Microwave method for preparing nanometer zinc oxide
A nano-zinc oxide and microwave technology, applied in the direction of zinc oxide/zinc hydroxide, can solve the problems of consumption of organic solvents, increase of product cost, uneven particle size distribution, etc., to shorten the reaction time, inhibit the growth of crystal grains, overcome the The effect of local overburning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
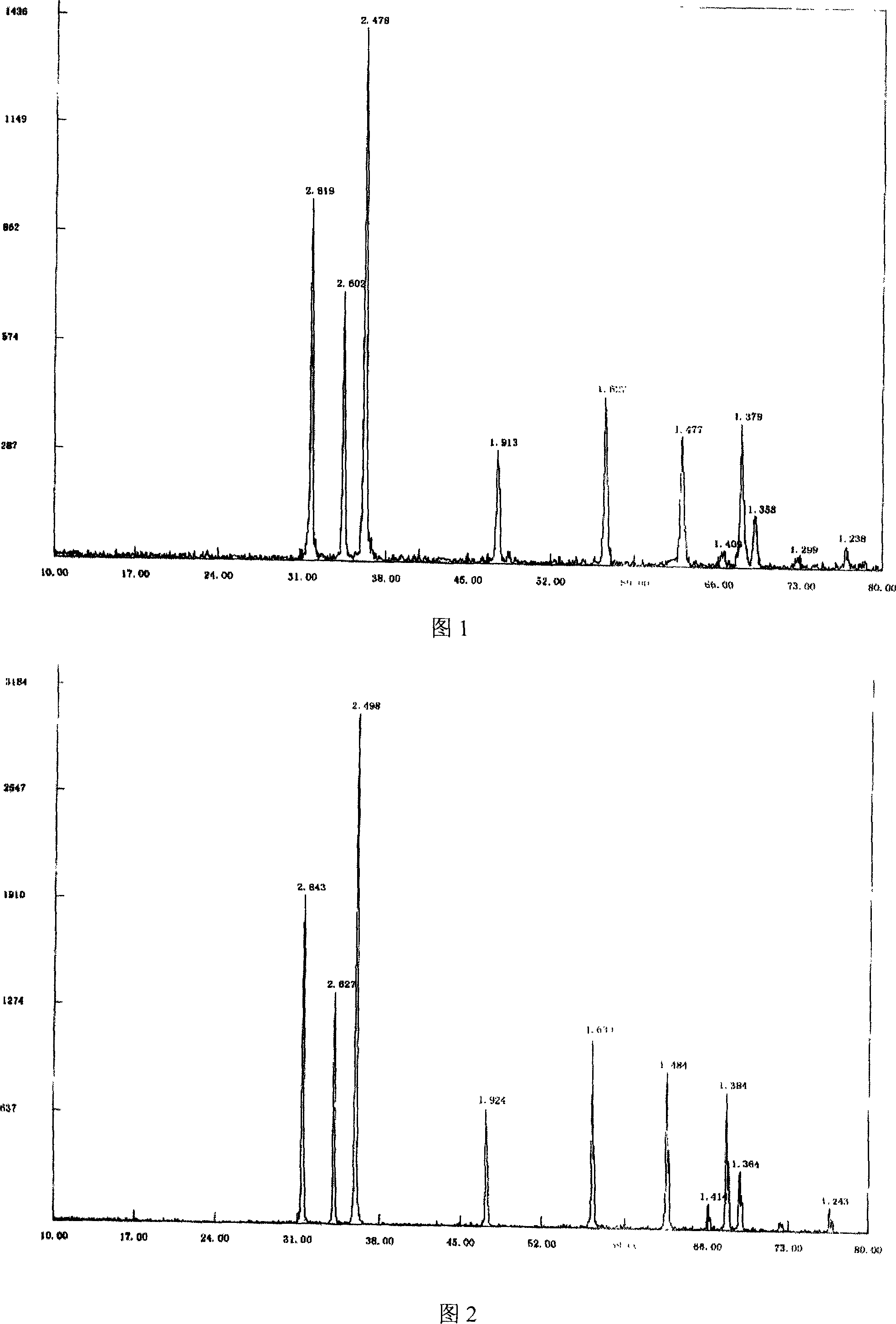
[0018] Weigh 100 grams of basic zinc carbonate, put it into a microwave oven, heat it to 700°C, and keep it warm for 20 minutes to prepare nano-zinc oxide. Accompanying drawing 1 is the X-ray diffraction pattern of preparation product, can find out from figure, each diffraction pattern peak and peak position correspond to JCPDS card 36-1451 (zinc oxide), there is no impurity peak to exist, and explanation product is all oxidation zinc. The resulting zinc oxide had a particle size of 34.5 nm.
Embodiment 2
[0020] Weigh 100 grams of basic zinc carbonate, put it into a microwave oven, heat it to 750°C, and keep it warm for 15 minutes to prepare nano-zinc oxide. Accompanying drawing 2 is the X-ray diffraction pattern of preparation product, can find out from figure, each diffraction pattern peak and peak position correspond to JCPDS card 36-1451 (zinc oxide), there is no impurity peak to exist, and explanation product is all oxidized zinc. The resulting zinc oxide had a particle size of 41.4 nm.
Embodiment 3
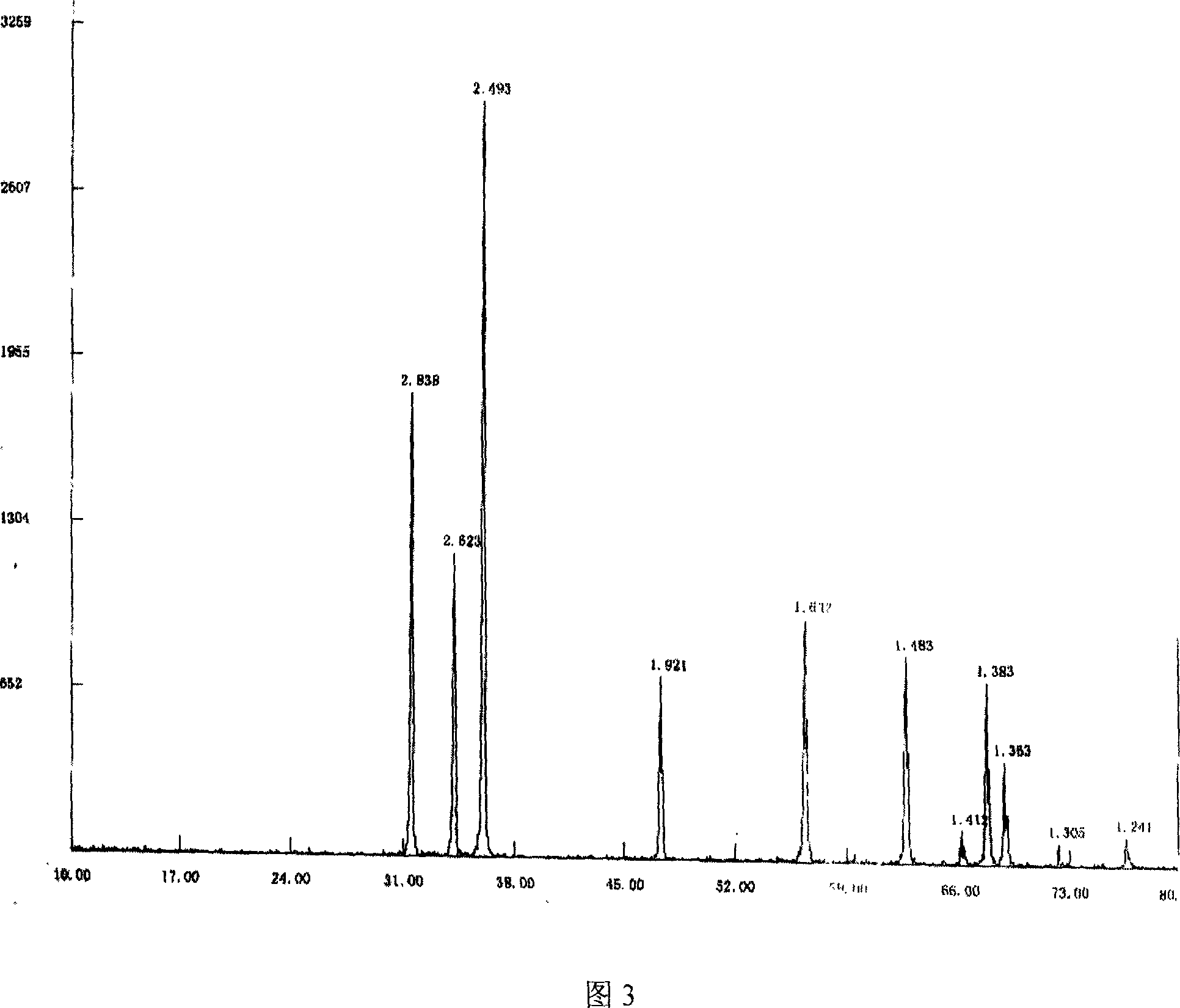
[0022] Weigh 100 grams of basic zinc carbonate, put it into a microwave oven and heat it to 800°C, and keep it warm for 10 minutes to prepare nano-zinc oxide. Accompanying drawing 3 is the X-ray diffraction pattern of preparation product, as can be seen from Fig. 3, each diffraction pattern peak and peak position correspond to JCPDS card 36-1451 (zinc oxide), there is no impurity peak to exist, and explanation product is all oxidation zinc. The resulting zinc oxide had a particle size of 51.7 nm.
[0023] The zinc oxide obtained in the above three examples was analyzed by X-ray diffraction method for phase and grain size. The analysis results are shown in Table 1. The results show that the particle size distribution of the zinc oxide obtained in the present invention is uniform.
[0024] Table 1
[0025] Phase analysis
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com