squeeze the juice to obtain a solid-liquid mixture;
[0034] C. Preparation of accelerator additive liquid: filter the solid-liquid mixture from the squeezed juice, sterilize the filtrate at 110°C for 20 minutes, and filter aseptically to remove the precipitate to obtain light green spinach juice, measure the reducing sugar content, store at 4°C for later use ;
[0035] D. Liquid seed culture: activate the slant-preserved strains on 10Bx wort slant medium at 25°C, and culture them in YM medium at 25°C with liquid ventilation;
[0036] E. Fermentation of Phaffia rhodozyme: Add the liquid seeds cultivated in step d with 6% of the total volume of the YM medium, and culture Phaffia rhodozyme at 25° C. with liqui...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com