Use of heparinase to decrease inflammatory responses
a technology of heparin and inflammatory response, which is applied in the direction of antibodies, peptide/protein ingredients, lyases, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the afflicted individual, destroying viable cells and tissues, and causing harm to the afflicted individual, so as to reduce the side effects of treatment, inhibit leukocyte rolling and chemokine gradient formation, and reduce the effect of inflammatory respons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
of Endothelial Cells with Heparinase to Release Heparin / Heparan Sulfate
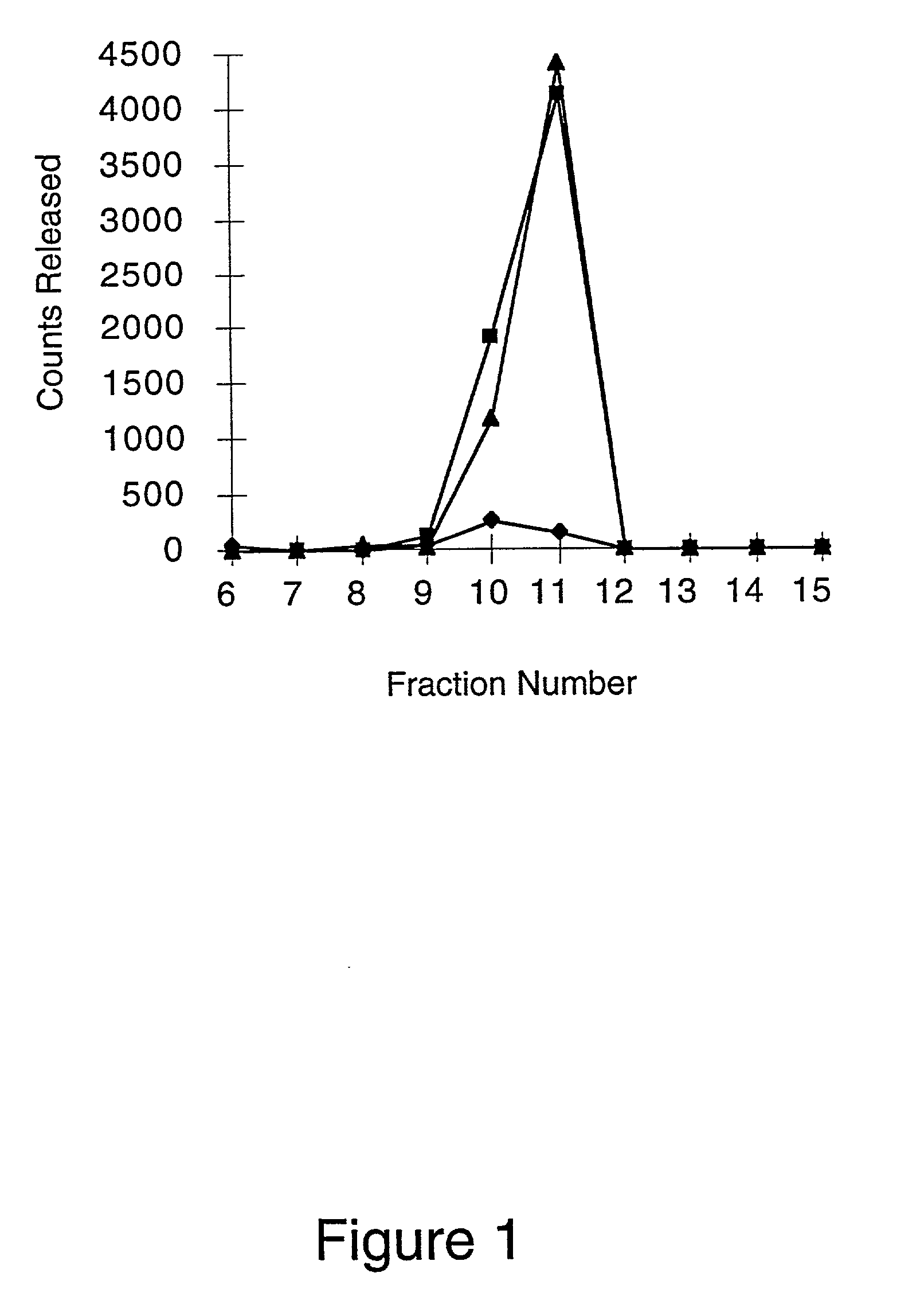
[0068] Heparinase alters the cell surface and basement membrane by cleaving the heparin and heparan sulfate moieties from the cell surface and extracellular matrix proteoglycans. Removal of these glycosaminoglycans will decrease leukocyte-endothelium interactions (leukocyte rolling) by decreasing binding of L-selectin on leukocytes to endothelium proteoglycans. In addition, the removal of heparin and heparan sulfate will decrease binding of chemokines to the endothelium, which will reduce leukocyte activation, sticking and extravasation. Production of bovine corneal endothelial cells with 35S- heparin / heparan sulfate proteoglycans and subsequent digestion of these radiolabeled proteoglycans with Flavobacterium heparinase III provides a qualitative assessment of the effect of the enzyme on the cell surface. Digestion of cell surface proteoglycans with heparinase III will release both heparin and heparan sulfate mo...
example 2
tion of the Extent of Removal and the Rate of Replacement of Heparin / Heparan Sulfate Moieties on Endothelial Cells and in Basement Membranes Treated with Heparinase
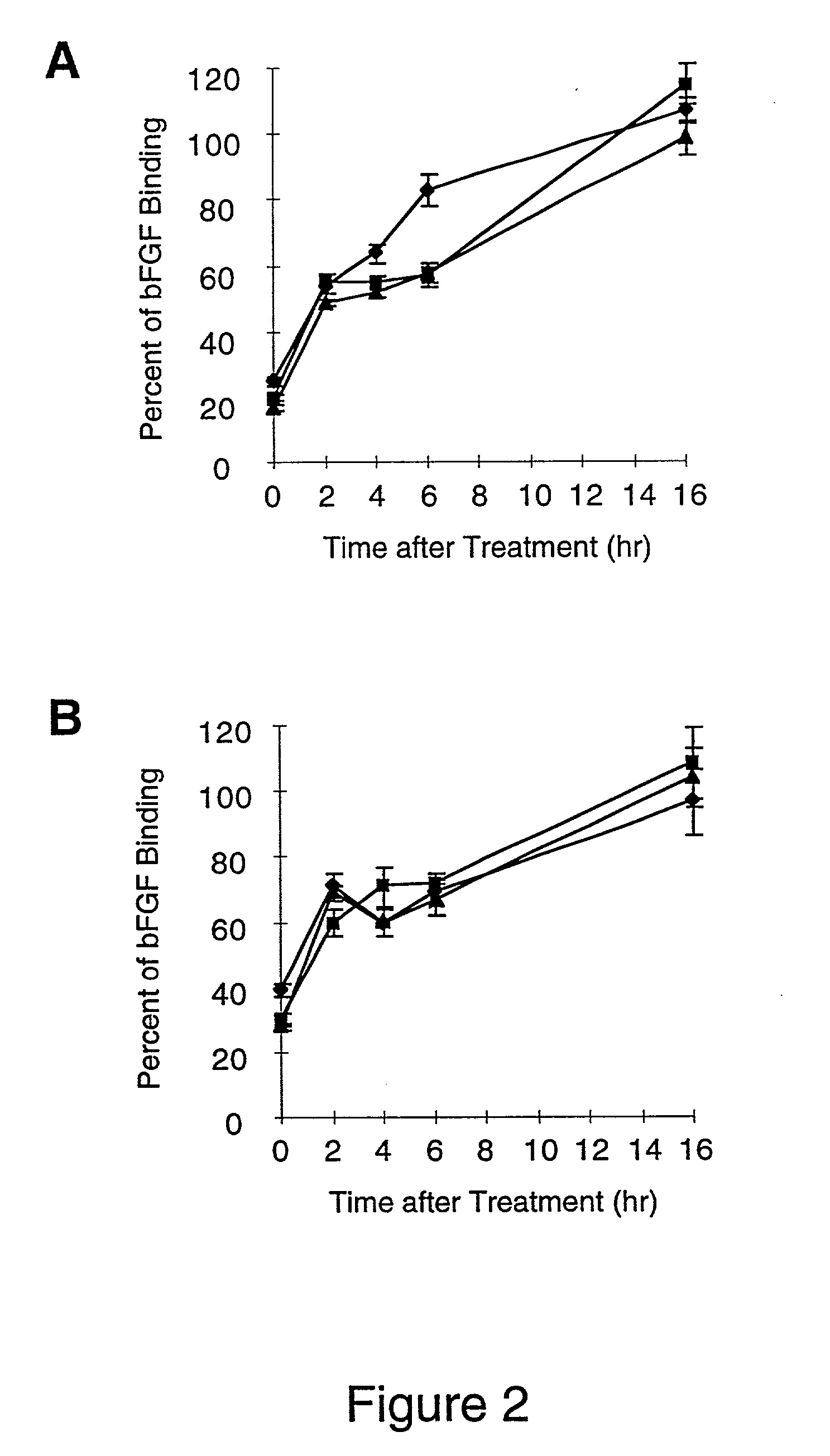
[0071] The growth factor, basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (bFGF), is a well characterized heparin binding protein, which is known to bind to the heparin moieties of proteoglycans on the cell surface and in the extracellular matrix (Maccarana, et al., J. Biol. Chem., 268:23898-23905, 1993). Binding of .sup.125I-labeled bFGF to cell surface and basement membrane proteoglycans was used to access the amount of heparin / heparan sulfate removed from unactivated and IL-1b activated endothelial cell layers and their basement membranes by heparinases I, II or III. Digestion of the cell surface and basement membrane with heparinase will remove both heparin and heparan sulfate moieties, because these moieties are interspersed on the same unbranched carbohydrate chains. .sup.125I-labeled bFGF binding was also used in this experiment to...
example 3
of Activated Endothelial Cell Layers and Basement Membranes with Heparinase to Release Heparin / Heparan Sulfate Bound Chemokine, IL-8
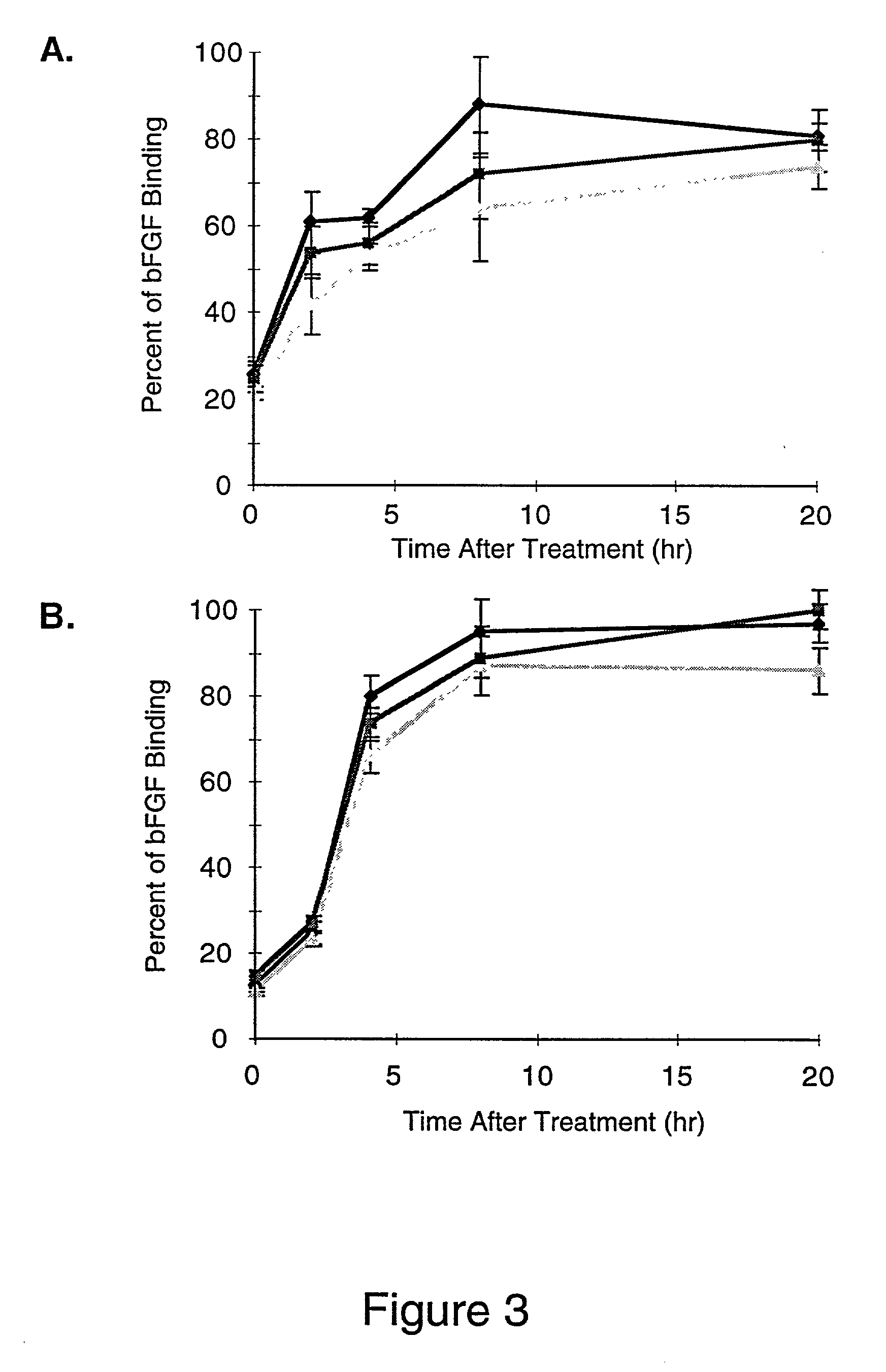
[0075] Removal of the bound chemokine gradient formed by activated endothelium adjacent to inflamed tissue will inhibit the accumulation of neutrophils within this tissue, and will decrease the inflammatory response. The chemokine, IL-8, is produced by endothelium activated by IL-1b and other cytokines and chemoattractants, which are secreted by inflamed tissues. If IL-8 bound to endothelium can be solubilized by treatment with heparinase, then it would be removed from the area of inflammation by blood flow and the localized inflammatory response would be inhibited. The in vitro removal and solubilization of 0.5 to 3 fold more endogenous, immobilized IL-8 (vs. secreted IL-8) from activated endothelium by heparinases I, II or III, or by heparinases I and III demonstrates that the bound chemokine gradient can be destroyed by heparinase treatment.
[0076] On...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com