Process for electrolytic production of ultra-pure zinc or zinc compounds from zinc primary and secondary raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
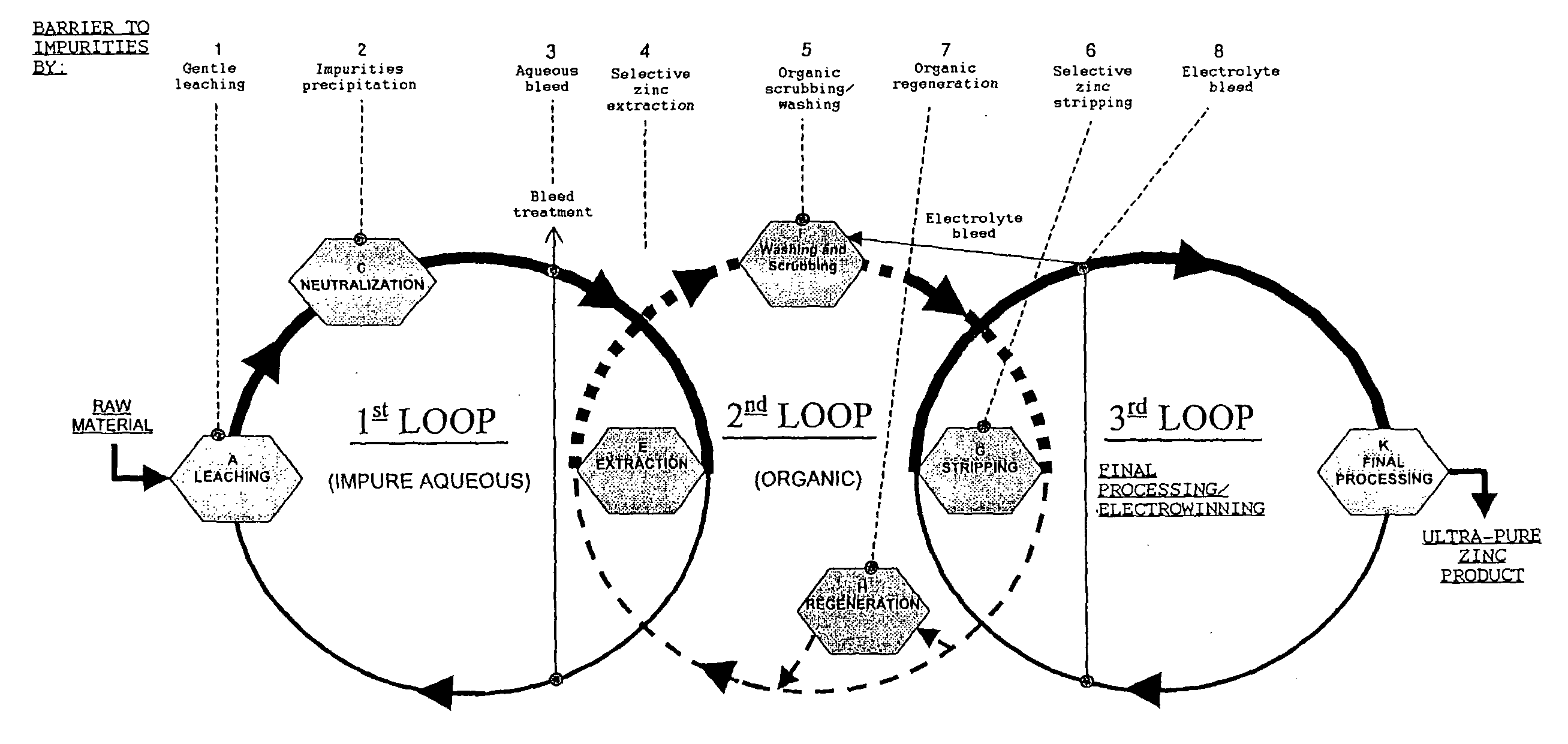
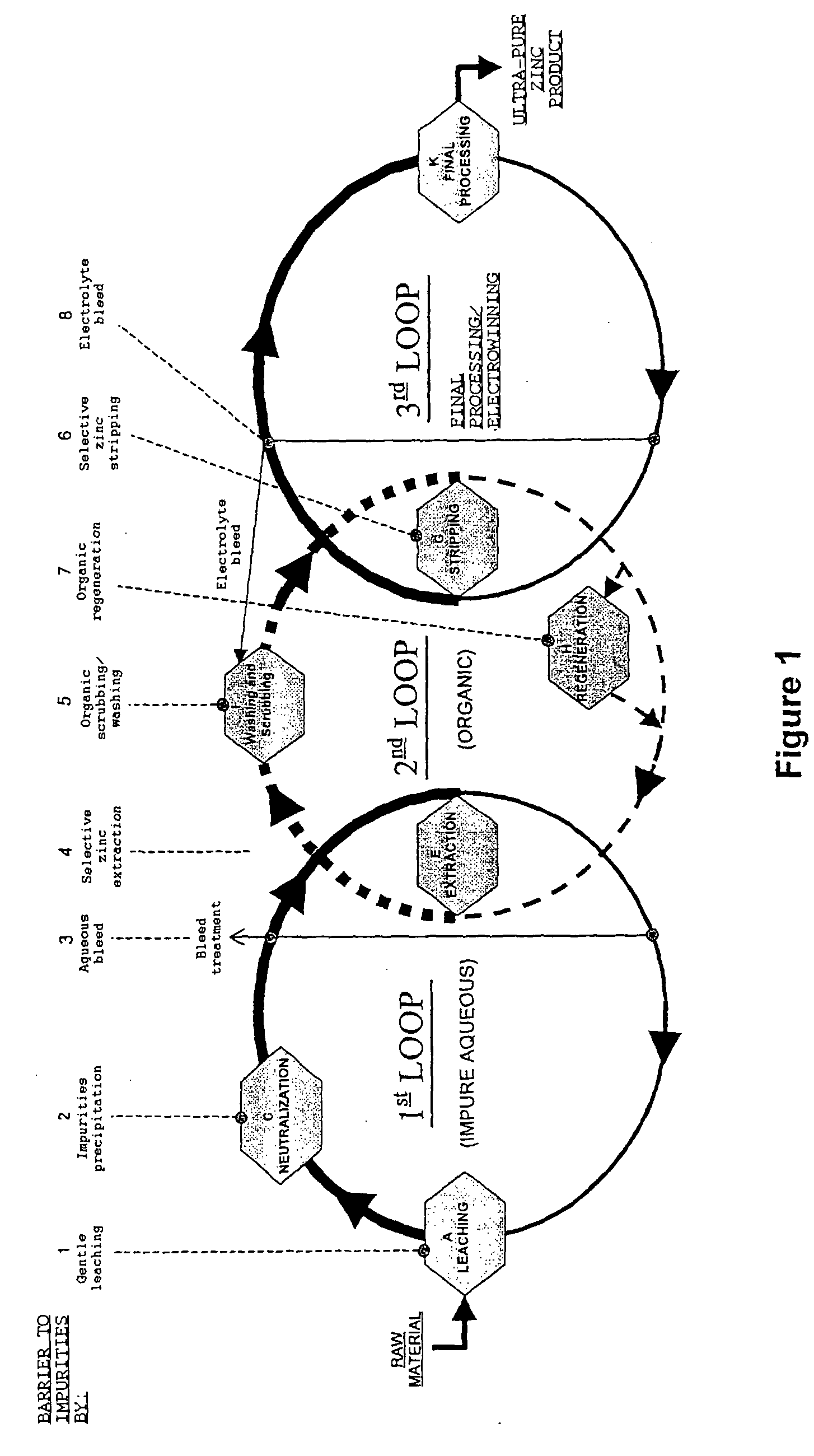
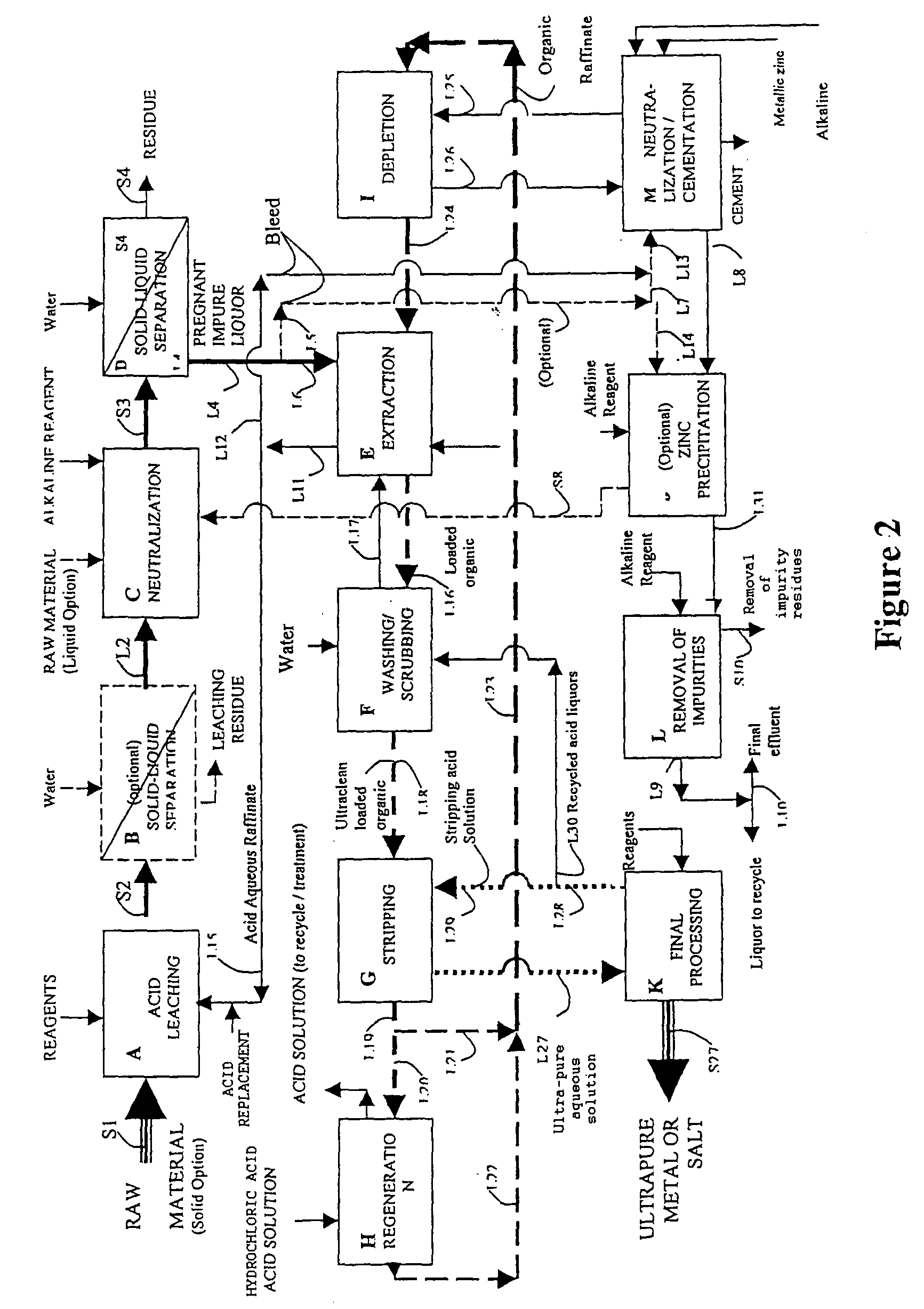
[0117] The invention will be better understood through a description of the process according to the invention, schematically represented in the flow chart wherein the stages of the process have been represented by capital letters from (A) to (M). See FIG. 2--
[0118] This example relates to the in-plant recovery of high-purity metallic zinc, by:
[0119] leaching the zinc contained in the raw material, achieved by the use of an aqueous solution of a blend of acids, a blend which contains sulphuric acid (representing 95% by weight equivalent of H.sup.+ in the blend)
[0120] Extraction of the dissolved zinc using an organic acid solvent (D.sub.2EPHA),
[0121] Stripping the zinc using an acid treatment of the zinc loaded in the organic solvent.
[0122] The solid raw material used as feed (S.sub.1) contains 10% by weight of zinc. The main impurities accompanying the zinc are: silicon (25% by weight), iron (2% by weight), calcium (2% by weight) and other impurities (magnesium, manganese, potassium...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com