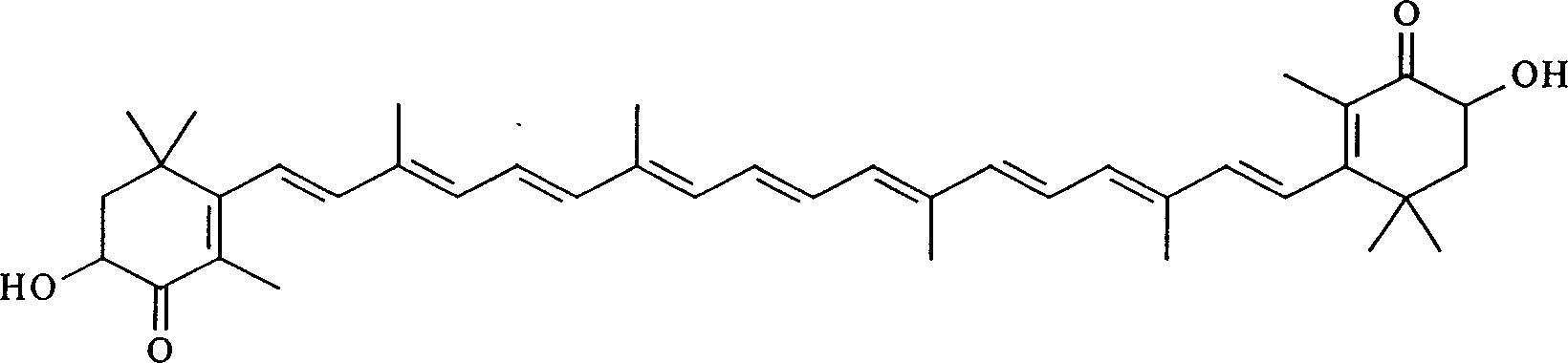
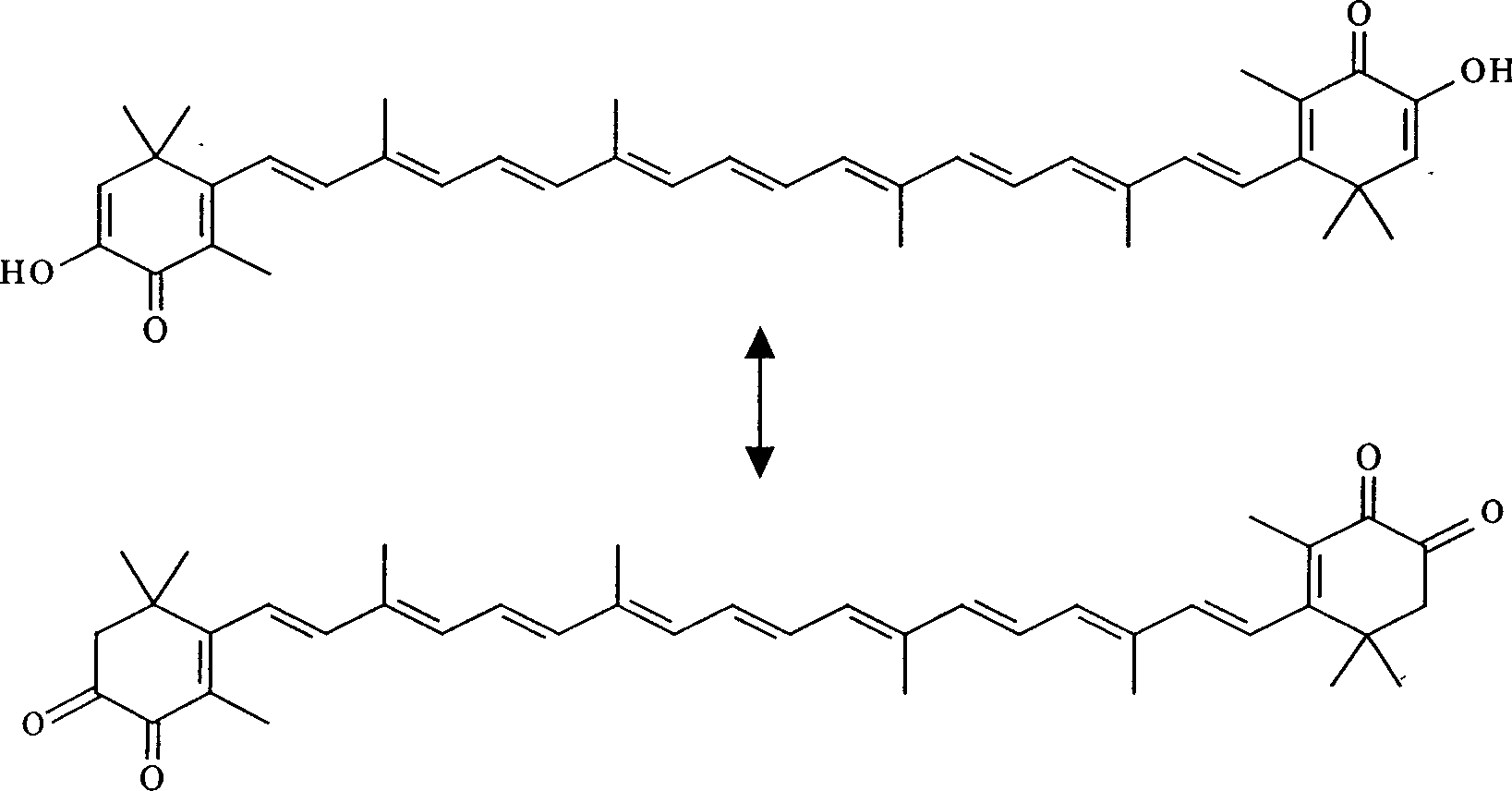
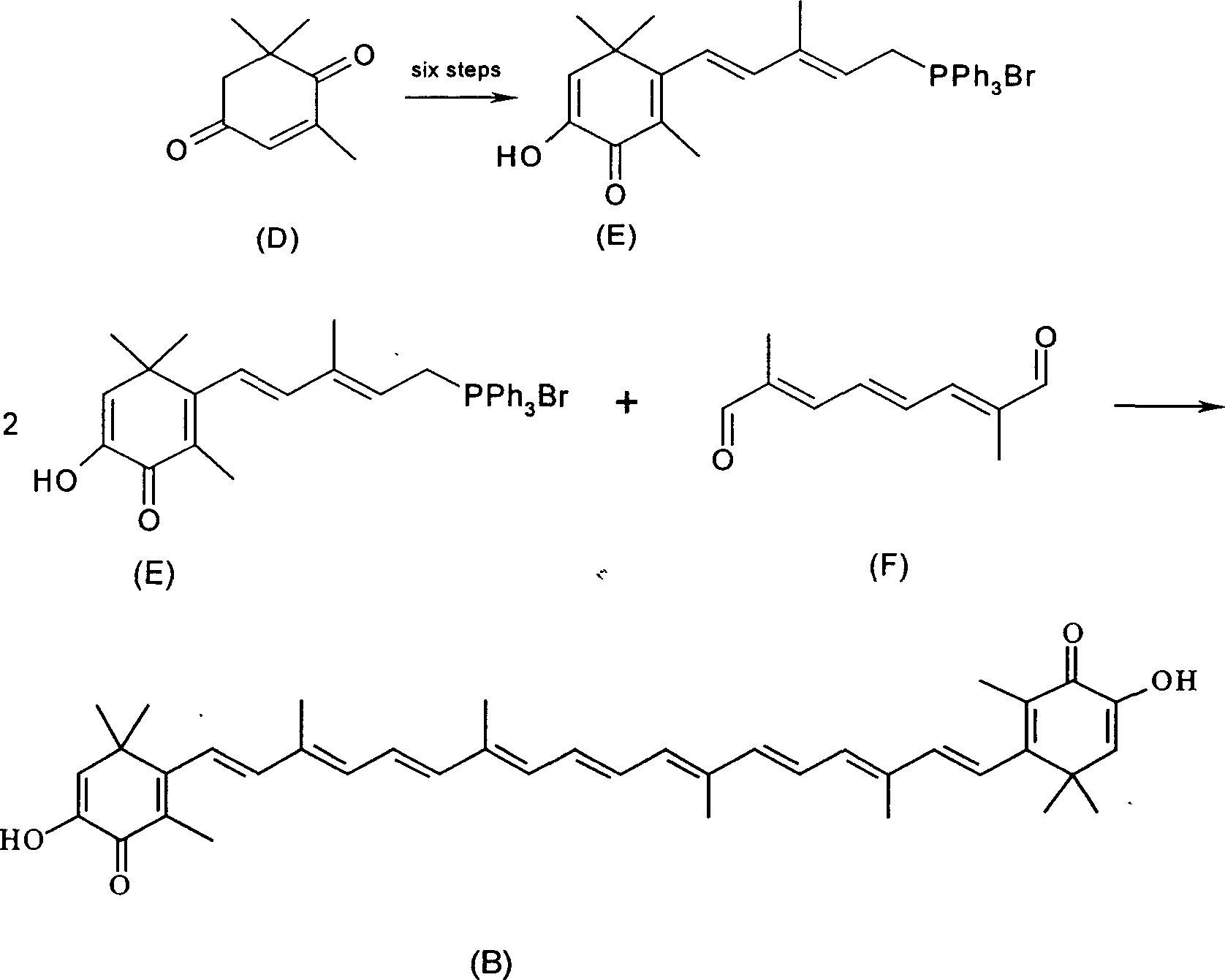
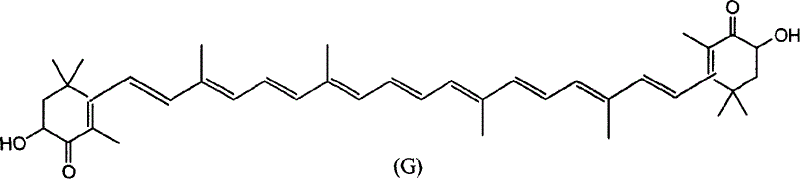
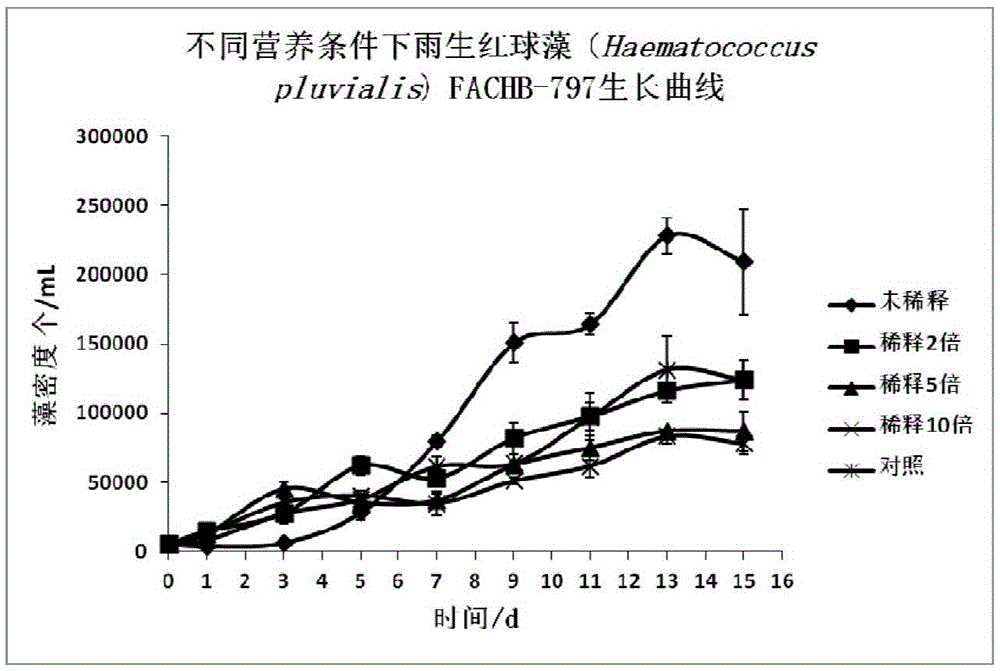
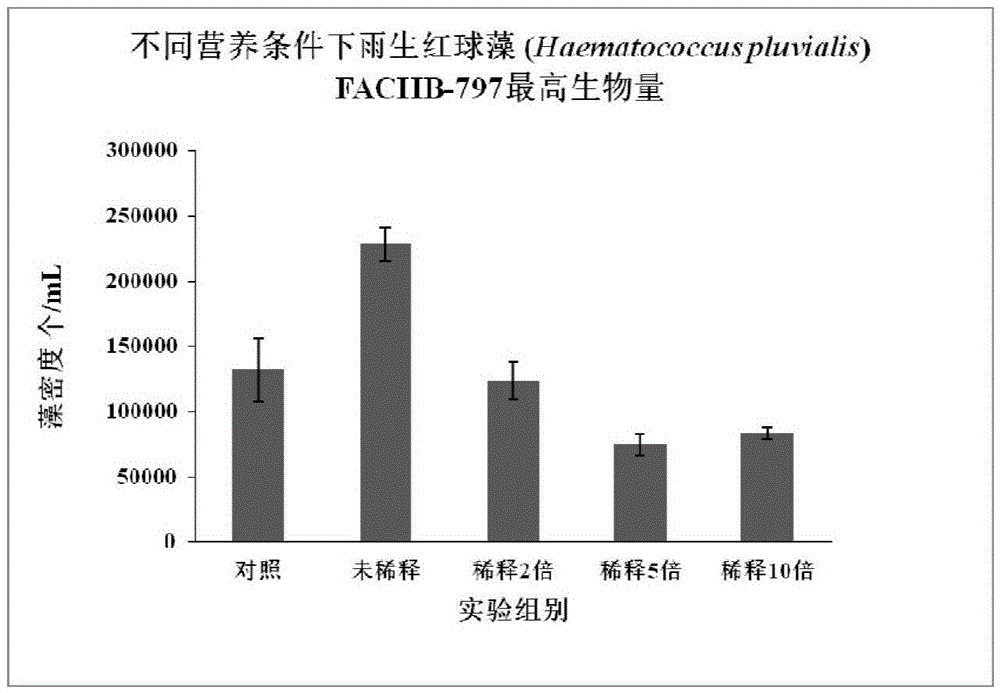
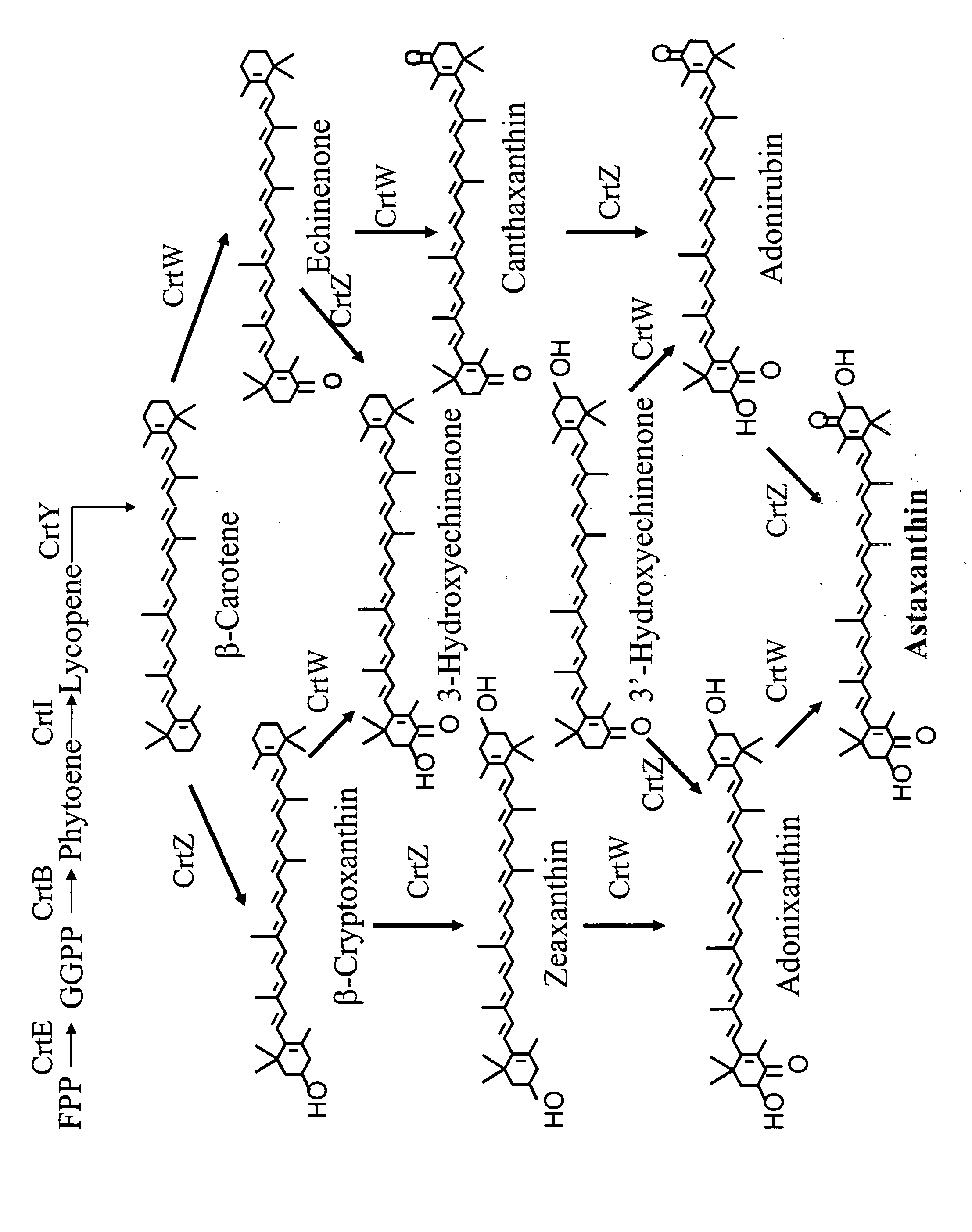
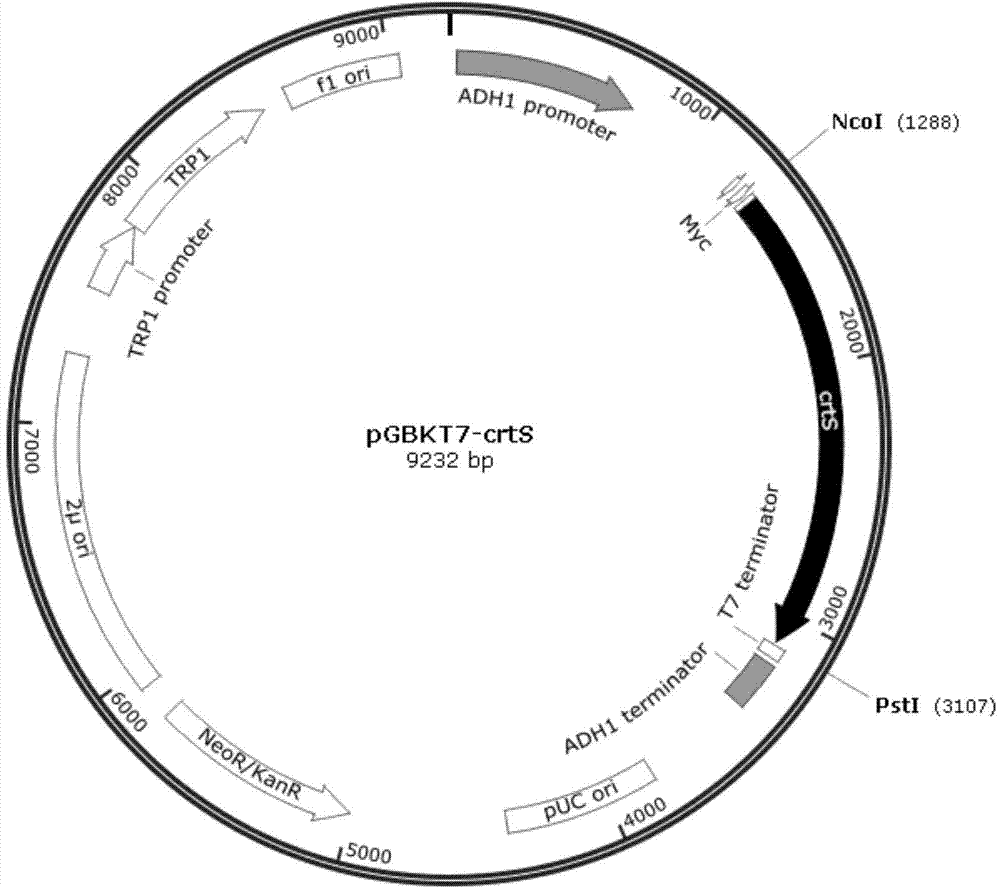
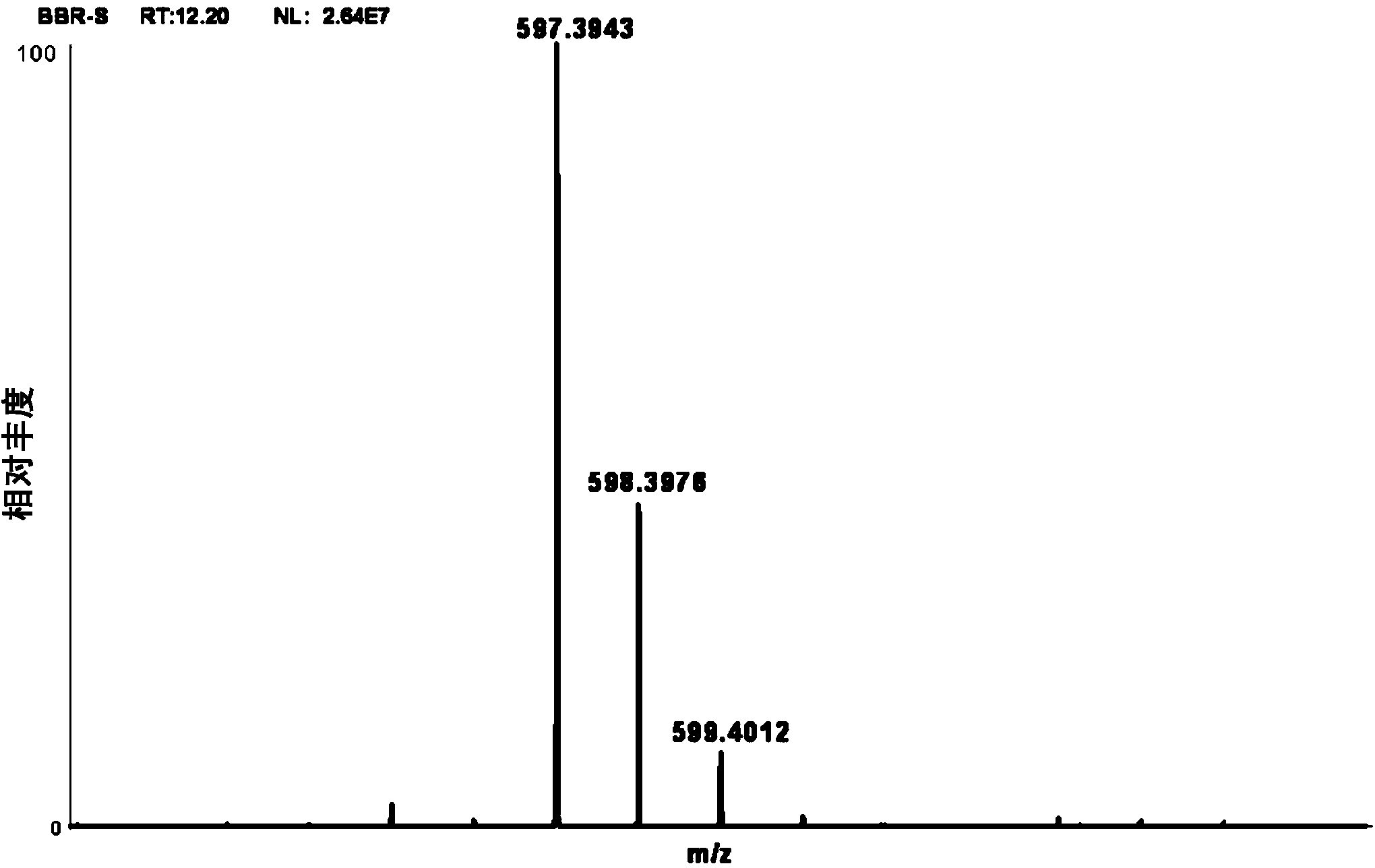
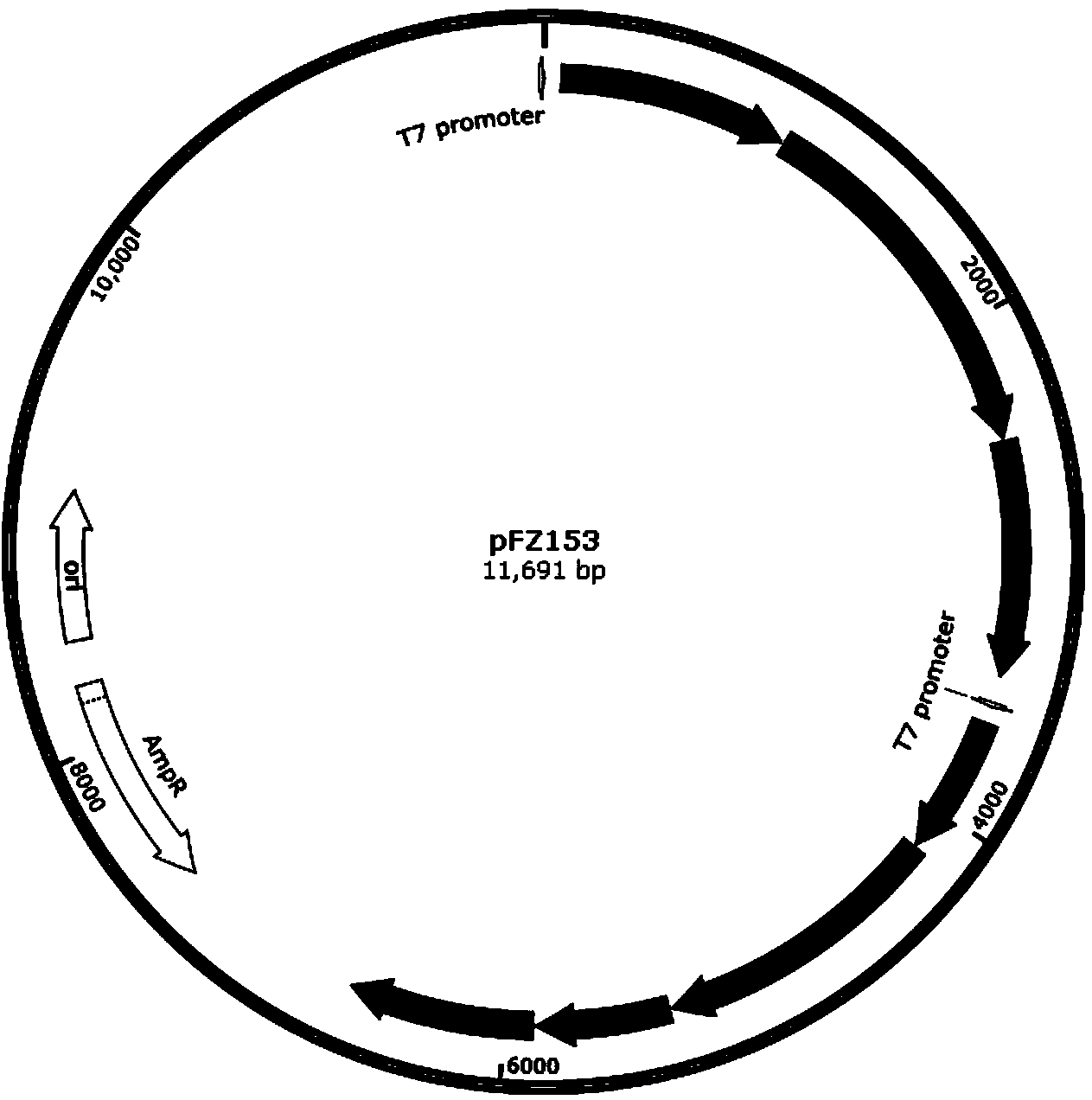
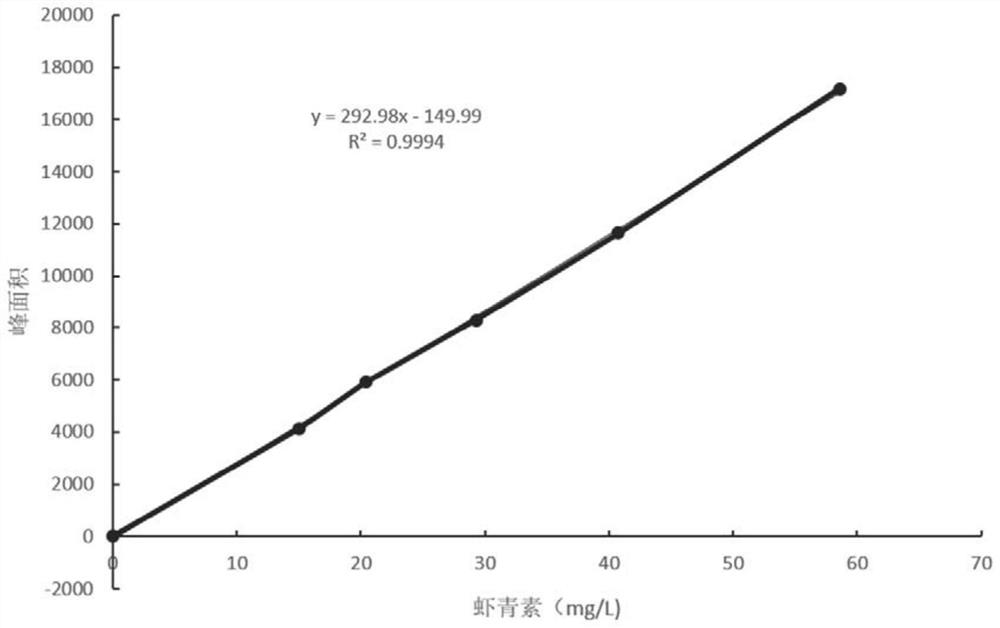
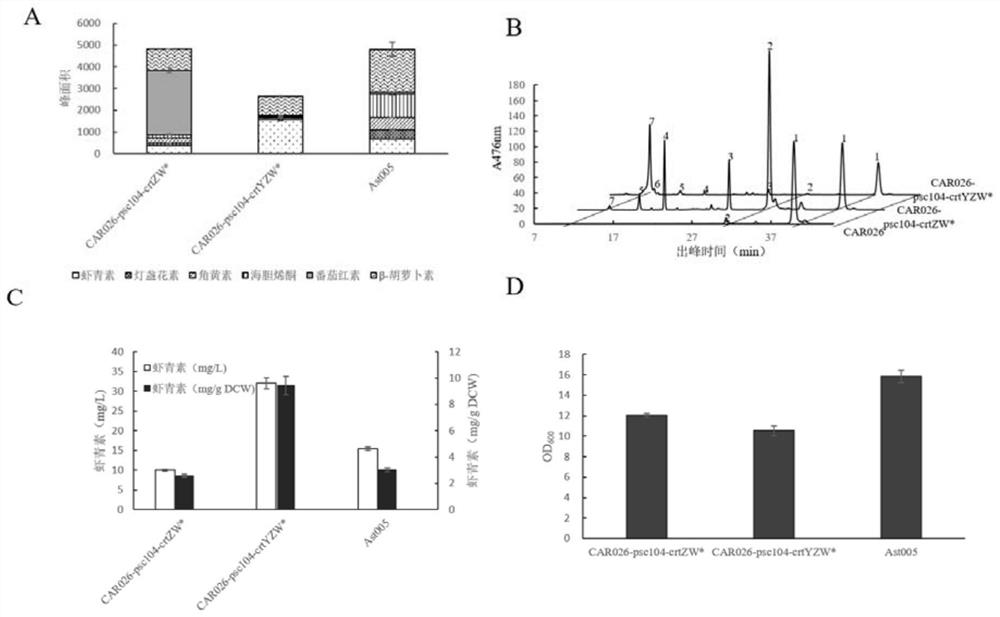
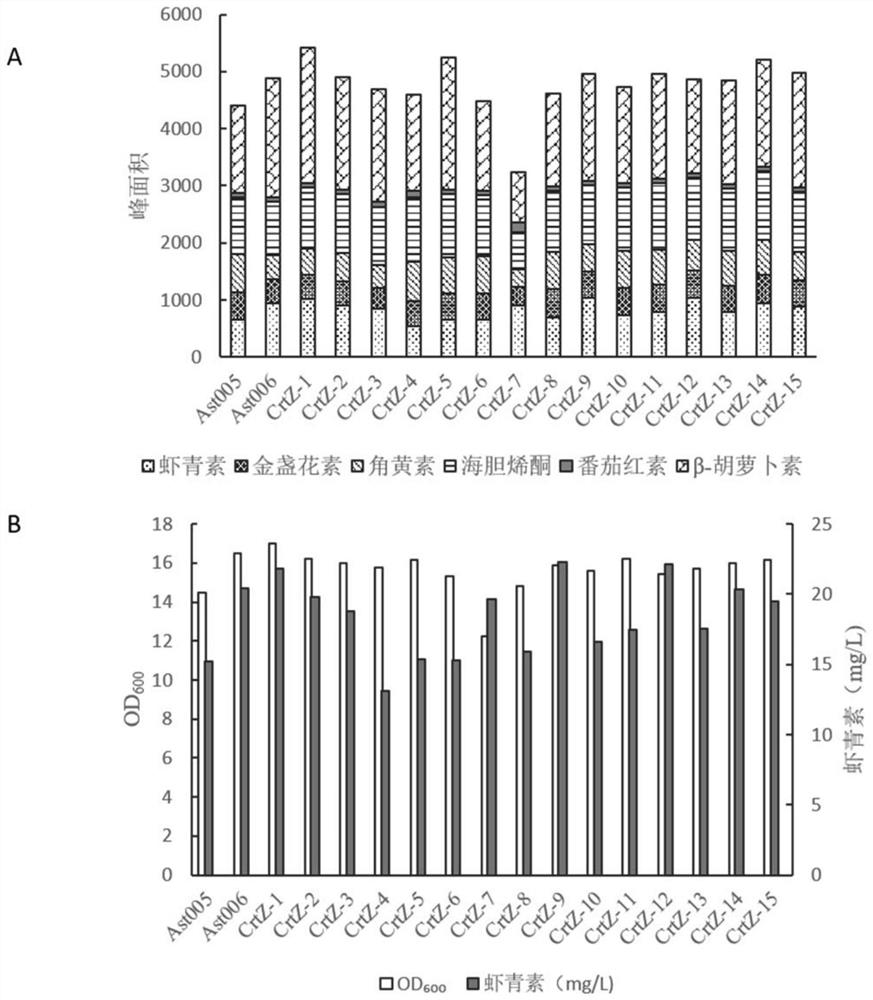
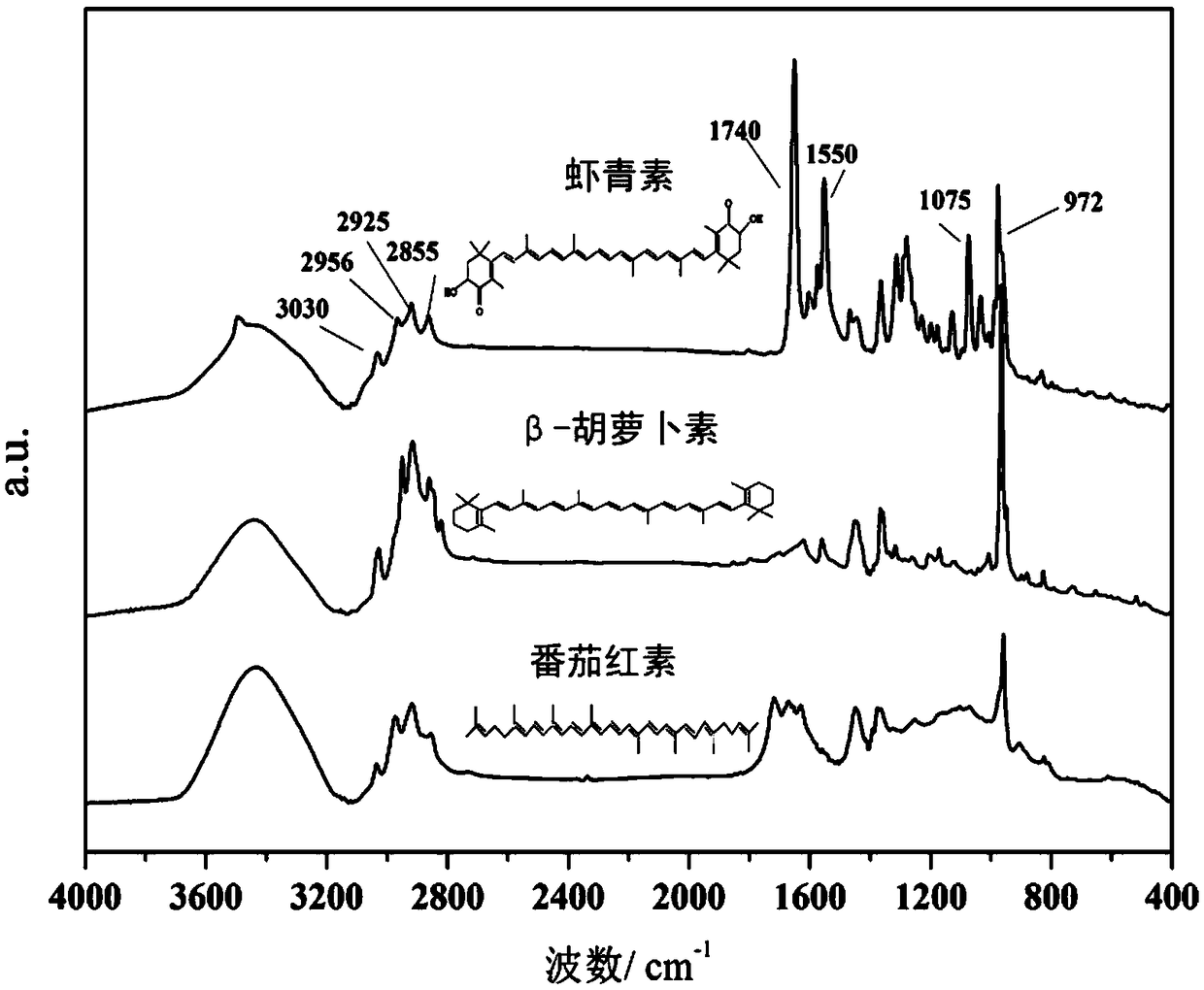
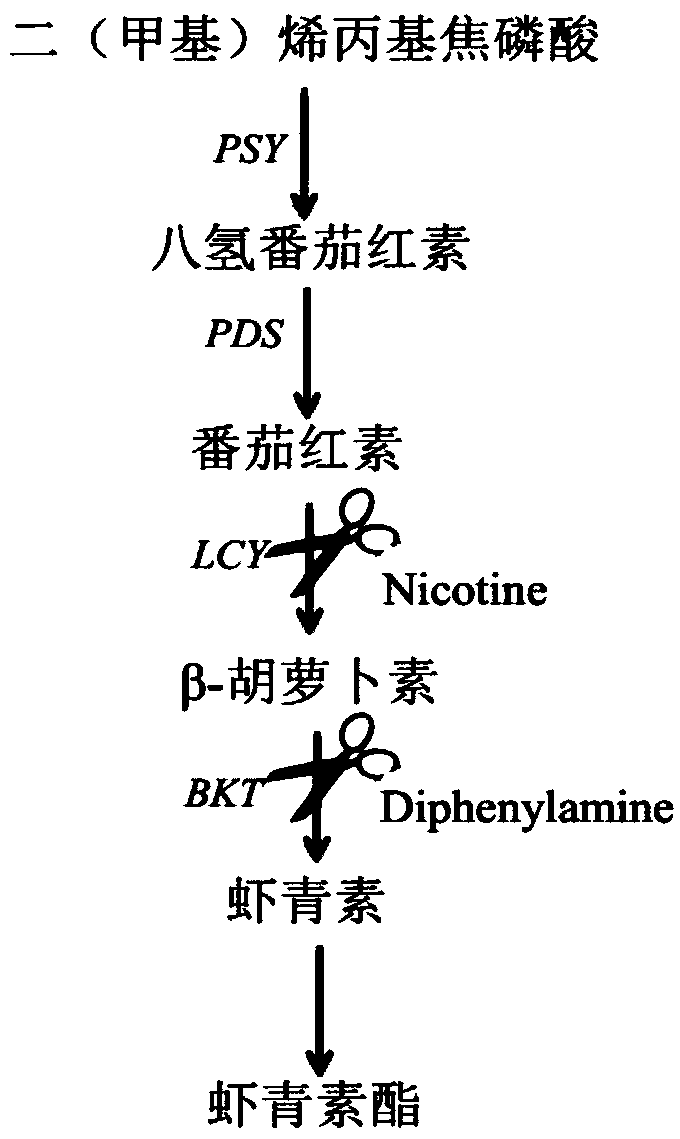
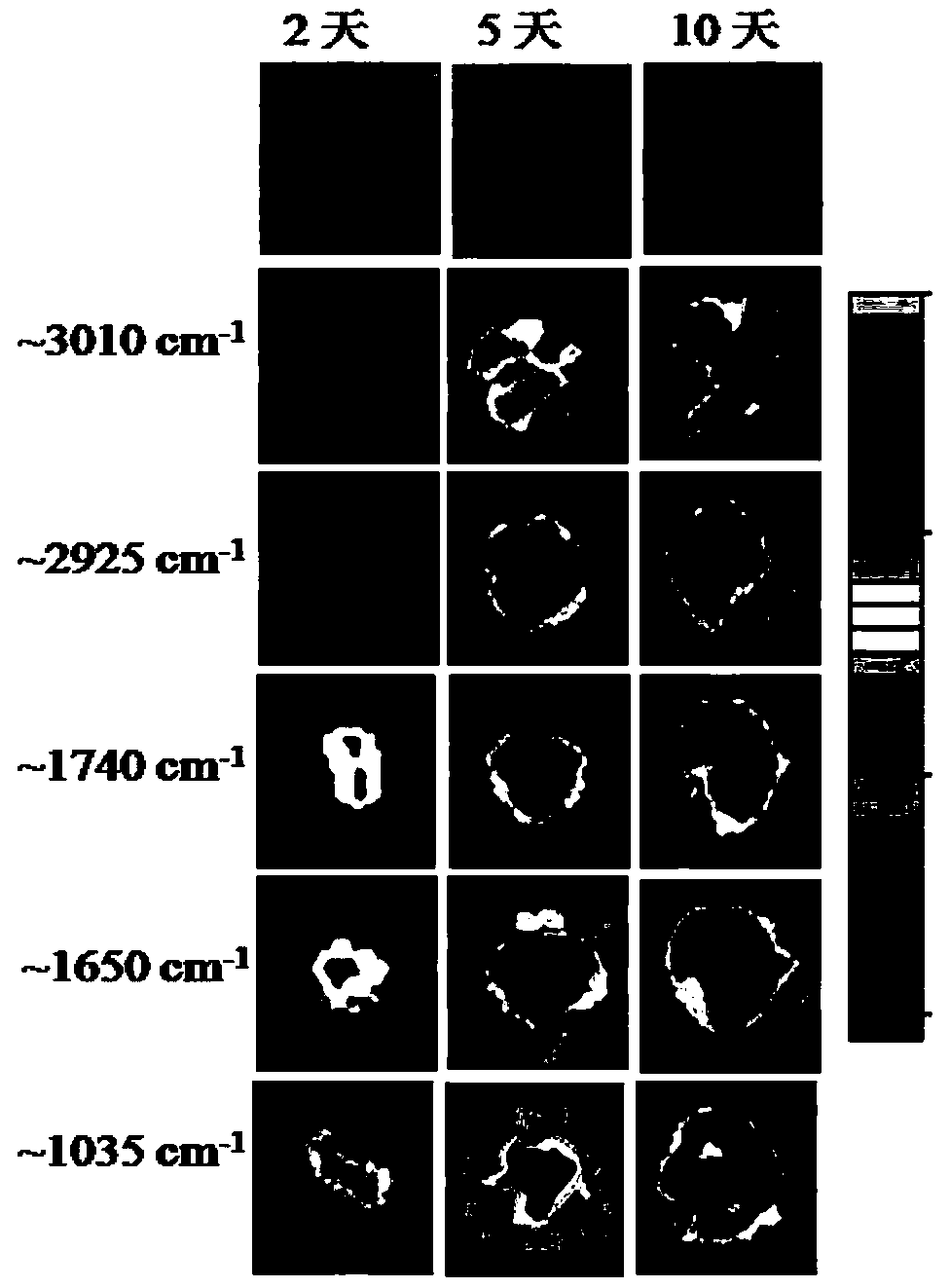
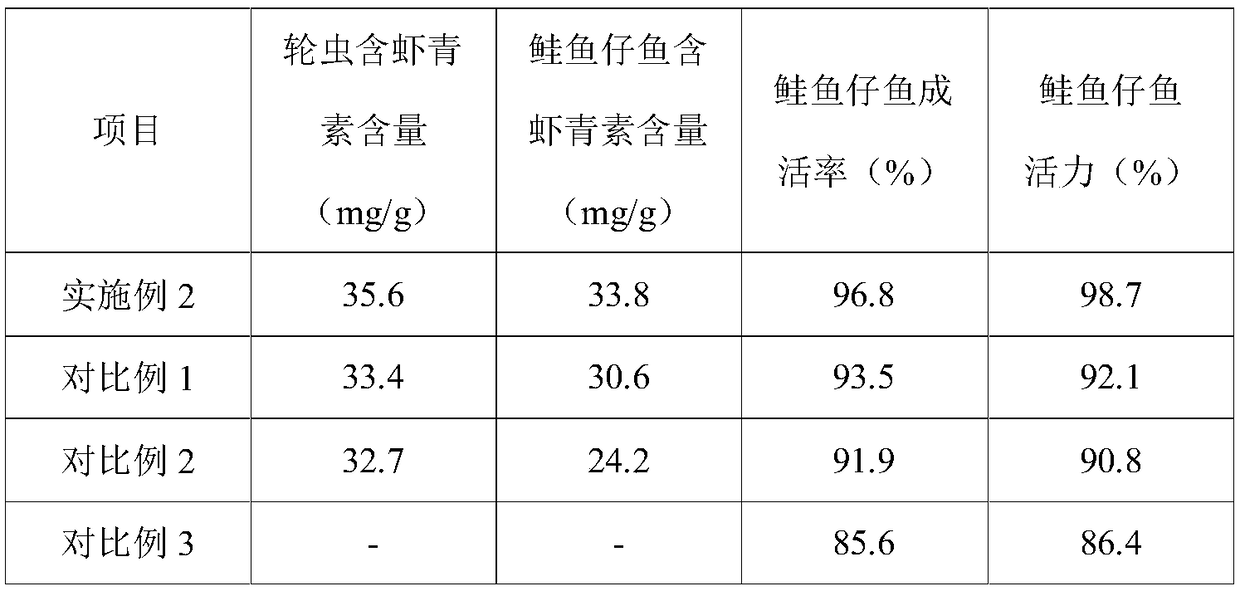
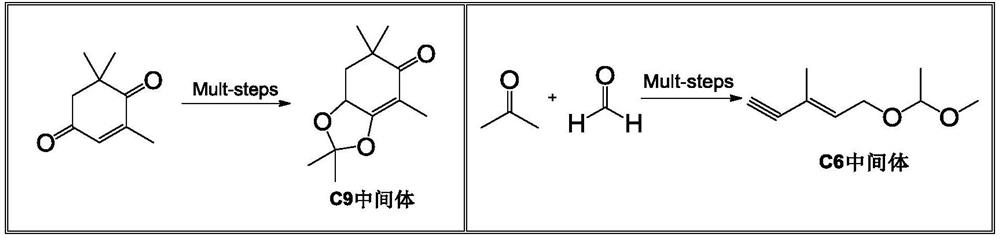
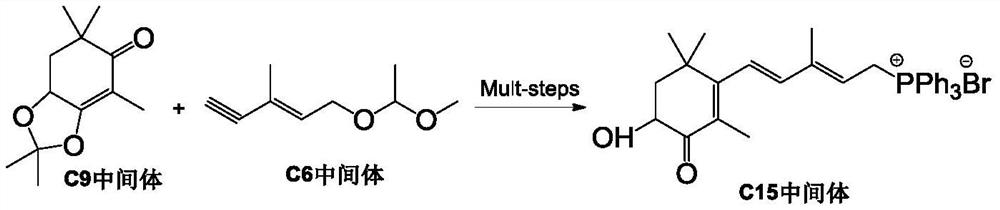
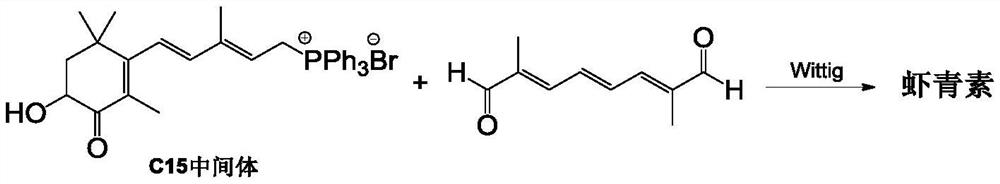
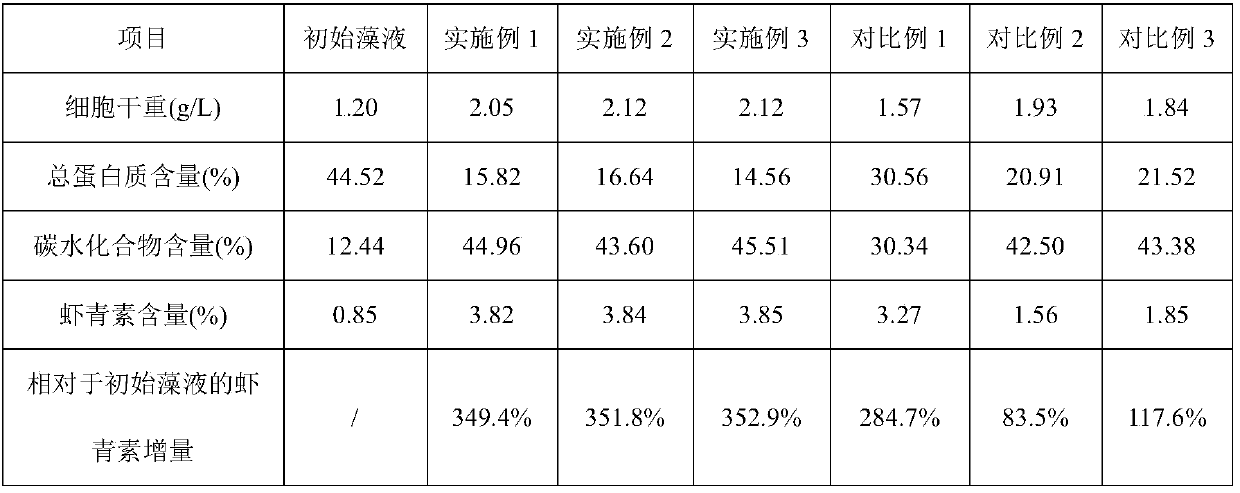
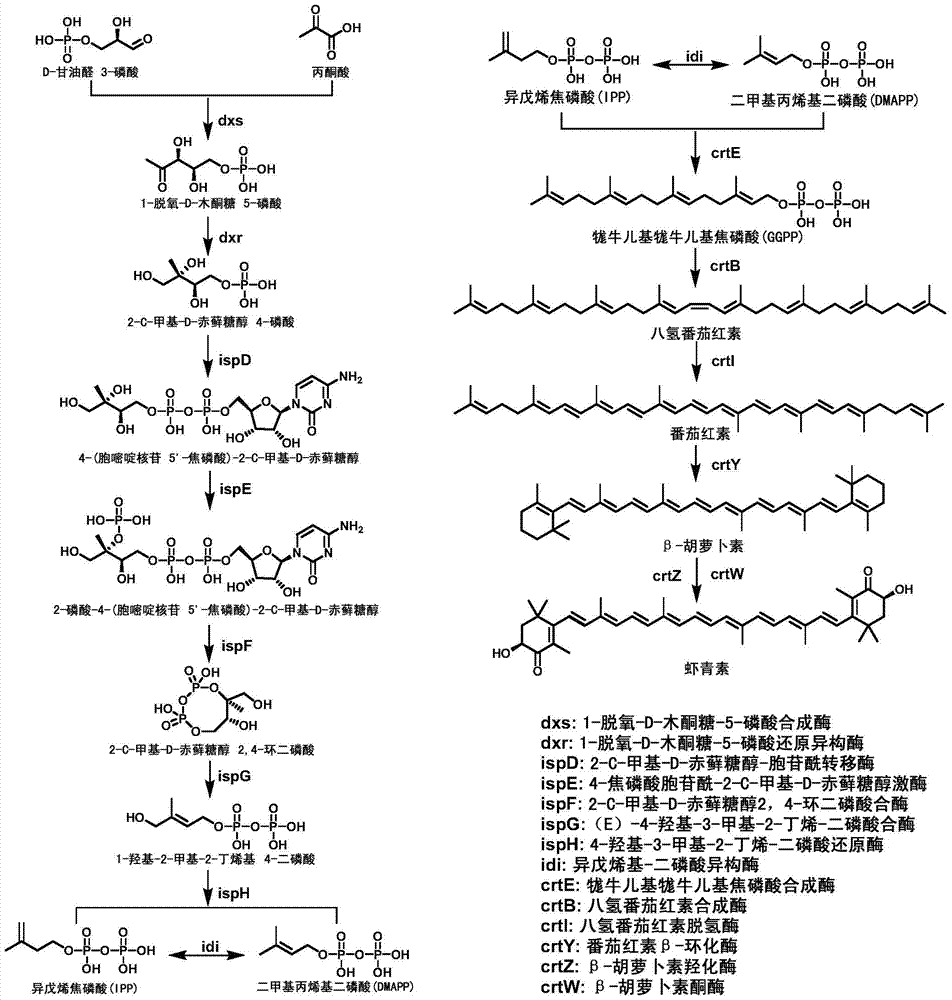
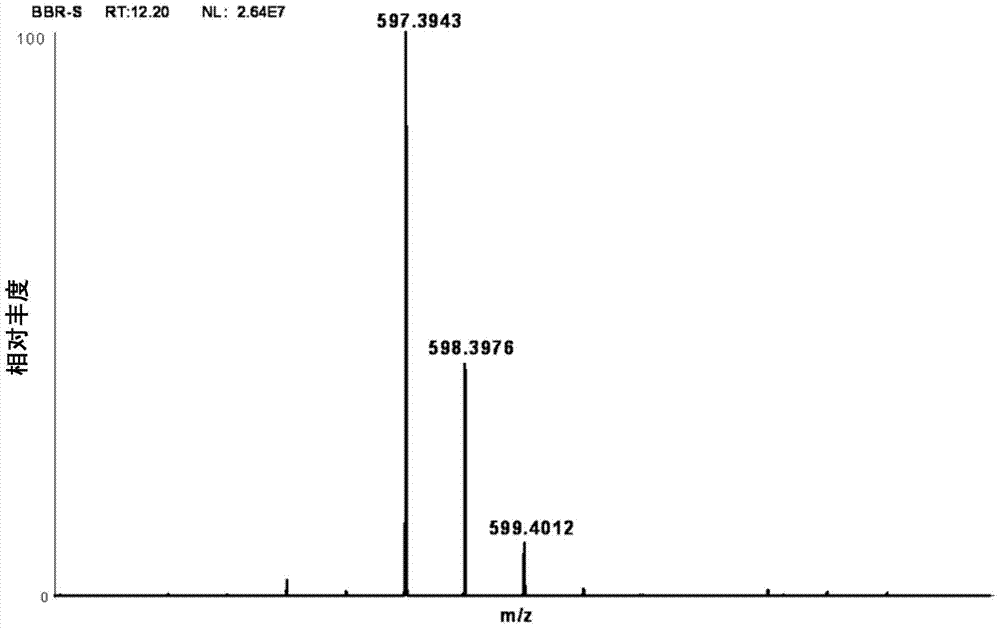
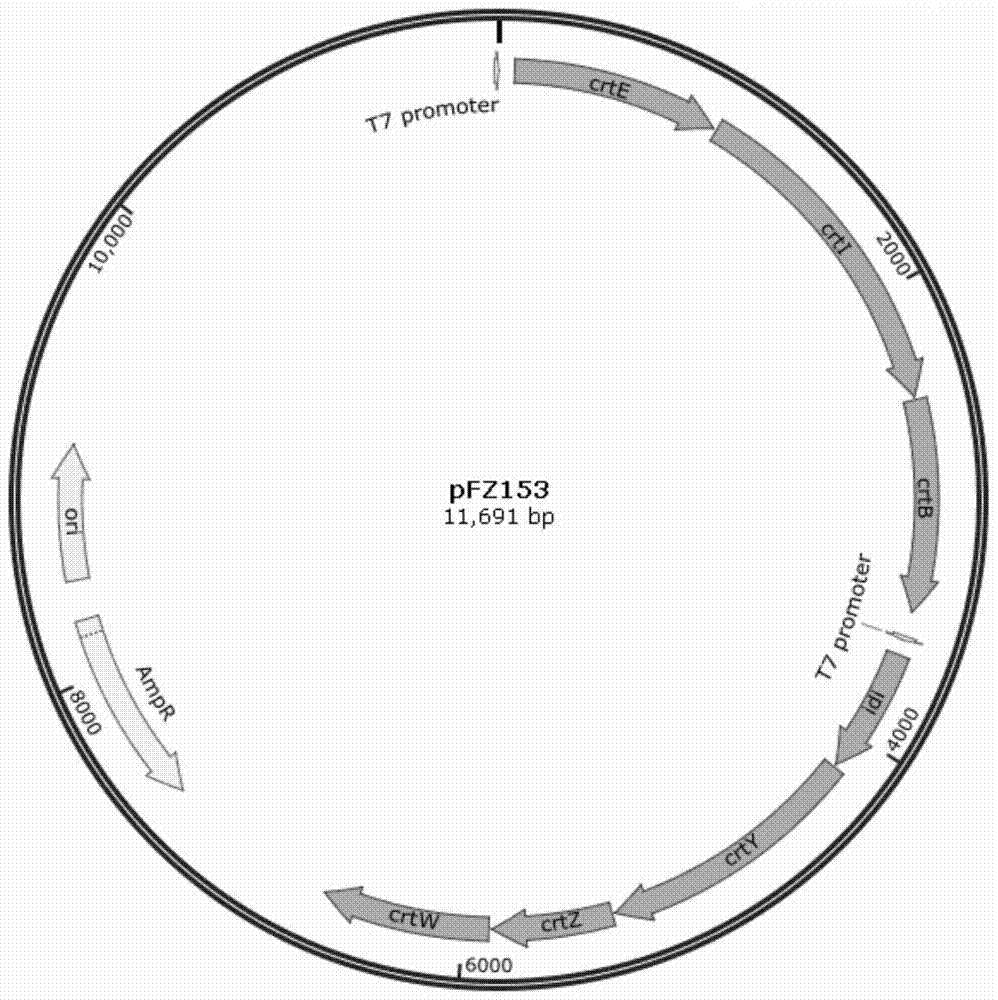
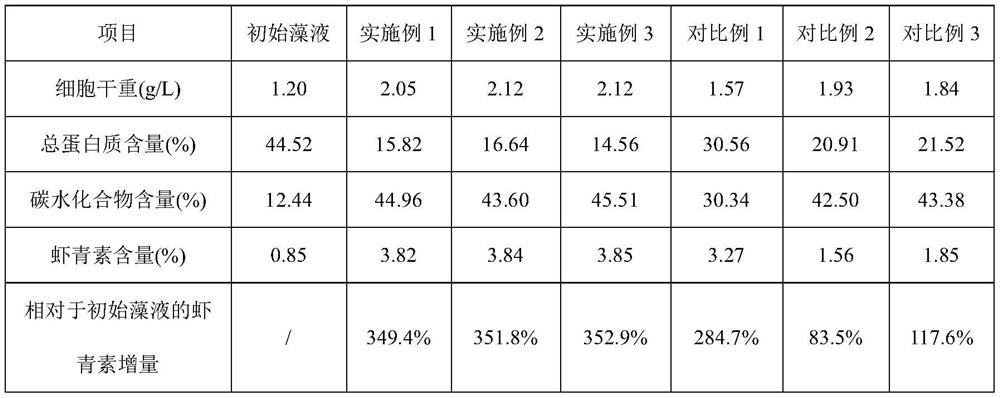
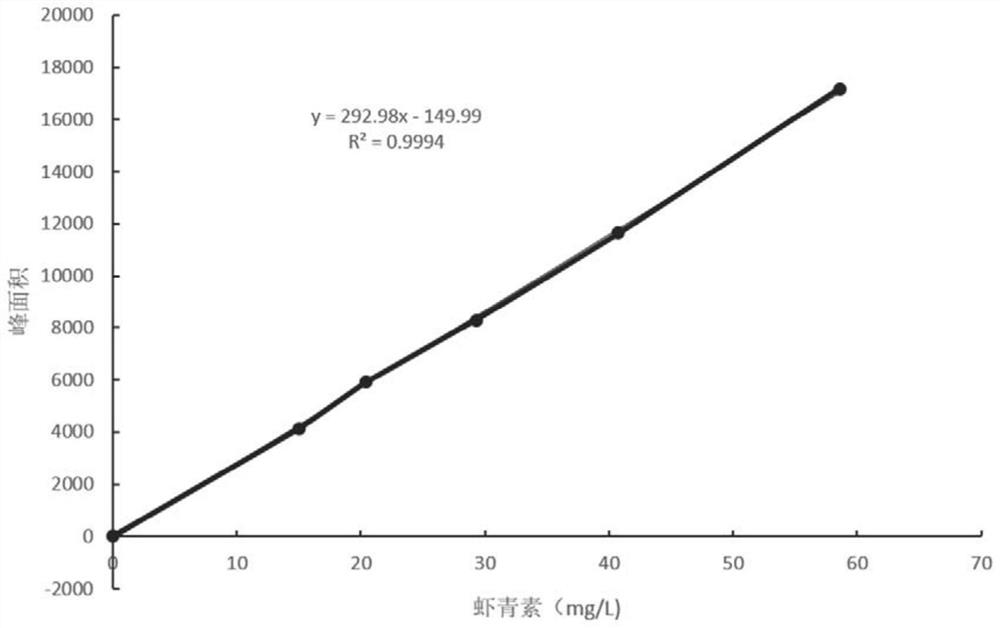
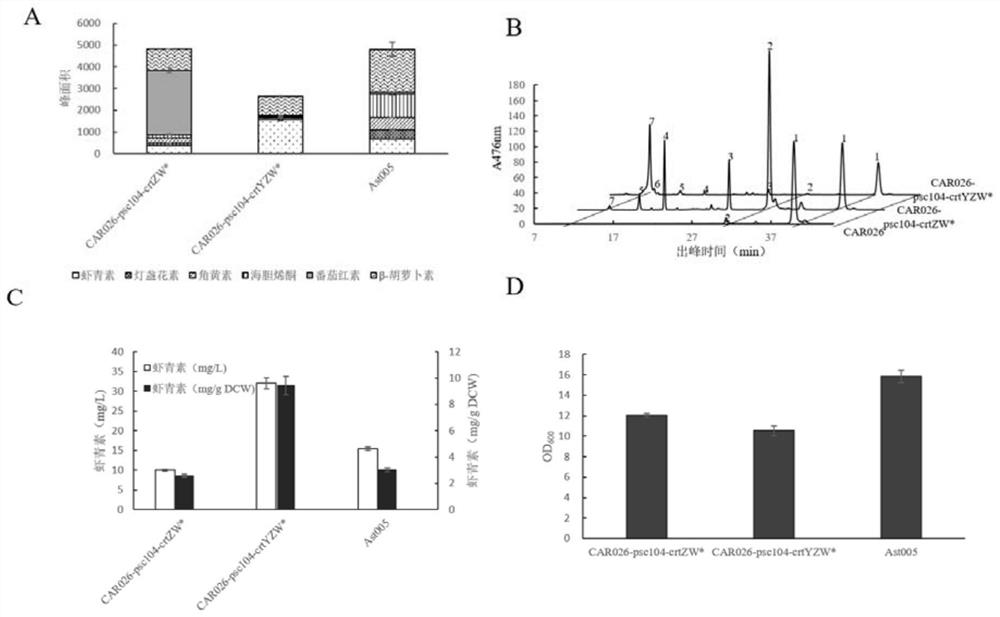
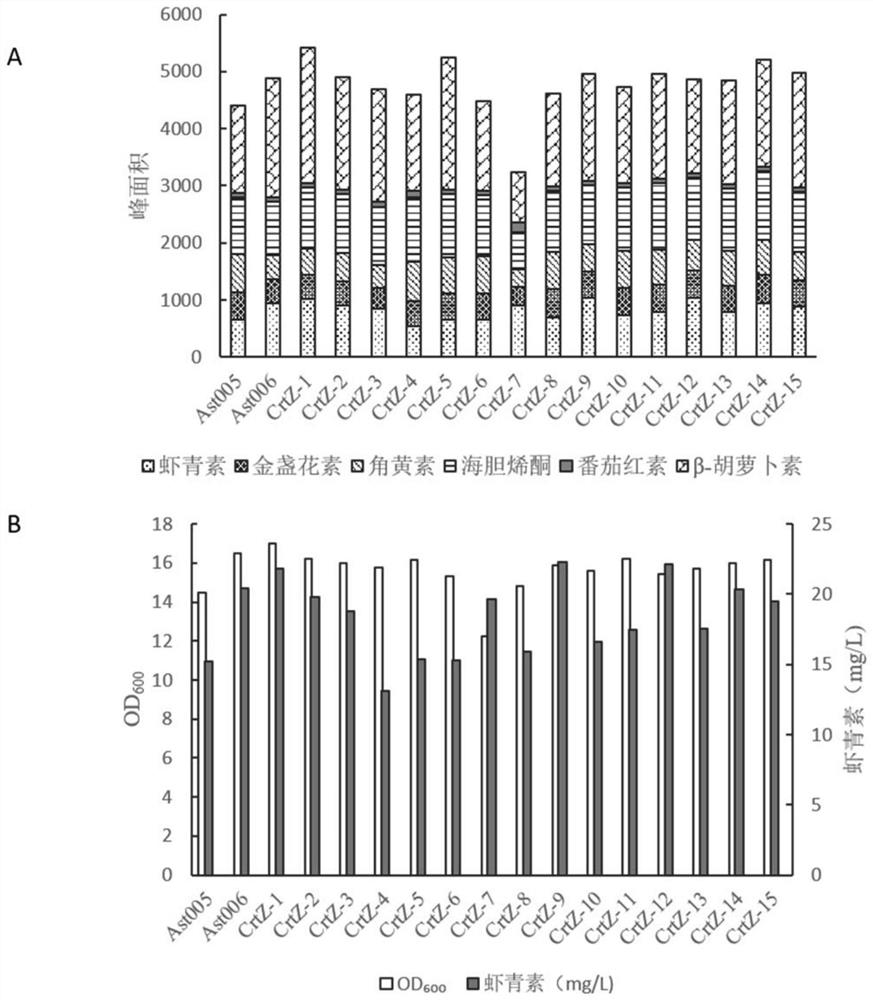
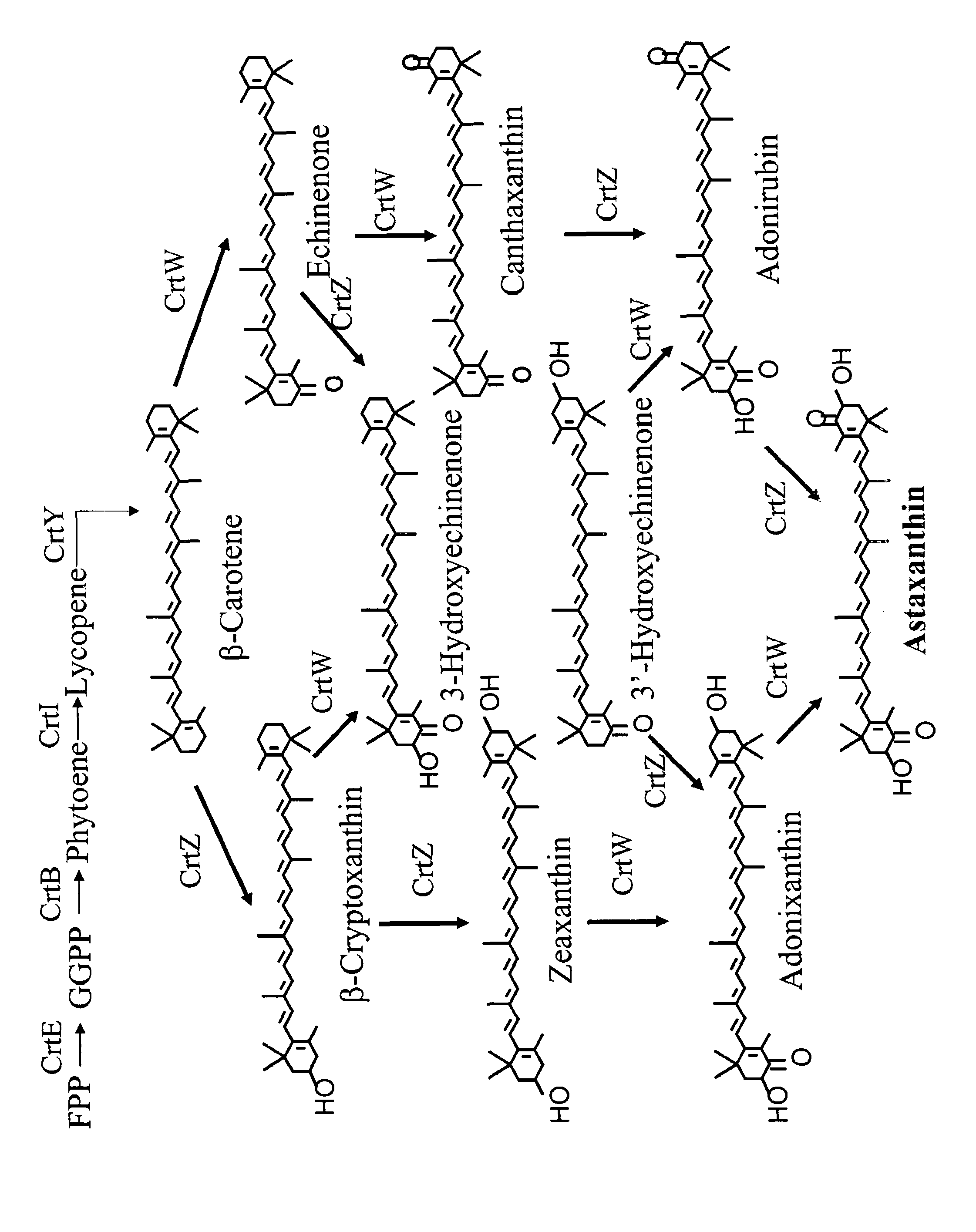
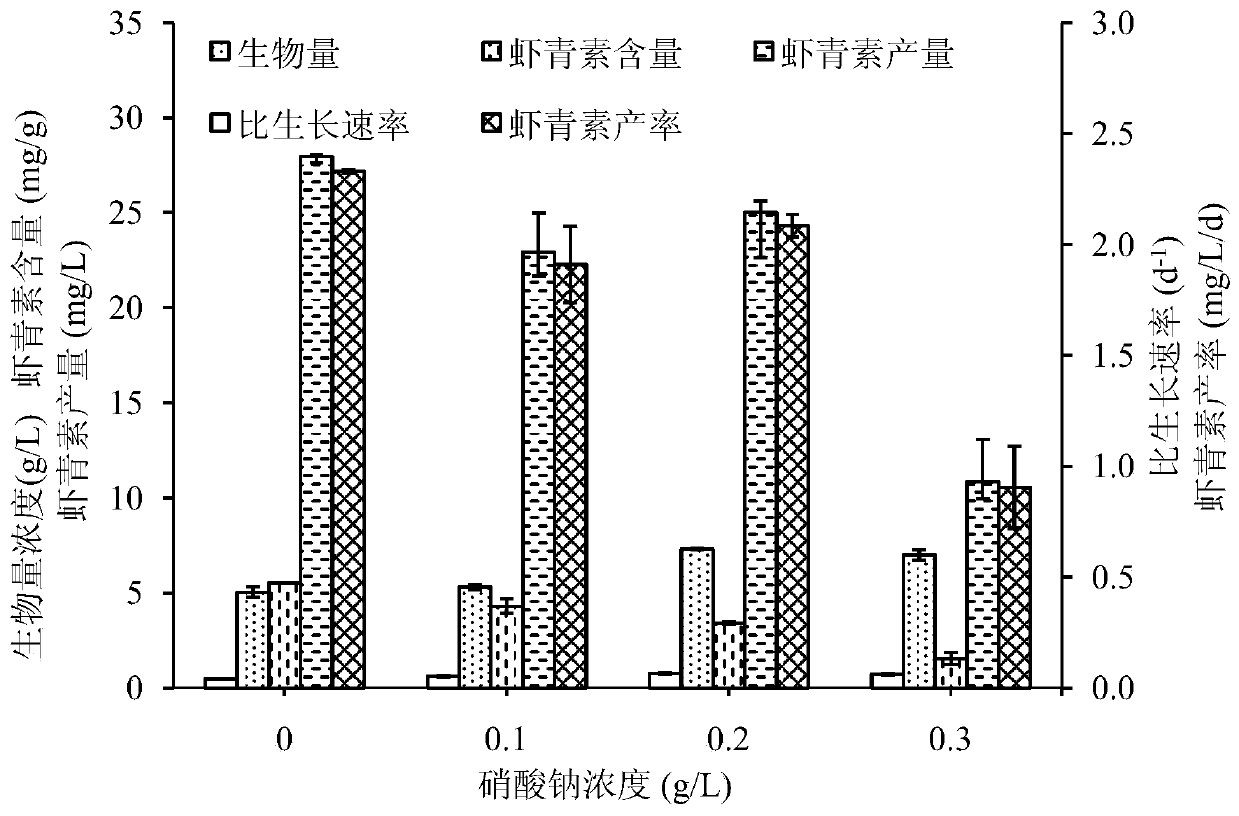
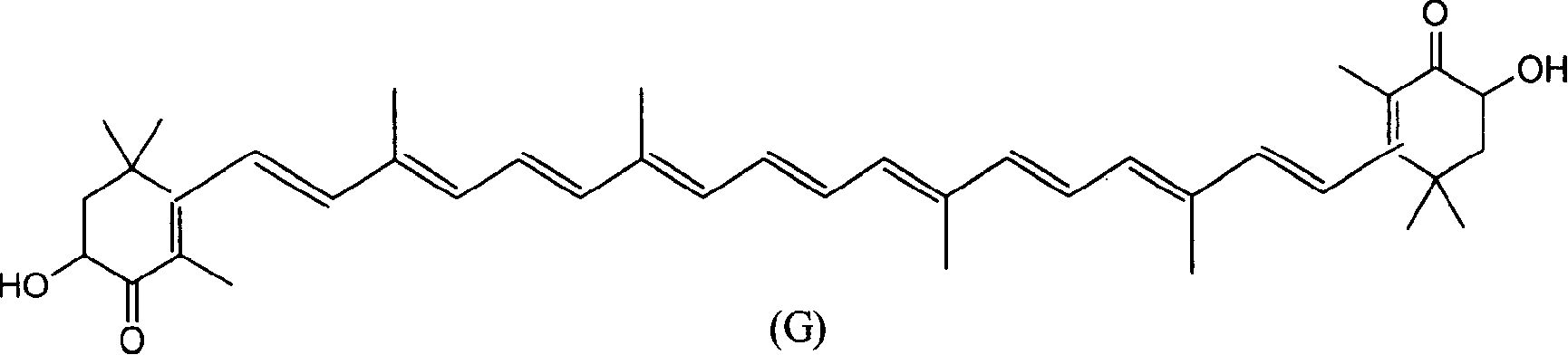
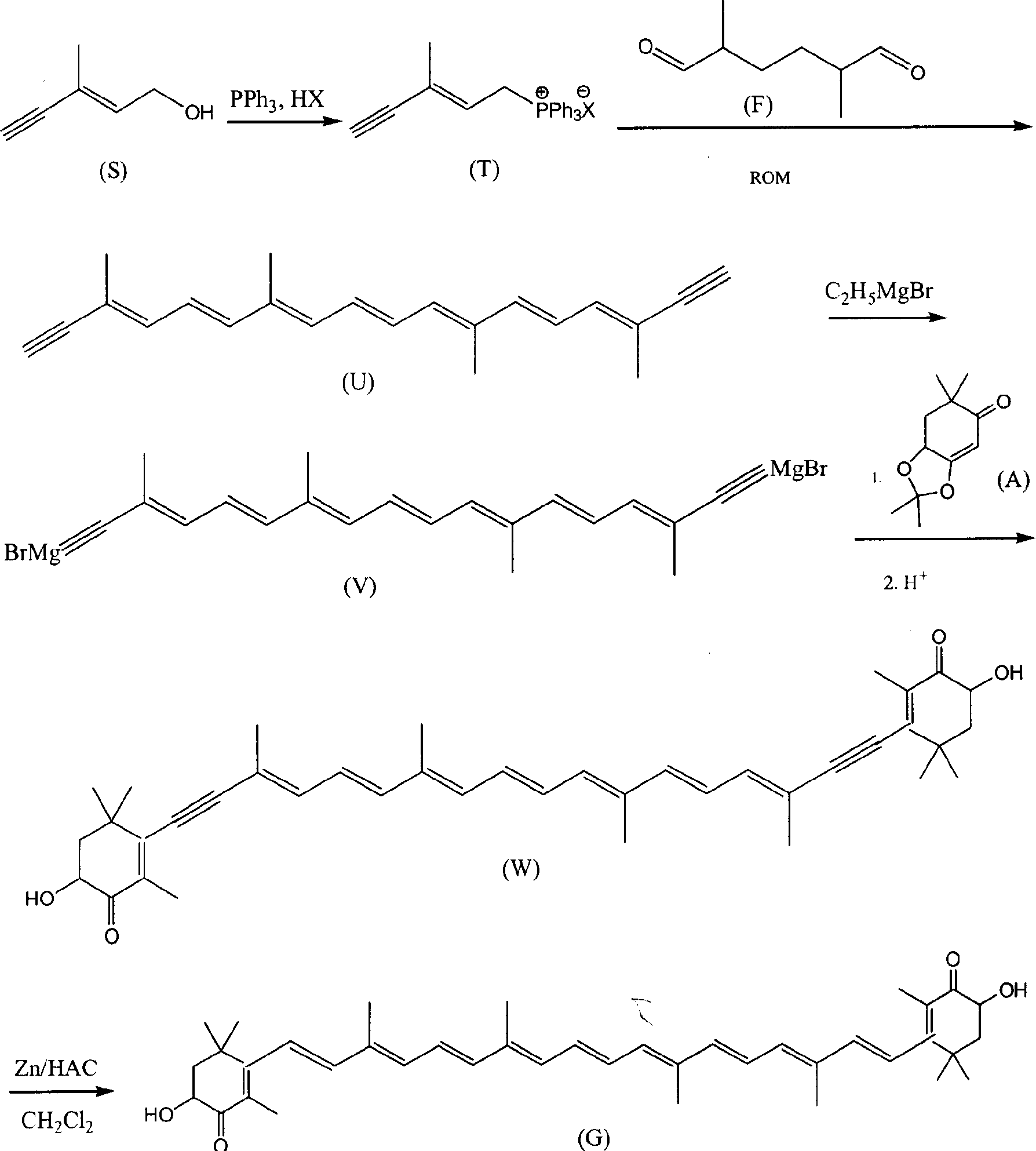
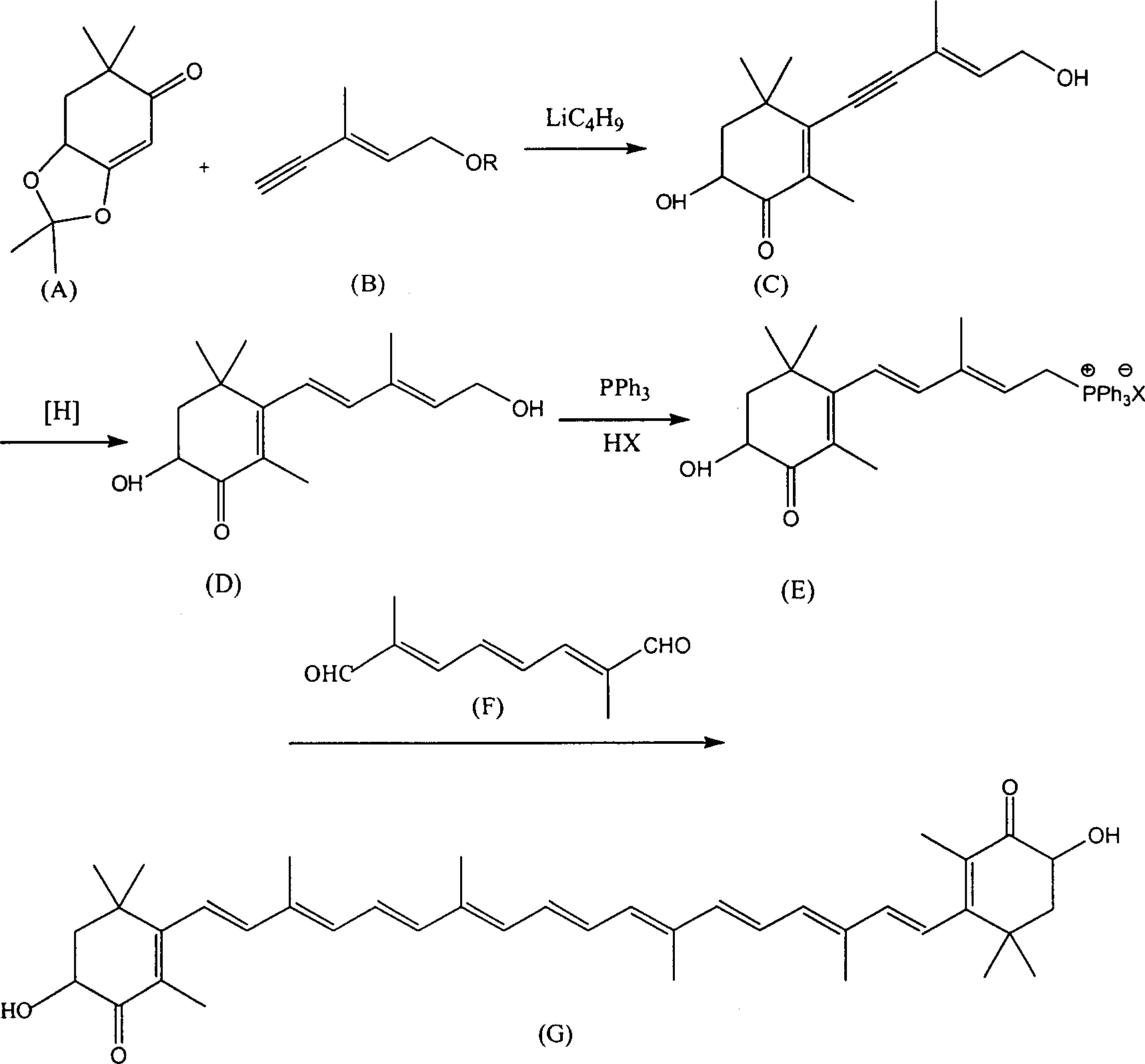
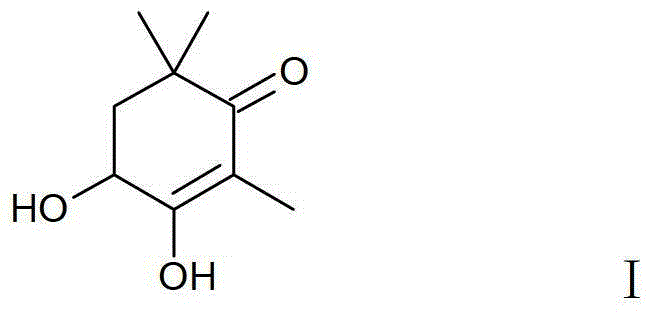
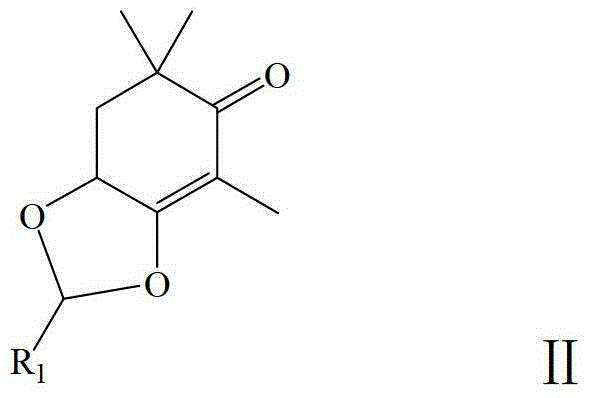
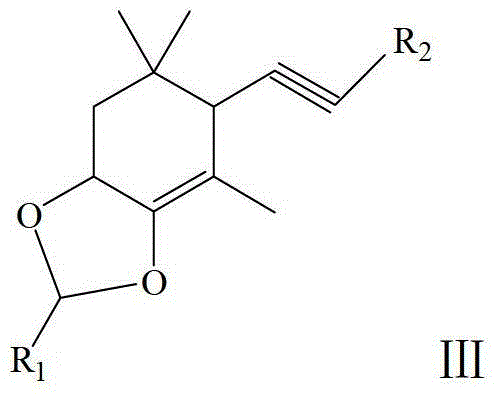
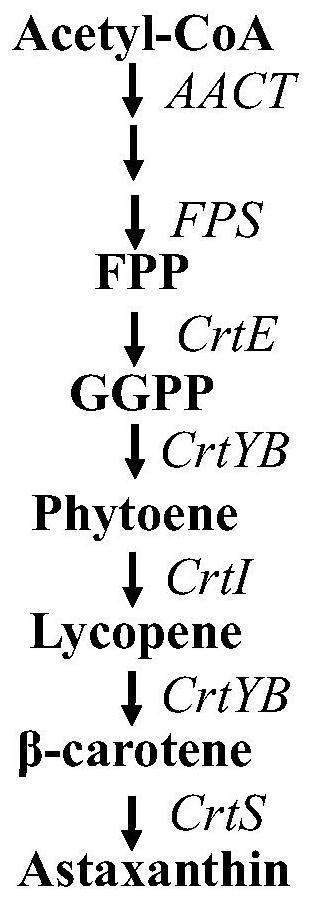
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Astaxanthin synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synthesis of astaxanthin
Synthesis of astacin is carried out by dispersing astaxanthin with mass concentration 1-6g / L and alkali in proportion 1:2-20 in alcohol solvent, agitating while inducing into oxygen, reacting at 30-80 degrees C to obtain reactant, removing alcohol solvent to obtain solid crude product, dissolving the crude product by methylene chloride, filtering, dissolving the filter residue by water to obtain alkali reactive liquid, neutralizing by acid to pH value 4-6, filtering, washing by water and drying to obtain final product. It is simple and convenient, has more yield and no by-product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +3
Method for synthesizing astaxsanthin
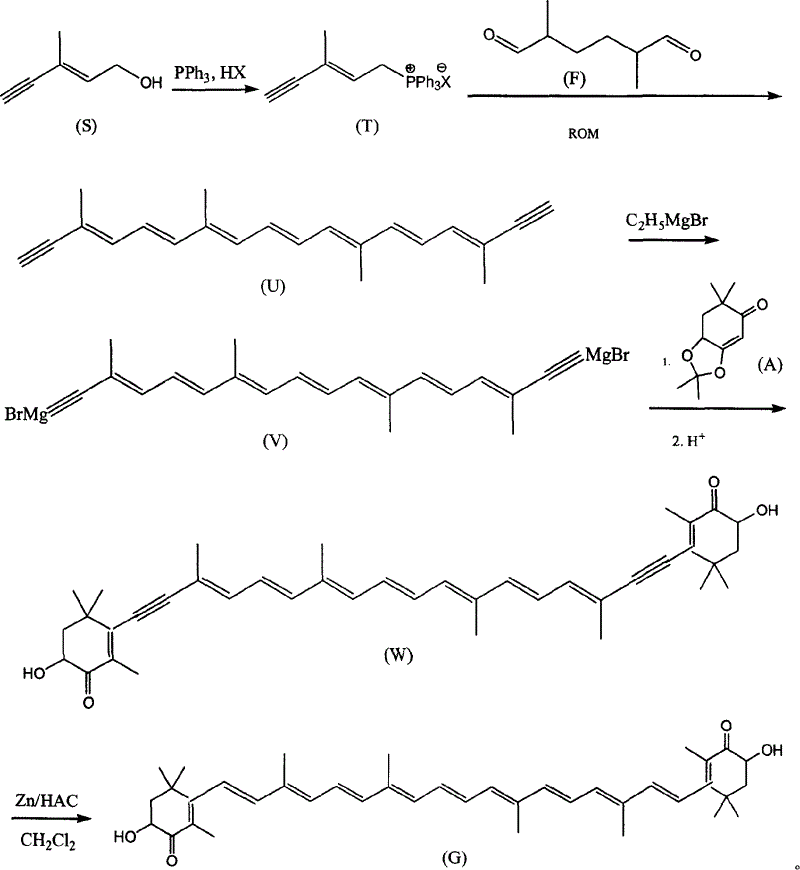
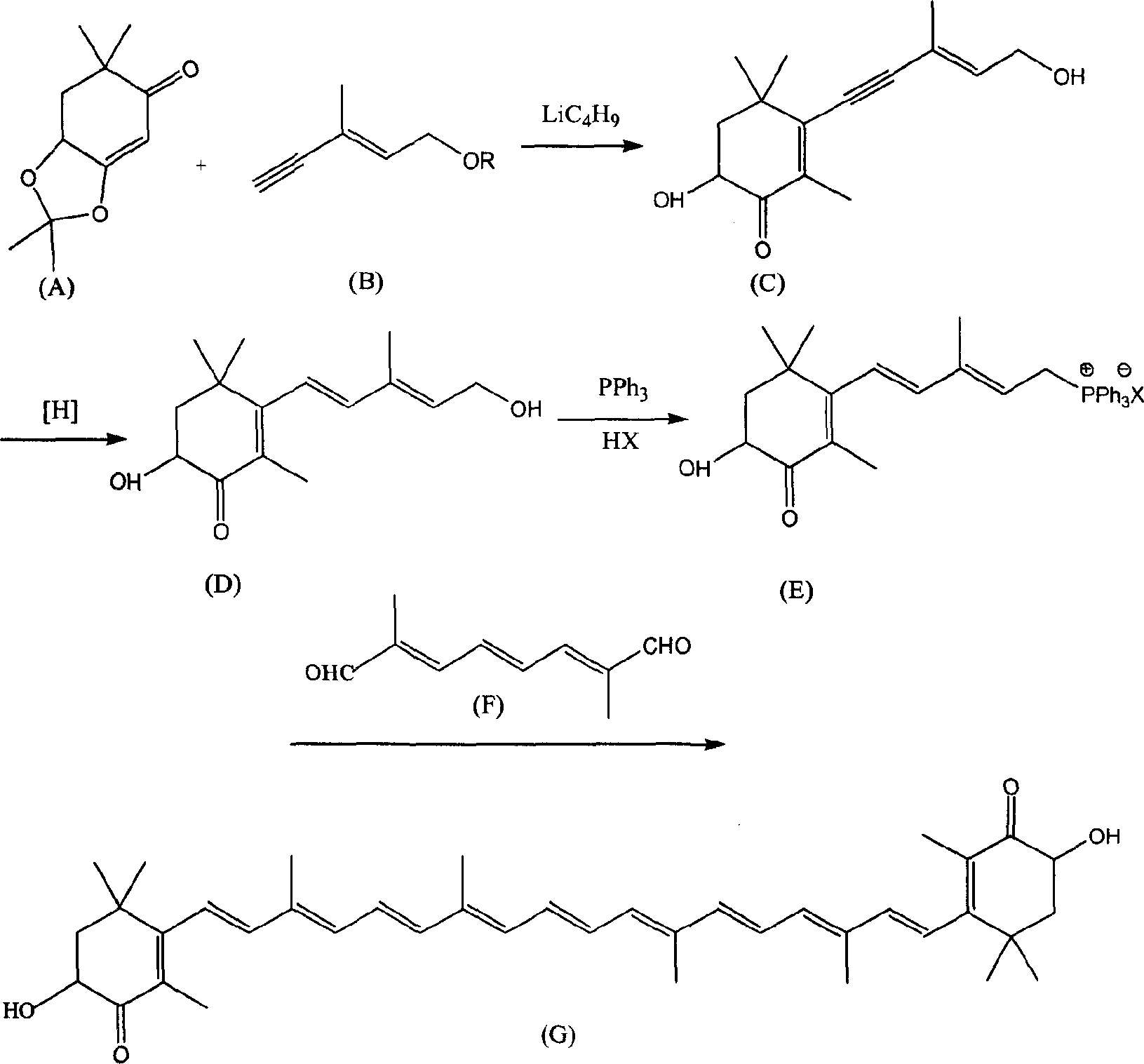
A process for synthesizing astaxanthin from the C6 alcohole as the by-product of preparing VA includes 4 reaction steps. Its advantages are high selectivity and high output rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +3
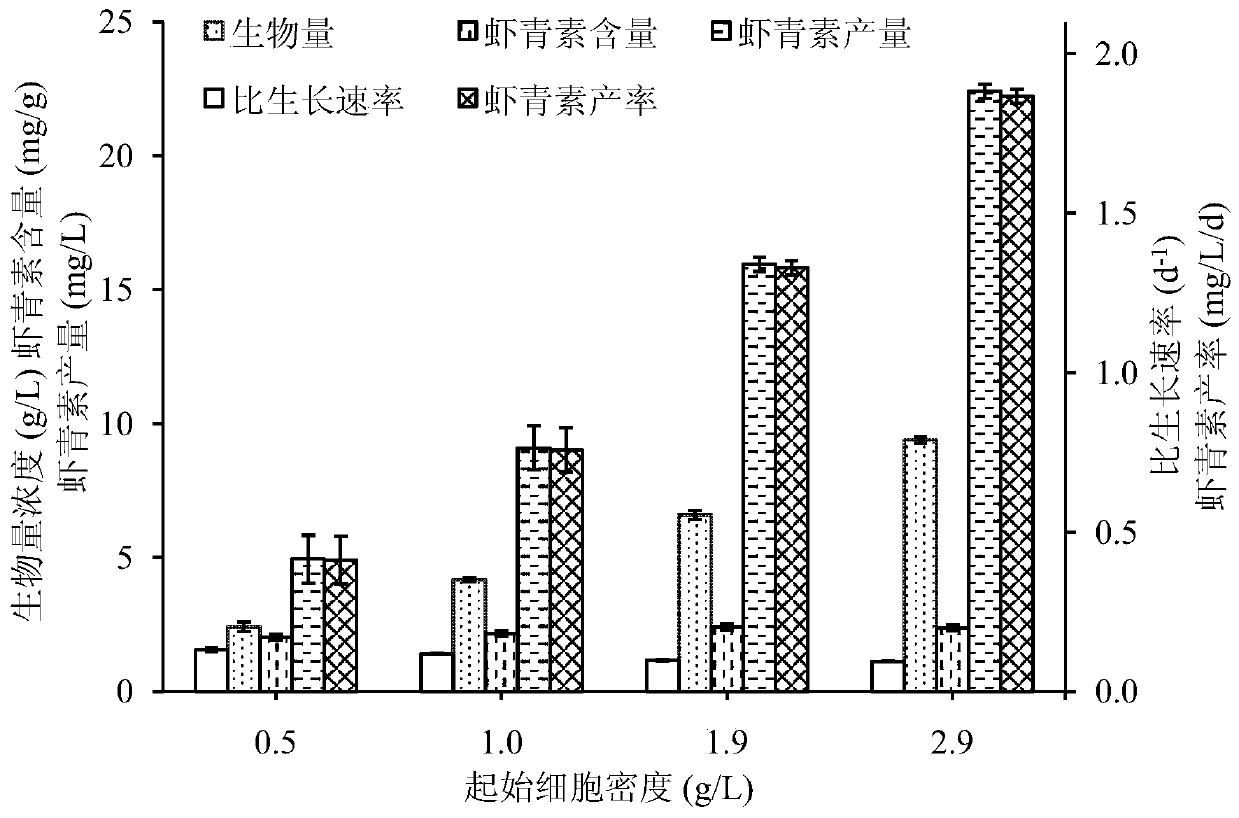
Method for biosynthesizing astaxanthin by using exponential intermittent feed supplement mode
InactiveCN101985645AIncrease productionAvoid inhibitionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBetaxanthinsPhaffia rhodozyma
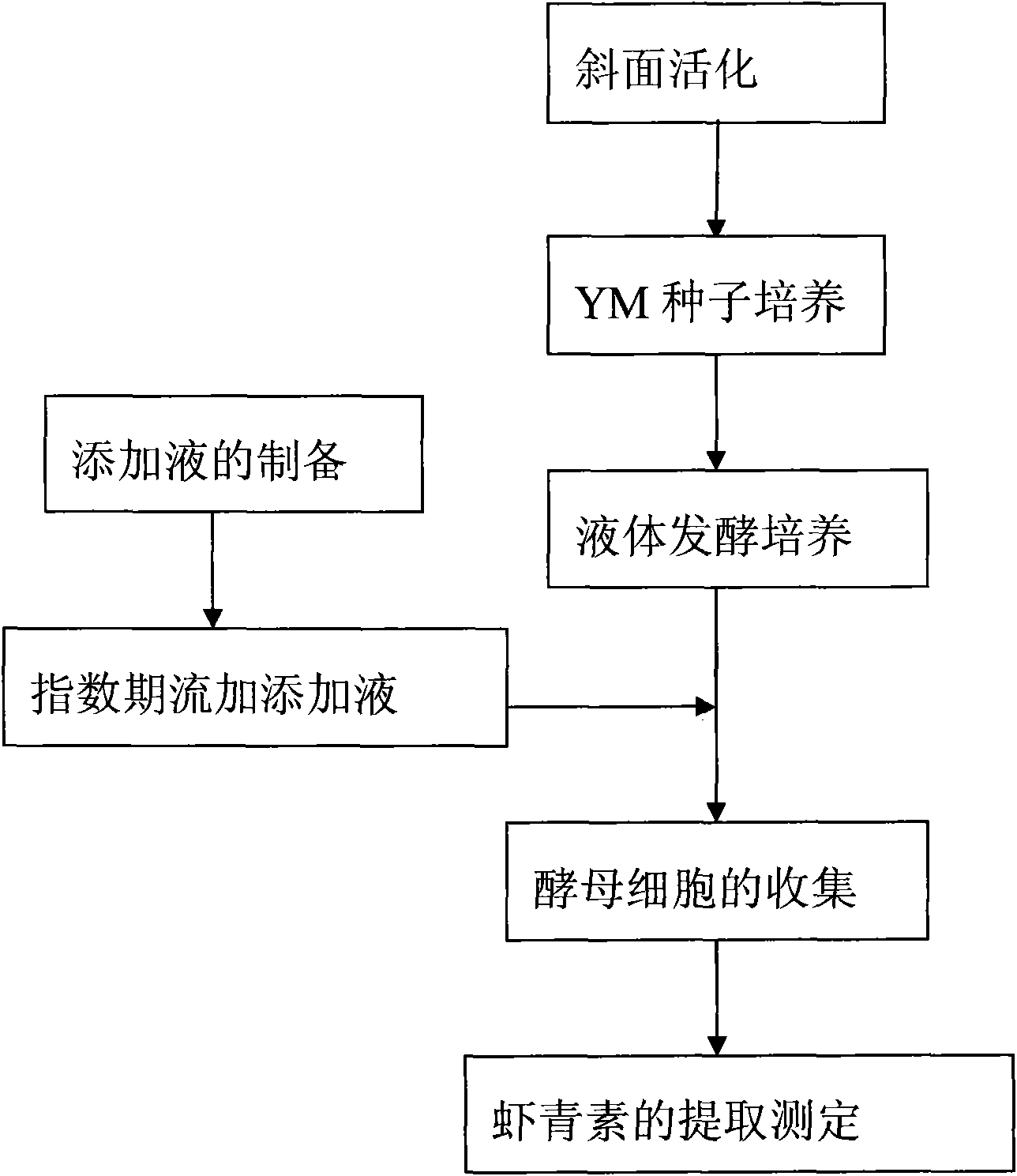
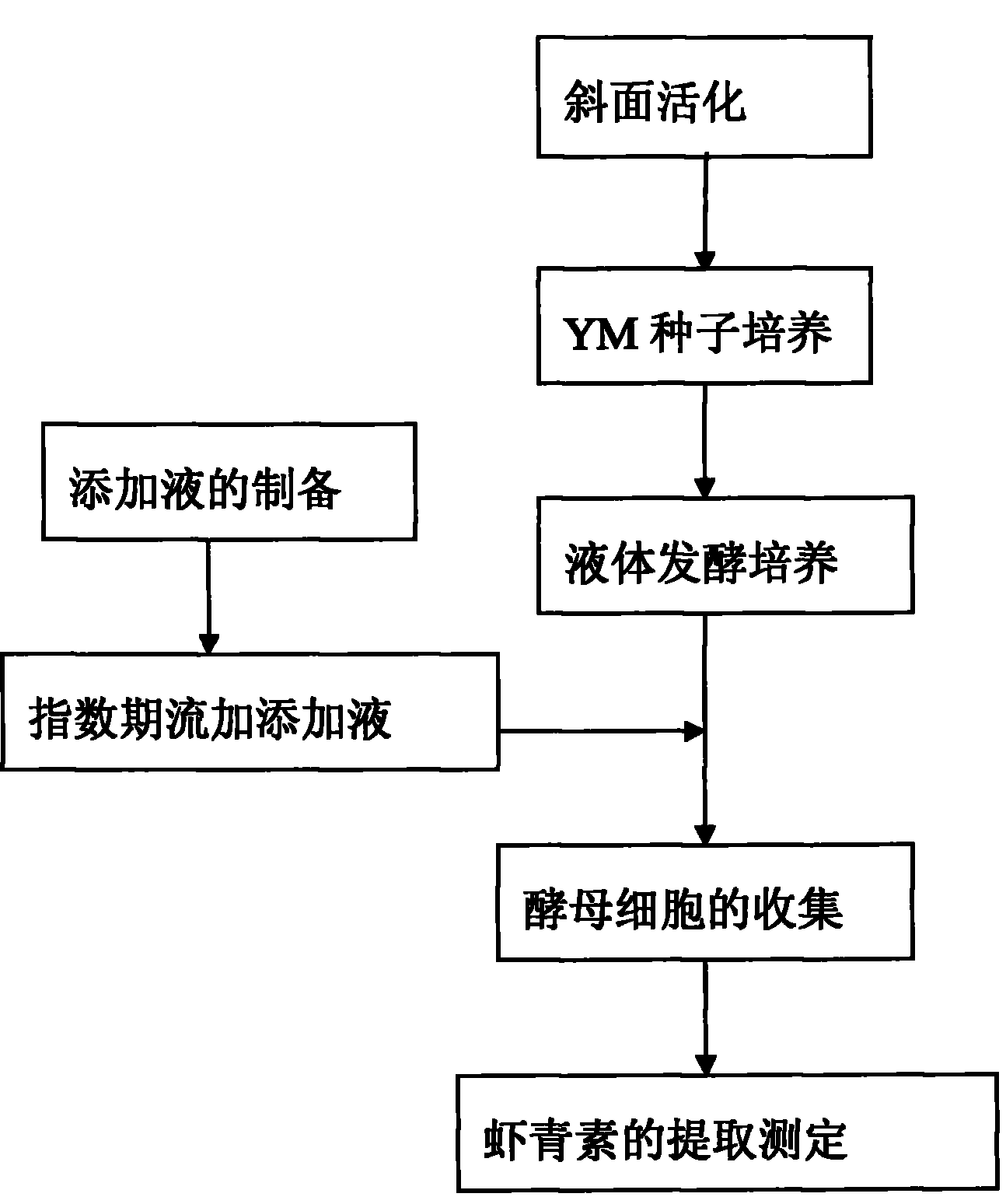
The invention relates to a method for biosynthesizing astaxanthin by using an exponential intermittent feed supplement mode. The method comprises the following steps: S1, taking subsidiary agricultural products rich in synthetic precursors of the astaxanthin to prepare an adding fluid and sterilizing the adding fluid for 15-30 minutes at the temperature of 115-121 DEG C; S2, taking and cultivating Phaffia rhodozyma in a liquid fermentation medium, feeding 0.5-5% the adding fluid in a batch mode at intervals of 3-12 hours after the exponential phase, and after carrying out fed-batch for 1-4 times, continuing to carry out cultivation 12-48 hours; and S3, extracting the astaxanthin. In the method of the invention, a small amount of astaxanthin synthetic accelerator is added in the exponential phase of the fermentation, thus avoiding premature addition of the astaxanthin synthetic accelerator from inhibiting yeast plant growth and greatly improving the yield of the astaxanthin at the same time, wherein the yield of the astaxanthin is improved by 20-95% compared with a control group. The extracted astaxanthin can be used as feed additives in high-grade aquatic products industry, fish breeding and poultry raising industry and the like. The invention has the advantages that the raw material price is low, the operation is simple and the popularization and application value is high.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
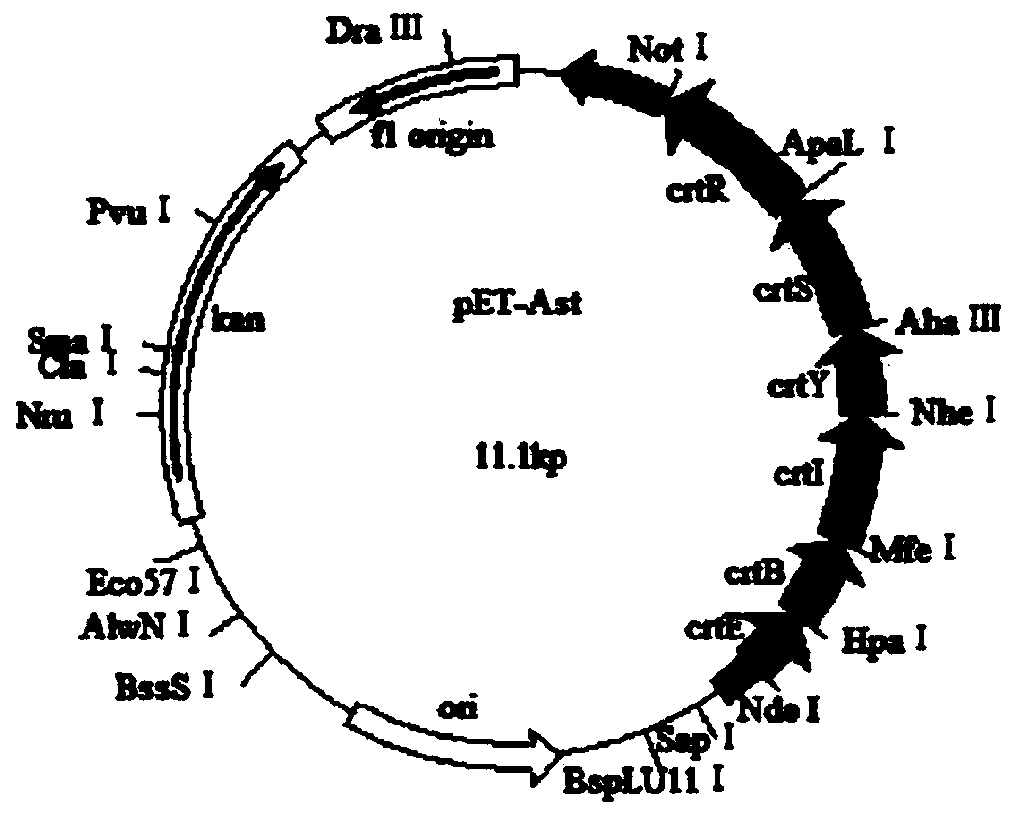
Astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant plasmid as well as preparation method and application of astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant plasmid
InactiveCN103805623ARealize accumulationBuild accuratelyMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAstaxanthinBetaxanthins
The invention discloses an astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast with a base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast, an application of the recombinant plasmid pET-Ast to the detection of astaxanthin synthetase activity of a target receptor, and an application method. After the astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast provided by the invention is introduced to an Escherichia coli BL21 strain, the accumulation of astaxanthin in a cell body of Escherichia coli is successfully realized, so that an astaxanthin production strain can be accurately and rapidly established. The preparation method of the astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast is simple and convenient, easy to operate and low in cost. By using the method disclosed by the invention, a gene sequence to be detected in the target receptor can be replaced with a related gene sequence in the recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast through digestion and connection, and then, the function of a gene to be detected in the target receptor can be simply and effectively detected and verified through detecting whether the astaxanthin is accumulated in a host cell body.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
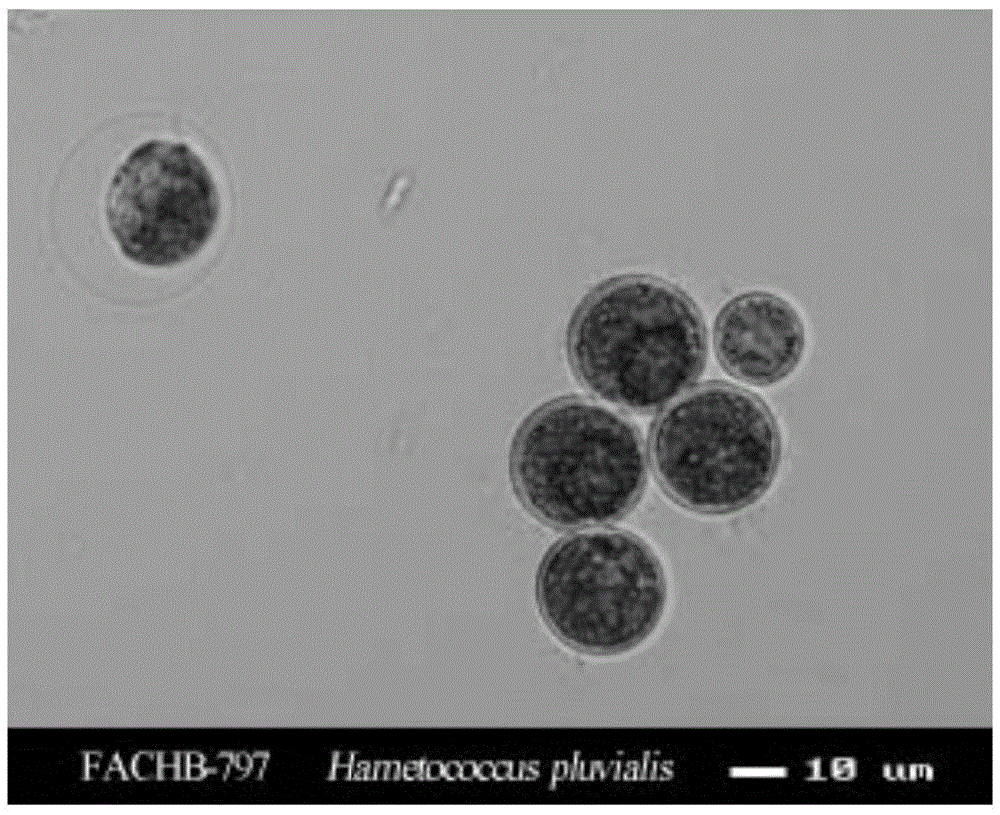
Method of regulating haematococcus pulvialis population density and synthesing and accumulating astaxanthin in photoreactor
InactiveCN1392250AImprove light utilizationIncrease light intensityTissue cultureFermentationMetaboliteAstaxanthin
The present invention relates to the process of regualting haemtococcus pluvialis population density and synthesizing and accumulating astaxanthin as intracellular secondary catabolite in a photobiological reactor system. The process includes establishing a photobiological reactor system with main reactor made of transparent material, outside controllable lighting facility, speed regulating vane wheel stirrer, water rolling wheel, ventilating and oxygen supplying unit, nutritious liquid compounding and temperature controlling unit and sterilizing unit; antering environment conditions to regulate haemtococcus pluvialis population density and synthesize, accumulate and collect astaxanthin; low temperature drying; etc. The natural astaxanthin is a kind of carotinoid with important physiological functions and very strong antioxidant activity.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for culturing haematococcus pluvialis and application of haematococcus pluvialis
InactiveCN105483016ALow costIncrease biomassUnicellular algaeTreatment involving filtrationEutrophicationBetaxanthins
The invention discloses a method I for culturing haematococcus pluvialis, a method II for improving biomass of haematococcus pluvialis, a method III for producing astaxanthin and a method IV for purifying domestic sewage. Through utilization of the method II, the biomass of haematococcus pluvialis can be greatly increased, haematococcus pluvialis can relatively quickly enter the astaxanthin synthesis period, the astaxanthin synthesis period can be greatly shortened, and good basis can be provided for follow-up increase of metabolite astaxanthin yield. Besides, the content of heavy metal and other pollutants in haematococcus pluvialis obtained by utilizing the method I is not obviously increased, so that the haematococcus pluvialis obtained by utilizing the method I can be used as a safe product for follow-up use. Meanwhile, through utilization of the method IV, the nitrogen content and the phosphorus content in sewage can be obviously reduced, and the sewage eutrophication degree is obviously relieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Mutant carotenoid ketolases
InactiveUS20070238149A1Improve conversion abilityHigh synthetic activityFungiBacteriaHeterologousAstaxanthin
CrtW carotenoid ketolases are provided that are useful for the production of astaxanthin and other cyclic ketocarotenoids. The mutant ketolase genes of the present invention encode polypeptides characterized by an improvement in astaxanthin synthesis activity when converting cyclic hydroxylated carotenoid intermediates into astaxanthin. Expression of the mutant carotenoid ketolases in heterologous hosts enabled increased production of astaxanthin relative to the Sphingomonas melonis DC18 CrtW.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Crayfish feed
InactiveCN107348244AShorten the growth cycleExtended growth cycleClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceAnimal protein
The invention discloses crayfish feed. The feed includes the following materials by weight: animal protein 40%-50%, plant protein 2%-5% and algae 45%-60%, wherein the animal protein includes yellow mealworms, earthworms, animal livers, river snail meat and small fish and shrimps; the plant protein includes soybean meal and corn flour; and the algae include edible fungi, lentinus edodes, kelp, spirulina and chlorella. According to the invention, the animal protein added into the feed contains rich protein which provides adequate nutritional energy for crayfish, facilitates fast growth and shortens a growth period. Meanwhile, with the addition of the algae which contain the edible fungi, the lentinus edodes, the spirulina and so on, the astaxanthin synthesis of the crayfish can be promoted, and the immune function of the crayfish can be enhanced; and the new shells of the crayfish can grow fast during a shelling period of the crayfish.
Owner:钟春明
Phaffia rhodozyma strain obtained by efficiently over-expressing endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene
InactiveCN104278015AImprove conversion efficiencyIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBinding site
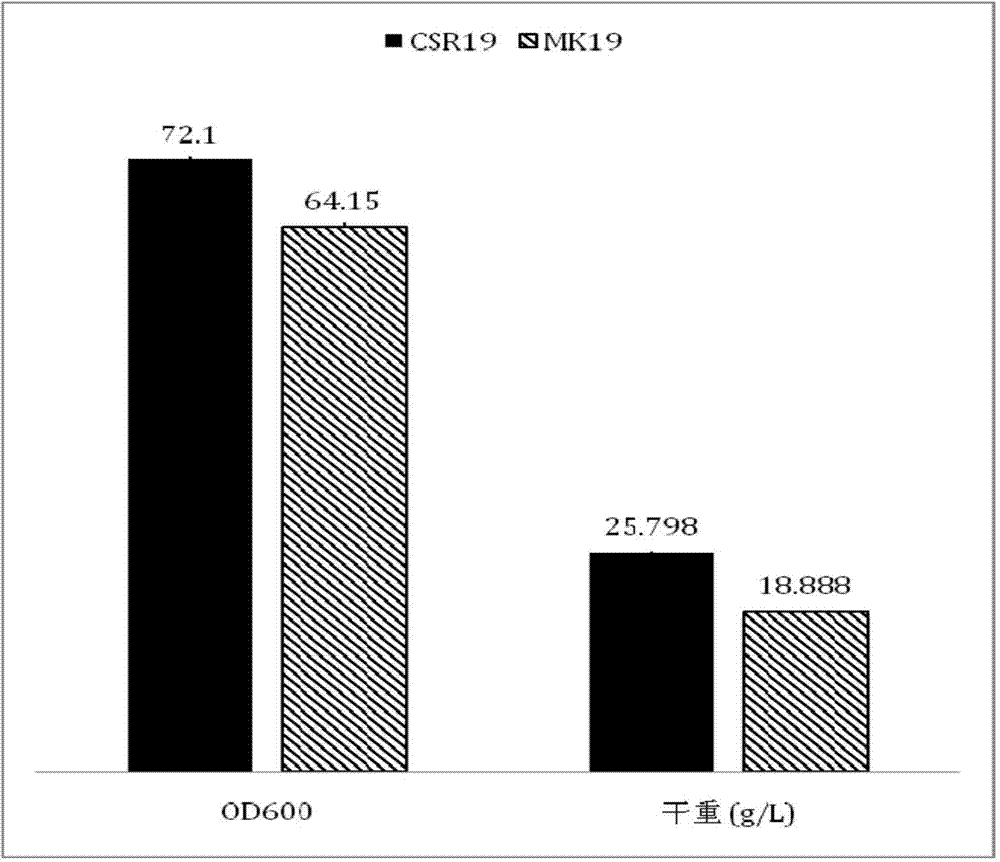
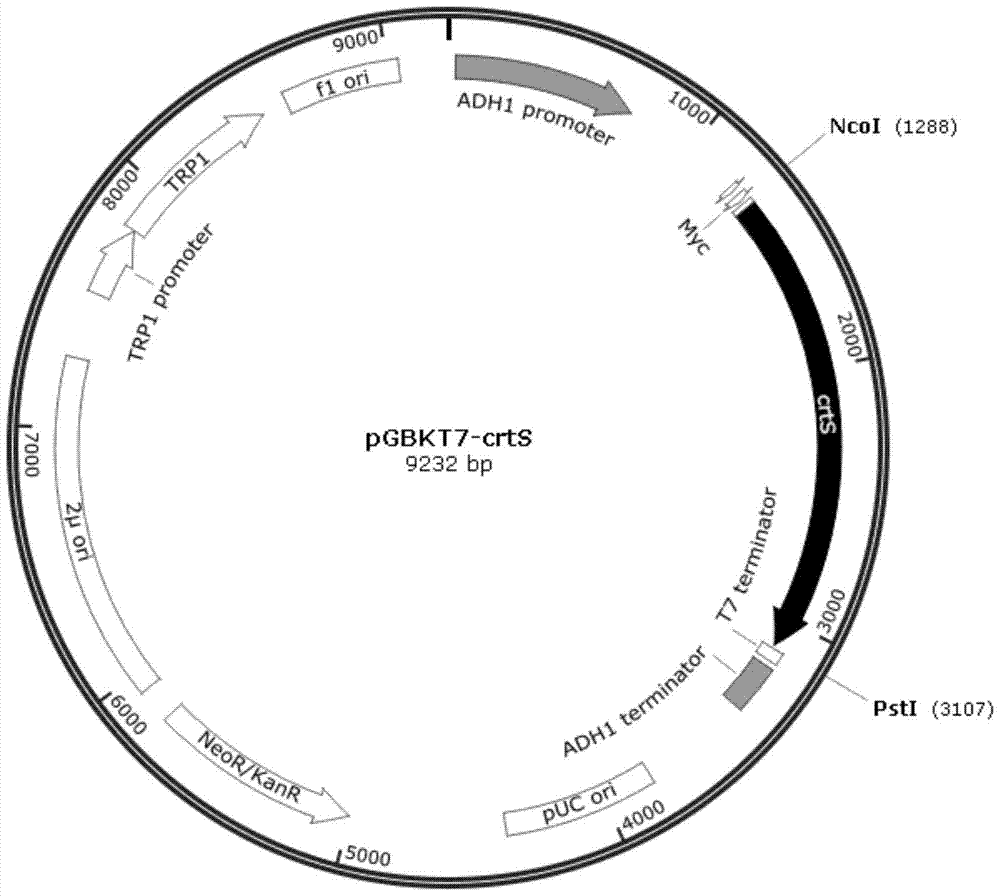
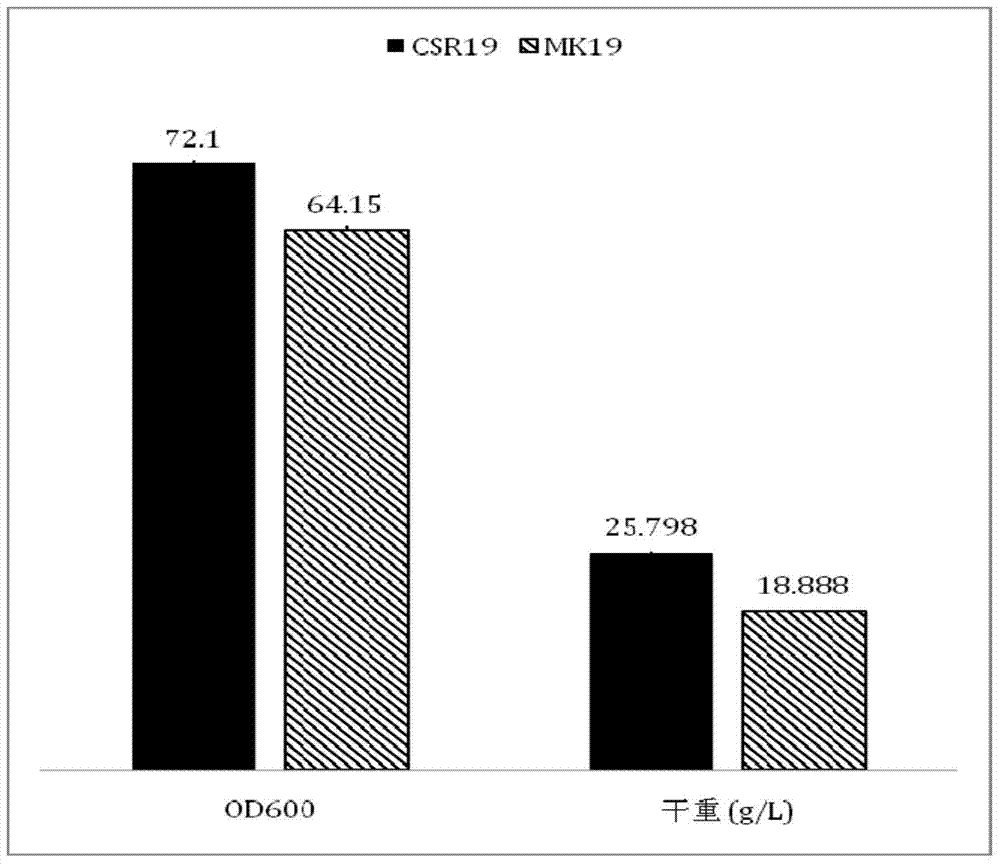
The invention discloses a phaffia rhodozyma strain obtained by efficiently an over-expressing endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene. The invention provides a phaffia rhodozyma genetic engineering strain capable of producing astaxanthin with high yield, obtained by over-expressing an endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene. A phaffia rhodozyma genetic engineering strain (MK19-pGBKT7crtS) capable of producing astaxanthin with high yield is obtained by over-expressing the astaxanthin synthetase gene crtS by virtue of free plasmids and the strain is named CSR19. An endogenous ribosome bind site sequence (Rbs. sequence for short) exists in front of the crtS gene expressed by the strain. By virtue of fermentation cultivation and in comparison with a receptor strain MK19, the astaxanthin yield of the engineering strain is increased by 33.5%, and the engineering strain is good in stability, and thus, the phaffia rhodozyma strain has a good application prospect in the feed industry.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bioproduction of astaxanthin using mutant carotenoid ketolase and carotenoid hydroxylase genes
Protein engineered nucleic acid fragments encoding a CrtO ketolase and a CrtZ hydroxylase are provided with increased astaxanthin synthesis activity. Methods using the present nucleic acid fragments are also provided for increasing or altering astaxanthin production in suitable production hosts.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Astaxanthin synthetase of sphingomonas, encoding gene of astaxanthin synthetase and method for genetic manipulation of sphingomonas
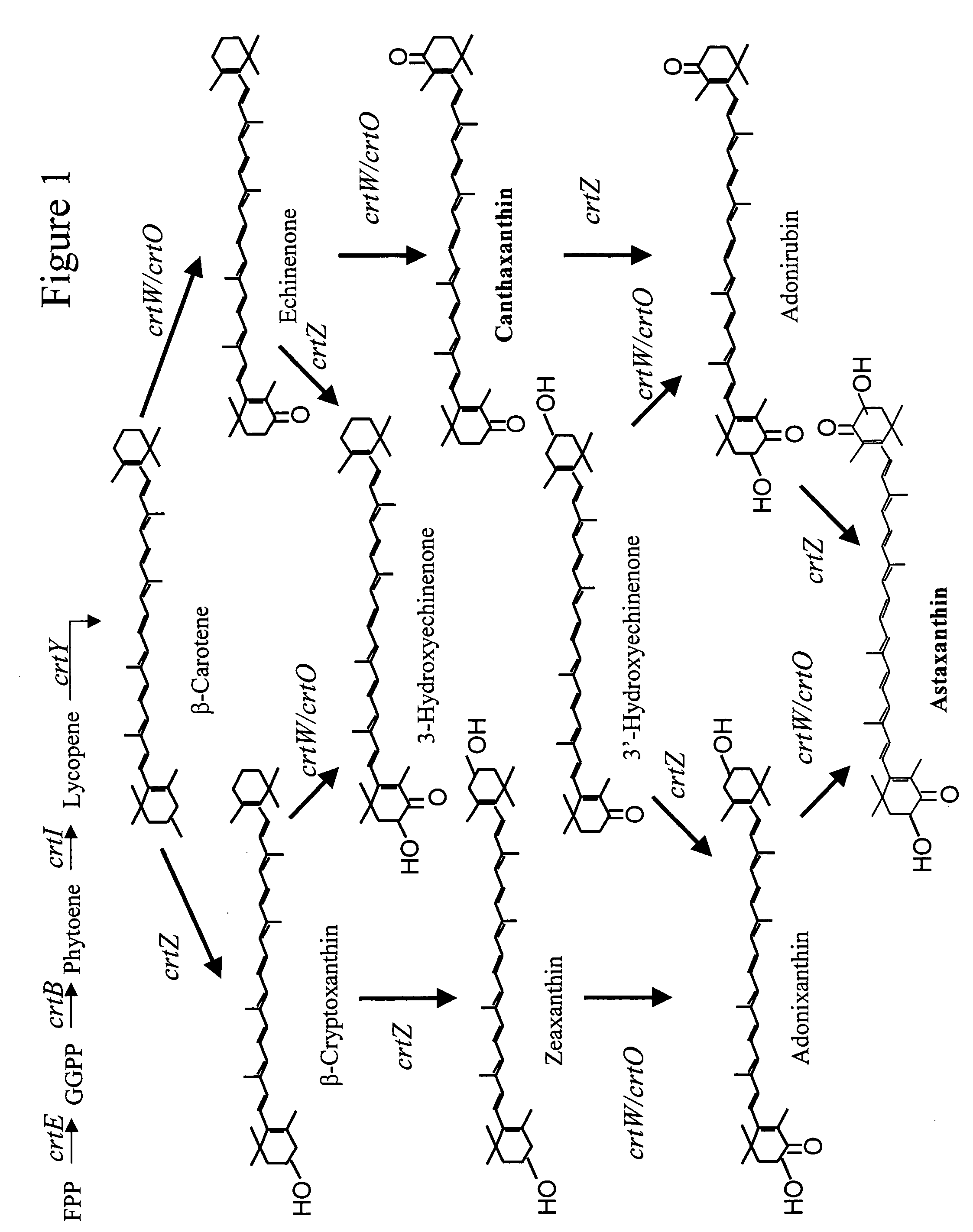
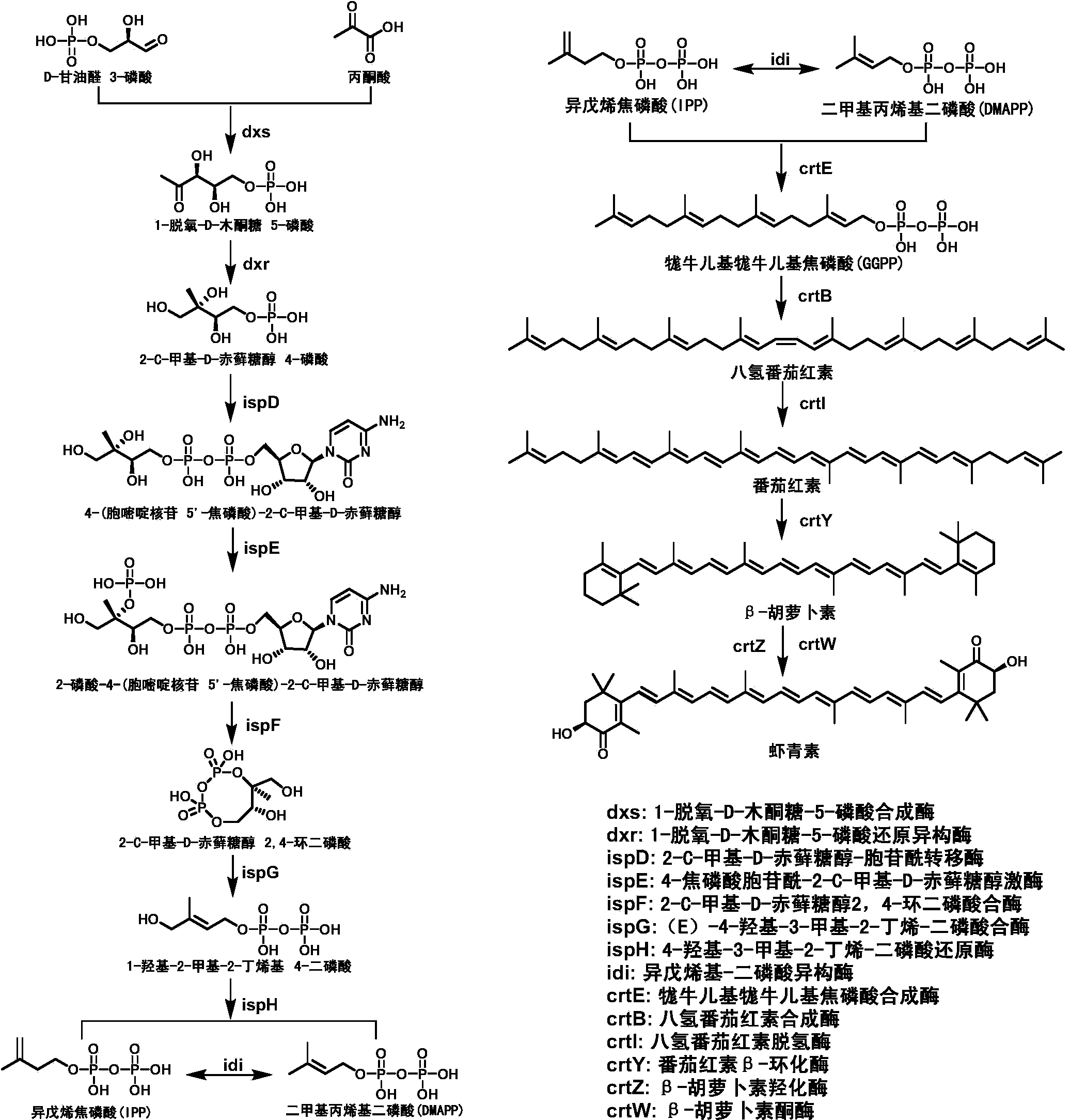
The invention discloses astaxanthin synthetase of sphingomonas, an encoding gene of astaxanthin synthetase and a method for genetic manipulation of sphingomonas. The invention verifies that the sphingomonas can be used for producing astaxanthin, a biological synthesis way capable of producing the astaxanthin is contained, an MEP way and a carotenoid synthesis way are used for producing the astaxanthin in the sphingomonas, and the fact that in the sphingomonas, crtE and crtZ having relatively low homology with the known genes have the function of synthesizing the astaxanthin, can be further proven. Both the enzyme and the encoding gene thereof required by the astaxanthin biosynthetic way of the sphingomonas are not reported in the prior art, so that more resources are provided to the biosynthetic metabolism and transformation of the carotenoid. Genetic manipulation can be carried out on the sphingomonas by taking pBBR1MCS2 as a carrier and taking EGFP as a reporter gene, so that a foundation is laid for the genetic modification of the environmental microorganism of the type and the finding of the degradation mechanisms.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOTECH +1
Construction and application of astaxanthin synthesis strain
ActiveCN112852694AImprove generation effectIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAstaxanthinPromoter
The invention discloses construction and an application of an astaxanthin synthesis strain. The invention provides a recombinant bacterium, which is prepared according to a method comprising the following steps of: expressing and synthesizing carotenoid related genes crtY gene, crtZ gene and crtW gene in escherichia coli, and regulating and controlling the expression of molecular chaperone genes groES and groEL in the escherichia coli to obtain the recombinant bacterium, according to the invention, the promoters with different intensities are utilized and gene copy is changed, so that coordinated expression among genes in a synthetic pathway of astaxanthin is realized, and the toxicity of metabolic intermediates is eliminated, so that the generation capacity of biosynthesis of astaxanthin is improved. In addition, stabilizing the expression of the exogenous gene and increasing the correct folding of the exogenous gene can also become an effective way for improving the biological activity of astaxanthin synthetic pathway enzyme and increasing the yield of astaxanthin.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Research method for synthetic process of haematococcus pluvialis astaxanthin based on infrared spectroscopy microscopic imaging technology
InactiveCN108918456ASolve the problem that high-throughput measurement cannot be taken into account at the same timeResolve resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansBeta-CaroteneLycopene
The invention discloses a research method for the synthetic process of haematococcus pluvialis astaxanthin based on an infrared spectroscopy microscopic imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps that inoculation and culture are carried out on haematococcus pluvialis; an inhibitor performs treatment on haematococcus pluvialis strains; the infrared spectroscopy of the astaxanthin,beta-carotene and lycopene are collected; the infrared microscopic spectroscopy of haematococcus pluvialis cells are detected; and comparison and analysis of imaging of the microscopic infrared spectroscopy are carried out. According to the method, the infrared microscopic spectroscopy imaging technology is utilized, the haematococcus pluvialis cells are treated by combining the inhibitor synthesized by carotenoid, and high-spatial-resolution in-situ observation is carried out on the contents of various components of the haematococcus pluvialis cells in the astaxanthi accumulation process, sothat the effects of the components in the synthesis path of the astaxanthin can be conveniently analyzed. The method has important significance in research of the synthesis path of the carotenoid inthe haematococcus pluvialis cells and large-scale breeding of the haematococcus pluvialis for production of the astaxanthin.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Culture method of seaweed for zooplankton bait
ActiveCN109504609AIncrease contentImprove the body's immunityUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesFood chainAstaxanthin
The invention provides a culture method of seaweed for zooplankton bait. Domestic wastewater is used as a raw material for culturing alga and astaxanthin is synthesized by illuminating induction of alga through low molecular weight organic matters. The culture method of the alga comprises the following steps: adding small molecule unsaturated fatty acid into a domestic wastewater culture medium and culturing at the illumination intensity of 3000 to 4500 Lux; after microalgae cells turn brown under illuminating induction culture, adjusting the components of the culture medium to contain indolesubstances and small molecular ester organic compounds without the small molecular unsaturated fatty acid; continuously culturing at the light intensity of 1000 to 3500 Lux. By taking the domestic wastewater as the culturing raw material of the alga, the method provided by the invention is green and environment-friendly and low in cost; the astaxanthin is short in synthesis period and high in content; the algae rich in the astaxanthin is used as the bait for zooplanktons and further is applied to aquaculture animals, so that the transmission effect of a food chain is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method for preparing astaxanthin by oxidizing canthaxanthin
The invention discloses a method for preparing astaxanthin by oxidizing canthaxanthin. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a substrate canthaxanthin in an organic solvent; performingreacting by using a high-valence iodide as an oxidant to prepare a dialkoxy ketal compound; and hydrolyzing the ketal compound under acidic conditions to obtain astaxanthin. Therefore, problems of complex route and harsh conditions in the prior art are solved, and a safer and more practical method is provided for astaxanthin synthesis.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Method for inducing algal cells to synthesize astaxanthin efficiently
ActiveCN109554429AInduced synthesisEasy to synthesizeMicroorganism based processesFermentationFrozen storageBetaxanthins
The invention provides a method for inducing algal cells to synthesize astaxanthin efficiently, and belongs to the technical field of astaxanthin synthesis, wherein the method includes the steps: a) settling and concentrating a high-yielding astaxanthin algae solution at a logarithmic growth stage; b) adding a cryopreservation solution to the concentrated algae solution, removing a supernatant, and rapidly freezing and storing after pre-freezing; c) inducing to culture an algae solution under irradiation of 420-440 nm blue light; and d) adding a fermentation auxiliary agent to a carbon source-free combination culture medium containing glucose, and carrying out vibration fermentation culture. The method has the beneficial effects: the method can help to reduce the damage of algae cells in the process of frozen storage of the algae solution; firstly, the morphological changes of the cells are induced by specific-wavelength blue light irradiation in the process of culture, and the synthesis of astaxanthin is promoted; then, the auxiliary agent is added in the fermentation process to increase the flux of pyruvic acid and acetyl CoA, a PP pathway and the TCA circulation are strengthened, and the metabolism synthesis of astaxanthin is improved.
Owner:云南维他源生物科技有限公司
Astaxanthin synthase of Sphingomonas and its encoding gene and method for genetic manipulation of Sphingomonas
ActiveCN104232595BRich genetic diversityPhosphorus-oxygen lyasesTransferasesAstaxanthinSynthetic enzyme
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOTECH +1
Method for inducing algae cells to efficiently synthesize astaxanthin
ActiveCN109554429BSlow growth rateReduce harmMicroorganism based processesFermentationAstaxanthinCryopreservation
The invention provides a method for inducing algae cells to efficiently synthesize astaxanthin, which belongs to the technical field of astaxanthin synthesis, comprising: a) settling and concentrating high-yield astaxanthin algae liquid in the logarithmic growth phase; b) adding to the concentrated algae liquid After freezing the solution, remove the supernatant, pre-freeze and quickly freeze and store it; c) Induce the cultivation of the algae liquid under 420-440nm blue light irradiation; d) Add fermentation aids to the carbon-free combined medium containing glucose for shaking fermentation nourish. The beneficial effect is: the method helps to reduce the damage to the algae cells during the frozen storage of the algae liquid. Firstly, the blue light of a specific wavelength is irradiated during the culture process to induce the change of the cell shape and promote the synthesis of astaxanthin, and then During the fermentation process, additives were added to increase the flux of pyruvate and acetyl CoA, strengthen the PP pathway and TCA cycle, and improve the metabolic synthesis of astaxanthin.
Owner:云南维他源生物科技有限公司
A method for making apple tree synthesize astaxanthin to improve its photo-oxidation resistance
InactiveCN102766641BEnhance the ability to resist photooxidationImprove photosynthetic efficiencyFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyBeta-Carotene
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV +1
Construction and Application of Astaxanthin Synthetic Strain
ActiveCN112852694BImprove generation effectIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAstaxanthinPromoter
The invention discloses the construction of an astaxanthin synthetic strain and its application. The invention provides a recombinant bacterium, which is prepared according to a method comprising the following steps: expressing the synthetic carotenoid-related genes crtY gene, crtZ gene and crtW gene in Escherichia coli, and regulating the expression of molecular chaperone genes groES and groEL in the Escherichia coli , the obtained recombinant bacteria; the present invention realizes the coordinated expression of genes in the astaxanthin synthesis pathway by using promoters of different strengths and changing the gene copy, eliminates the toxicity of metabolic intermediates, thereby increasing the production capacity of astaxanthin biosynthesis. In addition, stabilizing the expression of exogenous genes and increasing the correct folding of exogenous genes can also be an effective way to improve the biological activity of enzymes in the astaxanthin synthesis pathway and increase the production of astaxanthin.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Mutant carotenoid ketolases
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
A Phaffia strain that efficiently overexpresses endogenous astaxanthin synthase gene
InactiveCN104278015BIncrease productionImprove stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention discloses a phaffia rhodozyma strain obtained by efficiently an over-expressing endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene. The invention provides a phaffia rhodozyma genetic engineering strain capable of producing astaxanthin with high yield, obtained by over-expressing an endogenous astaxanthin synthetase gene. A phaffia rhodozyma genetic engineering strain (MK19-pGBKT7crtS) capable of producing astaxanthin with high yield is obtained by over-expressing the astaxanthin synthetase gene crtS by virtue of free plasmids and the strain is named CSR19. An endogenous ribosome bind site sequence (Rbs. sequence for short) exists in front of the crtS gene expressed by the strain. By virtue of fermentation cultivation and in comparison with a receptor strain MK19, the astaxanthin yield of the engineering strain is increased by 33.5%, and the engineering strain is good in stability, and thus, the phaffia rhodozyma strain has a good application prospect in the feed industry.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
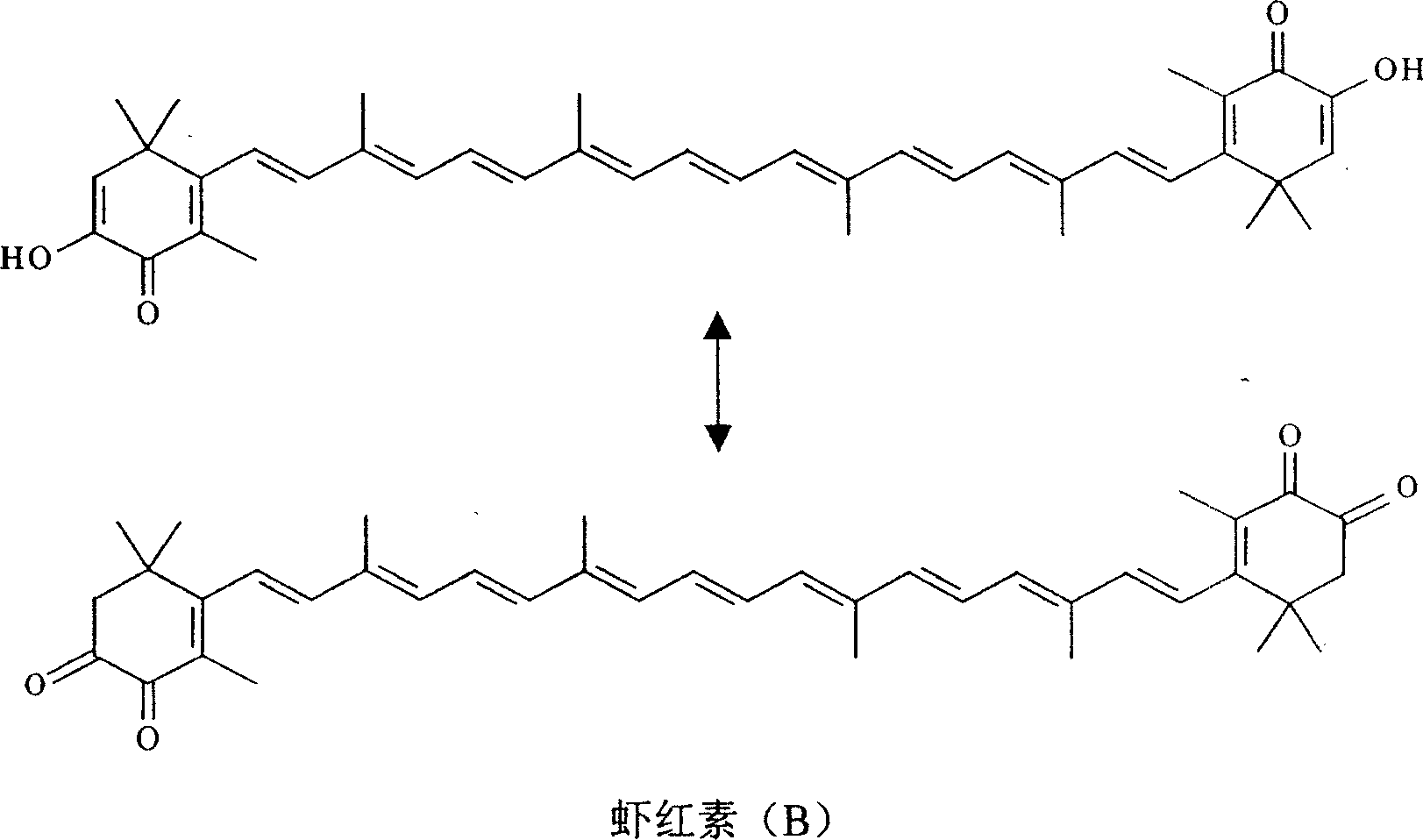
Synthesis of astaxanthin
Synthesis of astacin is carried out by dispersing astaxanthin with mass concentration 1-6g / L and alkali in proportion 1:2-20 in alcohol solvent, agitating while inducing into oxygen, reacting at 30-80 degrees C to obtain reactant, removing alcohol solvent to obtain solid crude product, dissolving the crude product by methylene chloride, filtering, dissolving the filter residue by water to obtain alkali reactive liquid, neutralizing by acid to pH value 4-6, filtering, washing by water and drying to obtain final product. It is simple and convenient, has more yield and no by-product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +3
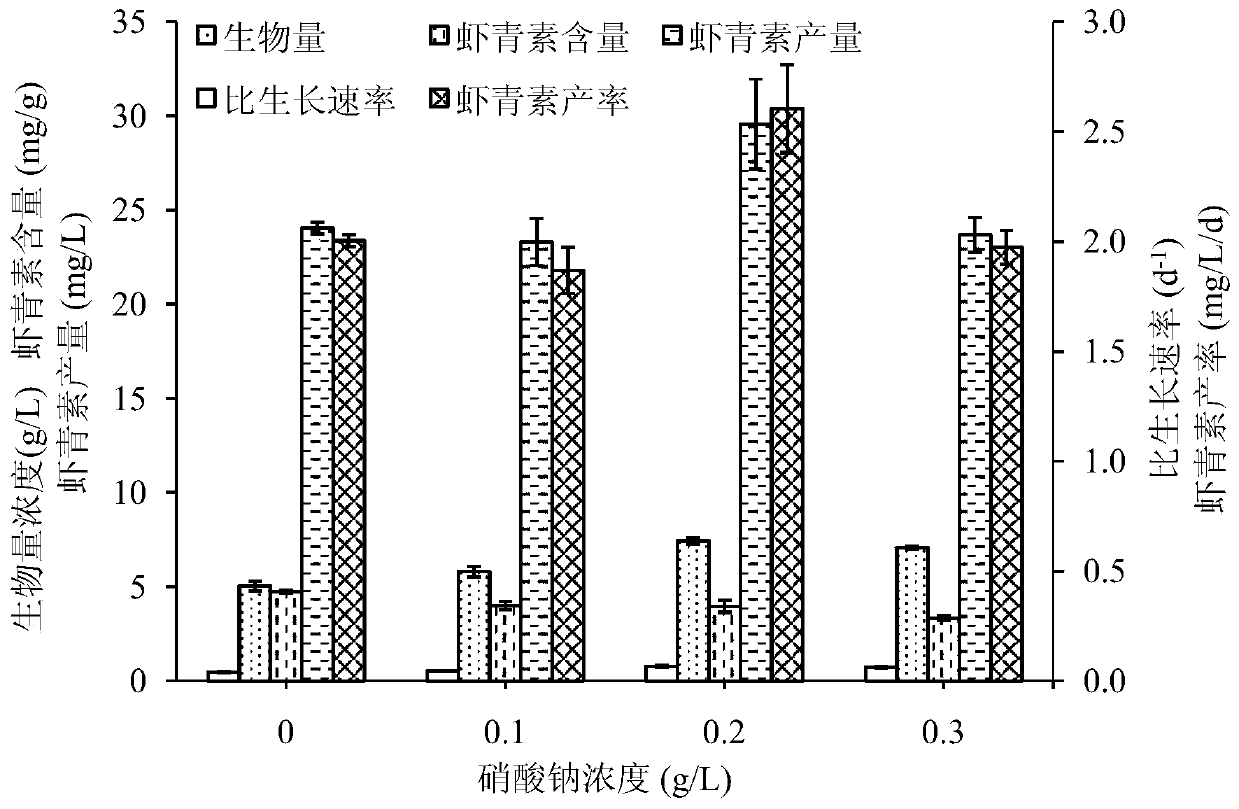
A method for inducing Chlorophyll algae to efficiently synthesize astaxanthin
ActiveCN106119331BIncrease productionHigh yieldUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesCulture fluidBetaxanthins
The invention provides a method for efficient astaxanthin synthesis by induction of chromochloris zofingiensis. The method includes steps: S1, activation culture, namely performing inoculation of chromochloris zofingiensis cells into a culture medium to obtain seed liquid by activation culture, to be more specific, subjecting the chromochloris zofingiensis cells to activation culture to a logarithmic phase, and taking the culture liquid in the logarithmic phase as the seed liquid; S2, induction culture, to be more specific, performing inoculation of the seed liquid obtained at the step S1 into an induction culture medium to carry out photoinduction culture, wherein a light source is white light or blue light, intensity of the light source is 60-330Mumol.m<-2>.s<-1>, a light-dark cycle is 12:12(h)-24:0(h), and the induction culture medium comprises glucose with concentration being 9-30g / L and sodium nitrate with concentration being 0-0.75g / L, and pH value of the induction culture medium is 6.0-7.0. According to the method, efficient astaxanthin synthesis can be realized by induction of chromochloris zofingiensis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
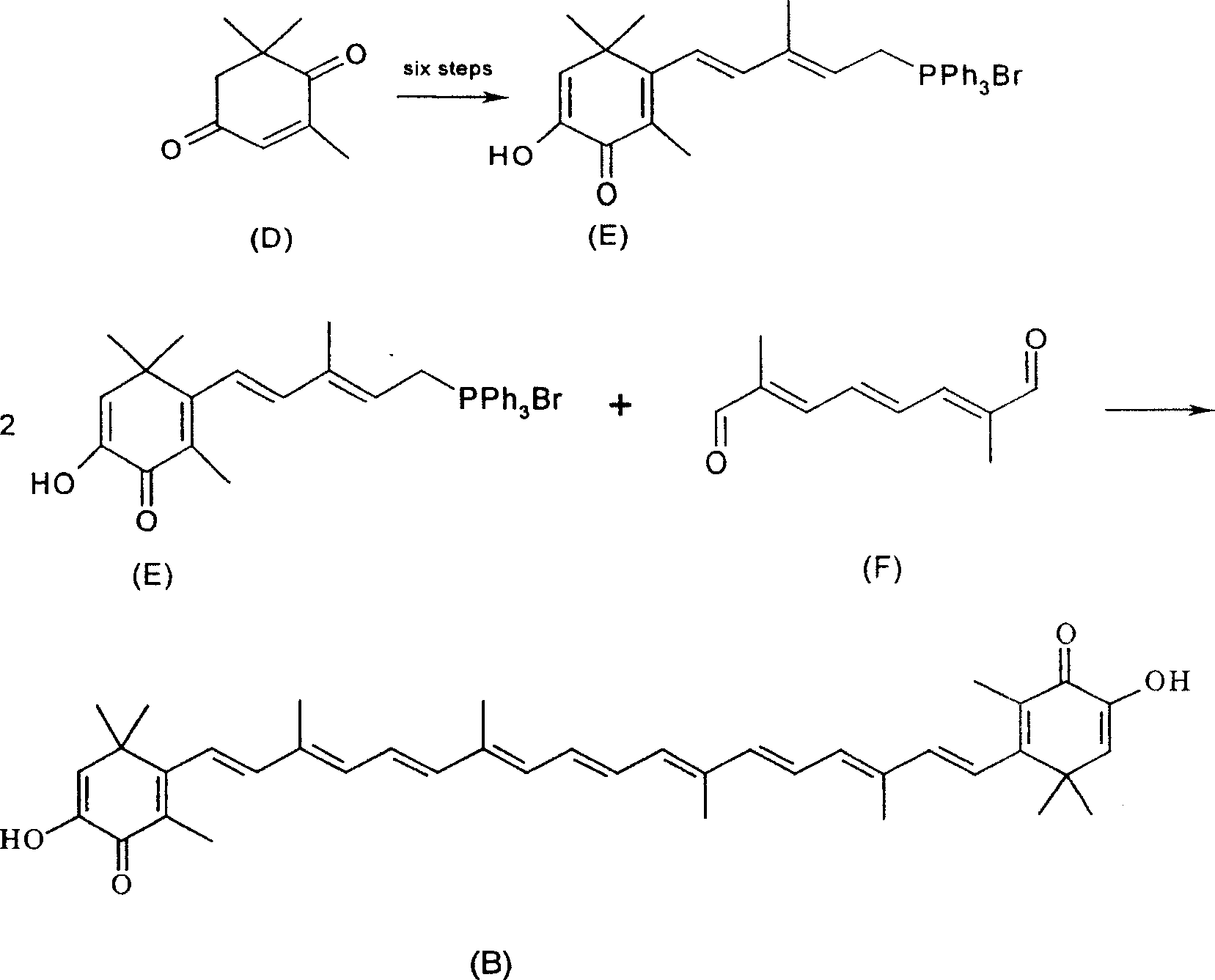
Method for synthesizing astaxsanthin
The present invention relates to a new method for the synthesis of astaxanthin, which consists of the following reactions: ∴ The method uses the by-product trans-C in the production of vitamin A 6 Alcohol is used as the starting material, and astaxanthin is synthesized through four-step reactions, which is a process with good reaction selectivity, high reaction yield, less pollution and simple operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +3
Method for increasing yield of phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin
ActiveCN112430637AReduce metabolic competitionIncrease metabolic fluxFungiStable introduction of DNAVersus genePhaffia rhodozyma
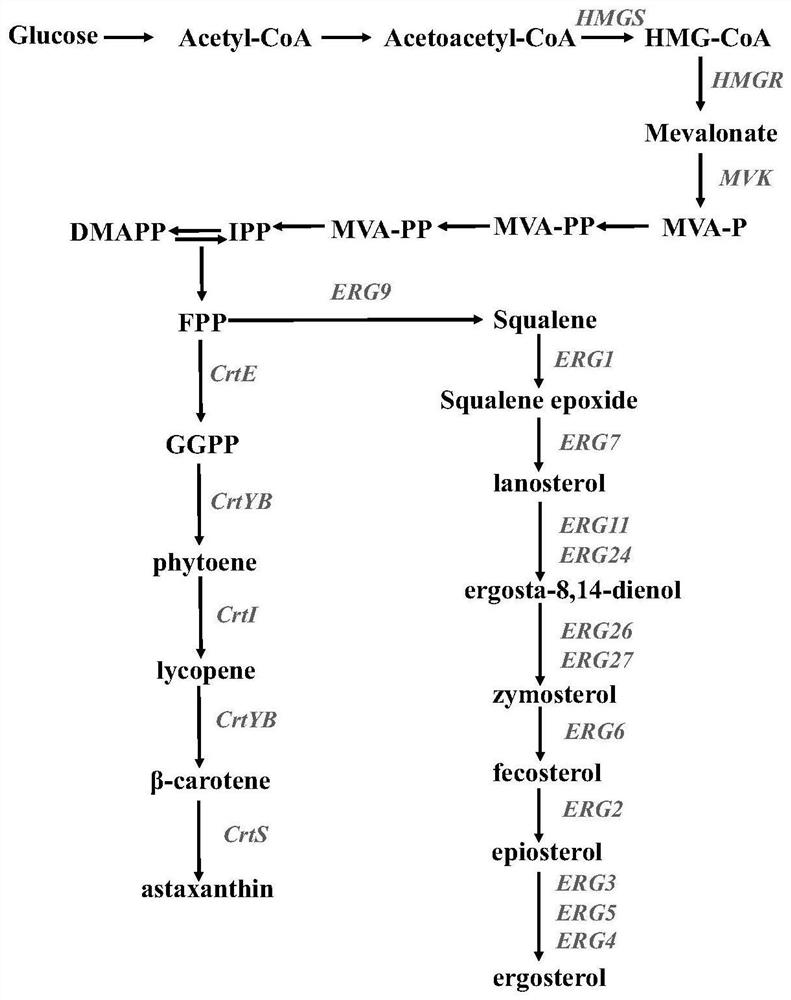
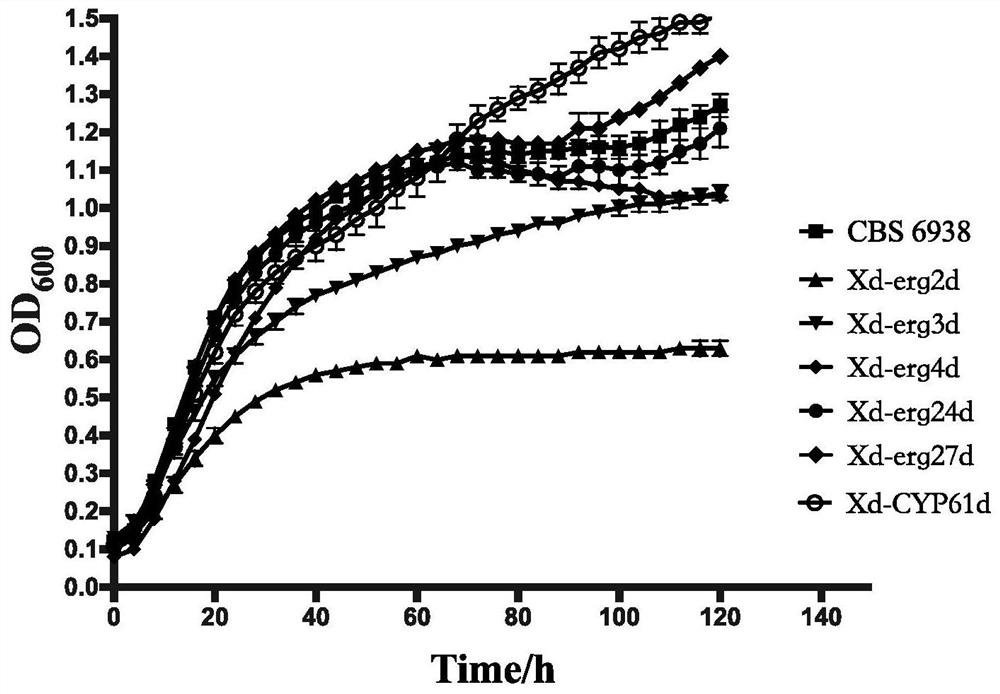
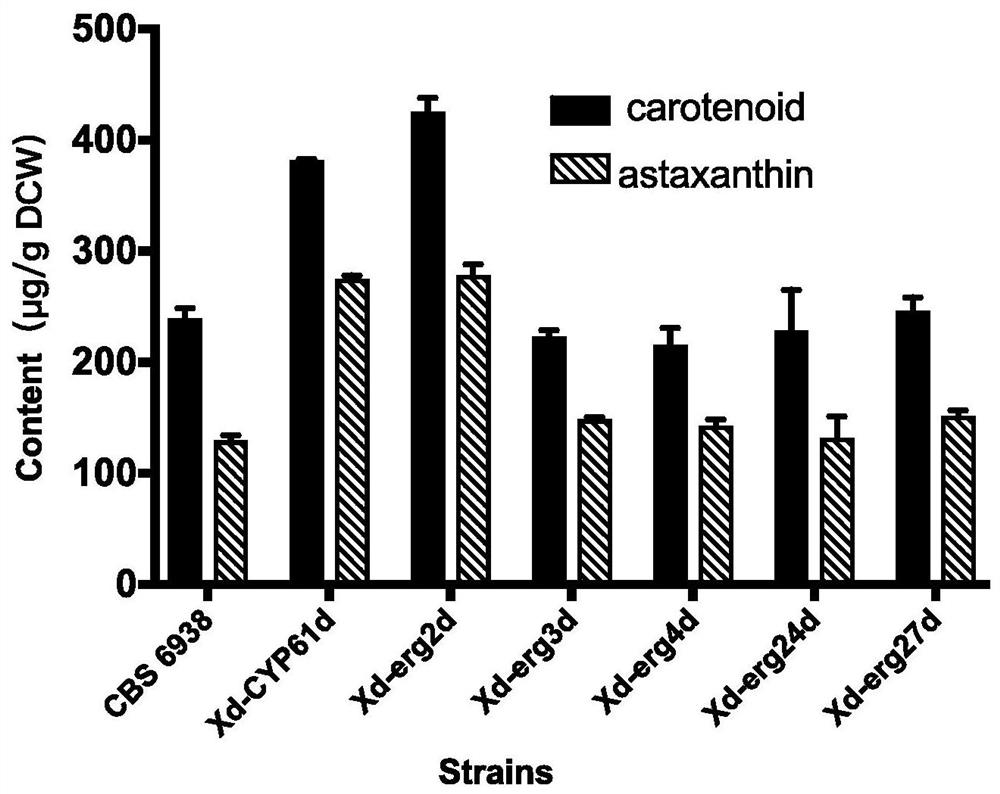
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and in particular, relates to a method for knocking out sterol synthesis genes to increase the yield of phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin. The fermentation yield of phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin is increased by knocking out a recombinant strain obtained by knocking out one or more genes in phaffia rhodozyma sterol synthase encoding genes; or, the fermentation yield of phaffia rhodozyma astaxanthin is increased by knocking out one or more of phaffia rhodozyma sterol synthetases and knocking out the combination of the phaffia rhodozyma sterolsynthetases and a CYP61 gene. The phaffia rhodozyma sterol synthesis gene is knocked out, so that the metabolic competition of sterol generation for astaxanthin synthesis is reduced or the feedback inhibition of sterol on a mevalonic acid pathway is reduced, and the metabolic flux and yield of astaxanthin synthesis are improved. The astaxanthin content of a single-gene knockout strain can be 2.2 times that of a control strain; the astaxanthin yield of a double-gene knockout strain can be increased by 38% on the basis of the single-gene knockout strain. The method can be applied to constructionof astaxanthin high-producing strains.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of regulating haematococcus pulvialis population density and synthesizing and accumulating astaxanthin by photoreactor
InactiveCN1181193CImprove light utilizationIncrease light intensityTissue cultureFermentationMetaboliteBetaxanthins
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for cultivating phaffiafhodozyma using astaxanthin synthesis accelerant
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Method for Synthesizing Astaxanthin Intermediate Using 2,6,6-trimethyl-3,4-dihydroxy-2-cyclohexen-1-one
ActiveCN103288613BEasy to recycleReduce concentrationPreparation from heterocyclic compoundsIsomerization2 cyclohexene 1 one
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing an astaxanthin intermediate by utilizing 2, 6, 6-trimethyl-3, 4-dihydroxy-2-cyclohexene-1-one. The method comprises the following steps of: dispersing the 2, 6, 6-trimethyl-3, 4-dihydroxy-2-cyclohexene-1-one in a non-polar solvent, adding an acid catalyst, dripping enol ether at room temperature for reaction, adding tertiary amine for termination reaction, then cooling, directly dissolving a reaction solution into an ethanol water solution with a compound obtained by reaction of an alkynyl reagent, then dripping into the ethanol water solution dissolving an acid, adding sodium carbonate for termination reaction after the end of dripping, performing reduced pressure distillation and recovery of the solvent, adding water into residues for stratification, extracting a water phase with dichloromethane, merging and drying organic phases, and then concentrating so as to synthesize the astaxanthin intermediate. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high yield of products, low isomerization of the products and the like.
Owner:广州巨元生化有限公司
Method for increasing yield of yeast astaxanthin by inactivating ubiquitin ligase and recombinant strain
ActiveCN114644991AAchieve knockoutIncrease productionFungiStable introduction of DNAUbiquitin ligasePhaffia rhodozyma
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a method for increasing the yield of yeast astaxanthin by inactivating ubiquitin ligase and a recombinant strain. The recombinant strain is obtained by genetic modification and knockout of at least one E3 ubiquitin ligase of an original strain phaffia rhodozyma, and the yield of astaxanthin of phaffia rhodozyma is increased by the obtained recombinant strain. The phaffia rhodozyma E3 ubiquitin ligase coding gene is knocked out, and the negative regulation effect of E3 ubiquitin ligase astaxanthin synthesis is eliminated, so that the yield of astaxanthin is increased. Compared with a control strain, the astaxanthin cell content of the E3 ubiquitin ligase gene knockout strain can be obviously improved by 8.3 times. The method can be applied to construction of astaxanthin high-yield strains and increase of astaxanthin yield.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com