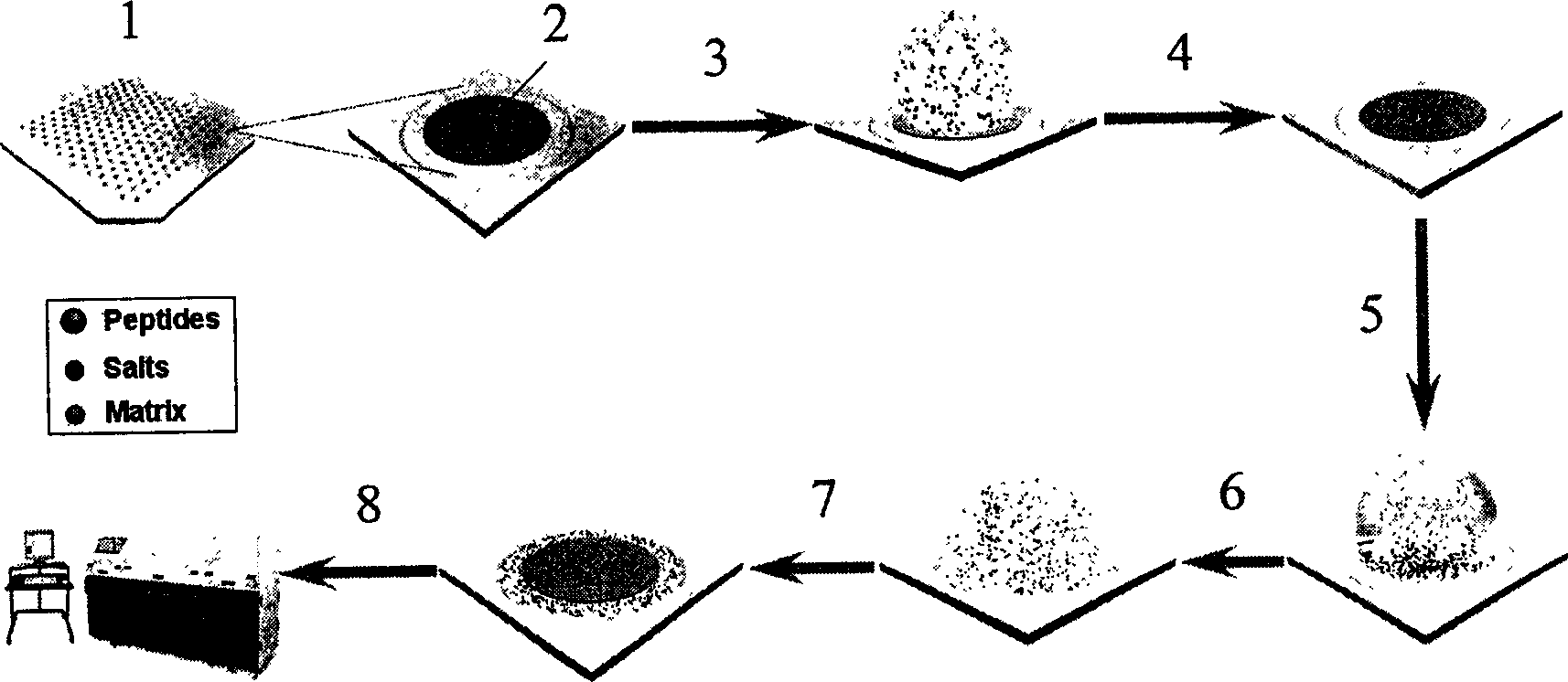
Method for one-step desalting and enriching on low-abundance protein target
A low-abundance protein enrichment technology, applied in the field of biochemical analysis, can solve the problems of limited protein or peptide adsorption, insufficient salt elution, loss, etc., and achieve the effects of reduced sample area, improved sensitivity, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Precisely position the perforated Kapton adhesive membrane by infrared laser to prepare the imprinted coating target plate of PMMA. The diameter of each imprinting spot is 990 microns, which is exactly half the diameter of the sample pool; 0.35 microliters of 60fmol / μL horse myocardium The erythrolytic peptide sample solution (solvent: 50% acetonitrile, 50% water, 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid) is dotted on the blotting coating and dried at room temperature; then the slightly excess volume is 0.7 microliters of organic matrix solution (α-CHCA, the solvent is 50% acetonitrile, 50% water, 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid) is applied to the surface of the imprinted coating, the excess solution will overflow the coating to the surrounding stainless steel area, and it will dry naturally at room temperature; the prepared sample It was sent to MALDI-TOF / TOF mass spectrometry (4700Proteomics Analyzer, Applied Biosystems) for detection. Mass spectrometry conditions: laser is Nd-YAG laser, wave...
Embodiment 2-4
[0033] Example 2-4 The influence of different polymer properties on MALDI-MS determination
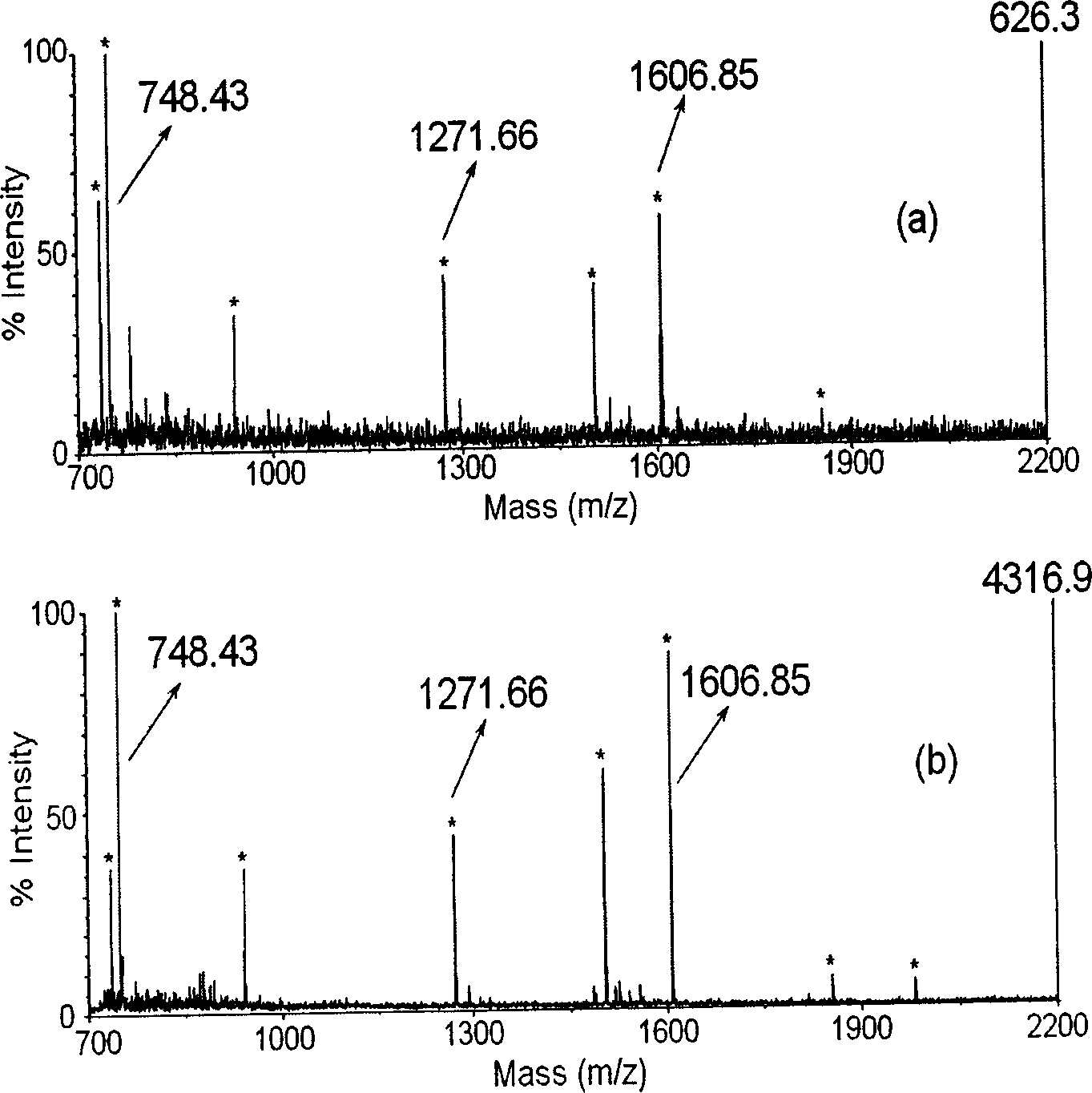
[0034] Adjust the polymer coating substrate to PMMA-C 60 , PSt, PSt-C 60 , Other conditions remain unchanged, repeat the above desalination and enrichment experiments. See the attached Figure 8 Shown.
Embodiment 5-8
[0035] Examples 5-8 verify the influence of different polymer properties on MALDI-MS determination
[0036] Adjust the sample solution to 40fmol / μL bovine serum albumin hydrolyzed peptide solution (solvent is 50% acetonitrile, 50% water, 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid), and the polymer coating substrates are PMMA and PMMA-C respectively 60 , PSt and PSt-C 60 , Other conditions remain unchanged, repeat the above desalination and enrichment experiments. See the attached Figure 7 Shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com